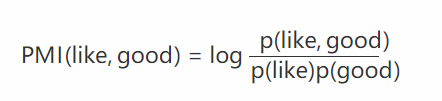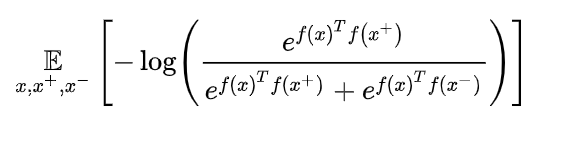互信息专题
第十四篇——互信息:相关不是因果,那相关是什么?
目录 一、背景介绍二、思路&方案三、过程1.思维导图2.文章中经典的句子理解3.学习之后对于投资市场的理解4.通过这篇文章结合我知道的东西我能想到什么? 四、总结五、升华 一、背景介绍 通过本文,可以了解到信息之
MI-SegNet: 基于互信息的超越领域泛化的超声图像分割
文章目录 MI-SegNet: Mutual Information-Based US Segmentation for Unseen Domain Generalization摘要方法实验结果 MI-SegNet: Mutual Information-Based US Segmentation for Unseen Domain Generalization 摘要 针对医
条件熵,信息增益(互信息)与特征选择
一定要先搞清楚什么是信息量,什么是信息熵。参考博文:https://blog.csdn.net/u010916338/article/details/91127242 一,什么是信息量? 简言之,就是把信源看做是一个随机变量。消息(信号)就是随机变量的取值,比如a1,a2···an。信息就是这些随机变量的不确程度(发生概率越低,不确定性越大),公式如下。为什么写成这样呢?原因有二。第一:概率和
熵、信息熵、交叉熵、相对熵、条件熵、互信息、条件熵的贝叶斯规则
熵 每条消息都含有信息。“信息熵”是“熵”的别名,用来衡量消息的不确定程度。 宽泛来讲,即消息所传达的信息的模糊程度,消息越模糊,其熵越高。 形象的说,熵是从 根据模糊消息—>得到精确信息 所需要花费的最小代价。 熵=信息量(的期望)=不确定性的多少。熵值是信息量的一个度量。 某种意义上说,熵就是最优策略。 《数学之美》中这样描述: 变量的不确定性越高,熵也就越大,要把它搞清楚,所
利用互信息比较不同的聚类结果
互信息(mutual information)和信息熵(information entropy)一样都是信息论里面的概念。信息熵在决策树里面用的比较多,可以度量样本集合的纯度。而互信息在聚类中有很大的作用,它可以衡量对同一个数据集不同的划分的之间的相似程度。 假设 Pa,Pb P^a,P^b表示数据集 X X上的两个不同的划分,XX包括n的样本。 Pa P^a包含 ka k_a个簇, Pa
告别互信息:跨模态人员重新识别的变分蒸馏
Farewell to Mutual Information: Variational Distillation for Cross-Modal Person Re-Identification 摘要: 信息瓶颈 (IB) 通过在最小化冗余的同时保留与预测标签相关的所有信息,为表示学习提供了信息论原理。尽管 IB 原理已应用于广泛的应用,但它的优化仍然是一个具有挑战性的问题,严重依赖于互信息的
Minepy—使用python计算最大互信息系数(MIC)
MIC 即:Maximal Information Coefficient 最大互信息系数。 https://blog.csdn.net/qtlyx/article/details/50780400 MIC可以用来衡量线性或非线性的相互关系。 算法对比 https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/53092905 MIC算法可以通过python的minpy包来实
安装minepy-用最大互信息系数法进行特征工程
利用minepy可以方便的利用最大互信息系数法进行特征工程,我在安装时遇到了以下问题,如图所示: 错误原因因该是我的visual studio安装出了问题,我打开相应位置,发现我没有platformSDK文件夹 我不想重装VS了,到网上寻找解决办法,发现可以从https://www.lfd.uci.edu/~gohlke/pythonlibs/网站上下载,如下图所示: 下载后,切换到目录,用
100天精通风控建模(原理+Python实现)——第15天:风控建模中的互信息是什么?怎么实现?
风控模型已在各大银行和公司都实际运用于业务,用于营销和风险控制等。本文以视频的形式阐述风控建模中卡方检验是什么,怎么实现。并提供风控建模原理和Python实现文章清单。 之前已经阐述了100天精通风控建模(原理+Python实现)——第1天:什么是风控建模? 100天精通风控建模(原理+Python实现)——第2天:风控建模有什么目的? 100天精通风控建模(原理+Python实
变分互信息蒸馏(Variational mutual information KD)
原文标题是Variational Information Distillation for Knowledge Transfer,是CVPR2019的录用paper。 VID方法 思路比较简单,就是利用互信息(mutual information,MI)的角度,增加teacher网络与student网络中间层特征的MI,motivation是因为MI可以表示两个变量的依赖程度,MI越大,表明
条件互信息的理解(Conditional Mutual Information)
在概率论,尤其是信息论中,条件互信息的基本形式是在给定第三个变量值的情况下,两个随机变量互信息的期望值。 对于离散随机变量X,Y,Z,其条件互信息为: 用图形表示条件互信息为: 具体的定义等后续补充。
拿捏!相关性分析,一键出图!皮尔逊、斯皮尔曼、肯德尔、最大互信息系数(MIC)、滞后相关性分析,直接运行!独家可视化程序!
适用平台:Matlab2020及以上 相关性分析是一种统计方法,用于衡量两个或多个变量之间的关系程度。通过相关性分析,我们可以了解变量之间的相互关系、依赖性,以及它们是如何随着彼此的变化而变化的。相关性分析通常包括计算相关系数或其他衡量关联度的指标。 ①量化特征之间的关联程度:通过相关系数的值,我们可以判断它们的关系是强烈的、中等还是弱。 ②特征降维:在大规模数据集中,相关性分析可以帮助我们
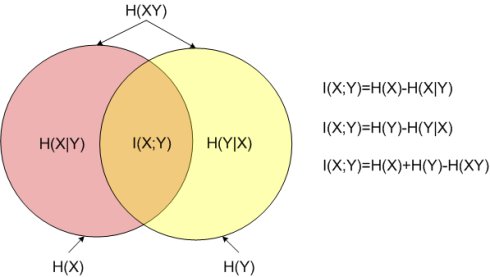
互信息,条件熵,联合熵
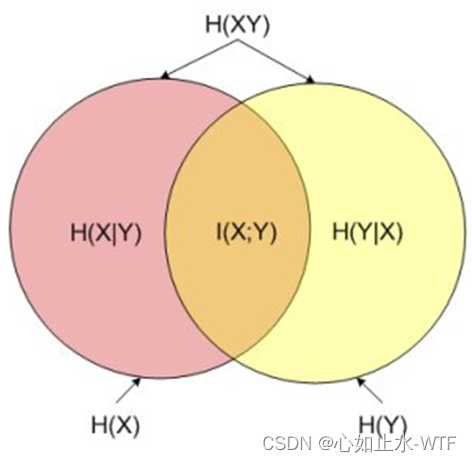
看到一个图介绍互信息,条件熵,联合熵,还不错,做个记录: 图上的红色和黄色圈分别代表X,Y原始的信息量H(X)/H(Y)/熵值。 (注意信息量度量的是一个具体事件发生了所带来的信息,而熵则是在结果出来之前对可能产生的信息量的期望) I(X;Y) : 表示互信息, 知道X,Y损失了多少信息量(知道Y,X损失了多少信息量)。 H(X|Y)或H(Y|X): 表示条件熵, 知道X,Y还剩多少信息量(H
自信息/熵/联合熵/条件熵/相对熵/交叉熵/互信息及其相互之间的关系
【深度学习基础】:信息论(一)_自信息/熵/联合熵/条件熵/相对熵/交叉熵/互信息及其相互之间的关系_bqw的博客-CSDN博客详解机器学习中的熵、条件熵、相对熵和交叉熵 - 遍地胡说 - 博客园
python计算两个图像的互信息
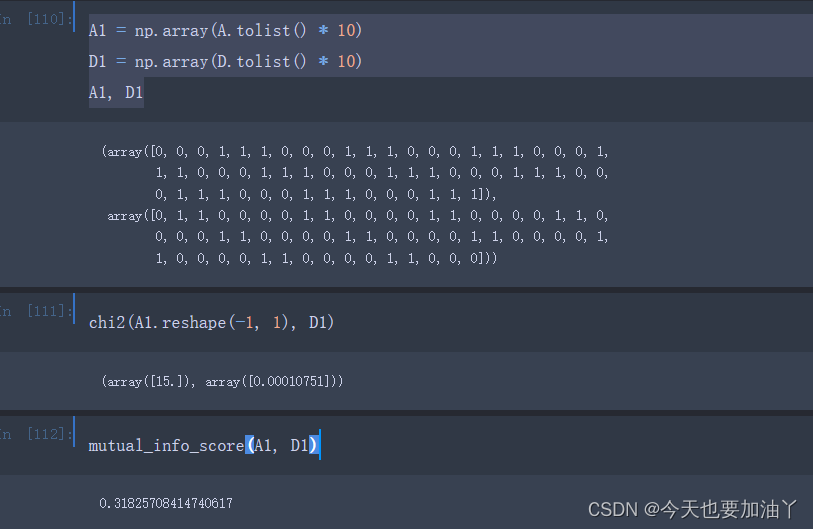
我们常用互信息来衡量两个图像的相似程度。互信息的计算方式如下: 使用python中的numpy包或者sklearn可以很方便的计算互信息,计算代码如下: import cv2import numpy as npimport sklearn.metrics as skmdef hxx_forward(x, y):return skm.mutual_info_score(x, y)
文本挖掘预处理之TF-IDF原理 and 互信息的原理
TF-IDF介绍(维基百科): tf-idf(英语:term frequency–inverse document frequency)是一种用于信息检索与文本挖掘的常用加权技术。tf-idf是一种统计方法,用以评估一字词对于一个文件集或一个语料库中的其中一份文件的重要程度。字词的重要性随着它在文件中出现的次数成正比增加,但同时会随着它在语料库中出现的频率成反比下降。tf-idf加权的各种形式常
基于互信息最大化的无监督学习图像特征表示------P02114198田园,P02114018刘颖,P02114050刘欣让
在概率论和信息论中,两个随机变量的互信息衡量了两个变量之间相互依赖的程度。通俗来说可以理解为两个变量交叠的信息,对于两个随机变量,互信息衡量了一个随机变量平均传达了多少关于另一个的信息。 正式地,两个离散随机变量X和Y的互信息可以定义为: 其中是和的联合概率分布函数,而和分别是和的边缘概率函数分布。 在连续随机变量的情形下,求和被替换成了二重定积分: 其中是和的联合概率密度函数,而和分
机器学习-特征选择:如何使用互信息特征选择挑选出最佳特征?
一、引言 特征选择在机器学习中扮演着至关重要的角色,它可以帮助我们从大量的特征中挑选出对目标变量具有最大预测能力的特征。互信息特征选择是一种常用的特征选择方法,它通过计算特征与目标变量之间的互信息来评估特征的重要性。 互信息是信息论中的一个概念,用于衡量两个随机变量之间的相互依赖程度。在特征选择中,互信息可以用来衡量特征与目标变量之间的相关性。通过计算特征与目标变量之间的互信息,我们可以得到每个
机器学习-特征选择:如何使用互信息特征选择挑选出最佳特征?
一、引言 特征选择在机器学习中扮演着至关重要的角色,它可以帮助我们从大量的特征中挑选出对目标变量具有最大预测能力的特征。互信息特征选择是一种常用的特征选择方法,它通过计算特征与目标变量之间的互信息来评估特征的重要性。 互信息是信息论中的一个概念,用于衡量两个随机变量之间的相互依赖程度。在特征选择中,互信息可以用来衡量特征与目标变量之间的相关性。通过计算特征与目标变量之间的互信息,我们可以得到每个
自监督、对比学习、contrastive learning、互信息、infoNCE等
===== 更新时间:21.2.7 祝大家节日快乐 ============ 73岁Hinton老爷子构思下一代神经网络:属于无监督对比学习 无监督学习主要有两类方法(所以在label少的时候,unsupervised learning可以帮助我们学到data本身的high-level information,这些information能够对 downstream task有很大的帮助。)
《利用RWR算法和正点互信息集成多种异构信息源预测lncRNA与疾病的相关性》论文梳理
引用: Fan, X. N., et al. (2019). “Prediction of lncRNA-disease associations by integrating diverse heterogeneous information sources with RWR algorithm and positive pointwise mutual information.” BMC B
互信息 java_互信息(Mutual Information)是度量两个事件集合之间的相关性(mutual depe...
互信息(Mutual Information)是度量两个事件集合之间的相关性(mutual dependence)。 平均互信息量定义: 互信息量I(xi;yj)在联合概率空间P(XY)中的统计平均值。 平均互信息I(X;Y)克服了互信息量I(xi;yj)的随机性,成为一个确定的量。 平均互信息量的物理含义 1) 观察者站在输出端: H(X/Y) —信道疑义度/损失熵.。Y关于X的后验不确定
特征选择-皮尔逊相关系数-互信息
特征选择 1.相关性 通过使用相关性,我们很容易看到特征之间的线性关系。这种关系可以用一条直线拟合。 下面通过皮尔逊相关系数(Pearson correlation coefficient)来解释特征的相关性: 下面每幅图上方的相关系数Cor(X1, X2)是计算出来的皮尔逊r值,从图中可以看出不同程度的相关性。 scipy.stats.pearsonr(),给定两个数据序列 ,会返回相关系