本文主要是介绍通过RSeQC判断RNA-seq测序数据文库类型和链特异性,指导Stringtie参数使用,希望对大家解决编程问题提供一定的参考价值,需要的开发者们随着小编来一起学习吧!
1、snakemake运行infer_experiment.py
rule check_ss:input:bed = config["REF"]["genome_bed12"],bam = rules.bam_index.output.bam,output:txt = "result/QC/check_ss/{sample}.txt",params:name = "{sample}"shell: """echo "sample name: {params.name}" > {output.txt}infer_experiment.py -r {input.bed} -i {input.bam} \-s 1000000 &> {output.txt}"""2、运行结果解读
This is PairEnd Data
Fraction of reads failed to determine: 0.0072
Fraction of reads explained by "1++,1--,2+-,2-+": 0.9441
Fraction of reads explained by "1+-,1-+,2++,2--": 0.0487
结果解读看官方文档:

官网:RSeQC: An RNA-seq Quality Control Package — RSeQC documentation![]() http://rseqc.sourceforge.net/#infer-experiment-py
http://rseqc.sourceforge.net/#infer-experiment-py
3、判断建库类型
对于双端测序,1++,1--,2+-,2-+与1+-,1-+,2++,2--的比例可以体现出文库类型;对于单端测序,++,--和+-,-+的比例亦然:
二者比例接近1时,文库为unstranded
前者明显大于后者时,文库为FR/fr-secondstrand stranded
后者明显大于前者时,文库为RF/fr-firststrand stranded
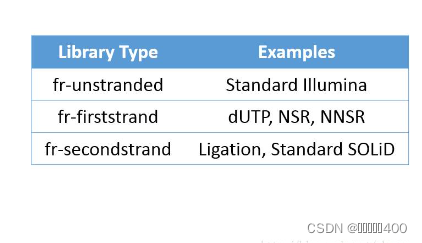
4、文库类型对应的软件参数
表格来源于Strand Settings | Griffith LabStrand-related settings There are various strand-related settings for RNA-seq tools that must be adjusted to account for library construction strategy. The following table provides read orientation codes and software settings for commonly used RNA-seq analysis tools including: IGV, TopHat, HISAT2, HTSeq, Picard, Kallisto, StringTie, and others. Each of these explanations/settings is provided for several commonly used RNA-seq library construction kits that produce either stranded or unstranded data. NOTE: A useful tool to infer strandedness of your raw sequence data is the check_strandedness tool. We provide a tutorial for using this tool here. NOTE: In the table below, the list of methods/kits for specific strand settings assumes that these kits are used as specified by their manufacturer. It is very possible that a sequencing provider/core may make modifications to these kits. For example, in one case we obtained RNAseq data processed with NEBNext Ultra II Directional kit (dUTP method). However instead of using the NEB hairpin adapters, IDT xGen UDI-UMI adapters were substituted, and this results in the insert strandedness being flipped (from RF/fr-firststrand to FR/fr-secondstrand). Because this level of detail is not always provided it is highly recommended to confirm your data’s strandedness empirically. Tool RF/fr-firststrand stranded (dUTP) FR/fr-secondstrand stranded (Ligation) Unstranded check_strandedness (output) RF/fr-firststrand FR/fr-secondstrand unstranded IGV (5p to 3p read orientation code) F2R1 F1R2 F2R1 or F1R2 TopHat (–library-type parameter) fr-firststrand fr-secondstrand fr-unstranded HISAT2 (–rna-strandness parameter) R/RF F/FR NONE HTSeq (–stranded/-s parameter) reverse yes no STAR n/a (STAR doesn’t use library strandedness info for mapping) NONE NONE Picard CollectRnaSeqMetrics (STRAND_SPECIFICITY parameter) SECOND_READ_TRANSCRIPTION_STRAND FIRST_READ_TRANSCRIPTION_STRAND NONE Kallisto quant (parameter) –rf-stranded –fr-stranded NONE StringTie (parameter) –rf –fr NONE FeatureCounts (-s parameter) 2 1 0 RSEM (–forward-prob parameter) 0 1 0.5 Salmon (–libType parameter) ISR (assuming paired-end with inward read orientation) ISF (assuming paired-end with inward read orientation) IU (assuming paired-end with inward read orientation) Trinity (–SS_lib_type parameter) RF FR NONE MGI CWL YAML (strand parameter) first second NONE RegTools (strand parameter) -s 1 -s 2 -s 0 Example methods/kits: dUTP, NSR, NNSR, Illumina TruSeq Strand Specific Total RNA, NEBNext Ultra II Directional Example methods/kits: Ligation, Standard SOLiD, NuGEN Encore, 10X 5’ scRNA data Example kits/data: Standard Illumina, NuGEN OvationV2, SMARTer universal low input RNA kit (TaKara), GDC normalized TCGA data Notes To identify which ‘–library-type’ setting to use with TopHat, Illumina specifically documents the types in the ‘RNA Sequencing Analysis with TopHat’ Booklet. For the TruSeq RNA Sample Prep Kit, the appropriate library type is ‘fr-unstranded’. For TruSeq stranded sample prep kits, the library type is specified as ‘fr-firststrand’. These posts are also very informative: How to tell which library type to use (fr-firststrand or fr-secondstrand)? and How to determine if a library Is strand-specific and Strandness in RNASeq by Hong Zheng. Another suggestion is to view aligned reads in IGV and determine the read orientation by one of two methods. First, you can have IGV color alignments according to strand using the ‘Color alignments’ by ‘First-of-pair strand’ setting. Second, to get more detailed information you can hover your cursor over a read aligned to an exon. ‘F2 R1’ means the second read in the pair aligns to the forward strand and the first read in the pair aligns to the reverse strand. For a positive DNA strand transcript (5’ to 3’) this would denote a fr-firststrand setting in TopHat, i.e. “the right-most end of the fragment (in transcript coordinates) is the first sequenced”. For a negative DNA strand transcript (3’ to 5’) this would denote a fr-secondstrand setting in TopHat. ‘F1 R2’ means the first read in the pair aligns to the forward strand and the second read in the pair aligns to the reverse strand. See above for the complete definitions, but its simply the inverse for ‘F1 R2’ mapping. Anything other than FR orientation is not covered here and discussion with the individual responsible for library creation would be required. Typically ‘RF’ orientation is reserved for large-insert mate-pair libraries. Other orientations like ‘FF’ and ‘RR’ seem impossible with Illumina sequence technology and suggest structural variation between the sample and reference. Additional details are provided in the TopHat manual. For HTSeq, the htseq-count manual indicates that for the ‘–stranded’ option, ‘stranded=no’ means that a read is considered overlapping with a feature regardless of whether it is mapped to the same or the opposite strand as the feature. For ‘stranded=yes’ and single-end reads, the read has to be mapped to the same strand as the feature. For paired-end reads, the first read has to be on the same strand and the second read on the opposite strand. For ‘stranded=reverse’, these rules are reversed. For the ‘CollectRnaSeqMetrics’ sub-command of Picard, the Picard manual indicates that one should use ‘FIRST_READ_TRANSCRIPTION_STRAND’ if the reads are expected to be on the transcription strand. https://rnabio.org/module-09-appendix/0009/12/01/StrandSettings/
https://rnabio.org/module-09-appendix/0009/12/01/StrandSettings/
| Tool | RF/fr-firststrand stranded | FR/fr-secondstrand stranded | Unstranded |
|---|---|---|---|
| StringTie (parameter) | –rf | –fr | NONE |
本次实验数据check_ss解读:
This is PairEnd Data
Fraction of reads failed to determine: 0.0322
Fraction of reads explained by "1++,1--,2+-,2-+": 0.0267
Fraction of reads explained by "1+-,1-+,2++,2--": 0.9410
判断文库为RF/fr-firststrand stranded
stringtie应该使用 --rf参数
家益师兄确实用的 --rf !!!!
这篇关于通过RSeQC判断RNA-seq测序数据文库类型和链特异性,指导Stringtie参数使用的文章就介绍到这儿,希望我们推荐的文章对编程师们有所帮助!





