本文主要是介绍3D目标检测数据集 KITTI(标签格式解析、3D框可视化、点云转图像、BEV鸟瞰图),希望对大家解决编程问题提供一定的参考价值,需要的开发者们随着小编来一起学习吧!
本文介绍在3D目标检测中,理解和使用KITTI 数据集,包括KITTI 的基本情况、下载数据集、标签格式解析、3D框可视化、点云转图像、画BEV鸟瞰图等,并配有实现代码。
目录
1、KITTI数据集3D框可视化
2、KITTI 3D数据集
3、下载数据集
4、标签格式
5、标定参数解析
6、点云数据-->投影到图像
7、图像数据-->投影到点云
8、可视化图像2D结果、3D结果
9、点云3D结果-->图像BEV鸟瞰图结果(坐标系转换)
10、绘制BEV鸟瞰图
11、BEV鸟瞰图画2d框
12、完整工程代码
1、KITTI数据集3D框可视化
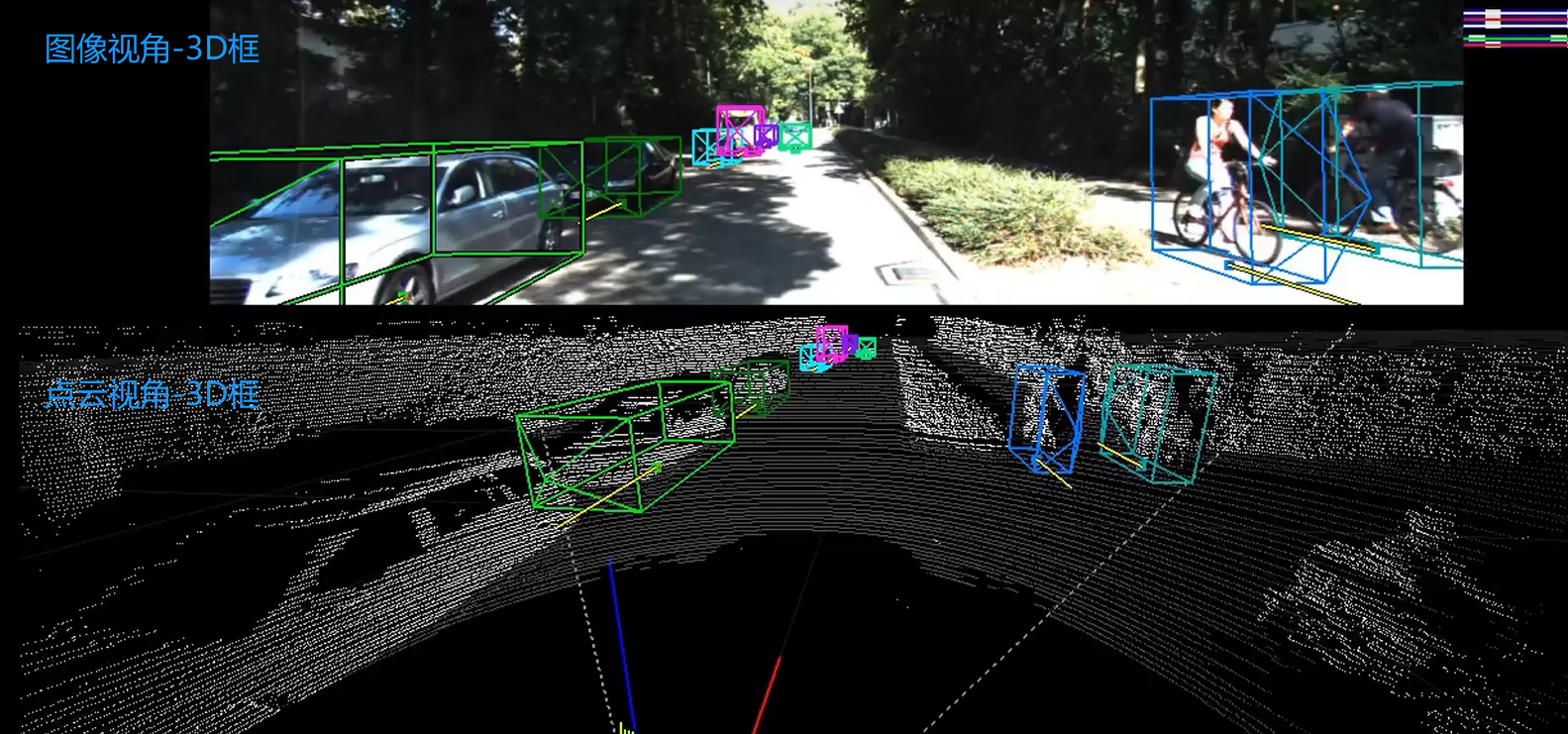
2、KITTI 3D数据集
kitti 3D数据集的基本情况:

KITTI整个数据集是在德国卡尔斯鲁厄采集的,采集时长6小时。KITTI官网放出的数据大约占采集全部的25%,去除了测试集中相关的数据片段,按场景可以分为“道路”、“城市”、“住宅区”、“校园”和“行人”5类。
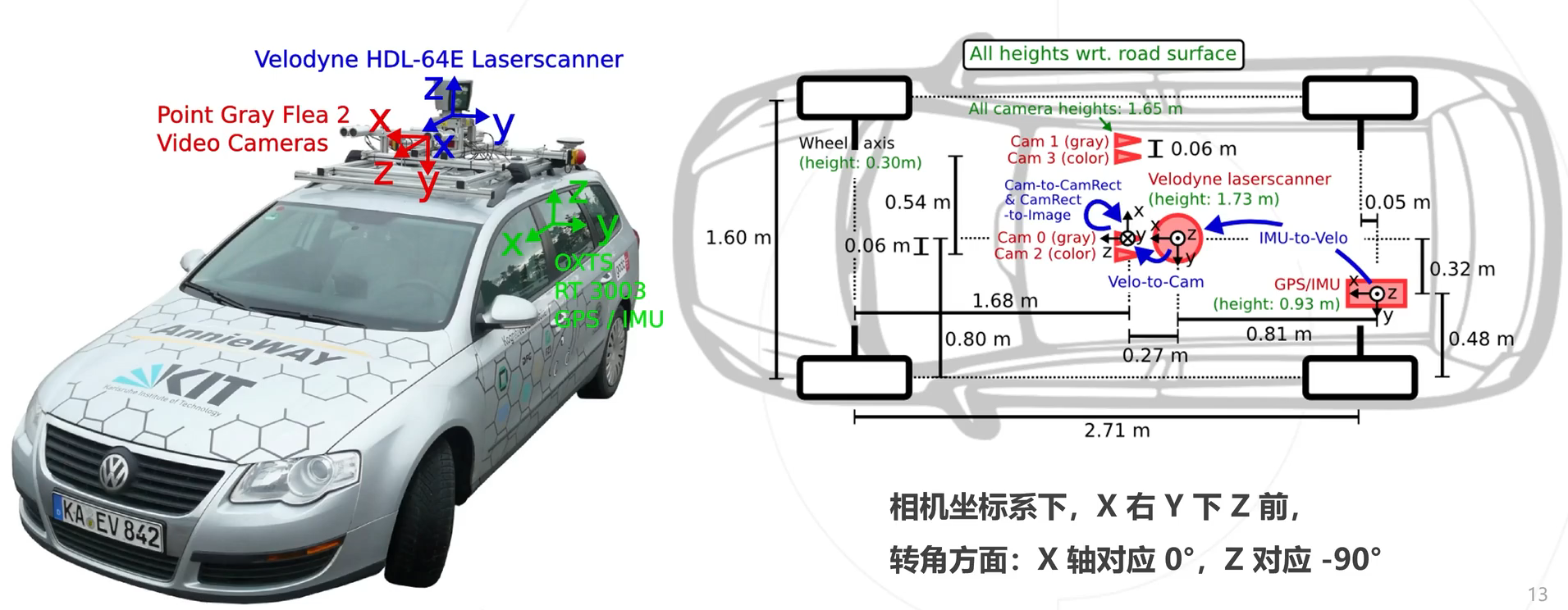
传感器配置:
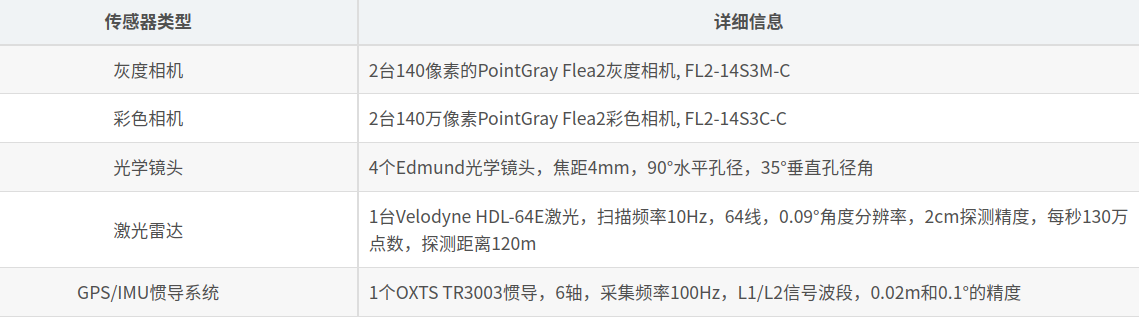
传感器安装位置:
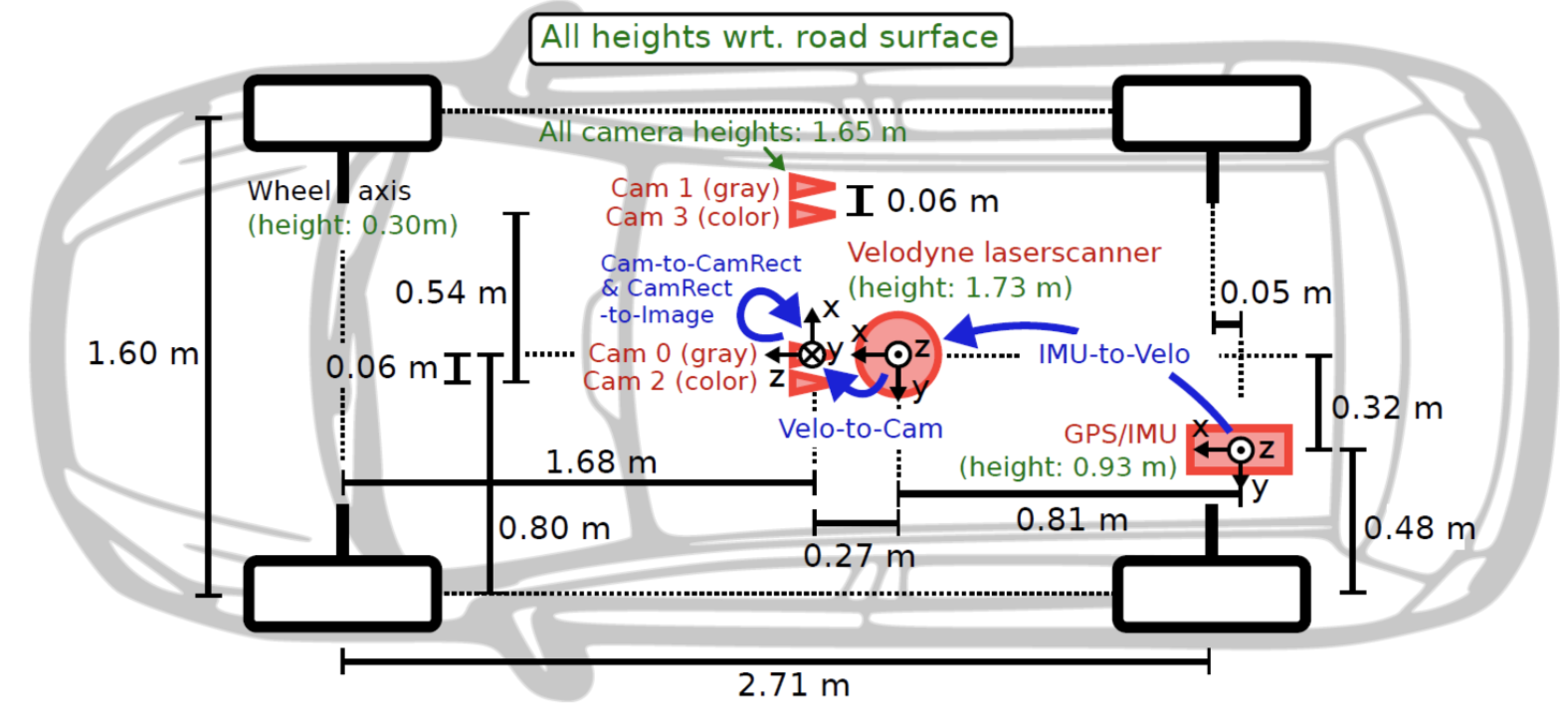
3、下载数据集
The KITTI Vision Benchmark Suite (cvlibs.net)

下载数据需要注册账号的,获取取百度网盘下载;文件的格式如下所示
图片格式:xxx.jpg
点云格式:xxx.bin(点云是以bin二进制的方式存储的)
标定参数:xxx.txt(一个文件中包括各个相机的内参、畸变校正矩阵、激光雷达坐标转到相机坐标的矩阵、IMU坐标转到激光雷达坐标的矩阵)
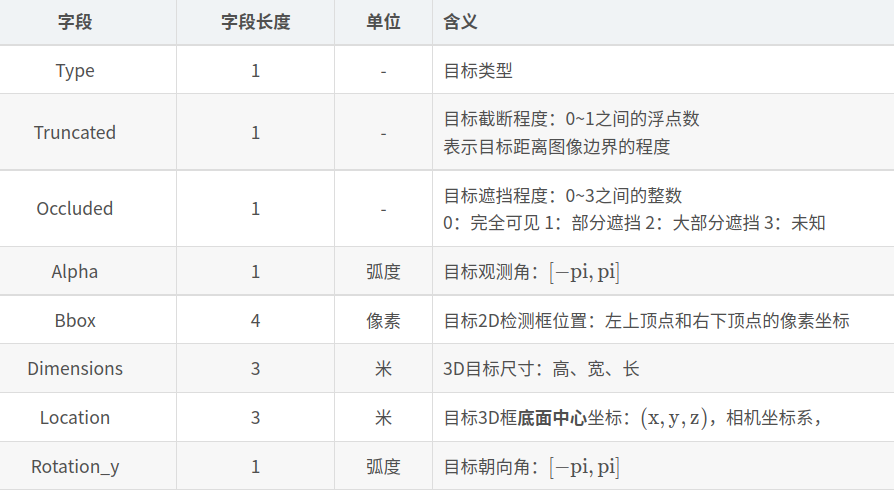
标签格式:xxx.txt(包含类别、截断情况、遮挡情况、观测角度、2D框左上角坐标、2D框右下角坐标、3D物体的尺寸-高宽长、3D物体的中心坐标-xyz、置信度)
4、标签格式
示例标签:Pedestrian 0.00 0 -0.20 712.40 143.00 810.73 307.92 1.89 0.48 1.20 1.84 1.47 8.41 0.01

这时可以看看这个视频:
Nuscenes、KITTI等多个BEV开源数据集介绍
5、标定参数解析
然后看一下标定参数:
P0-P3:是各个相机的内参矩阵;3×4的相机投影矩阵,0~3分别对应左侧灰度相机、右侧灰度相机、左侧彩色相机、右侧彩色相机。
R0_rect: 是左相机的畸变矫正矩阵;3×3的旋转修正矩阵。
Tr_velo_to_cam:是激光雷达坐标系 转到 相机坐标系矩阵;3×4的激光坐标系到Cam 0坐标系的变换矩阵。
Tr_imu_to_velo: 是IMU坐标转到激光雷达坐标的矩阵;3×4的IMU坐标系到激光坐标系的变换矩阵。

6、点云数据-->投影到图像
当有了点云数据信息,如何投影到图像中呢?本质上是一个坐标系转换的问题,流程思路如下:
- 已知点云坐标(x,y,z),当前是处于激光雷达坐标系
- 激光雷达坐标系 转到 相机坐标系,需要用到标定参数中的Tr_velo_to_cam矩阵,此时得到相机坐标(x1,y1,z1)
- 相机坐标系进行畸变矫正,需要用到标定参数中的R0_rect矩阵,此时得到相机坐标(x2,y2,z2)
- 相机坐标系转为图像坐标系,需要用到标定参数中的P0矩阵,即相机内存矩阵,此时得到图像坐标(u,v)
看一下示例效果:

接口代码:
'''
将点云数据投影到图像
'''
def show_lidar_on_image(pc_velo, img, calib, img_width, img_height):''' Project LiDAR points to image '''imgfov_pc_velo, pts_2d, fov_inds = get_lidar_in_image_fov(pc_velo,calib, 0, 0, img_width, img_height, True)imgfov_pts_2d = pts_2d[fov_inds,:]imgfov_pc_rect = calib.project_velo_to_rect(imgfov_pc_velo)import matplotlib.pyplot as pltcmap = plt.cm.get_cmap('hsv', 256)cmap = np.array([cmap(i) for i in range(256)])[:,:3]*255for i in range(imgfov_pts_2d.shape[0]):depth = imgfov_pc_rect[i,2]color = cmap[int(640.0/depth),:]cv2.circle(img, (int(np.round(imgfov_pts_2d[i,0])),int(np.round(imgfov_pts_2d[i,1]))),2, color=tuple(color), thickness=-1)Image.fromarray(img).save('save_output/lidar_on_image.png')Image.fromarray(img).show() return img
核心代码:
'''
将点云数据投影到相机坐标系
'''
def get_lidar_in_image_fov(pc_velo, calib, xmin, ymin, xmax, ymax,return_more=False, clip_distance=2.0):''' Filter lidar points, keep those in image FOV '''pts_2d = calib.project_velo_to_image(pc_velo)fov_inds = (pts_2d[:,0]<xmax) & (pts_2d[:,0]>=xmin) & \(pts_2d[:,1]<ymax) & (pts_2d[:,1]>=ymin)fov_inds = fov_inds & (pc_velo[:,0]>clip_distance)imgfov_pc_velo = pc_velo[fov_inds,:]if return_more:return imgfov_pc_velo, pts_2d, fov_indselse:return imgfov_pc_velo7、图像数据-->投影到点云
当有了图像RGB信息,如何投影到点云中呢?本质上是一个坐标系转换的问题,和上面的是逆过程,流程思路如下:
- 已知图像坐标(u,v),当前是处于图像坐标系
- 图像坐标系 转 相机坐标系,需要用到标定参数中的P0逆矩阵,即相机内存矩阵,得到相机坐标(x,y,z)
- 相机坐标系进行畸变矫正,需要用到标定参数中的R0_rect逆矩阵,得到相机坐标(x1,y1,z1)
- 矫正后相机坐标系 转 激光雷达坐标系,需要用到标定参数中的Tr_velo_to_cam逆矩阵,此时得到激光雷达坐标(x2,y2,z2)
8、可视化图像2D结果、3D结果
先看一下2D框的效果:

3D框的效果:

接口代码:
'''
在图像中画2D框、3D框
'''
def show_image_with_boxes(img, objects, calib, show3d=True):img1 = np.copy(img) # for 2d bboximg2 = np.copy(img) # for 3d bboxfor obj in objects:if obj.type=='DontCare':continuecv2.rectangle(img1, (int(obj.xmin),int(obj.ymin)), (int(obj.xmax),int(obj.ymax)), (0,255,0), 2) # 画2D框box3d_pts_2d, box3d_pts_3d = utils.compute_box_3d(obj, calib.P) # 获取图像3D框(8*2)、相机坐标系3D框(8*3)img2 = utils.draw_projected_box3d(img2, box3d_pts_2d) # 在图像上画3D框if show3d:Image.fromarray(img2).save('save_output/image_with_3Dboxes.png')Image.fromarray(img2).show()else:Image.fromarray(img1).save('save_output/image_with_2Dboxes.png')Image.fromarray(img1).show()
核心代码:
def compute_box_3d(obj, P):'''计算对象的3D边界框在图像平面上的投影输入: obj代表一个物体标签信息, P代表相机的投影矩阵-内参。输出: 返回两个值, corners_3d表示3D边界框在 相机坐标系 的8个角点的坐标-3D坐标。corners_2d表示3D边界框在 图像上 的8个角点的坐标-2D坐标。'''# 计算一个绕Y轴旋转的旋转矩阵R,用于将3D坐标从世界坐标系转换到相机坐标系。obj.ry是对象的偏航角R = roty(obj.ry) # 物体实际的长、宽、高l = obj.l;w = obj.w;h = obj.h;# 存储了3D边界框的8个角点相对于对象中心的坐标。这些坐标定义了3D边界框的形状。x_corners = [l/2,l/2,-l/2,-l/2,l/2,l/2,-l/2,-l/2];y_corners = [0,0,0,0,-h,-h,-h,-h];z_corners = [w/2,-w/2,-w/2,w/2,w/2,-w/2,-w/2,w/2];# 1、将3D边界框的角点坐标从对象坐标系转换到相机坐标系。它使用了旋转矩阵Rcorners_3d = np.dot(R, np.vstack([x_corners,y_corners,z_corners]))# 3D边界框的坐标进行平移corners_3d[0,:] = corners_3d[0,:] + obj.t[0];corners_3d[1,:] = corners_3d[1,:] + obj.t[1];corners_3d[2,:] = corners_3d[2,:] + obj.t[2];# 2、检查对象是否在相机前方,因为只有在相机前方的对象才会被绘制。# 如果对象的Z坐标(深度)小于0.1,就意味着对象在相机后方,那么corners_2d将被设置为None,函数将返回None。if np.any(corners_3d[2,:]<0.1):corners_2d = Nonereturn corners_2d, np.transpose(corners_3d)# 3、将相机坐标系下的3D边界框的角点,投影到图像平面上,得到它们在图像上的2D坐标。corners_2d = project_to_image(np.transpose(corners_3d), P);return corners_2d, np.transpose(corners_3d)def draw_projected_box3d(image, qs, color=(0,60,255), thickness=2):'''qs: 包含8个3D边界框角点坐标的数组, 形状为(8, 2)。图像坐标下的3D框, 8个顶点坐标。'''''' Draw 3d bounding box in imageqs: (8,2) array of vertices for the 3d box in following order:1 -------- 0/| /|2 -------- 3 .| | | |. 5 -------- 4|/ |/6 -------- 7'''qs = qs.astype(np.int32) # 将输入的顶点坐标转换为整数类型,以便在图像上绘制。# 这个循环迭代4次,每次处理一个边界框的一条边。for k in range(0,4):# Ref: http://docs.enthought.com/mayavi/mayavi/auto/mlab_helper_functions.html# 定义了要绘制的边的起始点和结束点的索引。在这个循环中,它用于绘制边界框的前四条边。i,j=k,(k+1)%4cv2.line(image, (qs[i,0],qs[i,1]), (qs[j,0],qs[j,1]), color, thickness)# 定义了要绘制的边的起始点和结束点的索引。在这个循环中,它用于绘制边界框的后四条边,与前四条边平行i,j=k+4,(k+1)%4 + 4cv2.line(image, (qs[i,0],qs[i,1]), (qs[j,0],qs[j,1]), color, thickness)# 定义了要绘制的边的起始点和结束点的索引。在这个循环中,它用于绘制连接前四条边和后四条边的边界框的边。i,j=k,k+4cv2.line(image, (qs[i,0],qs[i,1]), (qs[j,0],qs[j,1]), color, thickness)return image9、点云3D结果-->图像BEV鸟瞰图结果(坐标系转换)
思路流程:
- 读取点云数据,点云得存储格式是n*4,n是指当前文件点云的数量,4分别表示(x,y,z,intensity),即点云的空间三维坐标、反射强度
- 我们只需读取前两行即可,得到坐标点(x,y)
- 然后将坐标点(x,y),画散点图
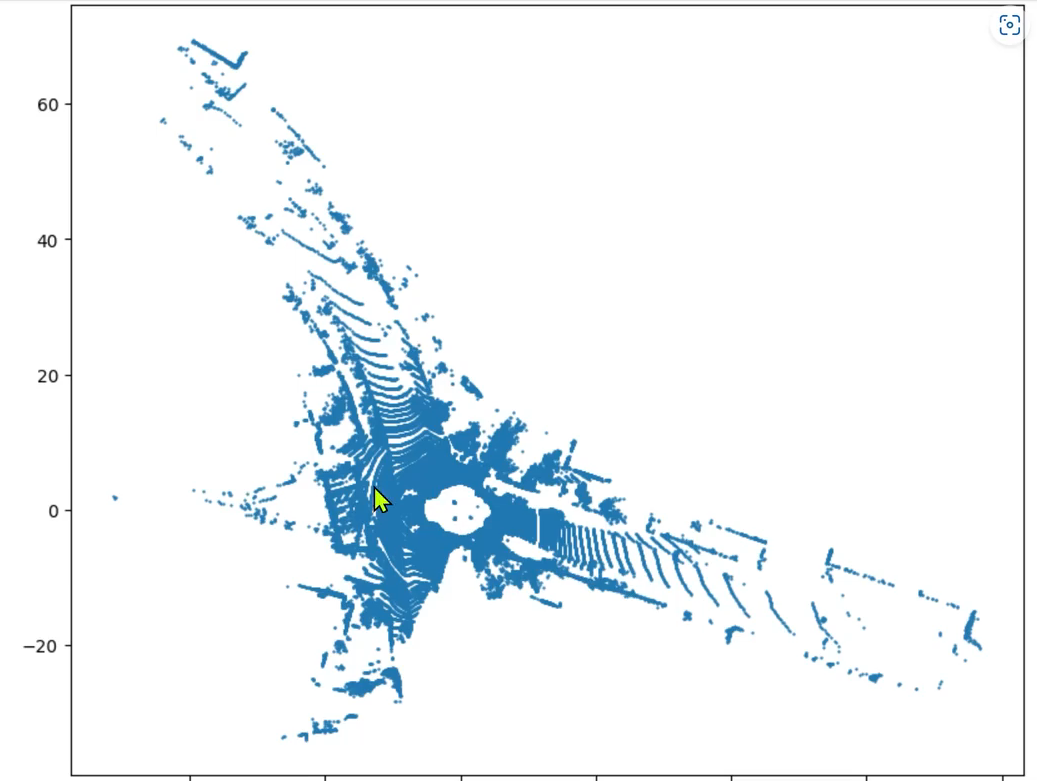
BEV鸟瞰图效果如下:
10、绘制BEV鸟瞰图
BEV图像示例效果:
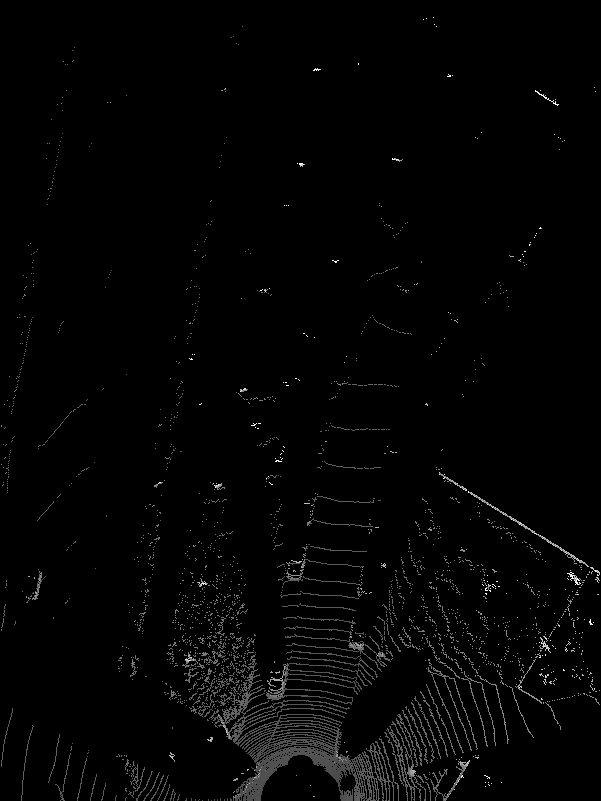

核心代码:
'''
可视化BEV鸟瞰图
'''
def show_lidar_topview(pc_velo, objects, calib):# 1-设置鸟瞰图范围side_range = (-30, 30) # 左右距离fwd_range = (0, 80) # 后前距离x_points = pc_velo[:, 0]y_points = pc_velo[:, 1]z_points = pc_velo[:, 2]# 2-获得区域内的点f_filt = np.logical_and(x_points > fwd_range[0], x_points < fwd_range[1])s_filt = np.logical_and(y_points > side_range[0], y_points < side_range[1])filter = np.logical_and(f_filt, s_filt)indices = np.argwhere(filter).flatten() x_points = x_points[indices]y_points = y_points[indices]z_points = z_points[indices]# 定义了鸟瞰图中每个像素代表的距离res = 0.1 # 3-1将点云坐标系 转到 BEV坐标系x_img = (-y_points / res).astype(np.int32)y_img = (-x_points / res).astype(np.int32)# 3-2调整坐标原点x_img -= int(np.floor(side_range[0]) / res)y_img += int(np.floor(fwd_range[1]) / res)print(x_img.min(), x_img.max(), y_img.min(), y_img.max()) # 4-填充像素值, 将点云数据的高度信息(Z坐标)映射到像素值height_range = (-3, 1.0)pixel_value = np.clip(a=z_points, a_max=height_range[1], a_min=height_range[0])def scale_to_255(a, min, max, dtype=np.uint8):return ((a - min) / float(max - min) * 255).astype(dtype)pixel_value = scale_to_255(pixel_value, height_range[0], height_range[1])# 创建图像数组x_max = 1 + int((side_range[1] - side_range[0]) / res)y_max = 1 + int((fwd_range[1] - fwd_range[0]) / res)im = np.zeros([y_max, x_max], dtype=np.uint8)im[y_img, x_img] = pixel_valueim2 = Image.fromarray(im)im2.save('save_output/BEV.png')im2.show()
11、BEV鸟瞰图画2d框
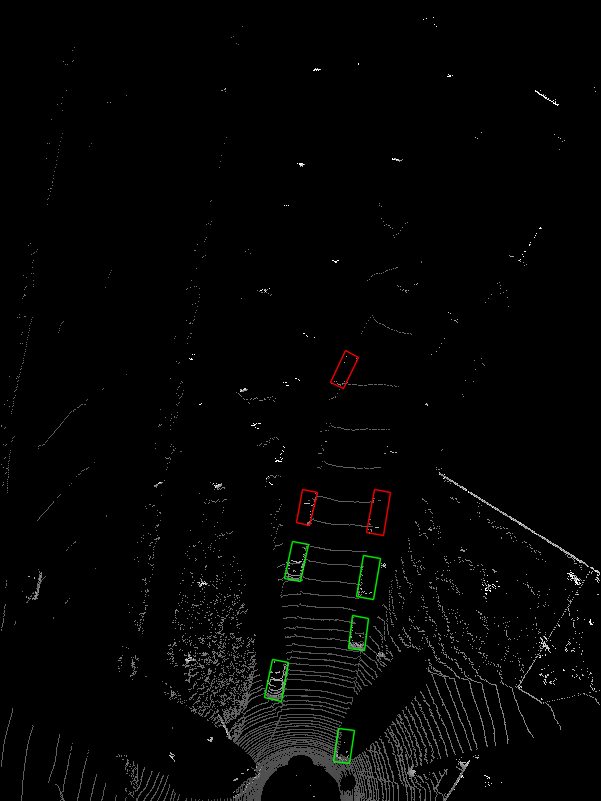
在BEV视图中画框,可视化结果:
接口代码:
'''
将点云数据3D框投影到BEV
'''
def show_lidar_topview_with_boxes(img, objects, calib):def bbox3d(obj):box3d_pts_2d, box3d_pts_3d = utils.compute_box_3d(obj, calib.P) # 获取3D框-图像、3D框-相机坐标系box3d_pts_3d_velo = calib.project_rect_to_velo(box3d_pts_3d) # 将相机坐标系的框 转到 激光雷达坐标系return box3d_pts_3d_velo # 返回nx3的点boxes3d = [bbox3d(obj) for obj in objects if obj.type == "Car"]gt = np.array(boxes3d)im2 = utils.draw_box3d_label_on_bev(img, gt, scores=None, thickness=1) # 获取激光雷达坐标系的3D点,选择x, y两维,画到BEV平面坐标系上im2 = Image.fromarray(im2)im2.save('save_output/BEV with boxes.png')im2.show()
核心代码:
# 设置BEV鸟瞰图参数
side_range = (-30, 30) # 左右距离
fwd_range = (0, 80) # 后前距离
res = 0.1 # 分辨率0.05mdef compute_box_3d(obj, P):'''计算对象的3D边界框在图像平面上的投影输入: obj代表一个物体标签信息, P代表相机的投影矩阵-内参。输出: 返回两个值, corners_3d表示3D边界框在 相机坐标系 的8个角点的坐标-3D坐标。corners_2d表示3D边界框在 图像上 的8个角点的坐标-2D坐标。'''# 计算一个绕Y轴旋转的旋转矩阵R,用于将3D坐标从世界坐标系转换到相机坐标系。obj.ry是对象的偏航角R = roty(obj.ry) # 物体实际的长、宽、高l = obj.l;w = obj.w;h = obj.h;# 存储了3D边界框的8个角点相对于对象中心的坐标。这些坐标定义了3D边界框的形状。x_corners = [l/2,l/2,-l/2,-l/2,l/2,l/2,-l/2,-l/2];y_corners = [0,0,0,0,-h,-h,-h,-h];z_corners = [w/2,-w/2,-w/2,w/2,w/2,-w/2,-w/2,w/2];# 1、将3D边界框的角点坐标从对象坐标系转换到相机坐标系。它使用了旋转矩阵Rcorners_3d = np.dot(R, np.vstack([x_corners,y_corners,z_corners]))# 3D边界框的坐标进行平移corners_3d[0,:] = corners_3d[0,:] + obj.t[0];corners_3d[1,:] = corners_3d[1,:] + obj.t[1];corners_3d[2,:] = corners_3d[2,:] + obj.t[2];# 2、检查对象是否在相机前方,因为只有在相机前方的对象才会被绘制。# 如果对象的Z坐标(深度)小于0.1,就意味着对象在相机后方,那么corners_2d将被设置为None,函数将返回None。if np.any(corners_3d[2,:]<0.1):corners_2d = Nonereturn corners_2d, np.transpose(corners_3d)# 3、将相机坐标系下的3D边界框的角点,投影到图像平面上,得到它们在图像上的2D坐标。corners_2d = project_to_image(np.transpose(corners_3d), P);return corners_2d, np.transpose(corners_3d)12、完整工程代码
工程目录:

kitti_vis_main.py(主代码入口)
from __future__ import print_functionimport os
import sys
import cv2
import os.path
from PIL import Image
BASE_DIR = os.path.dirname(os.path.abspath(__file__))
ROOT_DIR = os.path.dirname(BASE_DIR)
sys.path.append(BASE_DIR)
sys.path.append(os.path.join(ROOT_DIR, 'mayavi'))
from kitti_object import *def visualization():import mayavi.mlab as mlabdataset = kitti_object(os.path.join(ROOT_DIR, 'Kitti_3D_Vis/dataset/object')) # linux 路径data_idx = 10 # 选择第几张图像# 1-加载标签数据objects = dataset.get_label_objects(data_idx)print("There are %d objects.", len(objects))# 2-加载图像img = dataset.get_image(data_idx)img = cv2.cvtColor(img, cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB)img_height, img_width, img_channel = img.shape# 3-加载点云数据pc_velo = dataset.get_lidar(data_idx)[:,0:3] # (x, y, z)# 4-加载标定参数calib = dataset.get_calibration(data_idx)# 5-可视化原始图像print(' ------------ show raw image -------- ')Image.fromarray(img).show()# 6-在图像中画2D框print(' ------------ show image with 2D bounding box -------- ')show_image_with_boxes(img, objects, calib, False)# 7-在图像中画3D框print(' ------------ show image with 3D bounding box ------- ')show_image_with_boxes(img, objects, calib, True)# 8-将点云数据投影到图像print(' ----------- LiDAR points projected to image plane -- ')show_lidar_on_image(pc_velo, img, calib, img_width, img_height)# 9-画BEV图print('------------------ BEV of LiDAR points -----------------------------')show_lidar_topview(pc_velo, objects, calib)# 10-在BEV图中画2D框print('--------------- BEV of LiDAR points with bobes ---------------------')img1 = cv2.imread('save_output/BEV.png') img = cv2.cvtColor(img1, cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB)show_lidar_topview_with_boxes(img1, objects, calib)if __name__=='__main__':visualization()kitti_util.py
from __future__ import print_functionimport numpy as np
import cv2
from PIL import Image
import os# 设置BEV鸟瞰图参数
side_range = (-30, 30) # 左右距离
fwd_range = (0, 80) # 后前距离
res = 0.1 # 分辨率0.05mdef compute_box_3d(obj, P):'''计算对象的3D边界框在图像平面上的投影输入: obj代表一个物体标签信息, P代表相机的投影矩阵-内参。输出: 返回两个值, corners_3d表示3D边界框在 相机坐标系 的8个角点的坐标-3D坐标。corners_2d表示3D边界框在 图像上 的8个角点的坐标-2D坐标。'''# 计算一个绕Y轴旋转的旋转矩阵R,用于将3D坐标从世界坐标系转换到相机坐标系。obj.ry是对象的偏航角R = roty(obj.ry) # 物体实际的长、宽、高l = obj.l;w = obj.w;h = obj.h;# 存储了3D边界框的8个角点相对于对象中心的坐标。这些坐标定义了3D边界框的形状。x_corners = [l/2,l/2,-l/2,-l/2,l/2,l/2,-l/2,-l/2];y_corners = [0,0,0,0,-h,-h,-h,-h];z_corners = [w/2,-w/2,-w/2,w/2,w/2,-w/2,-w/2,w/2];# 1、将3D边界框的角点坐标从对象坐标系转换到相机坐标系。它使用了旋转矩阵Rcorners_3d = np.dot(R, np.vstack([x_corners,y_corners,z_corners]))# 3D边界框的坐标进行平移corners_3d[0,:] = corners_3d[0,:] + obj.t[0];corners_3d[1,:] = corners_3d[1,:] + obj.t[1];corners_3d[2,:] = corners_3d[2,:] + obj.t[2];# 2、检查对象是否在相机前方,因为只有在相机前方的对象才会被绘制。# 如果对象的Z坐标(深度)小于0.1,就意味着对象在相机后方,那么corners_2d将被设置为None,函数将返回None。if np.any(corners_3d[2,:]<0.1):corners_2d = Nonereturn corners_2d, np.transpose(corners_3d)# 3、将相机坐标系下的3D边界框的角点,投影到图像平面上,得到它们在图像上的2D坐标。corners_2d = project_to_image(np.transpose(corners_3d), P);return corners_2d, np.transpose(corners_3d)def project_to_image(pts_3d, P):'''将相机坐标系下的3D边界框的角点, 投影到图像平面上, 得到它们在图像上的2D坐标输入: pts_3d是一个nx3的矩阵, 包含了待投影的3D坐标点(每行一个点), P是相机的投影矩阵, 通常是一个3x4的矩阵。输出: 返回一个nx2的矩阵, 包含了投影到图像平面上的2D坐标点。P(3x4) dot pts_3d_extended(4xn) = projected_pts_2d(3xn) => normalize projected_pts_2d(2xn)<=> pts_3d_extended(nx4) dot P'(4x3) = projected_pts_2d(nx3) => normalize projected_pts_2d(nx2)'''n = pts_3d.shape[0] # 获取3D点的数量pts_3d_extend = np.hstack((pts_3d, np.ones((n,1)))) # 将每个3D点的坐标扩展为齐次坐标形式(4D),通过在每个点的末尾添加1,创建了一个nx4的矩阵。pts_2d = np.dot(pts_3d_extend, np.transpose(P)) # 将扩展的3D坐标点矩阵与投影矩阵P相乘,得到一个nx3的矩阵,其中每一行包含了3D点在图像平面上的投影坐标。每个点的坐标表示为[x, y, z]。pts_2d[:,0] /= pts_2d[:,2] # 将投影坐标中的x坐标除以z坐标,从而获得2D图像上的x坐标。pts_2d[:,1] /= pts_2d[:,2] # 将投影坐标中的y坐标除以z坐标,从而获得2D图像上的y坐标。return pts_2d[:,0:2] # 返回一个nx2的矩阵,其中包含了每个3D点在2D图像上的坐标。def draw_projected_box3d(image, qs, color=(0,60,255), thickness=2):'''qs: 包含8个3D边界框角点坐标的数组, 形状为(8, 2)。图像坐标下的3D框, 8个顶点坐标。'''''' Draw 3d bounding box in imageqs: (8,2) array of vertices for the 3d box in following order:1 -------- 0/| /|2 -------- 3 .| | | |. 5 -------- 4|/ |/6 -------- 7'''qs = qs.astype(np.int32) # 将输入的顶点坐标转换为整数类型,以便在图像上绘制。# 这个循环迭代4次,每次处理一个边界框的一条边。for k in range(0,4):# Ref: http://docs.enthought.com/mayavi/mayavi/auto/mlab_helper_functions.html# 定义了要绘制的边的起始点和结束点的索引。在这个循环中,它用于绘制边界框的前四条边。i,j=k,(k+1)%4cv2.line(image, (qs[i,0],qs[i,1]), (qs[j,0],qs[j,1]), color, thickness)# 定义了要绘制的边的起始点和结束点的索引。在这个循环中,它用于绘制边界框的后四条边,与前四条边平行i,j=k+4,(k+1)%4 + 4cv2.line(image, (qs[i,0],qs[i,1]), (qs[j,0],qs[j,1]), color, thickness)# 定义了要绘制的边的起始点和结束点的索引。在这个循环中,它用于绘制连接前四条边和后四条边的边界框的边。i,j=k,k+4cv2.line(image, (qs[i,0],qs[i,1]), (qs[j,0],qs[j,1]), color, thickness)return imagedef draw_box3d_label_on_bev(image, boxes3d, thickness=1, scores=None):# if scores is not None and scores.shape[0] >0:img = image.copy() num = len(boxes3d)for n in range(num):b = boxes3d[n]x0 = b[0, 0]y0 = b[0, 1]x1 = b[1, 0]y1 = b[1, 1]x2 = b[2, 0]y2 = b[2, 1]x3 = b[3, 0]y3 = b[3, 1]if (x0<30 and x1<30 and x2<30 and x3<30):u0, v0 = lidar_to_top_coords(x0, y0)u1, v1 = lidar_to_top_coords(x1, y1)u2, v2 = lidar_to_top_coords(x2, y2)u3, v3 = lidar_to_top_coords(x3, y3)color = (0, 255, 0) # greencv2.line(img, (u0, v0), (u1, v1), color, thickness, cv2.LINE_AA)cv2.line(img, (u1, v1), (u2, v2), color, thickness, cv2.LINE_AA)cv2.line(img, (u2, v2), (u3, v3), color, thickness, cv2.LINE_AA)cv2.line(img, (u3, v3), (u0, v0), color, thickness, cv2.LINE_AA)elif (x0<50 and x1<50 and x2<50 and x3<50):color = (255, 0, 0) # redu0, v0 = lidar_to_top_coords(x0, y0)u1, v1 = lidar_to_top_coords(x1, y1)u2, v2 = lidar_to_top_coords(x2, y2)u3, v3 = lidar_to_top_coords(x3, y3)cv2.line(img, (u0, v0), (u1, v1), color, thickness, cv2.LINE_AA)cv2.line(img, (u1, v1), (u2, v2), color, thickness, cv2.LINE_AA)cv2.line(img, (u2, v2), (u3, v3), color, thickness, cv2.LINE_AA)cv2.line(img, (u3, v3), (u0, v0), color, thickness, cv2.LINE_AA)else:color = (0, 0, 255) # blueu0, v0 = lidar_to_top_coords(x0, y0)u1, v1 = lidar_to_top_coords(x1, y1)u2, v2 = lidar_to_top_coords(x2, y2)u3, v3 = lidar_to_top_coords(x3, y3)cv2.line(img, (u0, v0), (u1, v1), color, thickness, cv2.LINE_AA)cv2.line(img, (u1, v1), (u2, v2), color, thickness, cv2.LINE_AA)cv2.line(img, (u2, v2), (u3, v3), color, thickness, cv2.LINE_AA)cv2.line(img, (u3, v3), (u0, v0), color, thickness, cv2.LINE_AA) return imgdef draw_box3d_predict_on_bev(image, boxes3d, thickness=1, scores=None):# if scores is not None and scores.shape[0] >0:img = image.copy() num = len(boxes3d)for n in range(num):b = boxes3d[n]x0 = b[0, 0]y0 = b[0, 1]x1 = b[1, 0]y1 = b[1, 1]x2 = b[2, 0]y2 = b[2, 1]x3 = b[3, 0]y3 = b[3, 1]color = (255, 255, 255) # whiteu0, v0 = lidar_to_top_coords(x0, y0)u1, v1 = lidar_to_top_coords(x1, y1)u2, v2 = lidar_to_top_coords(x2, y2)u3, v3 = lidar_to_top_coords(x3, y3)cv2.line(img, (u0, v0), (u1, v1), color, thickness, cv2.LINE_AA)cv2.line(img, (u1, v1), (u2, v2), color, thickness, cv2.LINE_AA)cv2.line(img, (u2, v2), (u3, v3), color, thickness, cv2.LINE_AA)cv2.line(img, (u3, v3), (u0, v0), color, thickness, cv2.LINE_AA)return imgdef lidar_to_top_coords(x, y, z=None):if 0:return x, yelse:# print("TOP_X_MAX-TOP_X_MIN:",TOP_X_MAX,TOP_X_MIN)xx = (-y / res).astype(np.int32)yy = (-x / res).astype(np.int32)# 调整坐标原点xx -= int(np.floor(side_range[0]) / res)yy += int(np.floor(fwd_range[1]) / res)return xx, yy# 解析标签数据
class Object3d(object):''' 3d object label '''def __init__(self, label_file_line):data = label_file_line.split(' ')data[1:] = [float(x) for x in data[1:]]# extract label, truncation, occlusionself.type = data[0] # 'Car', 'Pedestrian', ...self.truncation = data[1] # truncated pixel ratio [0..1]self.occlusion = int(data[2]) # 0=visible, 1=partly occluded, 2=fully occluded, 3=unknownself.alpha = data[3] # object observation angle [-pi..pi]# extract 2d bounding box in 0-based coordinatesself.xmin = data[4] # leftself.ymin = data[5] # topself.xmax = data[6] # rightself.ymax = data[7] # bottomself.box2d = np.array([self.xmin,self.ymin,self.xmax,self.ymax])# extract 3d bounding box informationself.h = data[8] # box heightself.w = data[9] # box widthself.l = data[10] # box length (in meters)self.t = (data[11],data[12],data[13]) # location (x,y,z) in camera coord.self.ry = data[14] # yaw angle (around Y-axis in camera coordinates) [-pi..pi]def print_object(self):print('Type, truncation, occlusion, alpha: %s, %d, %d, %f' % \(self.type, self.truncation, self.occlusion, self.alpha))print('2d bbox (x0,y0,x1,y1): %f, %f, %f, %f' % \(self.xmin, self.ymin, self.xmax, self.ymax))print('3d bbox h,w,l: %f, %f, %f' % \(self.h, self.w, self.l))print('3d bbox location, ry: (%f, %f, %f), %f' % \(self.t[0],self.t[1],self.t[2],self.ry))class Calibration(object):''' Calibration matrices and utils3d XYZ in <label>.txt are in rect camera coord.2d box xy are in image2 coordPoints in <lidar>.bin are in Velodyne coord.y_image2 = P^2_rect * x_recty_image2 = P^2_rect * R0_rect * Tr_velo_to_cam * x_velox_ref = Tr_velo_to_cam * x_velox_rect = R0_rect * x_refP^2_rect = [f^2_u, 0, c^2_u, -f^2_u b^2_x;0, f^2_v, c^2_v, -f^2_v b^2_y;0, 0, 1, 0]= K * [1|t]image2 coord:----> x-axis (u)||v y-axis (v)velodyne coord:front x, left y, up zrect/ref camera coord:right x, down y, front zRef (KITTI paper): http://www.cvlibs.net/publications/Geiger2013IJRR.pdfTODO(rqi): do matrix multiplication only once for each projection.'''def __init__(self, calib_filepath, from_video=False):if from_video:calibs = self.read_calib_from_video(calib_filepath)else:calibs = self.read_calib_file(calib_filepath)# Projection matrix from rect camera coord to image2 coordself.P = calibs['P2'] self.P = np.reshape(self.P, [3,4])# Rigid transform from Velodyne coord to reference camera coordself.V2C = calibs['Tr_velo_to_cam']self.V2C = np.reshape(self.V2C, [3,4])self.C2V = inverse_rigid_trans(self.V2C)# Rotation from reference camera coord to rect camera coordself.R0 = calibs['R0_rect']self.R0 = np.reshape(self.R0,[3,3])# Camera intrinsics and extrinsicsself.c_u = self.P[0,2]self.c_v = self.P[1,2]self.f_u = self.P[0,0]self.f_v = self.P[1,1]self.b_x = self.P[0,3]/(-self.f_u) # relative self.b_y = self.P[1,3]/(-self.f_v)def read_calib_file(self, filepath):''' Read in a calibration file and parse into a dictionary.'''data = {}with open(filepath, 'r') as f:for line in f.readlines():line = line.rstrip()if len(line)==0: continuekey, value = line.split(':', 1)# The only non-float values in these files are dates, which# we don't care about anywaytry:data[key] = np.array([float(x) for x in value.split()])except ValueError:passreturn datadef read_calib_from_video(self, calib_root_dir):''' Read calibration for camera 2 from video calib files.there are calib_cam_to_cam and calib_velo_to_cam under the calib_root_dir'''data = {}cam2cam = self.read_calib_file(os.path.join(calib_root_dir, 'calib_cam_to_cam.txt'))velo2cam = self.read_calib_file(os.path.join(calib_root_dir, 'calib_velo_to_cam.txt'))Tr_velo_to_cam = np.zeros((3,4))Tr_velo_to_cam[0:3,0:3] = np.reshape(velo2cam['R'], [3,3])Tr_velo_to_cam[:,3] = velo2cam['T']data['Tr_velo_to_cam'] = np.reshape(Tr_velo_to_cam, [12])data['R0_rect'] = cam2cam['R_rect_00']data['P2'] = cam2cam['P_rect_02']return datadef cart2hom(self, pts_3d):''' Input: nx3 points in CartesianOupput: nx4 points in Homogeneous by pending 1'''n = pts_3d.shape[0]pts_3d_hom = np.hstack((pts_3d, np.ones((n,1))))return pts_3d_hom# =========================== # ------- 3d to 3d ---------- # =========================== def project_velo_to_ref(self, pts_3d_velo):pts_3d_velo = self.cart2hom(pts_3d_velo) # nx4return np.dot(pts_3d_velo, np.transpose(self.V2C))def project_ref_to_velo(self, pts_3d_ref):pts_3d_ref = self.cart2hom(pts_3d_ref) # nx4return np.dot(pts_3d_ref, np.transpose(self.C2V))def project_rect_to_ref(self, pts_3d_rect):''' Input and Output are nx3 points '''return np.transpose(np.dot(np.linalg.inv(self.R0), np.transpose(pts_3d_rect)))def project_ref_to_rect(self, pts_3d_ref):''' Input and Output are nx3 points '''return np.transpose(np.dot(self.R0, np.transpose(pts_3d_ref)))def project_rect_to_velo(self, pts_3d_rect):''' Input: nx3 points in rect camera coord.Output: nx3 points in velodyne coord.''' pts_3d_ref = self.project_rect_to_ref(pts_3d_rect)return self.project_ref_to_velo(pts_3d_ref)def project_velo_to_rect(self, pts_3d_velo):pts_3d_ref = self.project_velo_to_ref(pts_3d_velo)return self.project_ref_to_rect(pts_3d_ref)def corners3d_to_img_boxes(self, corners3d):""":param corners3d: (N, 8, 3) corners in rect coordinate:return: boxes: (None, 4) [x1, y1, x2, y2] in rgb coordinate:return: boxes_corner: (None, 8) [xi, yi] in rgb coordinate"""sample_num = corners3d.shape[0]corners3d_hom = np.concatenate((corners3d, np.ones((sample_num, 8, 1))), axis=2) # (N, 8, 4)img_pts = np.matmul(corners3d_hom, self.P.T) # (N, 8, 3)x, y = img_pts[:, :, 0] / img_pts[:, :, 2], img_pts[:, :, 1] / img_pts[:, :, 2]x1, y1 = np.min(x, axis=1), np.min(y, axis=1)x2, y2 = np.max(x, axis=1), np.max(y, axis=1)boxes = np.concatenate((x1.reshape(-1, 1), y1.reshape(-1, 1), x2.reshape(-1, 1), y2.reshape(-1, 1)), axis=1)boxes_corner = np.concatenate((x.reshape(-1, 8, 1), y.reshape(-1, 8, 1)), axis=2)return boxes, boxes_corner# =========================== # ------- 3d to 2d ---------- # =========================== def project_rect_to_image(self, pts_3d_rect):''' Input: nx3 points in rect camera coord.Output: nx2 points in image2 coord.'''pts_3d_rect = self.cart2hom(pts_3d_rect)pts_2d = np.dot(pts_3d_rect, np.transpose(self.P)) # nx3pts_2d[:,0] /= pts_2d[:,2]pts_2d[:,1] /= pts_2d[:,2]return pts_2d[:,0:2]def project_velo_to_image(self, pts_3d_velo):''' Input: nx3 points in velodyne coord.Output: nx2 points in image2 coord.'''pts_3d_rect = self.project_velo_to_rect(pts_3d_velo)return self.project_rect_to_image(pts_3d_rect)# =========================== # ------- 2d to 3d ---------- # =========================== def project_image_to_rect(self, uv_depth):''' Input: nx3 first two channels are uv, 3rd channelis depth in rect camera coord.Output: nx3 points in rect camera coord.'''n = uv_depth.shape[0]x = ((uv_depth[:,0]-self.c_u)*uv_depth[:,2])/self.f_u + self.b_xy = ((uv_depth[:,1]-self.c_v)*uv_depth[:,2])/self.f_v + self.b_ypts_3d_rect = np.zeros((n,3))pts_3d_rect[:,0] = xpts_3d_rect[:,1] = ypts_3d_rect[:,2] = uv_depth[:,2]return pts_3d_rectdef project_image_to_velo(self, uv_depth):pts_3d_rect = self.project_image_to_rect(uv_depth)return self.project_rect_to_velo(pts_3d_rect)def rotx(t):''' 3D Rotation about the x-axis. '''c = np.cos(t)s = np.sin(t)return np.array([[1, 0, 0],[0, c, -s],[0, s, c]])def roty(t):''' Rotation about the y-axis. '''c = np.cos(t)s = np.sin(t)return np.array([[c, 0, s],[0, 1, 0],[-s, 0, c]])def rotz(t):''' Rotation about the z-axis. '''c = np.cos(t)s = np.sin(t)return np.array([[c, -s, 0],[s, c, 0],[0, 0, 1]])def transform_from_rot_trans(R, t):''' Transforation matrix from rotation matrix and translation vector. '''R = R.reshape(3, 3)t = t.reshape(3, 1)return np.vstack((np.hstack([R, t]), [0, 0, 0, 1]))def inverse_rigid_trans(Tr):''' Inverse a rigid body transform matrix (3x4 as [R|t])[R'|-R't; 0|1]'''inv_Tr = np.zeros_like(Tr) # 3x4inv_Tr[0:3,0:3] = np.transpose(Tr[0:3,0:3])inv_Tr[0:3,3] = np.dot(-np.transpose(Tr[0:3,0:3]), Tr[0:3,3])return inv_Trdef read_label(label_filename):lines = [line.rstrip() for line in open(label_filename)]objects = [Object3d(line) for line in lines]return objectsdef load_image(img_filename):return cv2.imread(img_filename)def load_velo_scan(velo_filename):scan = np.fromfile(velo_filename, dtype=np.float32)scan = scan.reshape((-1, 4))return scankitti_object.py
from __future__ import print_functionimport os
import sys
import cv2
import numpy as np
from PIL import Image
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
BASE_DIR = os.path.dirname(os.path.abspath(__file__))
ROOT_DIR = os.path.dirname(BASE_DIR)
sys.path.append(os.path.join(ROOT_DIR, 'mayavi'))
import kitti_util as utils'''
在图像中画2D框、3D框
'''
def show_image_with_boxes(img, objects, calib, show3d=True):img1 = np.copy(img) # for 2d bboximg2 = np.copy(img) # for 3d bboxfor obj in objects:if obj.type=='DontCare':continuecv2.rectangle(img1, (int(obj.xmin),int(obj.ymin)), (int(obj.xmax),int(obj.ymax)), (0,255,0), 2) # 画2D框box3d_pts_2d, box3d_pts_3d = utils.compute_box_3d(obj, calib.P) # 获取图像3D框(8*2)、相机坐标系3D框(8*3)img2 = utils.draw_projected_box3d(img2, box3d_pts_2d) # 在图像上画3D框if show3d:Image.fromarray(img2).save('save_output/image_with_3Dboxes.png')Image.fromarray(img2).show()else:Image.fromarray(img1).save('save_output/image_with_2Dboxes.png')Image.fromarray(img1).show()'''
可视化BEV鸟瞰图
'''
def show_lidar_topview(pc_velo, objects, calib):# 1-设置鸟瞰图范围side_range = (-30, 30) # 左右距离fwd_range = (0, 80) # 后前距离x_points = pc_velo[:, 0]y_points = pc_velo[:, 1]z_points = pc_velo[:, 2]# 2-获得区域内的点f_filt = np.logical_and(x_points > fwd_range[0], x_points < fwd_range[1])s_filt = np.logical_and(y_points > side_range[0], y_points < side_range[1])filter = np.logical_and(f_filt, s_filt)indices = np.argwhere(filter).flatten() x_points = x_points[indices]y_points = y_points[indices]z_points = z_points[indices]# 定义了鸟瞰图中每个像素代表的距离res = 0.1 # 3-1将点云坐标系 转到 BEV坐标系x_img = (-y_points / res).astype(np.int32)y_img = (-x_points / res).astype(np.int32)# 3-2调整坐标原点x_img -= int(np.floor(side_range[0]) / res)y_img += int(np.floor(fwd_range[1]) / res)print(x_img.min(), x_img.max(), y_img.min(), y_img.max()) # 4-填充像素值, 将点云数据的高度信息(Z坐标)映射到像素值height_range = (-3, 1.0)pixel_value = np.clip(a=z_points, a_max=height_range[1], a_min=height_range[0])def scale_to_255(a, min, max, dtype=np.uint8):return ((a - min) / float(max - min) * 255).astype(dtype)pixel_value = scale_to_255(pixel_value, height_range[0], height_range[1])# 创建图像数组x_max = 1 + int((side_range[1] - side_range[0]) / res)y_max = 1 + int((fwd_range[1] - fwd_range[0]) / res)im = np.zeros([y_max, x_max], dtype=np.uint8)im[y_img, x_img] = pixel_valueim2 = Image.fromarray(im)im2.save('save_output/BEV.png')im2.show()'''
将点云数据3D框投影到BEV
'''
def show_lidar_topview_with_boxes(img, objects, calib):def bbox3d(obj):box3d_pts_2d, box3d_pts_3d = utils.compute_box_3d(obj, calib.P) # 获取3D框-图像、3D框-相机坐标系box3d_pts_3d_velo = calib.project_rect_to_velo(box3d_pts_3d) # 将相机坐标系的框 转到 激光雷达坐标系return box3d_pts_3d_velo # 返回nx3的点boxes3d = [bbox3d(obj) for obj in objects if obj.type == "Car"]gt = np.array(boxes3d)im2 = utils.draw_box3d_label_on_bev(img, gt, scores=None, thickness=1) # 获取激光雷达坐标系的3D点,选择x, y两维,画到BEV平面坐标系上im2 = Image.fromarray(im2)im2.save('save_output/BEV with boxes.png')im2.show()'''
将点云数据投影到图像
'''
def show_lidar_on_image(pc_velo, img, calib, img_width, img_height):''' Project LiDAR points to image '''imgfov_pc_velo, pts_2d, fov_inds = get_lidar_in_image_fov(pc_velo,calib, 0, 0, img_width, img_height, True)imgfov_pts_2d = pts_2d[fov_inds,:]imgfov_pc_rect = calib.project_velo_to_rect(imgfov_pc_velo)import matplotlib.pyplot as pltcmap = plt.cm.get_cmap('hsv', 256)cmap = np.array([cmap(i) for i in range(256)])[:,:3]*255for i in range(imgfov_pts_2d.shape[0]):depth = imgfov_pc_rect[i,2]color = cmap[int(640.0/depth),:]cv2.circle(img, (int(np.round(imgfov_pts_2d[i,0])),int(np.round(imgfov_pts_2d[i,1]))),2, color=tuple(color), thickness=-1)Image.fromarray(img).save('save_output/lidar_on_image.png')Image.fromarray(img).show() return img'''
将点云数据投影到相机坐标系
'''
def get_lidar_in_image_fov(pc_velo, calib, xmin, ymin, xmax, ymax,return_more=False, clip_distance=2.0):''' Filter lidar points, keep those in image FOV '''pts_2d = calib.project_velo_to_image(pc_velo)fov_inds = (pts_2d[:,0]<xmax) & (pts_2d[:,0]>=xmin) & \(pts_2d[:,1]<ymax) & (pts_2d[:,1]>=ymin)fov_inds = fov_inds & (pc_velo[:,0]>clip_distance)imgfov_pc_velo = pc_velo[fov_inds,:]if return_more:return imgfov_pc_velo, pts_2d, fov_indselse:return imgfov_pc_velo'''
解析标签
'''
class kitti_object(object):'''Load and parse object data into a usable format.'''def __init__(self, root_dir, split='training'):'''root_dir contains training and testing folders'''self.root_dir = root_dirself.split = splitself.split_dir = os.path.join(root_dir, split)if split == 'training':self.num_samples = 7481elif split == 'testing':self.num_samples = 7518else:print('Unknown split: %s' % (split))exit(-1)self.image_dir = os.path.join(self.split_dir, 'image_2')self.calib_dir = os.path.join(self.split_dir, 'calib')self.lidar_dir = os.path.join(self.split_dir, 'velodyne')self.label_dir = os.path.join(self.split_dir, 'label_2')def __len__(self):return self.num_samplesdef get_image(self, idx):assert(idx<self.num_samples) img_filename = os.path.join(self.image_dir, '%06d.png'%(idx))return utils.load_image(img_filename)def get_lidar(self, idx): assert(idx<self.num_samples) lidar_filename = os.path.join(self.lidar_dir, '%06d.bin'%(idx))return utils.load_velo_scan(lidar_filename)def get_calibration(self, idx):assert(idx<self.num_samples) calib_filename = os.path.join(self.calib_dir, '%06d.txt'%(idx))return utils.Calibration(calib_filename)def get_label_objects(self, idx):assert(idx<self.num_samples and self.split=='training') label_filename = os.path.join(self.label_dir, '%06d.txt'%(idx))return utils.read_label(label_filename)def get_depth_map(self, idx):passdef get_top_down(self, idx):pass运行程序后kitti_vis_main.py后,回保存5张结果图片


后面还会介绍Nuscenes、Waymo等3D数据集。
这篇关于3D目标检测数据集 KITTI(标签格式解析、3D框可视化、点云转图像、BEV鸟瞰图)的文章就介绍到这儿,希望我们推荐的文章对编程师们有所帮助!




