本文主要是介绍Delving Deep into Rectifiers: Surpassing Human-Level Performance on ImageNet Classification,希望对大家解决编程问题提供一定的参考价值,需要的开发者们随着小编来一起学习吧!
序:在ISVRC2015 on ImageNet2012 classification dataset 上,取得了4.94%的 top-5 test error,这是第一次超越了人的识别了率(5.1%).
文章提出了两个内容:
(1) Parametric Rectified Linear Unit (PReLU) :使模型以接近0的额外计算代价和较小的过拟合风险训练模型。
(2) MSRA: 考虑到修正非线性的一种鲁棒的参数初始化方法,使得我们能够从头训练更深的模型,探索更深更宽的网络结构。
Introduction
神经网络的对训练数据的拟合能力不断提高,因为:(1)增加的复杂性(如增加的深度【25,29】,增大的宽度【33,24】,小步长的使用【33,24,2,25】)
(2)新的非线性激活【21,20,34,19,27,9】
(3)复杂层的设计【29,11】
另一方面,更好的泛化能力也取得,通过:
(1)有效的规则化技术【12,26,9,31】
(2)aggressive data augmentation【16,13,25,29】
(3)large-scale data【4,22】
在这些进步中,Rectified Linear Unit (ReLU),是近期深度网络成功的几个关键因素之一。It expedites (加快)convergence of training procedure [16], and leads to better solutions [21,8,20,34] than conventional sigmoid-like units.
尽管修正网络普遍,但是近期提出的模型和训练它们的理论指导【7,23】却很少关注这个修正器的属性。
He 从两个方面研究由修正器驱动的神经网络:
(1)PReLU:自适应地学习修正器的参数,以negligible extra computational cost 提高性能
(2) 明确的对非线性修正器进行建模,并提出一个sound initialization method,改方法帮助从头训练深度模型,并收敛。说的我们能更加灵活的探索更大的网络结构。
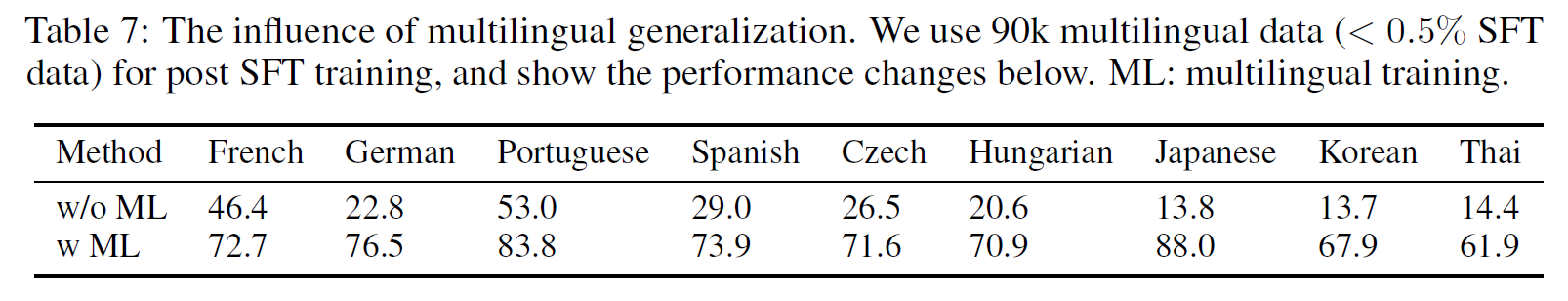
实验:在 1000-class ImageNet 2012 dataset, single-model result of 5.71% top-5 error, multi-model result achieves 4.94%
reported human-level performance: 5.1% [22]
Parametric Rectifiers
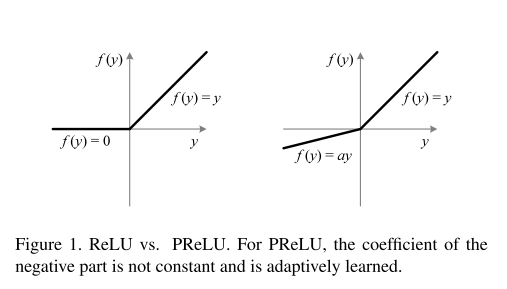
如下图所示:
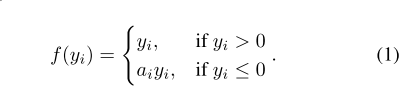
对上式:
(1)若 ai=0 ,则转换成普通的ReLU; 否则PReLU
(2)若 ai 很小并且是个固定的值,就变成了Leaky ReLU (LReLU) in [20] ( ai=0.01 ). 在[20]中的实验表明LReLU相比较ReLU对精度有很小的影响。
(3) ai 是个可学习的参数,若通道共享,则每层只增加了一个参数 –channel-shared variant;
若通道不共享,则channel-wise.
Comparison experiments
在【10】的model E上进行实验:
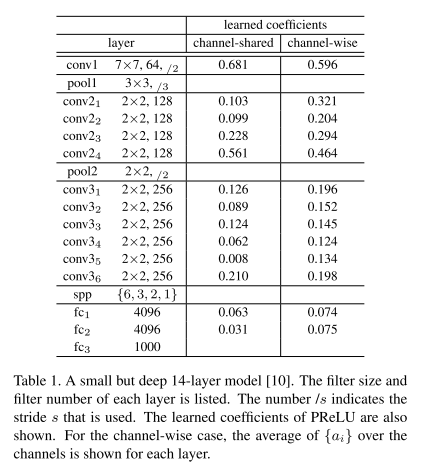
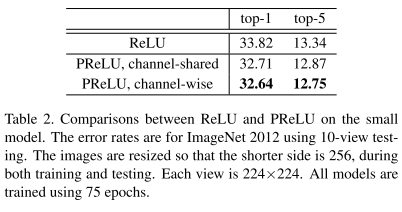
PReLU channel-shared version 仅引入了13个参数,却提高了很大的性能1.1%gain.
另外注意到连个有趣的现象:
(1)第一个conv layer 有较大的系数,很可能类似Gabor-like filters such as edge or texture detectors。
(2)for channel-wise version, 较深的卷积层通常有较小的系数,这暗示随着深度的增加,激活的梯度变得更加非线性化。
学到的模型在较早的阶段往往保持更多的信息,在较深的阶段变得更加具有判别性。
参数初始化方法
借用: http://blog.csdn.net/qq_26898461/article/details/50996507
Gaussian
Weights are randomly drawn from Gaussian distributions with fixed mean (e.g., 0) and fixed standard deviation (e.g., 0.01).
This is the most common initialization method in deep learning.
Xavier
This method proposes to adopt a properly scaled uniform or Gaussian distribution for initialization.
In Caffe (an openframework for deep learning) [2], It initializes the weights in network by drawing them from a distribution with zero mean and a specific variance,
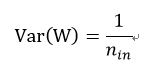
Where W is the initialization distribution for the neuron in question, and nin is the number of neurons feeding into it. The distribution used is typically Gaussian or uniform.
In Glorot & Bengio’s paper [1], itoriginally recommended using
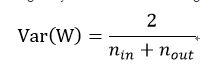
Where n_out is the number of neurons the result is fed to.
Reference:
[1] X. Glorot and Y. Bengio. Understanding the difficulty of training deepfeedforward neural networks. In International Conference on Artificial Intelligence and Statistics, pages 249–256, 2010.
[2] Y. Jia, E. Shelhamer, J. Donahue, S. Karayev, J. Long, R. Girshick, S.Guadarrama, and T. Darrell. Caffe: Convolutional architecture for fast featureembedding. arXiv:1408.5093, 2014.
MSRA
This method is proposed to solve the training of extremely deep rectified models directly from scratch [1].
In this method,weights are initialized with a zero-mean Gaussian distribution whose std is
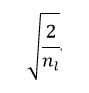
Where 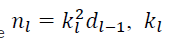
Reference:
[1] Kaiming He, Xiangyu Zhang, Shaoqing Ren, and Jian Sun. Delving Deep into Rectifiers: Surpassing Human-Level Performance on ImageNet Classification, Technical report, arXiv, Feb. 2015
这篇关于Delving Deep into Rectifiers: Surpassing Human-Level Performance on ImageNet Classification的文章就介绍到这儿,希望我们推荐的文章对编程师们有所帮助!