本文主要是介绍Leetcode刷题之——队列Queue|先入先出FIFO|广度优先搜索BFS|栈Stack|后入先出LIFO|深度优先搜索DFS,希望对大家解决编程问题提供一定的参考价值,需要的开发者们随着小编来一起学习吧!
Leetcode刷题之——队列Queue|先入先出FIFO|广度优先搜索BFS|栈Stack|后入先出LIFO|深度优先搜索DFS
- 1. 队列(Queue)——FIFO,先入先出的数据结构
- 1.1 循环队列
- 1.2 内置队列的常用方法(C++)
- 1.3 广度优先搜索(BFS)
- 2.栈(Stack)——LIFO, 后入先出的数据结构
- 2.1 栈的用法(C++)
- 2.2 深度优先搜索(DFS)
1. 队列(Queue)——FIFO,先入先出的数据结构
队列是一种典型的FIFO数据结构。
FIFO的数据结构中,将首先处理添加到队列中的第一个元素。
入队(Enqueue):队列中,插入(insert)称作入队, 新插入的元素将被添加到队列的末尾。
出队(Dequeue):出队时, 与入队相反,首先被操作的,是第一个元素。
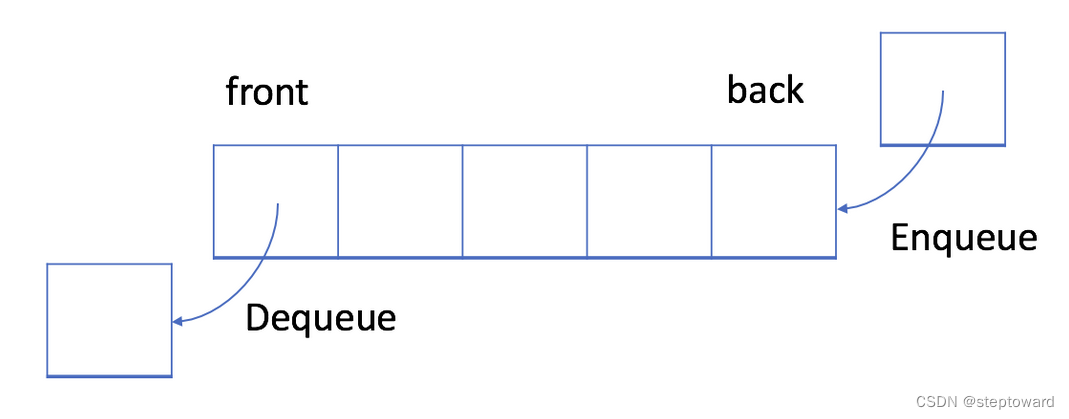
1.1 循环队列
普通队列就不讲了,一旦一个队列满了,即使在队列前面仍有空间也不能插入下一个元素,这在实际上并不常用。
循环队列就是主要设计出来解决上述问题的。
class MyCircularQueue {
private:vector<int> data;int head;int tail;int size;
public:/** Initialize your data structure here. Set the size of the queue to be k. */MyCircularQueue(int k) {data.resize(k);head = -1;tail = -1;size = k;}/** Insert an element into the circular queue. Return true if the operation is successful. */bool enQueue(int value) {if (isFull()) {return false;}if (isEmpty()) {head = 0;}tail = (tail + 1) % size;data[tail] = value;return true;}/** Delete an element from the circular queue. Return true if the operation is successful. */bool deQueue() {if (isEmpty()) {return false;}if (head == tail) {head = -1;tail = -1;return true;}head = (head + 1) % size;return true;}/** Get the front item from the queue. */int Front() {if (isEmpty()) {return -1;}return data[head];}/** Get the last item from the queue. */int Rear() {if (isEmpty()) {return -1;}return data[tail];}/** Checks whether the circular queue is empty or not. */bool isEmpty() {return head == -1;}/** Checks whether the circular queue is full or not. */bool isFull() {return ((tail + 1) % size) == head;}
};/*** Your MyCircularQueue object will be instantiated and called as such:* MyCircularQueue obj = new MyCircularQueue(k);* bool param_1 = obj.enQueue(value);* bool param_2 = obj.deQueue();* int param_3 = obj.Front();* int param_4 = obj.Rear();* bool param_5 = obj.isEmpty();* bool param_6 = obj.isFull();*/
1.2 内置队列的常用方法(C++)
当你想要按顺序处理元素时,使用队列可能是一个很好的选择。不过大多数流行语言都提供内置的队列库,因此无需自己重新发明轮子。
empty(): 判空 (和stack一样)
pop(): 出 (和stack一样)
push(): 进 (和stack, vector一样)
front(): 获取第一个
back():获取最后一个
1.3 广度优先搜索(BFS)
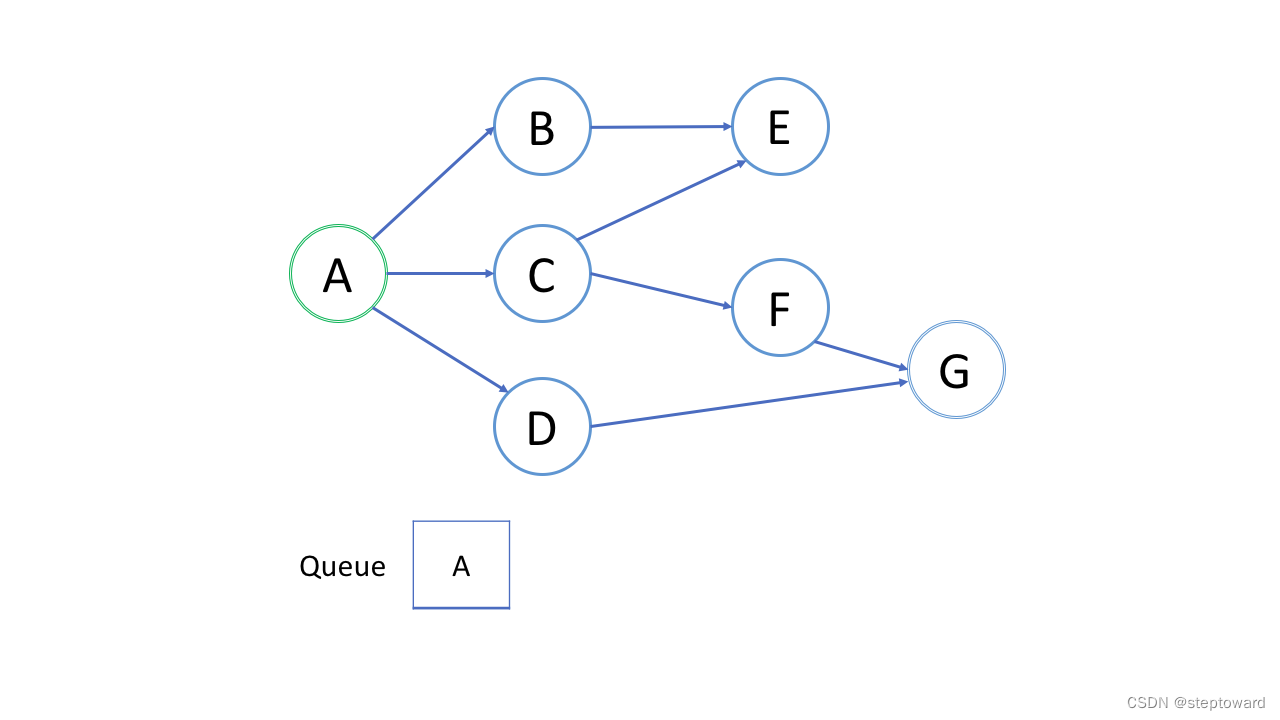
广度优先搜索(BFS)的一个常见应用是找出从根结点到目标结点的最短路径.
第一轮处理根结点;
第二轮处理根结点旁边的结点;
第三轮处理距根结点两步的结点;
如果在第 k 轮中将结点 X 添加到队列中,则根结点与 X 之间的最短路径的长度恰好是 k。
 BFS的模板代码(JAVA):
BFS的模板代码(JAVA):
每一轮中,逐个处理已经在队列中的结点,并将所有邻居添加到队列中。新添加的节点不会立即遍历,而是在下一轮中处理。
/*** Return the length of the shortest path between root and target node.*/
int BFS(Node root, Node target) {Queue<Node> queue; // store all nodes which are waiting to be processedint step = 0; // number of steps neeeded from root to current node// initializeadd root to queue;// BFSwhile (queue is not empty) {step = step + 1;// iterate the nodes which are already in the queueint size = queue.size();for (int i = 0; i < size; ++i) {Node cur = the first node in queue;return step if cur is target;for (Node next : the neighbors of cur) {add next to queue;}remove the first node from queue;}}return -1; // there is no path from root to target
}
2.栈(Stack)——LIFO, 后入先出的数据结构
栈是一种典型的LIFO数据结构。
LIFO的数据结构中,将首先处理添加到队列中的第一个元素。
入栈(Push):栈中,插入操作被称为入栈, 新插入的元素将被添加到堆栈的末尾。
出栈(Pop):出栈时, 与入栈相同,首先被操作的,是最后一个元素。
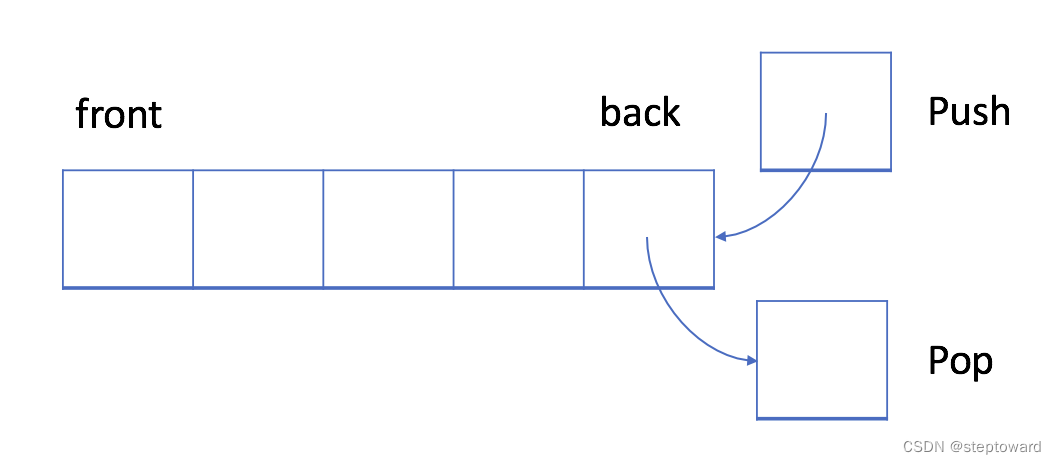
2.1 栈的用法(C++)
push(): 入栈
pop(): 退栈
empty(): 判空
top(): 获取第一个
2.2 深度优先搜索(DFS)
深度优先搜索(DFS)也可用于查找从根结点到目标结点的路径。与 BFS 不同,更早访问的结点可能不是更靠近根结点的结点。因此,在 DFS 中找到的第一条路径可能不是最短路径。
DFS的模板代码(JAVA):
显式栈实现 DFS:
/** Return true if there is a path from cur to target.*/
boolean DFS(int root, int target) {Set<Node> visited;Stack<Node> s;add root to s;while (s is not empty) {Node cur = the top element in s;return true if cur is target;for (Node next : the neighbors of cur) {if (next is not in visited) {add next to s;add next to visited;}}remove cur from s;}return false;
}
这篇关于Leetcode刷题之——队列Queue|先入先出FIFO|广度优先搜索BFS|栈Stack|后入先出LIFO|深度优先搜索DFS的文章就介绍到这儿,希望我们推荐的文章对编程师们有所帮助!






