本文主要是介绍机器学习-采用正态贝叶斯分类器、决策树、随机森林对abalone数据集分类,希望对大家解决编程问题提供一定的参考价值,需要的开发者们随着小编来一起学习吧!
1.abalone(鲍鱼)数据集描述
http://archive.ics.uci.edu/ml/datasets/Abalone
总共包含4177条数据,每条数据中包含8个特征值,一个分类(鲍鱼年龄,看看圈数),可以看做是分类问题或者回归问题
2.数据集预处理
数据的部分展示
Sex / nominal / -- / M, F, and I (infant)
Length / continuous / mm / Longest shell measurement
Diameter / continuous / mm / perpendicular to length
Height / continuous / mm / with meat in shell
Whole weight / continuous / grams / whole abalone
Shucked weight / continuous / grams / weight of meat
Viscera weight / continuous / grams / gut weight (after bleeding)
Shell weight / continuous / grams / after being dried
Rings / integer / -- / +1.5 gives the age in years
|
为了便于写程序,我把数据文件中的M、F、I分别替换成1,2,3。(注:为什么要这么做?方便编程而已,有些机器学习库直接读取的话可能会因为数据类型碰到一些问题)
3.代码实例(我采用opencv3.0中的机器学习库来做实验)
#include "opencv2/ml/ml.hpp"
#include "opencv2/core/core.hpp"
#include "opencv2/core/utility.hpp"
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string>
#include <map>
#include <vector>
#include<iostream>using namespace std;
using namespace cv;
using namespace cv::ml;static void help()
{printf("\nThis sample demonstrates how to use different decision trees and forests including boosting and random trees.\n""Usage:\n\t./tree_engine [-r <response_column>] [-ts type_spec] <csv filename>\n""where -r <response_column> specified the 0-based index of the response (0 by default)\n""-ts specifies the var type spec in the form ord[n1,n2-n3,n4-n5,...]cat[m1-m2,m3,m4-m5,...]\n""<csv filename> is the name of training data file in comma-separated value format\n\n");
}static void train_and_print_errs(Ptr<StatModel> model, const Ptr<TrainData>& data)
{bool ok = model->train(data);if (!ok){printf("Training failed\n");}else{printf("train error: %f\n", model->calcError(data, false, noArray()));printf("test error: %f\n\n", model->calcError(data, true, noArray()));}
}int main(int argc, char** argv)
{if (argc < 2){help();return 0;}const char* filename = 0;int response_idx = 0;std::string typespec;for (int i = 1; i < argc; i++){if (strcmp(argv[i], "-r") == 0)sscanf(argv[++i], "%d", &response_idx);else if (strcmp(argv[i], "-ts") == 0)typespec = argv[++i];else if (argv[i][0] != '-')filename = argv[i];else{printf("Error. Invalid option %s\n", argv[i]);help();return -1;}}printf("\nReading in %s...\n\n", filename);const double train_test_split_ratio = 0.5;//加载训练数据//Ptr<TrainData> data = TrainData::loadFromCSV(filename, 0, response_idx, response_idx + 1, typespec);Ptr<TrainData> data = TrainData::loadFromCSV(filename, 0);if (data.empty()){ printf("ERROR: File %s can not be read\n", filename);return 0;}data->setTrainTestSplit(train_test_split_ratio);printf("============正太贝叶斯分类器================\n");//创建正态贝叶斯分类器Ptr<NormalBayesClassifier> bayes = NormalBayesClassifier::create();//训练模型train_and_print_errs(bayes, data);//保存模型bayes->save("bayes_result.xml");//读取模型,强行使用一下,为了强调这种用法,当然此处完全没必要/*Ptr<NormalBayesClassifier> bayes2 = NormalBayesClassifier::load<NormalBayesClassifier>("bayes_result.xml");cout << bayes2->predict(test1Map) << endl;cout << bayes2->predict(test2Map) << endl;cout << bayes2->predict(test3Map) << endl;*/cout << "============================================" << endl;printf("======DTREE=====\n");//创建决策树Ptr<DTrees> dtree = DTrees::create();dtree->setMaxDepth(10); //设置决策树的最大深度dtree->setMinSampleCount(2); //设置决策树叶子节点的最小样本数dtree->setRegressionAccuracy(0); //设置回归精度dtree->setUseSurrogates(false); //不使用替代分叉属性dtree->setMaxCategories(16); //设置最大的类数量dtree->setCVFolds(0); //设置不交叉验证dtree->setUse1SERule(false); //不使用1SE规则dtree->setTruncatePrunedTree(false); //不对分支进行修剪dtree->setPriors(Mat()); //设置先验概率train_and_print_errs(dtree, data);dtree->save("dtree_result.xml");读取模型,强行使用一下,为了强调这种用法,当然此处完全没必要//Ptr<DTrees> dtree2 = DTrees::load<DTrees>("dtree_result.xml");//cout << dtree2->predict(test1Map) << endl;//cout << dtree2->predict(test2Map) << endl;//cout << dtree2->predict(test3Map) << endl;cout << "============================================" << endl;//if ((int)data->getClassLabels().total() <= 2) // regression or 2-class classification problem//{// printf("======BOOST=====\n");// Ptr<Boost> boost = Boost::create();// boost->setBoostType(Boost::GENTLE);// boost->setWeakCount(100);// boost->setWeightTrimRate(0.95);// boost->setMaxDepth(2);// boost->setUseSurrogates(false);// boost->setPriors(Mat());// train_and_print_errs(boost, data);//}printf("======RTREES=====\n");Ptr<RTrees> rtrees = RTrees::create();rtrees->setMaxDepth(10);rtrees->setMinSampleCount(2);rtrees->setRegressionAccuracy(0);rtrees->setUseSurrogates(false);rtrees->setMaxCategories(16);rtrees->setPriors(Mat());rtrees->setCalculateVarImportance(false);rtrees->setActiveVarCount(0);rtrees->setTermCriteria(TermCriteria(TermCriteria::MAX_ITER, 100, 0));train_and_print_errs(rtrees, data);cout << "============================================" << endl;return 0;
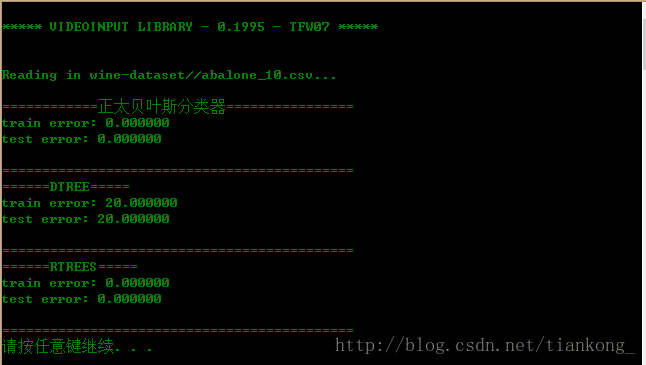
}读10条数据的效果:
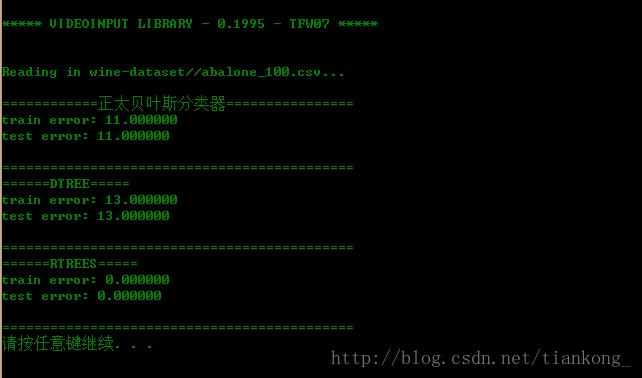
读100条数据的效果:
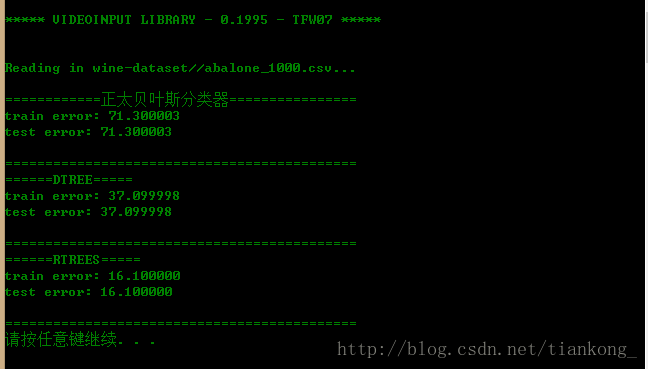
读1000条数据的效果:
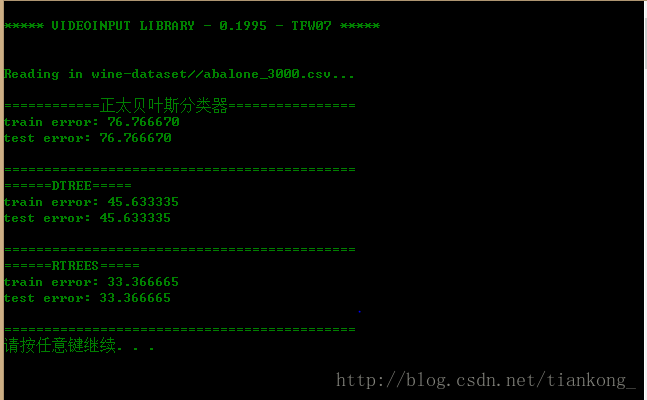
读3000条数据的效果:
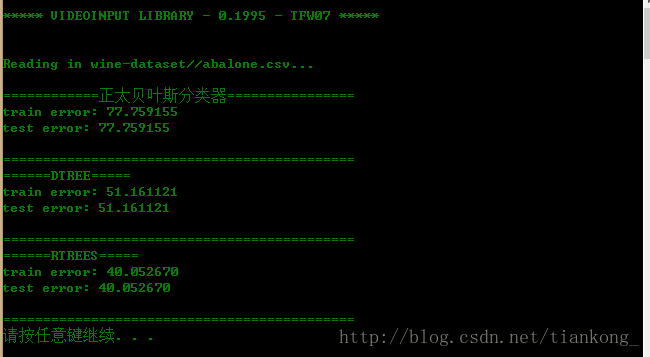
读4177条数据的效果:
仅从此次试验的运行过程中可以发现,随机森林的分类效果最好,但计算过程比较耗时,随着训练数据量的增大,三者的效果都趋于越来越差。
这篇关于机器学习-采用正态贝叶斯分类器、决策树、随机森林对abalone数据集分类的文章就介绍到这儿,希望我们推荐的文章对编程师们有所帮助!