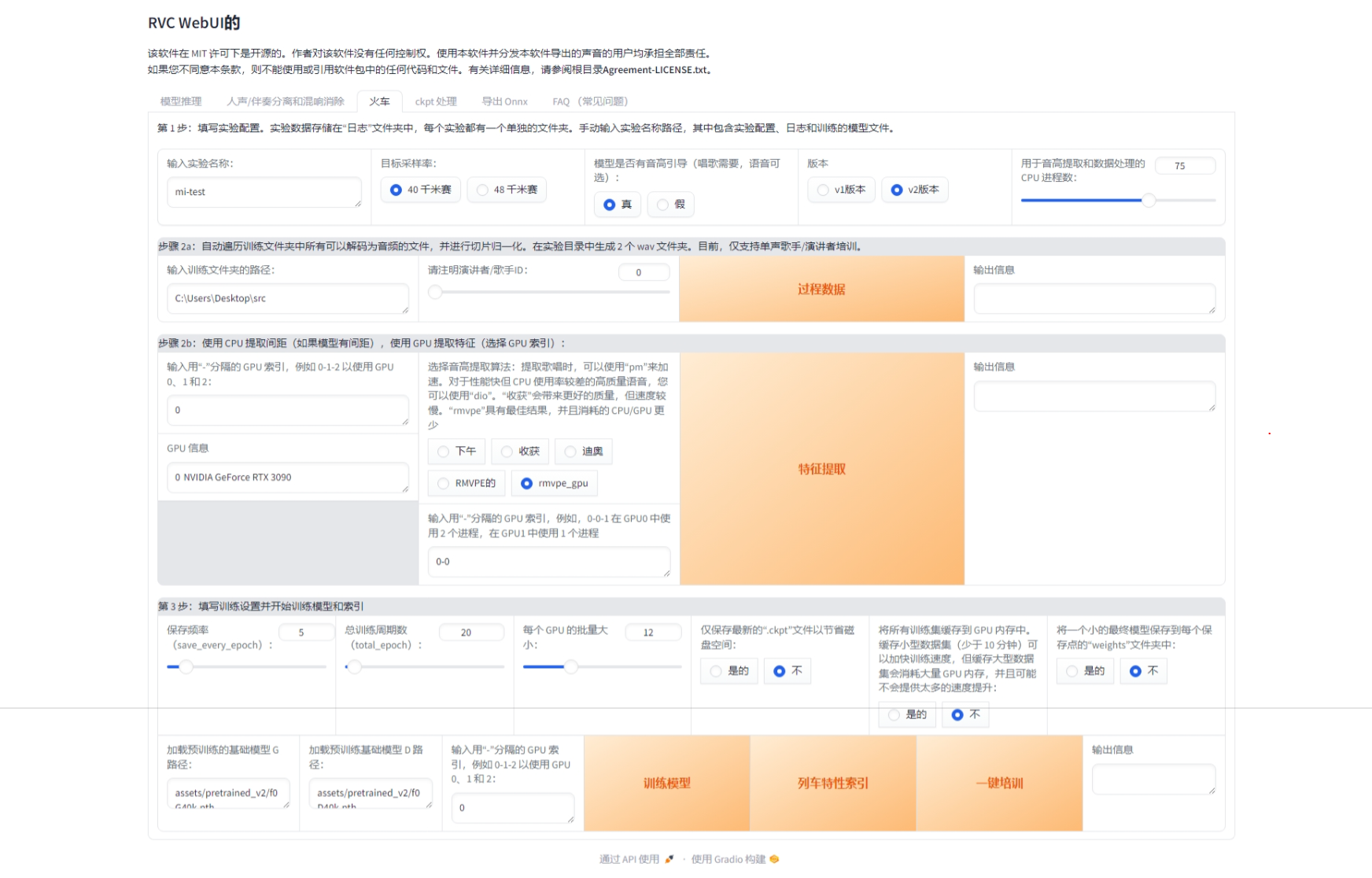
本文主要是介绍【Noise-Label】《Training a Neural Network Based on Unreliable Human Annotation of Medical Images》,希望对大家解决编程问题提供一定的参考价值,需要的开发者们随着小编来一起学习吧!

2018 IEEE 15th International Symposium on Biomedical Imaging (ISBI 2018)
文章目录
- 1 Background and Motivation
- 2 Innovations
- 3 Method
- 3.1 TRAINING A DEEP NEURAL NETWORK WITH A NOISY CHANNEL
- 4 Experiments
- 5 Conclusion(own)
1 Background and Motivation
不同于自然图像的 annotation,医学图像很难去 obtain a perfect set of labels,因为 the complexity of the medical data and the large variability between experts.
一个可行的方法
- cope with unreliable annotation is to collect labeling from multiple experts.(time consuming,需要专家和研究者的密切合作)
先驱们(CIFAR-10 或者 MNIST dataset 上)
- 《Training deep neural networks based on unreliable labels》
- 《Learning from noisy labels with deep neural networks》
- 《Training deep neural networks using a noise adaptation layer》
作者承接前人的工作,将其运用在 breast microcalcifications 的分类上, to predict whether a suspicious region on a medical image is malignant(恶性的) or benign(良性的)
2 Innovations
针对 UNRELIABLE HUMAN ANNOTATION OF MEDICAL IMAGES 提出了一种解决的办法,加 noisy label
3 Method
网络结构很简单,输入 28 维度的基于 RoI 提取的人工特征,two 24-d 的 hidden layer,然后 2 分类的 output layer
参数量
(28*24+ 24)+ (24*24+24)+ (24*2+2)= 29*24 + 25*24 +25*2
3.1 TRAINING A DEEP NEURAL NETWORK WITH A NOISY CHANNEL
- noisy channel:models the stochastic relation between the correct label and the observed noisy label.
训练的时候加 noisy channel component,测试的时候 remove
1)neural network model,the probability of input x x x being labeled as i i i is

k k k- c l a s s class class classification problems,label 为 1 , 2 , … … k 1,2,……k 1,2,……k
- h ( x ) h(x) h(x):non-linear function
- w o w_o wo, b o b_o bo:the parameters of the output soft-max layer(指的是计算 logits 的 w w w 和 b b b)
- y y y:correct medical diagnosis
2)noise model
θ ( i , j ) = p ( z = j ∣ y = i ) \theta(i,j)=p(z=j|y=i) θ(i,j)=p(z=j∣y=i)
- y y y:correct medical diagnosis
- z z z:manual annotation provided by an expert(annotation)
可以这么理解,网络学出来的可能是对的,但是标签是错的,用一个概率模型转换一下
3)The combined neural-net model with noisy labels


4)log-likelihood function

- t t t: t t t-th$ sample
- i i i: i i i-th classification
网络要学的 parameters 是 w w w 和 θ \theta θ 去 maximize the likelihood function,但是 y t y_t yt 是 hidden 的,解决这类问题的标配是 Expectation-Maximization(EM)algorithm,但是 EM 是 greedy optimization procedure,容易陷入到局部最优解!且需要反复的迭代(这就要训练模型好多次了,显然不太优雅),然后才能找到最优的模型参数,参考 Expectation Maximization 的 Introduction 部分!!!
5) 另辟蹊径
EM 不太可行,那怎么办呢?作者直接把公式(3)作为 neural network 的 objective function,把 θ \theta θ 看成是一个 linear function,简化一下公式(2)如下:

- P z P_z Pz:the soft-decision distribution of noisy label
- P y P_y Py:the soft-decision distribution of correct label
整个模型落地为

θ \theta θ 落地为
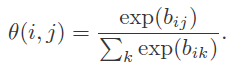
这里对 b 进行 softmax 怎么理解呢?是直接把 θ \theta θ * P y P_y Py 的结果当成 softmax 之后的结果与 one-hot 进行 loss 的计算呢?还是把 θ \theta θ * P y P_y Py 的结果当成 logits 与 one-hot 进行 loss 的计算!!!
6)歧义(degree of freedom)
我们想要的结果是,通过引入 noisy channel,学 θ \theta θ 把网络检测出来的正确结果( y y y),转化为标错的( z z z),但是有可能学到的是 θ T \theta^T θT,也即网络学到了 z z z,加 noisy channel 之后学到了 y y y!为了避免这种情况,作者先不加 noisy channel 进行训练,然后初始化加了 noisy channel 的网络,再进行训练!确保 noisy channel 是对 y → z y→z y→z 过程的学习!
4 Experiments
DDSM dataset
-
1410 clusters (705 of CC, and 705 of MLO), of which 372 were benign and 333 were malignant. CC 和 MLO 是两种不同的视角获取的图片
-
作者是取 RoI 然后分别从 CC 和 MLO 各提取人工特征 vector(14)
-
作者 generated noisy data from clean data by randomly changing some of the labels 来模拟专家标注的图片
-
10-fold cross validation(train and val)
-
3 methods
-
two different tissue-density categories


- 横坐标就是人工加入的干扰项的比例,比如 0.4 表示有 40% 的错标
- 可以注意到 Fig.5 加了 noisy label 比 baseline 高
- The noise probability that was learned in that case was 0.05.
future work 是把这些方法用到其他的 medical imaging task
5 Conclusion(own)
不晓得是不是自己理解错了,加 noisy layer 的目的是为了让网络去更好的拟合错误的标签!不加 noisy layer 网络可能是正确的(真实的),加了之后,去拟合错误的标签!总感觉怪怪的!
而且 baseline 要是在与加载预训练模型之后才有对比性,不然加载预训练模型的效果肯定会变好!!!
这篇关于【Noise-Label】《Training a Neural Network Based on Unreliable Human Annotation of Medical Images》的文章就介绍到这儿,希望我们推荐的文章对编程师们有所帮助!