本文主要是介绍threejs 组-层级模型 | 本地坐标和世界坐标 | 局部坐标系和世界坐标系 | 本地矩阵.materix和世界矩阵.matrixWorld,希望对大家解决编程问题提供一定的参考价值,需要的开发者们随着小编来一起学习吧!
文章目录
- 组- THREE.Group
- 递归遍历模型树结构object3D.traverse()
- object3D.add (object.Object3D..) 添加对象 和 object3D.remove(object.Object3D..) 移除对象
- 局部坐标系和世界坐标系
- 辅助坐标器 AxesHelper
- 本地坐标和世界坐标 - 基于世界坐标系的位置
- 本地坐标与世界坐标的理解
- 几何体与三维物体的三种变换:旋转,平移,缩放
- 移动几何体和移动物体
- 几何体旋转与三维物体旋转(缩放同理)
- 本地矩阵.materix和世界矩阵.matrixWorld
组- THREE.Group
语法:new THREE.Group()
继承链:Object3D → Group
说明:基本和三维物体Object3D一致,可以看作一个只用于分组没有实体的模型,可以分组操作模型。
作用:可以看作将模型进行分组,原来是直接将一个一个模型add进场景scene,现在是将所有模型先进行分组,然后将分组后的分组模型group添加进场景scene。
受threejs历史原因,有些时候代码中也会直接用Object3D甚至Mesh作为Group使用,可以但不推荐,语义化不够强。
group可以看作mesh1、mesh2的父对象,父对象旋转缩放平移变换,子对象跟着变化(父对象变换子对象也会变换)。
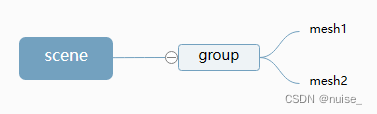
//创建两个网格模型mesh1、mesh2
const geometry = new THREE.BoxGeometry(20, 20, 20);
const material = new THREE.MeshLambertMaterial({color: 0x00ffff});
// 创建一个组
const group = new THREE.Group();
const mesh1 = new THREE.Mesh(geometry, material);
const mesh2 = new THREE.Mesh(geometry, material);
mesh2.translateX(25);
//把mesh1型插入到组group中,mesh1作为group的子对象
group.add(mesh1);
//把mesh2型插入到组group中,mesh2作为group的子对象
group.add(mesh2);
//把group插入到场景中作为场景子对象
scene.add(group);
递归遍历模型树结构object3D.traverse()
语法:object3D.traverse ( callback : Function ) : undefined
本质:遍历object3D实例的children属性
每个模型可以通过object3D.name属性命名,命名之后可以通过遍历模型树搭配object3D.getObjectByName(name) ,找到具体的模型。
案例:假设有一个小区房子
初始化状态小区房子都是蓝色的,需要将所有楼变成黄色
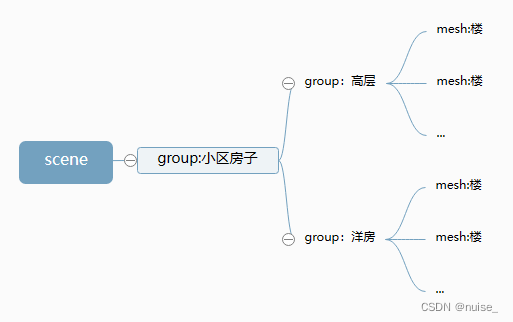
// 批量创建多个长方体表示高层楼
const group1 = new THREE.Group(); //所有高层楼的父对象
group1.name = "高层";
for (let i = 0; i < 5; i++) {const geometry = new THREE.BoxGeometry(20, 60, 10);const material = new THREE.MeshLambertMaterial({color: 0x00ffff});const mesh = new THREE.Mesh(geometry, material);mesh.position.x = i * 30; // 网格模型mesh沿着x轴方向阵列group1.add(mesh); //添加到组对象group1mesh.name = i + 1 + '号楼';// console.log('mesh.name',mesh.name);
}
group1.position.y = 30;const group2 = new THREE.Group();
group2.name = "洋房";
// 批量创建多个长方体表示洋房
for (let i = 0; i < 5; i++) {const geometry = new THREE.BoxGeometry(20, 30, 10);const material = new THREE.MeshLambertMaterial({color: 0x00ffff});const mesh = new THREE.Mesh(geometry, material);mesh.position.x = i * 30;group2.add(mesh); //添加到组对象group2mesh.name = i + 6 + '号楼';
}
group2.position.z = 50;
group2.position.y = 15;const model = new THREE.Group();
model.name='小区房子';
model.add(group1, group2);
model.position.set(-50,0,-25);// 递归遍历model包含所有的模型节点
model.traverse(function(obj) {console.log('所有模型节点的名称',obj.name);// obj.isMesh:if判断模型对象obj是不是网格模型'Mesh'if (obj.isMesh) {//判断条件也可以是obj.type === 'Mesh'obj.material.color.set(0xffff00);}
});
object3D.add (object.Object3D…) 添加对象 和 object3D.remove(object.Object3D…) 移除对象
object3D.add(object : Object3D, ...) :将参数添加到对象的children中,可以添加任意数量的对象。传入的对象如果本身有父级的话,会从原父级中删除该对象。因为一个对象仅能有一个父级。
object3D.remove(object : Object3D, ... ):从当前对象的children中移除对象,可以移除任意数量的对象。
局部坐标系和世界坐标系
| 坐标系 | 描述 | 辅助坐标系器添加位置 |
|---|---|---|
| 世界坐标系 | 只有一个,所处的公共场景 | 添加在场景上 |
| 局部坐标系/本地坐标系 | 物体自身的坐标系 (跟随物体) | 添加在三维物体上 |
辅助坐标器 AxesHelper
语法:new THREE.AxesHelper( size : Number )
参数:size (可选) 表示代表轴的线段长度.,默认为 1。
说明:红色®代表 X 轴. 绿色(G)代表 Y 轴. 蓝色(B)代表 Z 轴。
继承链:Object3D → Line → LineSegments
const geometry = new THREE.BoxGeometry(50,50,50)
const material = new THREE.MeshBasicMaterial({ color: 'pink' });
const axesHelper = new THREE.AxesHelper(100);
const mesh = new THREE.Mesh(geometry, material);
mesh.add(axesHelper) // 本地坐标系添加在三维物体上
mesh.position.set(25,25,25); // 为了方便观察,将三维物体的位置移动
scene.add(mesh);
const worldAxesHelper = new THREE.AxesHelper(150);
scene.add(worldAxesHelper);// 世界坐标系添加在场景上
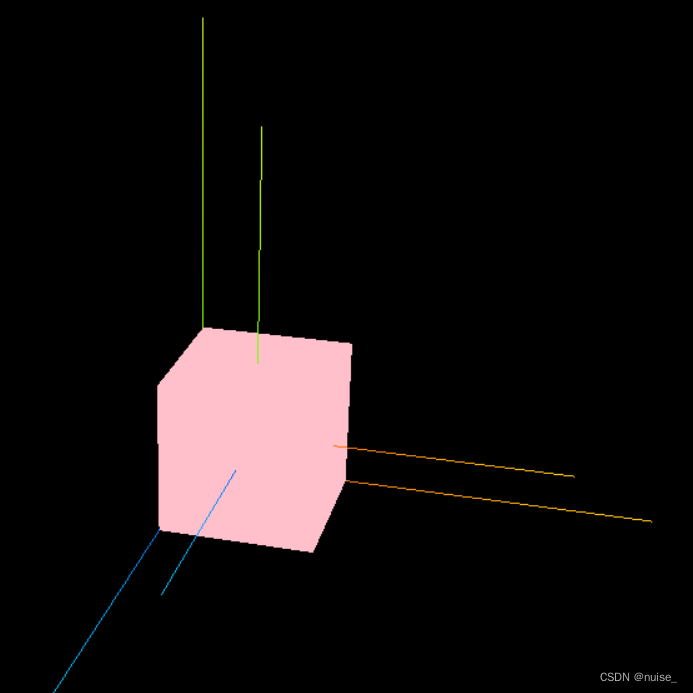
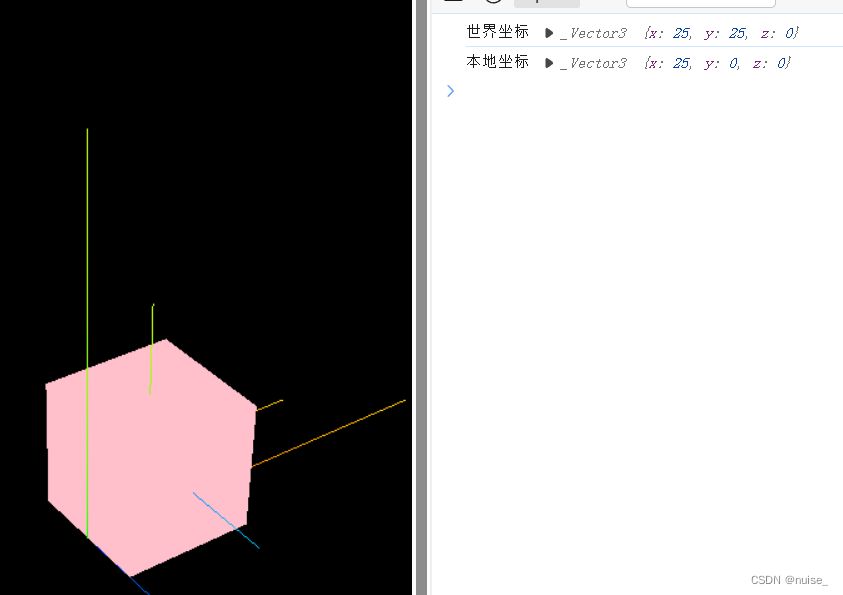
本地坐标和世界坐标 - 基于世界坐标系的位置
这里的本地坐标和世界坐标是相对于有无父元素来说,坐标都是基于世界坐标系的位置
打印上述案例的世界坐标与本地坐标,有以下两个发现:
1.可以看见本地坐标变了,但本地坐标系位置是没有变化的。 => 基于世界坐标的位置
2.打印世界坐标与本地坐标,可以发现都是一样的。 => 不一样的情况只是针对有无父元素
const geometry = new THREE.BoxGeometry(50,50,50)
const material = new THREE.MeshBasicMaterial({ color: 'pink' });
const axesHelper = new THREE.AxesHelper(100);
const mesh = new THREE.Mesh(geometry, material);
mesh.add(axesHelper) // 本地坐标系
mesh.position.set(25,25,25)
scene.add(mesh);
const worldAxesHelper = new THREE.AxesHelper(150);
scene.add(worldAxesHelper);// 世界坐标系
console.log("世界坐标",mesh.getWorldPosition(new THREE.Vector3()));
console.log("本地坐标",mesh.position);
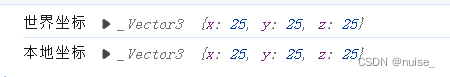
获取世界坐标的语法
object.getWorldPosition(Vector3) 获取世界坐标
语法:object.getWorldPosition(Vector3)
描述:读取一个模型的世界坐标,并把读取结果存储到参数Vector3中
本地坐标与世界坐标的理解
同一个三维物体拥有本地坐标与世界坐标两个坐标,在页面看见的位置是世界坐标的位置。
| - | 定义 |
|---|---|
| 本地坐标 | 三维物体的.position属性 |
| 世界坐标 | 三维物体自身.position和所有父对象.position累加的坐标 |
- 改变子对象的
.position,子对象在3D空间中的坐标会发生改变。 - 改变父对象的
.position,子对象在3D空间中的位置也会跟着变化,也就是说父对象.position和子对象.position叠加才是才是子对象的世界坐标。
const geometry = new THREE.BoxGeometry(50,50,50)
const material = new THREE.MeshBasicMaterial({ color: 'pink' });
const axesHelper = new THREE.AxesHelper(60);
const mesh = new THREE.Mesh(geometry, material);
mesh.add(axesHelper);
mesh.position.set(25,0,0) // 改变子元素的本地坐标
const group = new THREE.Group();
group.add(mesh);
scene.add(group);
group.position.set(0,25,0) // 改变父元素的本地坐标
const axesHelper1 = new THREE.AxesHelper(150);
scene.add(axesHelper1);
console.log("世界坐标",mesh.getWorldPosition(new THREE.Vector3()));
console.log("本地坐标",mesh.position);
几何体与三维物体的三种变换:旋转,平移,缩放
BufferGeometry重写了Object3D的同名方法,几何变换的本质是改变几何体的顶点数据
| 几何变换 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| bufferGeometry.scale ( x : Float, y : Float, z : Float ) | 从几何体原始位置开始缩放几何体 |
| bufferGeometry.translate ( x : Float, y : Float, z : Float ) | 从几何体原始位置开始移动几何体,本质改变的是顶点坐标 |
| bufferGeometry.rotateX/rotateY/rotateZ( radians : Float ) | 沿着局部坐标系的主轴旋转几何体,参数是弧度 |
移动几何体和移动物体
一般情况下选择移动物体。当顶点本身就偏离需要将几何体中心移动到原点时,选择移动几何体(消除中心点偏移)。
几何体的变换由于直接将最终计算结果设置为顶点坐标,所以很难追逐到是否发生了变换。
| - | 使用 | 描述 | 特点 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 移动几何体 | bufferGeometry.translate (x: Float, y: Float, z: Float) | 改变几何体,geometry.attributes.position属性 | 顶点改变,局部位置不变 |
| 移动物体 | object3D.position: Vector3 object3D.translateX ( distance : Float ) | 移动对象的局部位置 | 局部位置改变,局部坐标系跟随 |
移动几何体
1.几何体顶点变化
2.局部坐标不变,局部坐标系不变。
const bufferGeometry = new THREE.BufferGeometry();
const vertices = new Float32Array([-50, 50, 0, 50, 50, 0, -50, -50, 0,50, -50,0
]);
bufferGeometry.setAttribute("position", new THREE.BufferAttribute(vertices, 3));
const indices = new Uint16Array([0, 2, 1, 2, 3, 1]);
bufferGeometry.setIndex(new THREE.BufferAttribute(indices, 1));
const material = new THREE.MeshBasicMaterial();
const bufferPlane = new THREE.Mesh(bufferGeometry, material);
bufferGeometry.translate(50,0,0) // 移动几何体:x轴加50
scene.add(bufferPlane);const axesHelper = new THREE.AxesHelper(100);
bufferPlane.add(axesHelper)
const worldAxesHelper = new THREE.AxesHelper(150);
scene.add(worldAxesHelper);
// 物体的局部坐标仍然在(0,0,0),局部坐标系也没变化(与世界坐标重叠) 几何体的顶点坐标x轴都加了50
console.log(bufferPlane.position,bufferGeometry.attributes.position.array)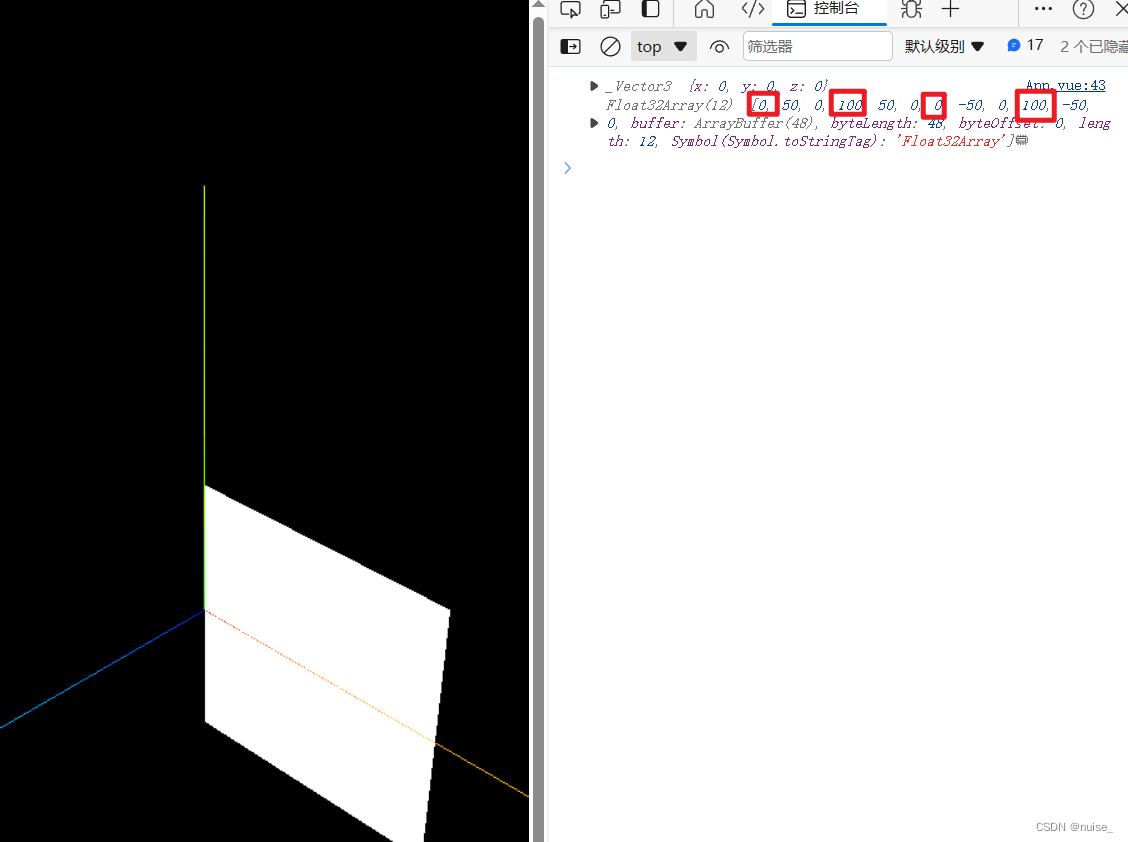
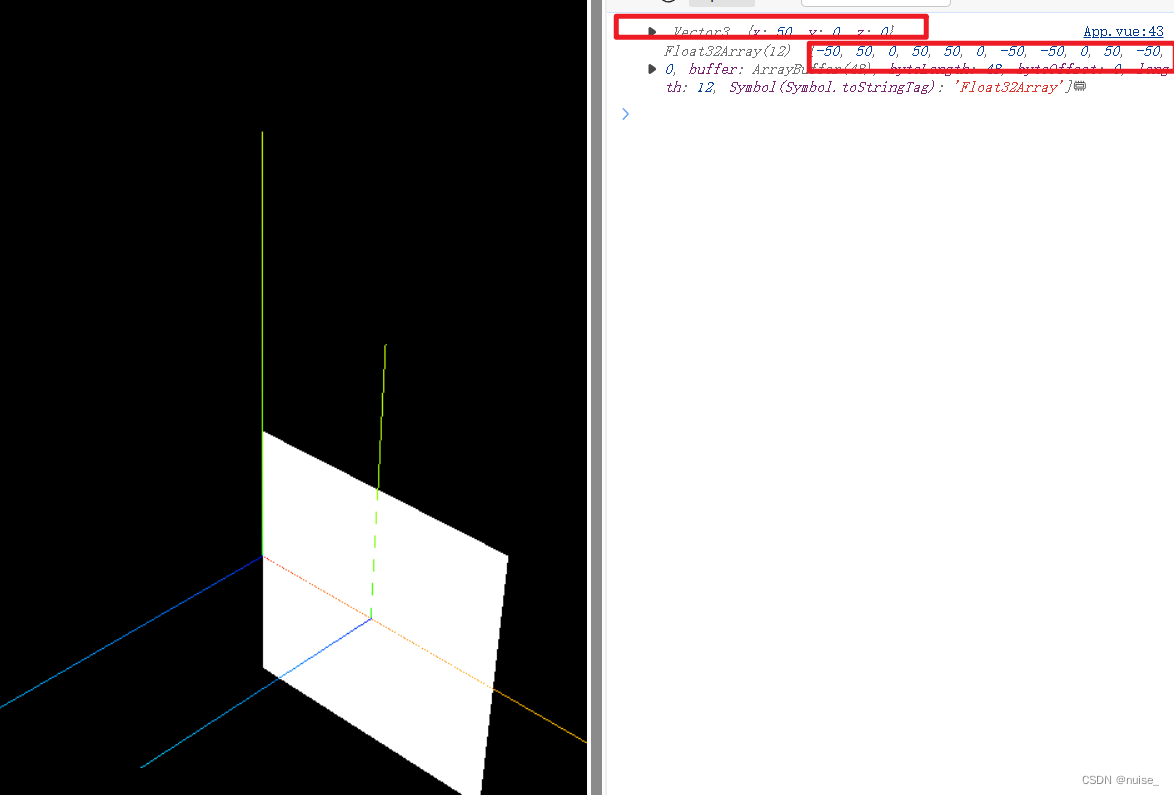
移动三维物体
1.几何体顶点不变
2.局部坐标变化,局部坐标系跟随。
const bufferGeometry = new THREE.BufferGeometry();
const vertices = new Float32Array([-50, 50, 0, 50, 50, 0, -50, -50, 0,50, -50,0
]);
bufferGeometry.setAttribute("position", new THREE.BufferAttribute(vertices, 3));
const indices = new Uint16Array([0, 2, 1, 2, 3, 1]);
bufferGeometry.setIndex(new THREE.BufferAttribute(indices, 1));
const material = new THREE.MeshBasicMaterial();
const bufferPlane = new THREE.Mesh(bufferGeometry, material);
bufferPlane.translateX (50); // 移动物,沿世界坐标系的x轴移动50个单位
scene.add(bufferPlane);
const axesHelper = new THREE.AxesHelper(100);
bufferPlane.add(axesHelper)
const worldAxesHelper = new THREE.AxesHelper(150);
scene.add(worldAxesHelper);
console.log(bufferPlane.position,bufferGeometry.attributes.position.array)
几何体旋转与三维物体旋转(缩放同理)
| - | 方法 | 本质修改 | 特点 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 几何体旋转 | bufferGeometry.rotateX( rad : Float) | 顶点坐标 | 1.局部坐标系不变。 2. object3D.rotation 不变。3.几何体的顶点位置改变。 |
| 物体旋转 | object3D.rotateX/.rotateY /.rotateZ ( rad : Float) 设置该属性值:object3D.rotation : Euler 绕空间坐标系的轴旋转 局部坐标系会一起旋转 | 修改object3D.rotation: Euler属性 | 1.局部坐标系跟随三维物体一起旋转。 2. object3D.rotation 改变。3.几何体的顶点位置不变。 |
几何体旋转
1.局部坐标系不变。
2.object3D.rotation 不变。
3.几何体的顶点位置改变。
const bufferGeometry = new THREE.BufferGeometry();
const vertices = new Float32Array([-50, 50, 0, 50, 50, 0, -50, -50, 0,50, -50,0
]);
bufferGeometry.setAttribute("position", new THREE.BufferAttribute(vertices, 3));
const indices = new Uint16Array([0, 2, 1, 2, 3, 1]);
bufferGeometry.setIndex(new THREE.BufferAttribute(indices, 1));
const material = new THREE.MeshBasicMaterial({side:THREE.DoubleSide,
});
const bufferPlane = new THREE.Mesh(bufferGeometry, material);
bufferPlane.position.set(25,0,0); //为了方便观察局部坐标系,这里移动三维物体
bufferGeometry.rotateX(Math.PI / 2);// 几何体旋转
scene.add(bufferPlane);const axesHelper = new THREE.AxesHelper(100);
bufferPlane.add(axesHelper)
const worldAxesHelper = new THREE.AxesHelper(150);
scene.add(worldAxesHelper);
console.log(bufferPlane.position,bufferPlane.rotation,bufferGeometry.attributes.position.array)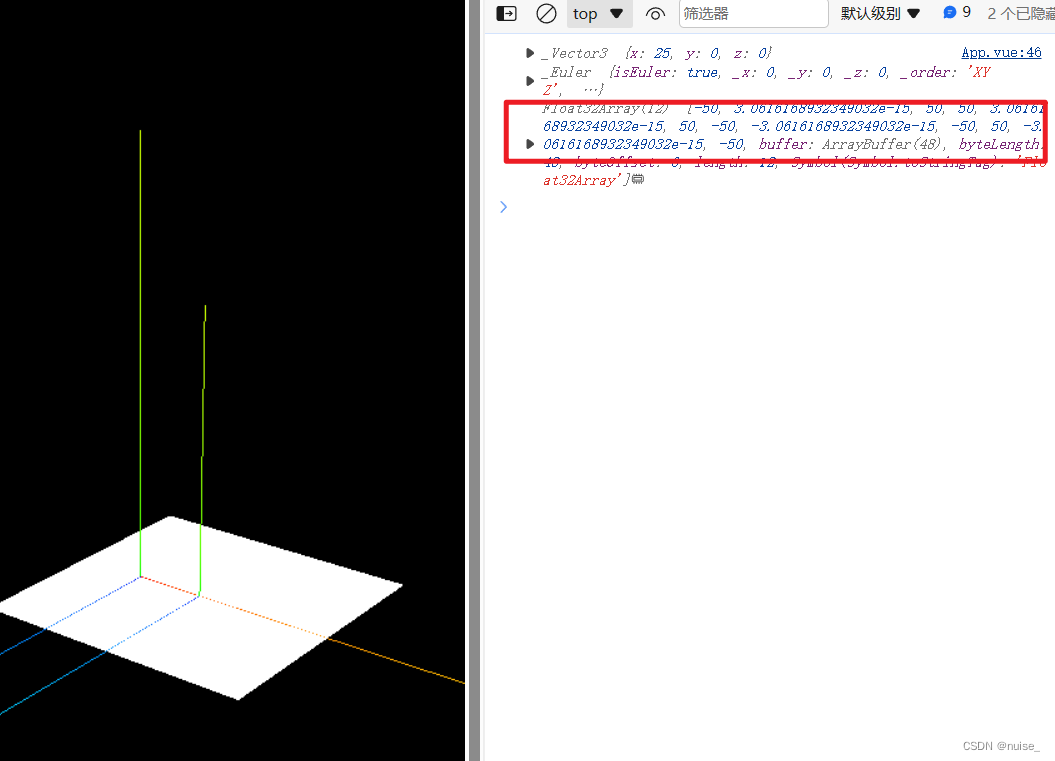
三维物体的旋转
1.局部坐标系跟随三维物体一起旋转。
2.object3D.rotation 改变。
3.几何体的顶点位置不变。
const bufferGeometry = new THREE.BufferGeometry();
const vertices = new Float32Array([-50, 50, 0, 50, 50, 0, -50, -50, 0,50, -50,0
]);
bufferGeometry.setAttribute("position", new THREE.BufferAttribute(vertices, 3));
const indices = new Uint16Array([0, 2, 1, 2, 3, 1]);
bufferGeometry.setIndex(new THREE.BufferAttribute(indices, 1));
const material = new THREE.MeshBasicMaterial({side:THREE.DoubleSide,
});
const bufferPlane = new THREE.Mesh(bufferGeometry, material);bufferPlane.position.set(25,0,0); //为了方便观察局部坐标系,这里移动三维物体
bufferPlane.rotateX(Math.PI / 2) // 物体旋转
scene.add(bufferPlane);const axesHelper = new THREE.AxesHelper(100);
bufferPlane.add(axesHelper)
const worldAxesHelper = new THREE.AxesHelper(150);
scene.add(worldAxesHelper);
console.log(bufferPlane.position,bufferPlane.rotation,bufferGeometry.attributes.position.array)
本地矩阵.materix和世界矩阵.matrixWorld
可以类比本地坐标与世界坐标,物体的运动参考坐标系永远是世界坐标系。
| - | 定义 | 属性 |
|---|---|---|
| 本地矩阵 | 三维物体的旋转、平移和缩放变换,本地矩阵materix是平移矩阵、缩放矩阵和旋转矩阵的乘积。 | object3D.matrix: Matrix4 默认是4*4的单位矩阵 |
| 世界坐标 | 三维物体自身本地矩阵及其所有所有祖宗对象本地矩阵的乘积,或者每一个对象的世界矩阵是对象本地矩阵和父对象的世界矩阵的乘积。 | object3D.matrixWorld : Matrix4 |
更新本地矩阵属性object3D.updateMatrix():提取位置.positon、缩放.scale、四元数.quaternion转化为变换矩阵,然后矩阵的乘积设置为本地矩阵。
更新世界矩阵属性object3D.updateMatrixWorld ( force : Boolean ),①会更新该三维物体的本地矩阵属性,②本地矩阵与父对象的世界矩阵做乘积,③依次更新该三维物体后代的世界矩阵(迭代①②③)。
执行渲染器的
render()方法时,会自动更新场景对象scene所有子孙对象的世界矩阵与本地矩阵
三维物体的变换
由基本变换的属性和改变属性的方法组成
| 变换 | 方法 | 本地矩阵 |
|---|---|---|
| 平移 | object3D.position: Vector3object3D.translateX ( distance : Float )object3D.translateY ( distance : Float ) object3D.translateZ ( distance : Float ) | 平移矩阵:下列矩阵的转置 |
| 缩放 | object3D.scale : Vector3 | 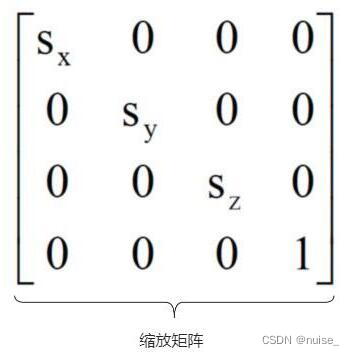 |
| 旋转 | 角度属性object3D.rotation : Euler等价于 四元数属性object3D.quaternion: Quaternion封装了一些改变属性的方法: object3D.rotateX (rad : Float) object3D.rotateY (rad : Float) object3D.rotateZ (rad : Float) |
这篇关于threejs 组-层级模型 | 本地坐标和世界坐标 | 局部坐标系和世界坐标系 | 本地矩阵.materix和世界矩阵.matrixWorld的文章就介绍到这儿,希望我们推荐的文章对编程师们有所帮助!





