本文主要是介绍TUM数据集groundtruth轨迹与估计轨迹统一参考系,希望对大家解决编程问题提供一定的参考价值,需要的开发者们随着小编来一起学习吧!
TUM数据集groundtruth轨迹与估计轨迹(ORBSLAM2运行的结果)统一参考系
参考:https://blog.csdn.net/luo870604851/article/details/85006243
阅读ORBSLAM的相关论文并且在UBuntu系统上编译好ORB-SLAM2后,准备运行下程序,获得估计的轨迹后,评估下轨迹的误差。这里运行的是rgbd_dataset_freiburg1_desk数据集,关于深度图和RGB图、估计轨迹和真实轨迹的时间戳的对齐,使用的是associate.py文件,具体可以参考高翔大佬的一起做RGB-D SLAM 第二季 (一)。绘制两者的轨迹后,发现两者完全没有对上,然后看了groudtruth.txt和KeyFrameTrajectory.txt文件后,发现估计轨迹是以第一帧坐标系作为参考,而真值轨迹应该是以某个固定的坐标系作为参考。为了能评估轨迹误差,必须要知道两个参考系之间的变换矩阵T。

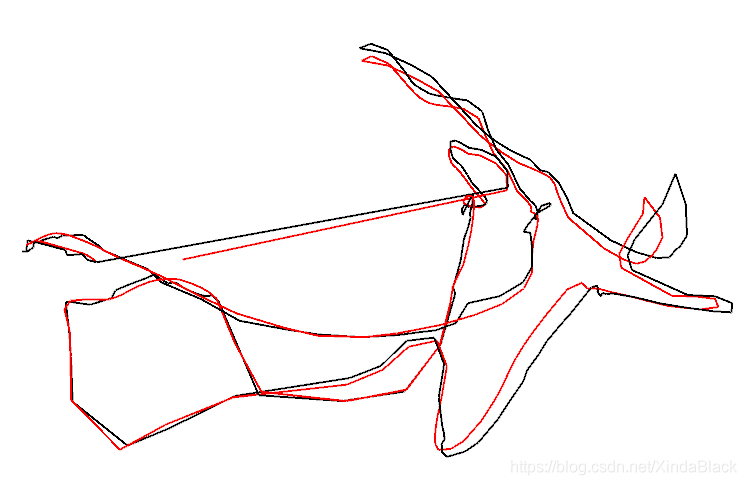
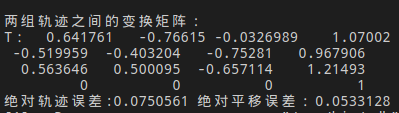
首先考虑的是,在时间戳对齐后,求取第一帧groundtruth轨迹的逆作为T,下图是运行的结果。在论文中给出的是绝对位移误差为0.046m,而这里计算的结果为0.053m,误差比较大。(这个差的还算比较小的了,其它的数据集也试过了,误差更大。)
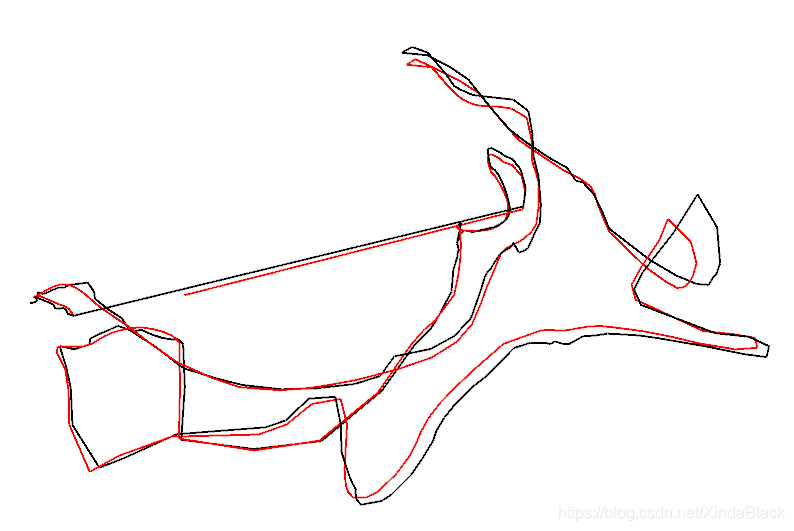
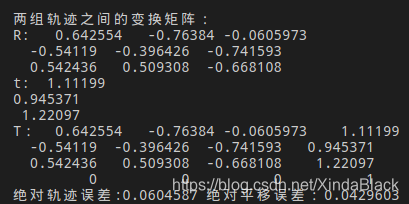
从上面的结果可以看出,直接取第一帧groundtruth轨迹的逆作为T,最后求得的误差要比论文里给出的要大。分析原因,上述两个参考系之间的变换矩阵T只由一帧计算得,存在比较大的误差。因此,可以把所有帧均考虑进来,构建最小二乘问题来估计T,这就是一个ICP问题,在视觉SLAM十四讲的第七章有给出求解方式。这可以使用SVD方法求解,也可以用非线性优化的方式求解。从下面的图中可以看出,估计的绝对平移误差为0.043m,现在比较符合论文中的结果。
下面给出读取轨迹文件并统一参考系,显示轨迹,计算轨迹误差的代码。
#include <pangolin/pangolin.h>
#include <Eigen/Core>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <thread>
#include <sophus/se3.hpp>class Trajectory{public:void showAssociateTrajectory();vector<double> calTrajectoryError();void readAssociateTrajectory(const string &strAssociateTrajectoryFile);vector<double> mvimageTimeStamps, mvposeTimeStamps, mvtruthTimeStamps;vector<Eigen::Isometry3d, Eigen::aligned_allocator<Eigen::Isometry3d>> mvpose;vector<Eigen::Isometry3d, Eigen::aligned_allocator<Eigen::Isometry3d>> mvgroundTruthPose;
};vector<Eigen::Isometry3d, Eigen::aligned_allocator<Eigen::Isometry3d>> pose;
vector<Eigen::Isometry3d, Eigen::aligned_allocator<Eigen::Isometry3d>> groundTruthPose;// Input -> The path of associated trcjectory file.
void Trajectory::readAssociateTrajectory( const string &strAssociateTrajectoryFile){ifstream fin(strAssociateTrajectoryFile);string str;if(!fin){cerr << "Failed to open trajectory file at:" << strAssociateTrajectoryFile << endl;exit(-1);}// Read trajectory filedouble data[7];// bool isFirstFrame = true;// orbslam保存的轨迹是以第一帧为世界坐标系,需要将groundtruth轨迹的世界坐标变换到估计轨迹的固定坐标// Eigen::Isometry3d Tinv; while(!fin.eof()){ double realTimeStamp, truthTimeStamp;Eigen::Vector3d v;fin >> realTimeStamp;if(fin.fail()) { // 在读数据后判断,避免多读一行数据!!break;}mvposeTimeStamps.push_back(realTimeStamp);//读取实际轨迹for(size_t i = 0; i < 7; i++){fin >> data[i];}Eigen::Quaterniond q(data[6],data[3],data[4],data[5]);Eigen::Isometry3d T(q);T.pretranslate(Eigen::Vector3d(data[0],data[1],data[2])); //左乘,相对与旋转前的坐标pose.push_back(T);fin >> truthTimeStamp;//读取轨迹真值for(size_t i = 0; i < 7; i++){fin >> data[i];}Eigen::Quaterniond q1(data[6],data[3],data[4],data[5]);Eigen::Isometry3d T1(q1);T1.pretranslate(Eigen::Vector3d(data[0],data[1],data[2]));// if(isFirstFrame){// Tinv = T1.inverse();// cout << "两组轨迹之间的变换矩阵:" << endl;// cout << "T:" << Tinv.matrix() << endl;// isFirstFrame = false; // }mvtruthTimeStamps.push_back(truthTimeStamp);// groundTruthPose.push_back(Tinv*T1); groundTruthPose.push_back(T1); }// // 将groundtruth轨迹的世界坐标系转换到估计轨迹的世界坐标系下Eigen::Vector3d estiMid, truthMid; // 两组点的质心vector<Eigen::Vector3d> vEsti, vTruth; // 两组点的去质心坐标int N = pose.size();for(size_t i = 0; i < N ; i++){estiMid += pose[i].translation();truthMid += groundTruthPose[i].translation();}estiMid /= N;truthMid /=N;vEsti.resize(N); vTruth.resize(N);for(int i = 0; i < N; i++){vEsti[i] = pose[i].translation() - estiMid;vTruth[i] = groundTruthPose[i].translation() - truthMid;}Eigen::Matrix3d W = Eigen::Matrix3d::Zero();for(size_t i = 0 ; i < N ; i++){W += vEsti[i]*(vTruth[i].transpose());}Eigen::JacobiSVD<Eigen::Matrix3d> svd (W, Eigen::ComputeFullU|Eigen::ComputeFullV);Eigen::Matrix3d u = svd.matrixU();Eigen::Matrix3d v = svd.matrixV();Eigen::Matrix3d R = u * (v.transpose());Eigen::Vector3d t = estiMid - R * truthMid;Eigen::Isometry3d T = Eigen::Isometry3d::Identity();cout << "两组轨迹之间的变换矩阵:" << endl;cout << "R: " << R << endl; //这两行输出注释掉,结果会出错?!(迷~~)cout << "t: " << t << endl;// // 方式1 (方式一和方式二T必须初始化成单位矩阵)T.translate(t);T.rotate(R);// // 方式2// T.rotate(R); // 旋转后,translate()是相对旋转后的坐标,pretranslate()是相对于旋转前的坐标// T.pretranslate(t); // 带pre的函数表示左乘,不带的表示右乘// // 方式3// // T.matrix().block(0, 0, 3, 3) = R;// // T.matrix().col(3) = t.homogeneous(); // 将平移向量变成对应的齐次坐标// // T.matrix().row(3) = Eigen::Vector4d(0, 0, 0, 1);cout << "T:" << T.matrix() << endl;for(auto &p: groundTruthPose){p = T*p;}mvpose = pose;mvgroundTruthPose = groundTruthPose;
}void Trajectory::showAssociateTrajectory(){assert(pose.size() == groundTruthPose.size()); assert(!pose.empty() && !groundTruthPose.empty());pangolin::CreateWindowAndBind("Trajectory Viewer", 1024, 768); //创建一个窗口glEnable(GL_DEPTH_TEST); //启动深度测试,OpenGL只绘制最前面的一层,绘制时检查当前像素前面是否有别的像素,如果别的像素挡住了它,那它就不会绘制glEnable(GL_BLEND); //在openGL中使用颜色混合glBlendFunc(GL_SRC_ALPHA, GL_ONE_MINUS_SRC_ALPHA); //选择混合选项// 1. 定义相机投影模型:ProjectionMatrix(w, h, fu, fv, u0, v0, zNear, zFar)// 2. 定义观测方位向量:// 观测点位置:(mViewpointX mViewpointY mViewpointZ)// 观测目标位置:(0, 0, 0)// 观测的方位向量:(0.0,-1.0, 0.0)pangolin::OpenGlRenderState s_cam(pangolin::ProjectionMatrix(1024, 768, 500, 500, 512, 289, 0.1, 1000),pangolin::ModelViewLookAt(0, -0.1, -1.8, 0, 0, 0, 0.0, -1.0, 0.0));// 定义地图面板// 前两个参数(0.0, 1.0)表明宽度和面板纵向宽度和窗口大小相同// 中间两个参数(pangolin::Attach::Pix(175), 1.0)表明右边所有部分用于显示图形// 最后一个参数(-1024.0f/768.0f)为显示长宽比pangolin::View &d_cam = pangolin::CreateDisplay().SetBounds(0.0, 1.0 ,0.0 , 1.0, -1024.0f/768.0f).SetHandler(new pangolin::Handler3D(s_cam));while(pangolin::ShouldQuit() == false){//消除缓冲区中的当前可写的颜色缓冲和深度缓冲glClear(GL_COLOR_BUFFER_BIT | GL_DEPTH_BUFFER_BIT); // |和& -> 总是要计算两个数d_cam.Activate(s_cam);// 设置为白色,glClearColor(red, green, blue, alpha),数值范围(0, 1)glClearColor(1.0f, 1.0f, 1.0f, 1.0f);glLineWidth(2);//画出连线for(size_t i = 0; i < pose.size(); i++){glColor3f(0.0, 0.0, 0.0);glBegin(GL_LINES);auto p1 = pose[i], p2 = pose[i+1];glVertex3d(p1.translation()[0], p1.translation()[1], p1.translation()[2]);glVertex3d(p2.translation()[0], p2.translation()[1], p2.translation()[2]);glEnd();glColor3f(1.0, 0.0, 0.0); //红色是参考轨迹glBegin(GL_LINES);p1 = groundTruthPose[i];p2 = groundTruthPose[i+1];glVertex3d(p1.translation()[0], p1.translation()[1], p1.translation()[2]);glVertex3d(p2.translation()[0], p2.translation()[1], p2.translation()[2]);glEnd();}pangolin::FinishFrame();usleep(5000); // sleep 5 ms}
}vector<double> Trajectory::calTrajectoryError(){assert(pose.size() == groundTruthPose.size()); assert(!pose.empty() && !groundTruthPose.empty());double ATE_all = 0, ATE_trans = 0;vector<double> ATE;for(size_t i = 0; i < pose.size() ; i++){Sophus::SE3d p1(pose[i].rotation(),pose[i].translation());Sophus::SE3d p2(groundTruthPose[i].rotation(),groundTruthPose[i].translation());double error = ((p2.inverse() * p1).log()).norm();ATE_all += error * error;error = (groundTruthPose[i].translation() - pose[i].translation()).norm();ATE_trans += error*error;}ATE_all = ATE_all / double(pose.size());ATE_all = sqrt(ATE_all);ATE_trans = ATE_trans / double(pose.size());ATE_trans = sqrt(ATE_trans);ATE.push_back(ATE_all);ATE.push_back(ATE_trans);return ATE;
}
这篇关于TUM数据集groundtruth轨迹与估计轨迹统一参考系的文章就介绍到这儿,希望我们推荐的文章对编程师们有所帮助!




