本文主要是介绍【小沐学NLP】Python实现TF-IDF算法(nltk、sklearn、jieba),希望对大家解决编程问题提供一定的参考价值,需要的开发者们随着小编来一起学习吧!
文章目录
- 1、简介
- 1.1 TF
- 1.2 IDF
- 1.3 TF-IDF
- 2.1 TF-IDF(sklearn)
- 2.2 TF-IDF(nltk)
- 2.3 TF-IDF(Jieba)
- 2.4 TF-IDF(python)
- 结语
1、简介
TF-IDF(term frequency–inverse document frequency)是一种用于信息检索与数据挖掘的常用加权技术。TF是词频(Term Frequency),IDF是逆文本频率指数(Inverse Document Frequency)。
TF-IDF是一种统计方法,用以评估一字词对于一个文件集或一个语料库中的其中一份文件的重要程度。字词的重要性随着它在文件中出现的次数成正比增加,但同时会随着它在语料库中出现的频率成反比下降。
TF-IDF的主要思想是:如果某个词或短语在一篇文章中出现的频率TF高,并且在其他文章中很少出现,则认为此词或者短语具有很好的类别区分能力,适合用来分类。
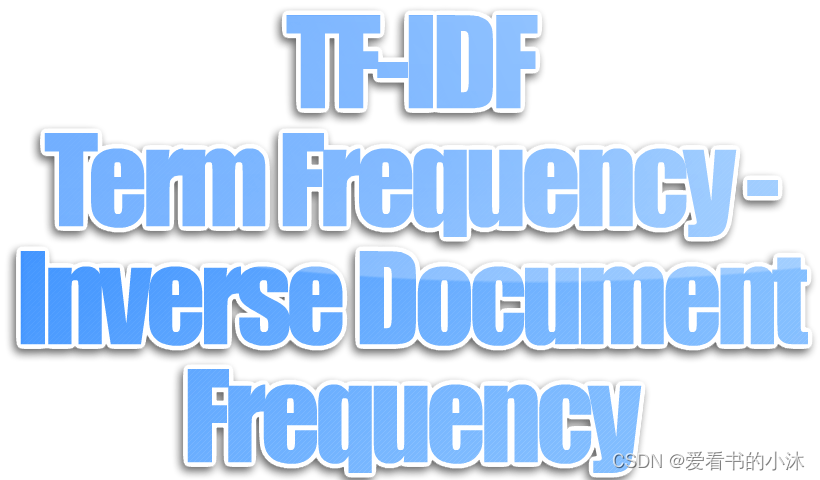
当有TF(词频)和IDF(逆文档频率)后,将这两个词相乘,就能得到一个词的TF-IDF的值。某个词在文章中的TF-IDF越大,那么一般而言这个词在这篇文章的重要性会越高,所以通过计算文章中各个词的TF-IDF,由大到小排序,排在最前面的几个词,就是该文章的关键词。

1.1 TF
TF(Term Frequency,词频),某个词在文档中出现的次数或频率。如果某篇文档中的某个词出现多次,那这个词可能是比较重要的词。当然,需要排除停用词。
词频(TF)=某个词在文档中出现的次数/文档的总词数

1.2 IDF
IDF(Inverse Document Frequency,逆文档频率),这是一个词语“权重”的度量,如果一个词在多篇文档中词频较低,也就表示这是一个比较少见的词,则这个词 IDF 值越大。
逆文档频率(IDF)=log(语料库的文档总数/(包含该词的文档数+1))

分母之所以要加 1,是为了避免分母为 0。这属于一种平滑方法。在不同的库中,实现 IDF 时,使用的平滑方法不完全相同。
1.3 TF-IDF
将 TF 和 IDF 相乘就得到 TF-IDF。
TF−IDF=词频(TF)×逆文档频率(IDF)
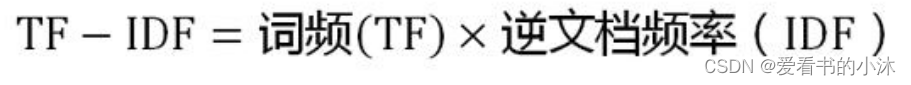
一个词的重要程度跟它在文档中出现的次数成正比,跟它在语料库出现的次数成反比。某一特定文件内的高词语频率,以及该词语在整个文件集合中的低文件频率,可以产生出高权重的TF-IDF。因此,TF-IDF倾向于过滤掉常见的词语,保留重要的词语。
例如,考虑一个包含 100 个单词的文档, 其中单词 apple 出现了 5 次。苹果的术语频率(即 TF)为 (5 / 100) = 0.05。现在,假设我们有 1000 万份文档,其中 1000 份中出现了 apple 这个词。然后,反向文档频率(即 IDF)计算为 log(10,000,000 / 1,000) = 4。
因此,TF-IDF 权重是这些量的乘积:0.05 * 4 = 0.20。 # 2、测试
2.1 TF-IDF(sklearn)
scikit-learn包进行TF-IDF分词权重计算主要用到了两个类:CountVectorizer和TfidfTransformer。其中CountVectorizer是通过fit_transform函数将文本中的词语转换为词频矩阵,矩阵元素a[i][j] 表示j词在第i个文本下的词频。即各个词语出现的次数,通过get_feature_names()可看到所有文本的关键字,通过toarray()可看到词频矩阵的结果。

对象TfidfVectorizer的定义如下:
class sklearn.feature_extraction.text.TfidfVectorizer(*, input='content', encoding='utf-8', decode_error='strict', strip_accents=None, lowercase=True, preprocessor=None, tokenizer=None, analyzer='word', stop_words=None, token_pattern='(?u)\b\w\w+\b', ngram_range=(1, 1), max_df=1.0, min_df=1, max_features=None, vocabulary=None, binary=False, dtype=<class 'numpy.float64'>, norm='l2', use_idf=True, smooth_idf=True, sublinear_tf=False
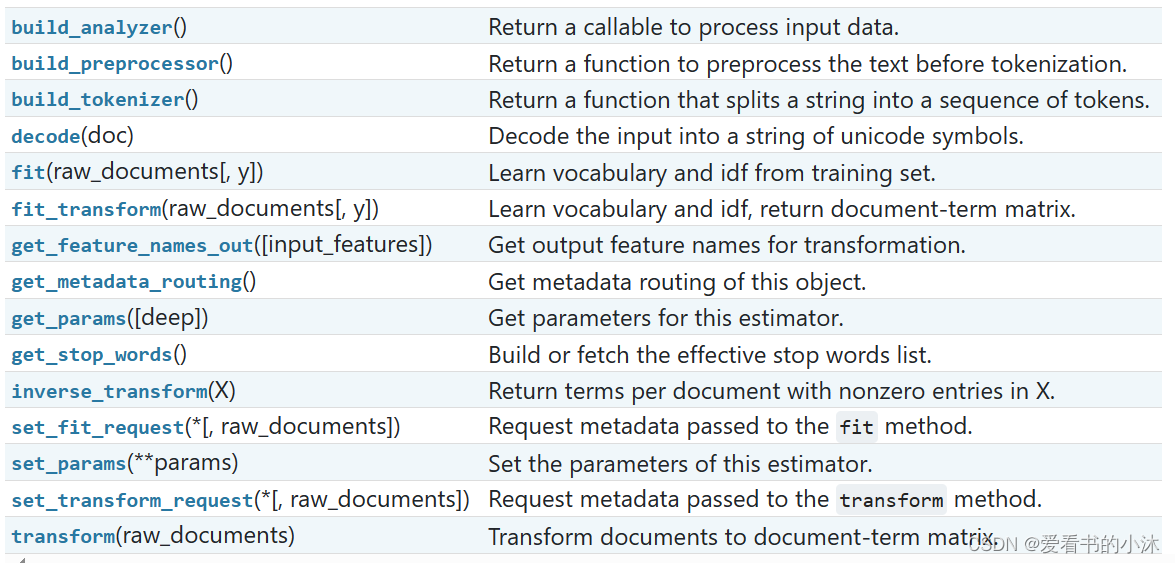
对象TfidfVectorizer的方法如下:
安装库:
pip install scikit-learn
测试代码如下:
from sklearn.feature_extraction.text import TfidfTransformer
from sklearn.feature_extraction.text import CountVectorizercorpus = ["stray birds of summer come to my window to sing and fly away","and yellow leaves of autumn which have no ongs flutter and fall there with a sign","it is the tears of the earth that keep here smiles in bloom","if you shed tears when you miss the sun you also miss the stars","listen my heart to the whispers of the world with which it makes love to you",
]#tfidf_vec = CountVectorizer()
tfidf_vec = TfidfVectorizer()# 使用 fit_transform() 得到 TF-IDF 矩阵
tfidf_matrix = tfidf_vec.fit_transform(corpus)
print(tfidf_matrix)
print(tfidf_matrix.toarray())
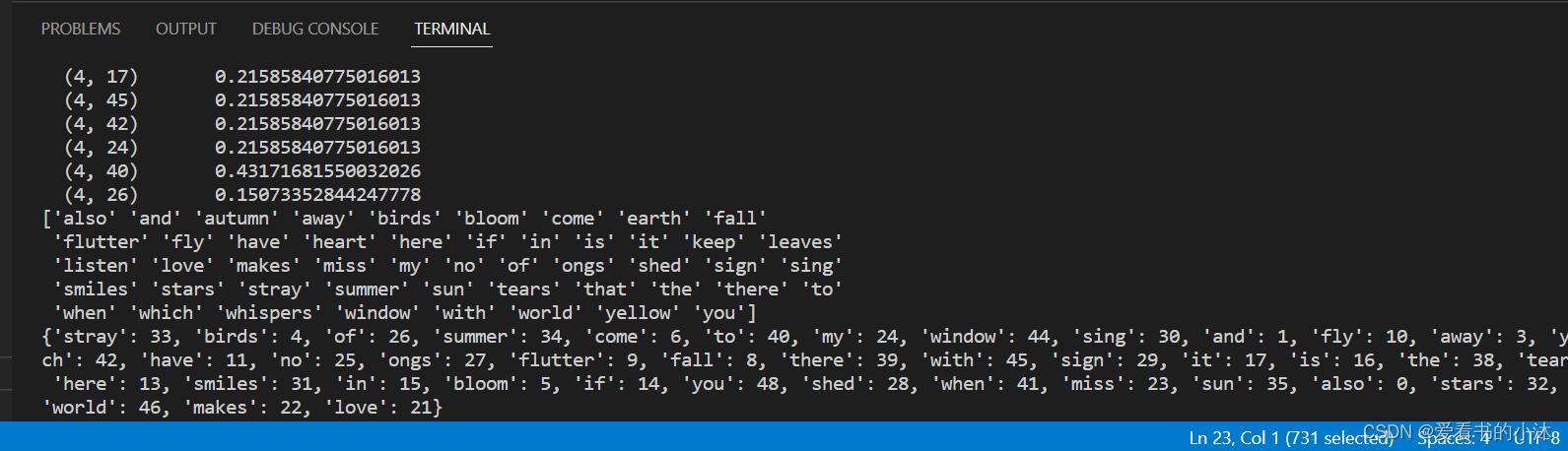
print(tfidf_matrix.shape)# 使用 get_feature_names() 得到不重复的单词
print(tfidf_vec.get_feature_names_out())# 得到每个单词对应的 ID
print(tfidf_vec.vocabulary_)
# Importing the TfidfVectorizer class from sklearn.feature_extraction.text module
from sklearn.feature_extraction.text import TfidfVectorizer# Creating a list of documents (corpus) to vectorize
corpus = ['This is the first document.','This document is the second document.','And this is the third one.','Is this the first document?',
]# Initializing a TfidfVectorizer object with default parameters
vectorizer = TfidfVectorizer()# Fitting the vectorizer to the corpus and transforming it into a sparse matrix of tf-idf values
X = vectorizer.fit_transform(corpus)# Printing the shape of the matrix (number of documents, number of features)
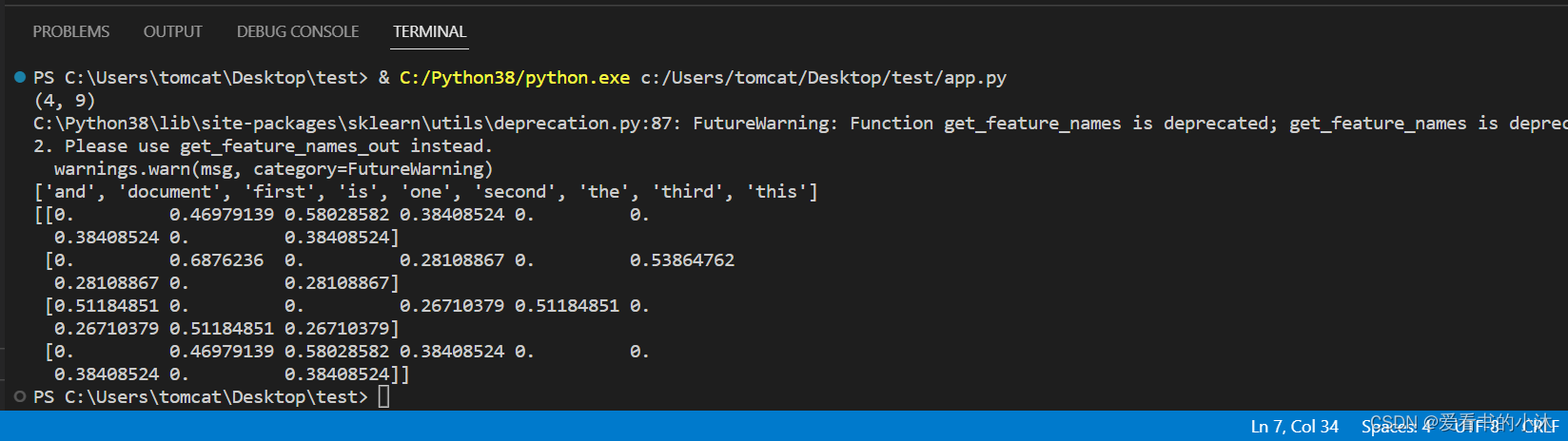
print(X.shape)
# Output: (4, 9)# Printing the feature names (words) that the vectorizer extracted from the corpus
print(vectorizer.get_feature_names())
# Output: ['and', 'document', 'first', 'is', 'one', 'second', 'the', 'third', 'this']# Printing the matrix in a dense format
print(X.toarray())
from sklearn.feature_extraction.text import CountVectorizer
from sklearn.feature_extraction.text import TfidfTransformercorpus_doc = ["stray birds of summer come to my window to sing and fly away","and yellow leaves of autumn which have no ongs flutter and fall there with a sign","it is the tears of the earth that keep here smiles in bloom","if you shed tears when you miss the sun you also miss the stars","listen my heart to the whispers of the world with which it makes love to you",
]test_doc = ["with we dreamt that we were strangers", "of the were"]#该类会将文本中的词语转换为词频矩阵,矩阵元素a[i][j] 表示j词在i类文本下的词频
vectorizer = CountVectorizer(max_features=10)
#该类会统计每个词语的tf-idf权值
tf_idf_transformer = TfidfTransformer()
#将文本转为词频矩阵并计算tf-idf
tf_idf = tf_idf_transformer.fit_transform(vectorizer.fit_transform(corpus_doc))
#将tf-idf矩阵抽取出来,元素a[i][j]表示j词在i类文本中的tf-idf权重
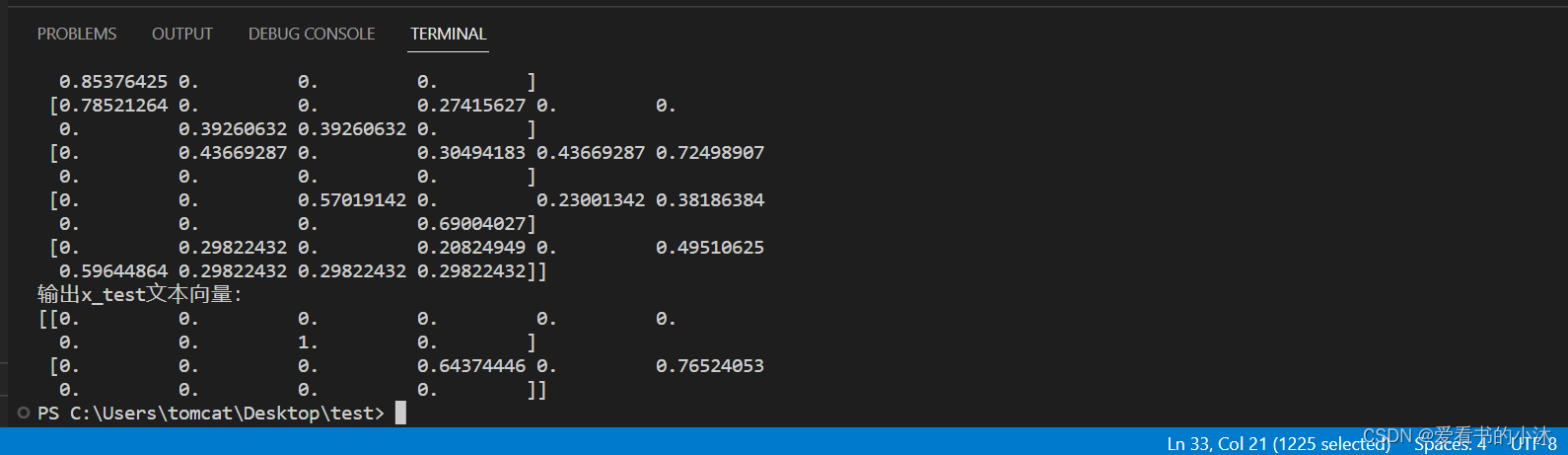
x_train_weight = tf_idf.toarray()print(tf_idf)
print(vectorizer.vocabulary_)#对测试集进行tf-idf权重计算
tf_idf = tf_idf_transformer.transform(vectorizer.transform(test_doc))
x_test_weight = tf_idf.toarray() # 测试集TF-IDF权重矩阵print('输出x_train文本向量:')
print(x_train_weight)
print('输出x_test文本向量:')
print(x_test_weight)
#coding=utf-8
from sklearn.feature_extraction.text import TfidfVectorizerdocument = ["yxy have a pen.","yxy have an apple."]tfidf_model = TfidfVectorizer().fit(document)
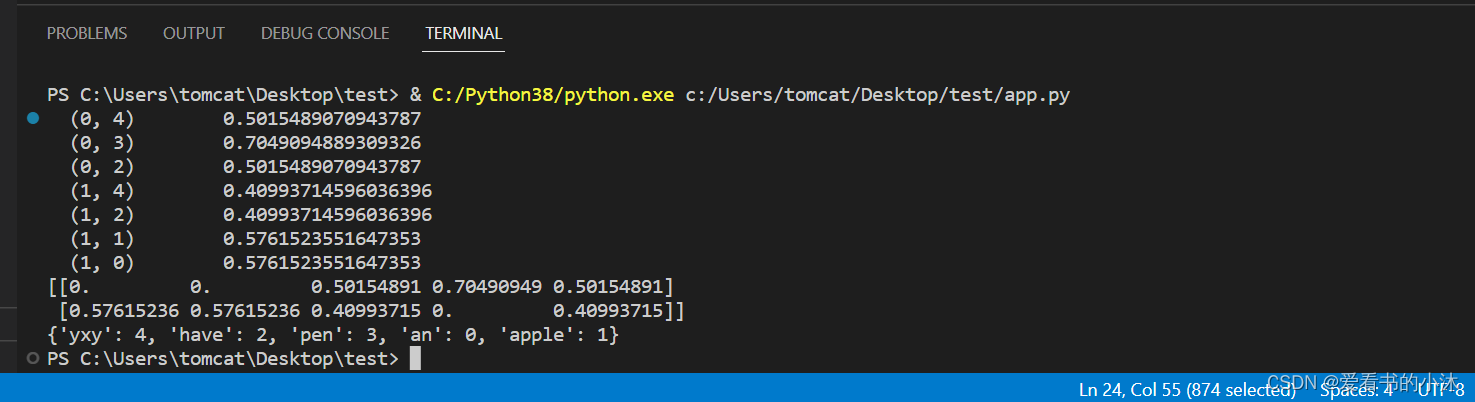
sparse_result = tfidf_model.transform(document) # 得到tf-idf矩阵,稀疏矩阵表示法print(sparse_result)
# (0, 4) 0.5015489070943787 # 第0个字符串,对应词典序号为4的词的TFIDF为0.5015489070943787
# (0, 3) 0.7049094889309326
# (0, 2) 0.5015489070943787
# (1, 4) 0.40993714596036396
# (1, 2) 0.40993714596036396
# (1, 1) 0.5761523551647353
# (1, 0) 0.5761523551647353print(sparse_result.todense()) # 转化为更直观的一般矩阵
# [[0. 0. 0.50154891 0.70490949 0.50154891]
# [0.57615236 0.57615236 0.40993715 0. 0.40993715]]print(tfidf_model.vocabulary_) # 词语与列的对应关系
# {'yxy': 4, 'have': 2, 'pen': 3, 'an': 0, 'apple': 1}
from sklearn.feature_extraction.text import TfidfTransformer
from sklearn.feature_extraction.text import CountVectorizer # corpus 模拟语料库
corpus=["yxy third document","yxy yxy document"]# 1、TfidfTransformer是把TF矩阵转成TF-IDF矩阵,所以需要先词频统计CountVectorizer,转换成TF-IDF矩阵
# 先计算了TF然后再转换成了TF-IDF
tfvectorizer=CountVectorizer()
count_vector=tfvectorizer.fit_transform(corpus) # Tf 矩阵
transformer = TfidfTransformer() # 转换Tf矩阵
tfidf = transformer.fit_transform(count_vector) # 将TF转换成Tf-Idf
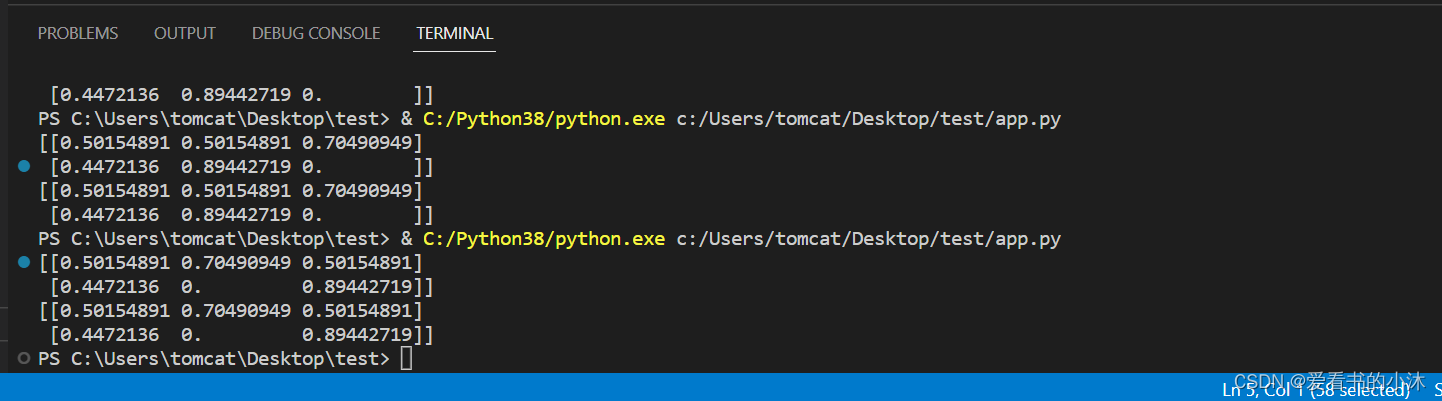
arr=tfidf.toarray()
print(arr)# 2、一步到位的方法
# TF-IDF一步到位
from sklearn.feature_extraction.text import TfidfVectorizer
tfidf = TfidfVectorizer()
# tfidf.fit(corpus) # use vectorizer to fit the corpus
# corpus_vector=tfidf.transform(corpus).toarray()
corpus_vector=tfidf.fit_transform(corpus).toarray()
print(corpus_vector)
2.2 TF-IDF(nltk)
使用nltk自带的TF-IDF函数对词表中每个词计算其TF-IDF值。
安装库:
pip install nltk
测试代码如下:
from nltk.text import TextCollection
from nltk.tokenize import word_tokenizecorpus_doc = ["stray birds of summer come to my window to sing and fly away","and yellow leaves of autumn which have no ongs flutter and fall there with a sign","it is the tears of the earth that keep here smiles in bloom","if you shed tears when you miss the sun you also miss the stars","listen my heart to the whispers of the world with which it makes love to you",
]#构建语料库corpus
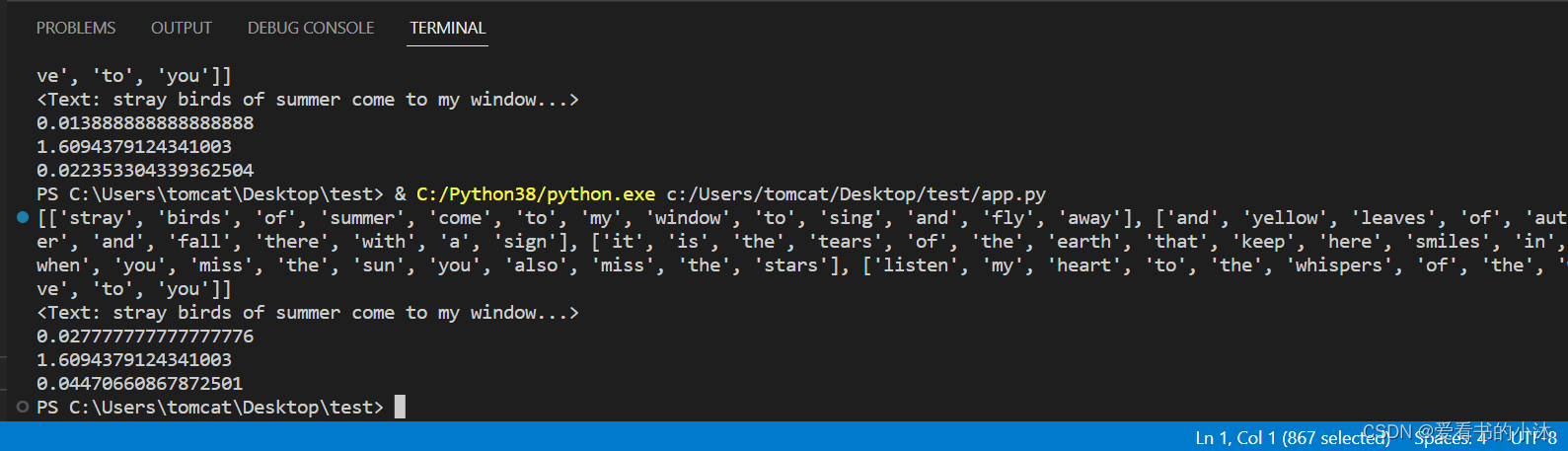
corpus_doc=[word_tokenize(word) for word in corpus_doc] #对每个句子进行分词
print(corpus_doc) #输出分词后的结果
corpus=TextCollection(corpus_doc) #构建语料库
print(corpus) #输出语料库#计算语料库中"which"的tf值
tf=corpus.tf('miss', corpus)
print(tf)#计算语料库中"which"的idf值
idf=corpus.idf('miss')
print(idf)#计算语料库中"which"的tf-idf值
tf_idf=corpus.tf_idf('miss',corpus)
print(tf_idf)
这是一种抽取式文本摘要技术。下面使用 Tf-IDF 算法总结了文本。
import mathfrom nltk import sent_tokenize, word_tokenize, PorterStemmer
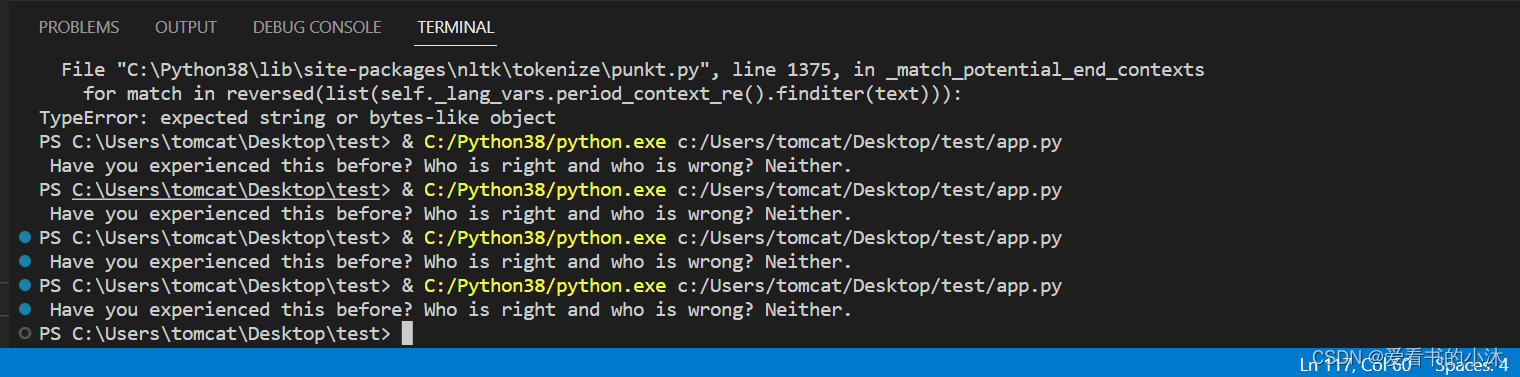
from nltk.corpus import stopwords def _create_frequency_matrix(sentences):frequency_matrix = {}stopWords = set(stopwords.words("english"))ps = PorterStemmer()for sent in sentences:freq_table = {}words = word_tokenize(sent)for word in words:word = word.lower()word = ps.stem(word)if word in stopWords:continueif word in freq_table:freq_table[word] += 1else:freq_table[word] = 1frequency_matrix[sent[:15]] = freq_tablereturn frequency_matrixdef _create_tf_matrix(freq_matrix):tf_matrix = {}for sent, f_table in freq_matrix.items():tf_table = {}count_words_in_sentence = len(f_table)for word, count in f_table.items():tf_table[word] = count / count_words_in_sentencetf_matrix[sent] = tf_tablereturn tf_matrixdef _create_documents_per_words(freq_matrix):word_per_doc_table = {}for sent, f_table in freq_matrix.items():for word, count in f_table.items():if word in word_per_doc_table:word_per_doc_table[word] += 1else:word_per_doc_table[word] = 1return word_per_doc_tabledef _create_idf_matrix(freq_matrix, count_doc_per_words, total_documents):idf_matrix = {}for sent, f_table in freq_matrix.items():idf_table = {}for word in f_table.keys():idf_table[word] = math.log10(total_documents / float(count_doc_per_words[word]))idf_matrix[sent] = idf_tablereturn idf_matrixdef _create_tf_idf_matrix(tf_matrix, idf_matrix):tf_idf_matrix = {}for (sent1, f_table1), (sent2, f_table2) in zip(tf_matrix.items(), idf_matrix.items()):tf_idf_table = {}for (word1, value1), (word2, value2) in zip(f_table1.items(),f_table2.items()): # here, keys are the same in both the tabletf_idf_table[word1] = float(value1 * value2)tf_idf_matrix[sent1] = tf_idf_tablereturn tf_idf_matrixdef _score_sentences(tf_idf_matrix) -> dict:"""score a sentence by its word's TFBasic algorithm: adding the TF frequency of every non-stop word in a sentence divided by total no of words in a sentence.:rtype: dict"""sentenceValue = {}for sent, f_table in tf_idf_matrix.items():total_score_per_sentence = 0count_words_in_sentence = len(f_table)for word, score in f_table.items():total_score_per_sentence += scoresentenceValue[sent] = total_score_per_sentence / count_words_in_sentencereturn sentenceValuedef _find_average_score(sentenceValue) -> int:"""Find the average score from the sentence value dictionary:rtype: int"""sumValues = 0for entry in sentenceValue:sumValues += sentenceValue[entry]# Average value of a sentence from original summary_textaverage = (sumValues / len(sentenceValue))return averagedef _generate_summary(sentences, sentenceValue, threshold):sentence_count = 0summary = ''for sentence in sentences:if sentence[:15] in sentenceValue and sentenceValue[sentence[:15]] >= (threshold):summary += " " + sentencesentence_count += 1return summarytext = '''
Those Who Are Resilient Stay In The Game Longer “On the mountains of truth you can never climb in vain:
either you will reach a point higher up today, or you will be training your powers so that you will be able to climb higher tomorrow.”
— Friedrich Nietzsche Challenges and setbacks are not meant to defeat you,
but promote you. However, I realise after many years of defeats, it can crush your spirit and it is easier to give up than risk further setbacks
and disappointments. Have you experienced this before? To be honest, I don’t have the answers.
I can’t tell you what the right course of action is; only you will know.
However, it’s important not to be discouraged by failure when pursuing a goal or a dream,
since failure itself means different things to different people. To a person with a Fixed Mindset failure is a blow to their self-esteem,
yet to a person with a Growth Mindset, it’s an opportunity to improve and find new ways to overcome their obstacles. Same failure,
yet different responses. Who is right and who is wrong? Neither. Each person has a different mindset that decides their outcome.
Those who are resilient stay in the game longer and draw on their inner means to succeed.'
''''''
We already have a sentence tokenizer, so we just need
to run the sent_tokenize() method to create the array of sentences.
'''
# 1 Sentence Tokenize
sentences = sent_tokenize(text)
total_documents = len(sentences)
#print(sentences)# 2 Create the Frequency matrix of the words in each sentence.
freq_matrix = _create_frequency_matrix(sentences)
#print(freq_matrix)'''
Term frequency (TF) is how often a word appears in a document, divided by how many words are there in a document.
'''
# 3 Calculate TermFrequency and generate a matrix
tf_matrix = _create_tf_matrix(freq_matrix)
#print(tf_matrix)# 4 creating table for documents per words
count_doc_per_words = _create_documents_per_words(freq_matrix)
#print(count_doc_per_words)'''
Inverse document frequency (IDF) is how unique or rare a word is.
'''
# 5 Calculate IDF and generate a matrix
idf_matrix = _create_idf_matrix(freq_matrix, count_doc_per_words, total_documents)
#print(idf_matrix)# 6 Calculate TF-IDF and generate a matrix
tf_idf_matrix = _create_tf_idf_matrix(tf_matrix, idf_matrix)
#print(tf_idf_matrix)# 7 Important Algorithm: score the sentences
sentence_scores = _score_sentences(tf_idf_matrix)
#print(sentence_scores)# 8 Find the threshold
threshold = _find_average_score(sentence_scores)
#print(threshold)# 9 Important Algorithm: Generate the summary
summary = _generate_summary(sentences, sentence_scores, 1.3 * threshold)
print(summary)
2.3 TF-IDF(Jieba)
jieba.analyse.extract_tags()提取关键字的原理是使用TF-IDF算法。
安装库:
pip install Jieba
测试代码如下:
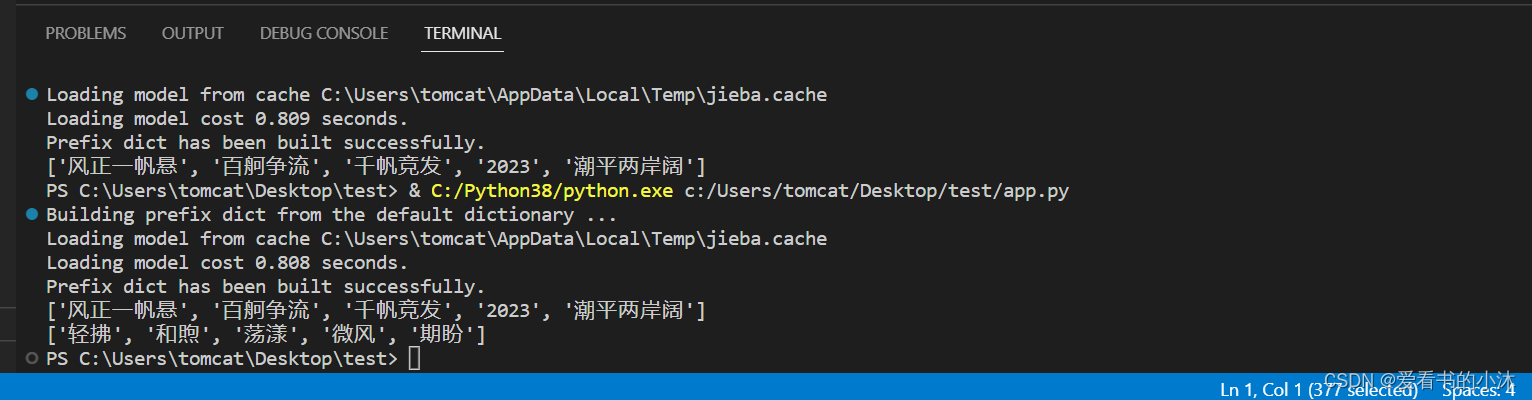
import jieba.analysesentence='2023,每一个你,都在认真果敢地拼,步履坚定地闯。潮平两岸阔,风正一帆悬。经济的大海辽阔浩瀚,为每一次起航注入力量。百舸争流、千帆竞发,终将汇聚乘风逐浪的磅礴之力。'
keywords=jieba.analyse.extract_tags(sentence, topK=5, withWeight=False, allowPOS=())
print(keywords)sentence='今天的阳光特别和煦舒适,微风轻拂,荡漾着每一颗期盼的心。人生,总要在温暖中前行。春天,已经在向我们招手了。'
keywords=jieba.analyse.extract_tags(sentence, topK=5, withWeight=False, allowPOS=())
#keywords = jieba.analyse.extract_tags(sentence, topK=20, withWeight=True, allowPOS=('n','nr','ns'))
print(keywords)
sentence 为待提取的文本
topK 为返回几个 TF/IDF 权重最大的关键词,默认值为 20
withWeight 为是否一并返回关键词权重值,默认值为 False
allowPOS是允许的提取的词性,默认为allowPOS=‘ns’, ‘n’, ‘vn’, ‘v’,提取地名、名词、动名词、动词
2.4 TF-IDF(python)
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
from collections import defaultdict
import math
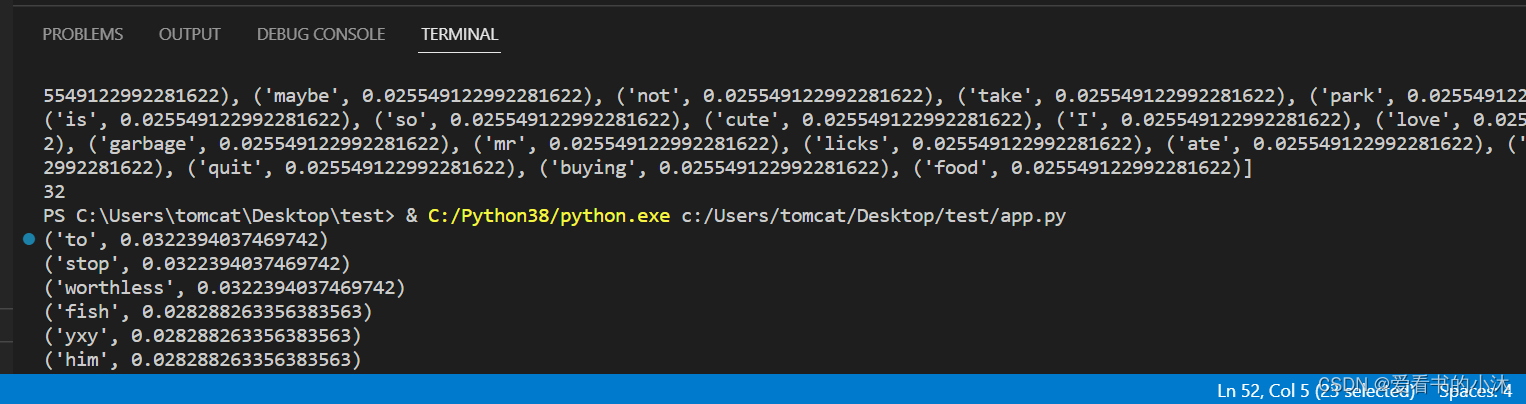
import operatordef loadDataSet():dataset = [ ['fish', 'yxy', 'has', 'flea', 'problems', 'help', 'please'], # 切分的词条['maybe', 'not', 'take', 'him', 'to', 'yxy', 'park', 'book'],['fish', 'dalmation', 'is', 'so', 'cute', 'I', 'love', 'him'],['stop', 'posting', 'book', 'moon', 'sun'],['mr', 'licks', 'ate', 'fish', 'steak', 'how', 'to', 'stop', 'him'],['quit', 'buying', 'moon', 'yxy', 'food', 'book'] ]return datasetdef computeTFIDF(list_words):#总词频统计doc_frequency=defaultdict(int)for word_list in list_words:for i in word_list:doc_frequency[i]+=1#计算每个词的TF值word_tf={} #存储没个词的tf值for i in doc_frequency:word_tf[i]=doc_frequency[i]/sum(doc_frequency.values())#计算每个词的IDF值doc_num=len(list_words)word_idf={} #存储每个词的idf值word_doc=defaultdict(int) #存储包含该词的文档数for i in doc_frequency:for j in list_words:if i in j:word_doc[i]+=1for i in doc_frequency:word_idf[i]=math.log(doc_num/(word_doc[i]+1))#计算每个词的TF*IDF的值word_tf_idf={}for i in doc_frequency:word_tf_idf[i]=word_tf[i]*word_idf[i]# 对字典按值由大到小排序dict_feature_select=sorted(word_tf_idf.items(),key=operator.itemgetter(1),reverse=True)return dict_feature_selectif __name__=='__main__':data_list=loadDataSet() #加载数据tfidf=computeTFIDF(data_list) #所有词的TF-IDF值print(*tfidf, sep="\n")print(len(tfidf))
结语
如果您觉得该方法或代码有一点点用处,可以给作者点个赞,或打赏杯咖啡;╮( ̄▽ ̄)╭
如果您感觉方法或代码不咋地//(ㄒoㄒ)//,就在评论处留言,作者继续改进;o_O???
如果您需要相关功能的代码定制化开发,可以留言私信作者;(✿◡‿◡)
感谢各位大佬童鞋们的支持!( ´ ▽´ )ノ ( ´ ▽´)っ!!!
这篇关于【小沐学NLP】Python实现TF-IDF算法(nltk、sklearn、jieba)的文章就介绍到这儿,希望我们推荐的文章对编程师们有所帮助!





