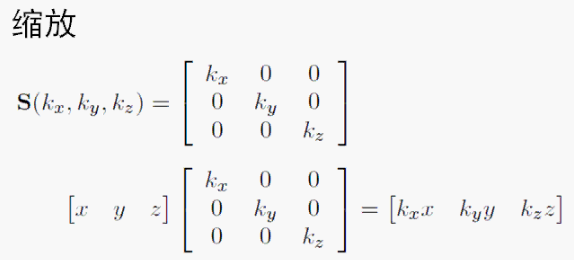本文主要是介绍3D数学 矩阵和线性变换之缩放,希望对大家解决编程问题提供一定的参考价值,需要的开发者们随着小编来一起学习吧!
矩阵和线性变换之缩放
1. 具有缩放效果的矩阵是怎样的?
我们这里只做沿着x、y、z轴方向的缩放,至于沿着任意方向的缩放比较复杂而且也很少用,所以暂时不介绍。如下图所示,原理非常简单,x、y、z乘上对应的缩放系数kx,ky,kz就得到了缩放后的结果。
2. 缩放矩阵编程示例
void Matrix3X3::setScale(Vector3& vec)
{m11 = vec.x; m12 = 0; m13 = 0;m21 = 0; m22 = vec.y; m23 = 0;m31 = 0; m32 = 0; m33 = vec.z;
}3. 缩放矩阵编程完整示例代码
//Vector3.h#pragma onceclass Vector3{
public:Vector3();Vector3(float X,float Y,float Z);//变为零向量void Zero();//求负向量Vector3 operator-() const;//求向量大小(长度或模)float Length() const;//标准化该向量void Normal();//向量的加法Vector3 operator+(Vector3 &rhs) const;Vector3& operator+=(Vector3 &rhs);//向量的减法Vector3 operator-(Vector3 &rhs) const;Vector3& operator-=(Vector3 &rhs);//向量乘标量Vector3 operator*(float scalar);//向量乘等于标量Vector3& operator*=(float scalar);//向量除以等于标量Vector3& operator/=(float scalar);//向量除以标量Vector3 operator/(float scalar);//距离公式float Distance(Vector3 &vec) const;//向量点乘float operator*(Vector3 &rhs) const;//向量叉积Vector3 CrossProduct(Vector3& vec) const;public:float x,y,z;};//标量乘向量
Vector3 operator*(float scalar, Vector3& vec);
//Vector3.cpp#include "Vector3.h"
#include <cmath>Vector3::Vector3():x(0.0),y(0.0),z(0.0)
{}Vector3::Vector3(float X,float Y,float Z):x(X),y(Y),z(Z)
{}void Vector3::Zero()
{x = y = z = 0;
}Vector3 Vector3::operator-() const
{return Vector3(-x,-y,-z);
}float Vector3::Length() const
{return sqrt(x*x+y*y+z*z);
}Vector3 Vector3::operator*(float scalar)
{return Vector3(this->x * scalar, this->y * scalar, this->z * scalar);
}Vector3& Vector3::operator*=(float scalar)
{return *this = *this * scalar;
}Vector3& Vector3::operator/=(float scalar)
{return *this = *this / scalar;
}Vector3 operator*(float scalar, Vector3& vec)
{return vec*scalar;
}Vector3 Vector3::operator/(float scalar)
{float temp = 1/ scalar;return *this * temp;
}void Vector3::Normal()
{//计算机计算乘法的速度比除法快float temp = 1 / Length();x *= temp;y *= temp;z *= temp;
}Vector3 Vector3::operator+(Vector3& rhs) const
{return Vector3(x+rhs.x,y+rhs.y,z+rhs.z);
}Vector3& Vector3::operator+=(Vector3& rhs)
{*this = *this + rhs;return *this;
}Vector3 Vector3::operator-(Vector3& rhs) const
{return Vector3(x-rhs.x,y-rhs.y,z-rhs.z);
}Vector3& Vector3::operator-=(Vector3& rhs)
{*this = *this - rhs;return *this;
}float Vector3::Distance(Vector3& vec) const
{return (*this - vec).Length();
}float Vector3::operator*(Vector3& rhs) const
{return this->x * rhs.x + this->y * rhs.y + this->z * rhs.z;
}Vector3 Vector3::CrossProduct(Vector3& vec) const
{return Vector3(this->y * vec.z - this->z * vec.y,this->z * vec.x - this->x * vec.z,this->x * vec.y - this->y * vec.x);
}//MathUtil.h#pragma once#include <math.h>enum E_Axis{Axis_x,Axis_y,Axis_z};
const float Pi = 3.14159;
//Matrix3X3.h#pragma once
#include "MathUtil.h"
#include "Vector3.h"class Matrix3X3
{
public://矩阵相乘Matrix3X3 operator*(Matrix3X3& rhs);//矩阵乘等矩阵Matrix3X3& operator*=(Matrix3X3& rhs);void setRotate(E_Axis axis,float theta);void setScale(Vector3 &vec);
public:float m11,m12,m13;float m21,m22,m23;float m31,m32,m33;
};//向量乘以矩阵
Vector3 operator*(Vector3& vec,Matrix3X3& mat);
//向量乘等矩阵
Vector3& operator*=(Vector3& vec,Matrix3X3& mat);//Matrix3X3.cpp#include "Matrix3X3.h"
#include <assert.h>Matrix3X3 Matrix3X3::operator*(Matrix3X3& rhs)
{Matrix3X3 tempMat;tempMat.m11 = this->m11 * rhs.m11 + this->m12 * rhs.m21 + this->m13 * rhs.m31;tempMat.m12 = this->m11 * rhs.m12 + this->m12 * rhs.m22 + this->m13 * rhs.m32;tempMat.m13 = this->m11 * rhs.m13 + this->m12 * rhs.m23 + this->m13 * rhs.m33;tempMat.m21 = this->m21 * rhs.m11 + this->m22 * rhs.m21 + this->m23 * rhs.m31;tempMat.m22 = this->m21 * rhs.m12 + this->m22 * rhs.m22 + this->m23 * rhs.m32;tempMat.m23 = this->m21 * rhs.m13 + this->m22 * rhs.m23 + this->m23 * rhs.m33;tempMat.m31 = this->m31 * rhs.m11 + this->m32 * rhs.m21 + this->m33 * rhs.m31;tempMat.m32 = this->m31 * rhs.m12 + this->m32 * rhs.m22 + this->m33 * rhs.m32;tempMat.m33 = this->m31 * rhs.m13 + this->m32 * rhs.m23 + this->m33 * rhs.m33;return tempMat;
}Matrix3X3& Matrix3X3::operator*=(Matrix3X3& rhs)
{*this = *this * rhs;return *this;
}Vector3 operator*(Vector3& vec,Matrix3X3& mat)
{Vector3 tempVec;tempVec.x = vec.x * mat.m11 + vec.y * mat.m21 + vec.z * mat.m31;tempVec.y = vec.x * mat.m12 + vec.y * mat.m22 + vec.z * mat.m32;tempVec.z = vec.x * mat.m13 + vec.y * mat.m23 + vec.z * mat.m33;return tempVec;
}Vector3& operator*=(Vector3& vec,Matrix3X3& mat)
{vec = vec * mat;return vec;
}void Matrix3X3::setRotate(E_Axis axis,float theta)
{float sinValue,cosValue;sinValue = sin(theta);cosValue = cos(theta);switch(axis){case Axis_x:{m11 = 1; m12 = 0; m13 = 0;m21 = 0; m22 = cosValue; m23 = sinValue;m31 = 0; m32 = -sinValue; m33 = cosValue;break;}case Axis_y:{m11 = cosValue; m12 = 0; m13 = -sinValue;m21 = 0; m22 = 1; m23 = 0;m31 = sinValue; m32 = 0; m33 = cosValue;break;}case Axis_z:{m11 = cosValue; m12 = sinValue; m13 = 0;m21 = -sinValue; m22 = cosValue; m23 = 0;m31 = 0; m32 = 0; m33 = 1;break;}default:assert(false);}}void Matrix3X3::setScale(Vector3& vec)
{m11 = vec.x; m12 = 0; m13 = 0;m21 = 0; m22 = vec.y; m23 = 0;m31 = 0; m32 = 0; m33 = vec.z;
}//main.cpp#include <iostream>
#include "Vector3.h"
#include "Matrix3X3.h"using namespace std;float ToZero(float num)
{return (abs(num) < 0.0001 ? 0 : num);
}void print_v(Vector3 v)
{cout << "[ " << ToZero(v.x) << ", " << ToZero(v.y) << ", " << ToZero(v.z) << " ]" << endl;cout << endl;
}void print_m(Matrix3X3 m)
{cout << m.m11 << "\t" << m.m12 << "\t" << m.m13 << endl;cout << m.m21 << "\t" << m.m22 << "\t" << m.m23 << endl;cout << m.m31 << "\t" << m.m32 << "\t" << m.m33 << endl;cout << endl;
}int main()
{Vector3 a(10,20,30),b,s(1,2,3);Matrix3X3 M;M.setScale(s);print_v(a);b = a * M;print_v(b);system("pause");return 0;
}4. 代码运行结果
[ 10, 20, 30 ]
[ 10, 40, 90 ]
这篇关于3D数学 矩阵和线性变换之缩放的文章就介绍到这儿,希望我们推荐的文章对编程师们有所帮助!