本文主要是介绍Benewake(北醒) TF-Luna/TFmini-S/TF03 串口版本雷达在树莓派 Raspberry Pi 上的运用(Python),希望对大家解决编程问题提供一定的参考价值,需要的开发者们随着小编来一起学习吧!
目录
- Raspberry Pi 接口定义
- 正确连接所需的定制电缆:
- 接线示意图:
- Python code:
- 完整代码
英文版本请参考参考以下链接
链接: https://pan.baidu.com/s/1D0n11Mz2odnOAju-TNJ5kQ 提取码: xf5u
本文介绍了如何将北醒单点雷达TFluna/TFmini-S/TF02-pro/TF03与 Raspberry Pi 4B 连接,它应该适用于所有其他版本的 Raspberry Pi。
1.最终用户手上有树莓派和TF-Luna
2.树莓派上安装了操作系统(在Raspbian version 10 buster上测试)
3.串口已经开启
4.安装了Python2或3 5. 编写脚本需要 Python 编辑器。 我在我的 RasPi 上安装了 Thonny。
注:如果已安装完整版 Raspbian,则完整版中包含所有必需的软件包。
Raspberry Pi 接口定义
下图是Raspberry Pi开发板的接口定义:


我们使用串行引脚将 TF系列 与 Raspberry Pi 连接起来。 Pin-8 (TXD) 和 Pin-10 (RXD) 。 由于TF-Luna的工作电压为5V,因此可以将2和6或4和6脚用作电源。
正确连接所需的定制电缆:
如果我们看TF-Luna的连接器,它是GH1.25-4P连接器。 另一方面,Raspberry Pi 有针头。 因此,我们需要一根电缆,其一侧具有 4P 1.55MM 条形连接器(也称为水平贴片插座),另一侧具有杜邦母连接器,用于将其插入 Raspberry Pi。 下图显示了为此目的定制的电缆。

接线示意图:
下图显示了 TF-Luna 与 Raspberry Pi 的连接图。

需要注意的是,如果您将更多设备连接到您的树莓派,那么强烈建议使用大电流电源,因为默认适配器只有 2A 的电流容量。 因此,请根据整个系统的电流要求来选择电源。 实际的连接设置可以在下图中看到。

Python code:
在本节中,我们将讨论用于从 TF-Luna 读取数据的 Python 代码的主要部分。 下表显示了TF-Luna使用的串口协议和数据格式:


按照上述数据序列,我们将使用 Python 从 TF-Luna 获取字节。 首先,我们需要安装可以使用 pip installer 完成的串口库(适用于 Python2 和 3):
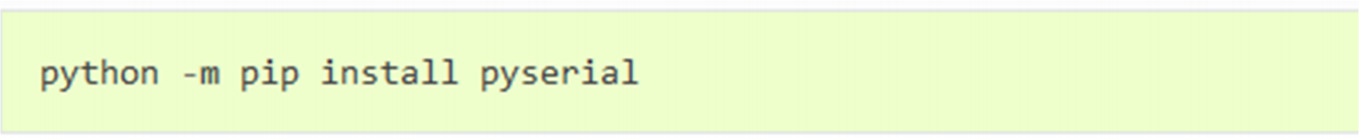
成功安装库后,就可以编写脚本并导入串口库了。
import serial
创建 Serial 类的对象并传递必要的参数(串口和波特率):
ser = serial.Serial("/dev/ttyAMA0", 115200)
main 函数从这里开始,它搜索端口是否打开并调用函数 read_data():
if __name__ == "__main__":try:if ser.isOpen() == False:ser.open()read_data()except KeyboardInterrupt(): # ctrl + c in terminal.if ser != None:ser.close()print("program interrupted by the user")
函数 read_data() 检查字节,进行一些必要的字节移位,然后在终端中打印数据:
# we define a new function that will get the data from LiDAR and publish it
def read_data():while True:counter = ser.in_waiting # count the number of bytes of the serial portif counter > 8:bytes_serial = ser.read(9)ser.reset_input_buffer()if bytes_serial[0] == 0x59 and bytes_serial[1] == 0x59: # python3print("TF-Luna python3 portion")distance = bytes_serial[2] + bytes_serial[3]*256strength = bytes_serial[4] + bytes_serial[5]*256temperature = bytes_serial[6] + bytes_serial[7]*256 # For TFLunatemperature = (temperature/8) - 256print("Distance:"+ str(distance))print("Strength:" + str(strength))if temperature != 0:print("Chip Temperature:" + str(temperature))ser.reset_input_buffer()if bytes_serial[0] == "Y" and bytes_serial[1] == "Y":distL = int(bytes_serial[2].encode("hex"), 16)distH = int(bytes_serial[3].encode("hex"), 16)stL = int(bytes_serial[4].encode("hex"), 16)stH = int(bytes_serial[5].encode("hex"), 16)distance = distL + distH*256strength = stL + stH*256tempL = int(bytes_serial[6].encode("hex"), 16)tempH = int(bytes_serial[7].encode("hex"), 16)temperature = tempL + tempH*256temperature = (temperature/8) - 256print("TF-Luna python2 portion")print("Distance:"+ str(distance) + "\n")print("Strength:" + str(strength) + "\n")print("Chip Temperature:" + str(temperature) + "\n")ser.reset_input_buffer()
这段代码有两部分; 第一部分与 Python3 兼容(上半部分),第二部分与 Python2 兼容(下半部分)。 对于不同的字节位置,请参考表三。
激光雷达测得的距离如下图所示。

完整代码
import serial
ser = serial.Serial("/dev/ttyAMA0", 115200)
# we define a new function that will get the data from LiDAR and publish it
def read_data():while True:counter = ser.in_waiting # count the number of bytes of the serial portif counter > 8:bytes_serial = ser.read(9)ser.reset_input_buffer()if bytes_serial[0] == 0x59 and bytes_serial[1] == 0x59: # python3print("TF-Luna python3 portion")distance = bytes_serial[2] + bytes_serial[3]*256strength = bytes_serial[4] + bytes_serial[5]*256temperature = bytes_serial[6] + bytes_serial[7]*256 # For TFLunatemperature = (temperature/8) - 256print("Distance:"+ str(distance))print("Strength:" + str(strength))if temperature != 0:print("Chip Temperature:" + str(temperature))ser.reset_input_buffer()if bytes_serial[0] == "Y" and bytes_serial[1] == "Y":distL = int(bytes_serial[2].encode("hex"), 16)distH = int(bytes_serial[3].encode("hex"), 16)stL = int(bytes_serial[4].encode("hex"), 16)stH = int(bytes_serial[5].encode("hex"), 16)distance = distL + distH*256strength = stL + stH*256tempL = int(bytes_serial[6].encode("hex"), 16)tempH = int(bytes_serial[7].encode("hex"), 16)temperature = tempL + tempH*256temperature = (temperature/8) - 256print("TF-Luna python2 portion")print("Distance:"+ str(distance) + "\n")print("Strength:" + str(strength) + "\n")print("Chip Temperature:" + str(temperature) + "\n")ser.reset_input_buffer()
if __name__ == "__main__":try:if ser.isOpen() == False:ser.open()read_data()except KeyboardInterrupt():if ser != None:ser.close()print("program interrupted by the user")
这篇关于Benewake(北醒) TF-Luna/TFmini-S/TF03 串口版本雷达在树莓派 Raspberry Pi 上的运用(Python)的文章就介绍到这儿,希望我们推荐的文章对编程师们有所帮助!






