本文主要是介绍【李群李代数】【manif 】基于固定信标的2D机器人定位 (Error State Kalman Filter)...,希望对大家解决编程问题提供一定的参考价值,需要的开发者们随着小编来一起学习吧!
demo演示
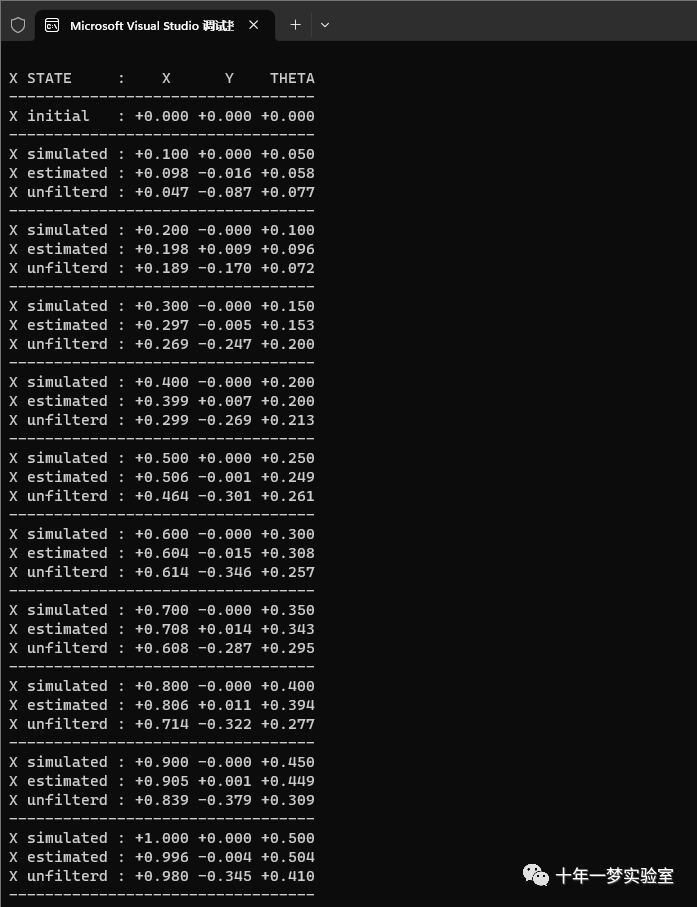
运行结果
我们考虑一个机器人在平面上被少量的准时地标或_信标 包围。
机器人以轴向速度和角速度的形式接收控制动作,并且能够测量信标相对于其自身参考系的位置。
机器人位姿 X 在 SE(2) 中,信标位置 b_k 在 R^2 中,
| cos th -sin th x |
* X = | sin th cos th y | //位置和方向
| 0 0 1 |
* b_k = (bx_k, by_k) // 世界坐标系中的lmk坐标
控制信号 u 是 se(2) 中的旋量,包括纵向速度 v 和角速度 w,没有横向速度分量,在采样时间 dt 上积分。
* u = (v*dt, 0, w*dt)
控制被带有协方差的加性高斯噪声 u_noise 破坏
* Q = diagonal(sigma_v^2, sigma_s^2, sigma_w^2).
此噪声解释了通过 sigma_s 非零值可能出现的横向滑移 u_s,
*当控制 u 到达时,机器人位姿更新为 X <-- X * Exp(u) = X + u。
地标测量是范围和方位类型,但为了简单起见,它们采用笛卡尔形式。
它们的噪声 n 是零均值高斯分布,并用协方差矩阵 R 指定。
我们注意到刚性运动动作 y = h(X,b) = X^-1 * b
* y_k = (brx_k, bry_k) // 机器人坐标系中的lmk坐标
我们考虑位于已知位置的信标 b_k。
我们将要估计的位姿定义为 SE(2) 中的 X。
估计误差 dx 及其协方差 P 在 X 处的切线空间中表示。
*所有这些变量再次总结如下
* * X : 机器人位姿,SE(2)
* u :机器人控制量,(v*dt ; 0 ; w*dt) in se(2)
* Q : 控制扰动协方差
* b_k : 第 k 个地标位置,R^2
* y :机器人坐标系中的笛卡尔地标测量,R^2
* R : 测量噪声的协方差
* The motion and measurement models are运动和测量模型是
* X_(t+1) = f(X_t, u) = X_t * Exp ( w ) //运动方程
* y_k = h(X, b_k) = X^-1 * b_k //测量方程
下面的算法首先包括一个模拟器来产生测量结果,然后使用这些测量结果来估计状态,使用基于李的误差状态卡尔曼滤波器。最后,打印模拟状态和估计状态以及未过滤状态(即没有卡尔曼校正)可以评估估计的质量。
#include "manif/SE2.h"#include <vector>#include <iostream>
#include <iomanip>using std::cout;
using std::endl;using namespace Eigen;typedef Array<double, 2, 1> Array2d;
typedef Array<double, 3, 1> Array3d;int main()
{std::srand((unsigned int) time(0));// START CONFIGURATION////const int NUMBER_OF_LMKS_TO_MEASURE = 3;// Define the robot pose element and its covariancemanif::SE2d X, X_simulation, X_unfiltered;Matrix3d P;X_simulation.setIdentity();X.setIdentity();X_unfiltered.setIdentity();P.setZero();// Define a control vector and its noise and covariancemanif::SE2Tangentd u_simu, u_est, u_unfilt;Vector3d u_nom, u_noisy, u_noise;Array3d u_sigmas;Matrix3d U;u_nom << 0.1, 0.0, 0.05;u_sigmas << 0.1, 0.1, 0.1;U = (u_sigmas * u_sigmas).matrix().asDiagonal();// Declare the Jacobians of the motion wrt robot and controlmanif::SE2d::Jacobian J_x, J_u;// Define three landmarks in R^2Eigen::Vector2d b0, b1, b2, b;b0 << 2.0, 0.0;b1 << 2.0, 1.0;b2 << 2.0, -1.0;std::vector<Eigen::Vector2d> landmarks;landmarks.push_back(b0);landmarks.push_back(b1);landmarks.push_back(b2);// Define the beacon's measurementsVector2d y, y_noise;Array2d y_sigmas;Matrix2d R;std::vector<Vector2d> measurements(landmarks.size());y_sigmas << 0.01, 0.01;R = (y_sigmas * y_sigmas).matrix().asDiagonal();// Declare the Jacobian of the measurements wrt the robot poseMatrix<double, 2, 3> H; // H = J_e_x// Declare some temporariesVector2d e, z; // expectation, innovationMatrix2d E, Z; // covariances of the aboveMatrix<double, 3, 2> K; // Kalman gainmanif::SE2Tangentd dx; // optimal update step, or error-statemanif::SE2d::Jacobian J_xi_x; // Jacobian is typedef MatrixMatrix<double, 2, 3> J_e_xi; // Jacobian////// CONFIGURATION DONE// DEBUGcout << std::fixed << std::setprecision(3) << std::showpos << endl;cout << "X STATE : X Y THETA" << endl;cout << "----------------------------------" << endl;cout << "X initial : " << X_simulation.log().coeffs().transpose() << endl;cout << "----------------------------------" << endl;// END DEBUG// START TEMPORAL LOOP////// Make 10 steps. Measure up to three landmarks each time.for (int t = 0; t < 10; t++){I. Simulation ###############################################################################/// simulate noiseu_noise = u_sigmas * Array3d::Random(); // control noiseu_noisy = u_nom + u_noise; // noisy controlu_simu = u_nom;u_est = u_noisy;u_unfilt = u_noisy;/// first we move - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - -X_simulation = X_simulation + u_simu; // overloaded X.rplus(u) = X * exp(u)/// then we measure all landmarks - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - -for (std::size_t i = 0; i < landmarks.size(); i++){b = landmarks[i]; // lmk coordinates in world frame/// simulate noisey_noise = y_sigmas * Array2d::Random(); // measurement noisey = X_simulation.inverse().act(b); // landmark measurement, before adding noisey = y + y_noise; // landmark measurement, noisymeasurements[i] = y; // store for the estimator just below}II. Estimation ###############################################################################/// First we move - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - -X = X.plus(u_est, J_x, J_u); // X * exp(u), with JacobiansP = J_x * P * J_x.transpose() + J_u * U * J_u.transpose();/// Then we correct using the measurements of each lmk - - - - - - - - -for (int i = 0; i < NUMBER_OF_LMKS_TO_MEASURE; i++){// landmarkb = landmarks[i]; // lmk coordinates in world frame// measurementy = measurements[i]; // lmk measurement, noisy// expectatione = X.inverse(J_xi_x).act(b, J_e_xi); // note: e = R.tr * ( b - t ), for X = (R,t).H = J_e_xi * J_xi_x; // note: H = J_e_x = J_e_xi * J_xi_xE = H * P * H.transpose();// innovationz = y - e;Z = E + R;// Kalman gainK = P * H.transpose() * Z.inverse(); // K = P * H.tr * ( H * P * H.tr + R).inv// Correction stepdx = K * z; // dx is in the tangent space at X// UpdateX = X + dx; // overloaded X.rplus(dx) = X * exp(dx)P = P - K * Z * K.transpose();}III. Unfiltered ##############################################################################// move also an unfiltered version for comparison purposesX_unfiltered = X_unfiltered + u_unfilt;IV. Results ##############################################################################// DEBUGcout << "X simulated : " << X_simulation.log().coeffs().transpose() << endl;cout << "X estimated : " << X.log().coeffs().transpose() << endl;cout << "X unfilterd : " << X_unfiltered.log().coeffs().transpose() << endl;cout << "----------------------------------" << endl;// END DEBUG}////// END OF TEMPORAL LOOP. DONE.return 0;
}
The End
这篇关于【李群李代数】【manif 】基于固定信标的2D机器人定位 (Error State Kalman Filter)...的文章就介绍到这儿,希望我们推荐的文章对编程师们有所帮助!






