本文主要是介绍COLMAP利用已知相机内外参重建NeRF的blender模型,希望对大家解决编程问题提供一定的参考价值,需要的开发者们随着小编来一起学习吧!
文章目录
- 前言
- 一、数据准备
- 二、从blender数据构造colmap数据集
- 三、COLMAP重建流程
- 1. 抽取图像特征
- 2. 导入指定相机内参
- 3. 特征匹配
- 4. 三角测量
- 5. 使用指定相机参数进行稠密重建
- 6. 立体匹配
- 7. 稠密点云融合
- 8. 网格重建
- 总结
前言
本文的目的是根据已知相机参数的blender模型,使用colmap进行稀疏重建和稠密重建。使用的blender数据是NeRF提供的synthetic数据集中的lego模型,其中的几张图片如下:
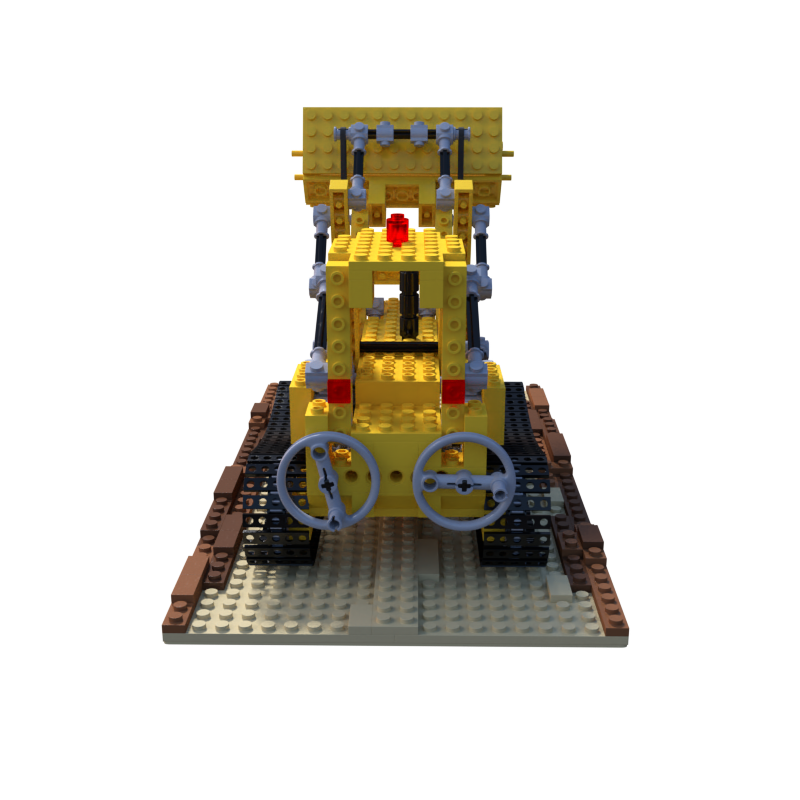

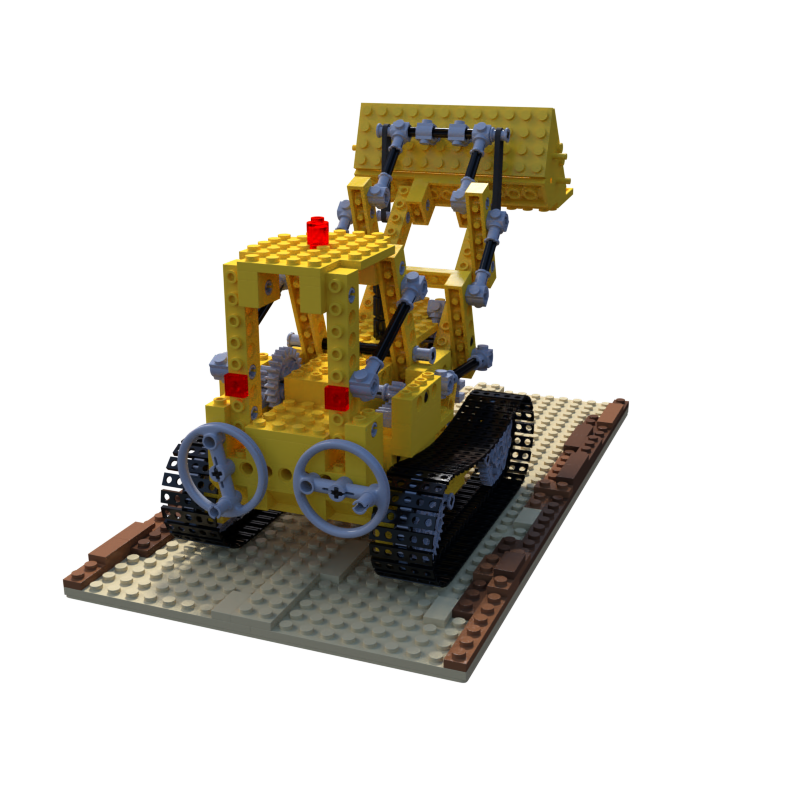
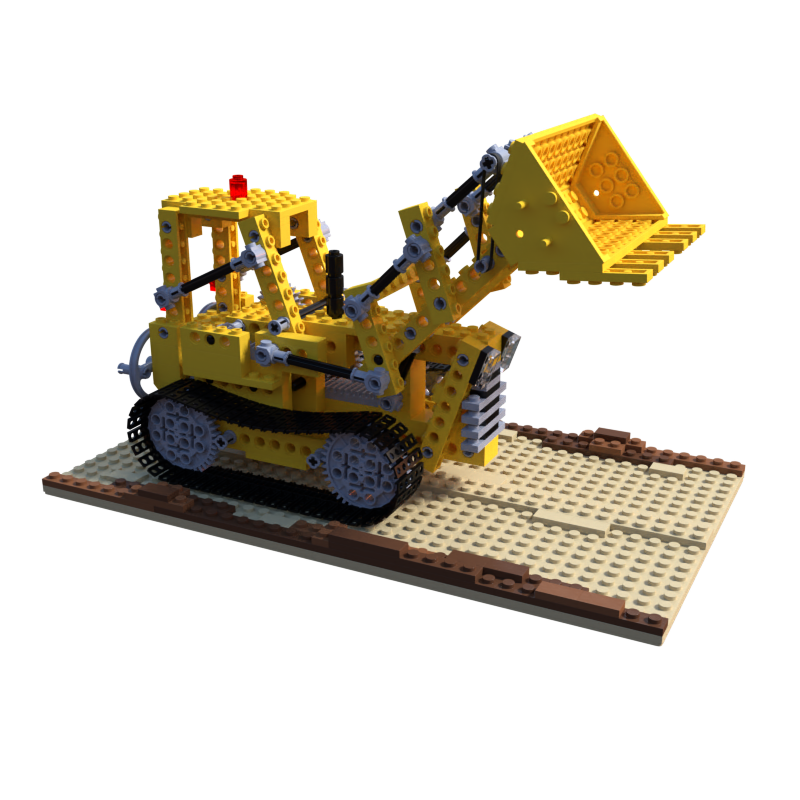
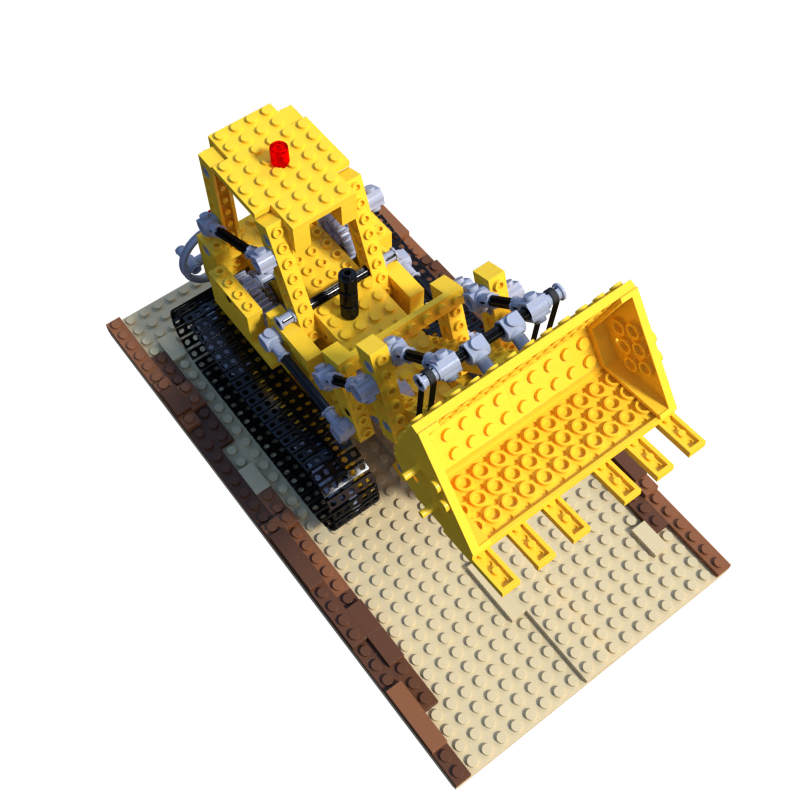
一、数据准备
文件夹应按如下层级组织:
E:\rootpath├─created│ └─sparse│ +── cameras.txt│ +── images.txt│ +── points3D.txt├─dense├─images│ +── r_0.png│ +── r_1.png│ +── ...├─model└─triangulated└─sparse+── transforms_train.json +── blender_camera2colmap.py +── transform_colmap_camera.py
其中 created/sparse 文件夹下的 cameras.txt 对应我们指定的相机内参,images.txt 对应每张图片的相机外参信息,points3D.txt 对应稠密重建需要用到的稀疏点云。 dense 文件夹下保存colmap稠密重建结果,images 文件夹下存放输入的图片,也就是NeRF的训练视图, model 文件夹下存放colmap导出的稀疏重建结果,triangulated/sparse 文件夹下保存colmap稀疏重建结果,transforms_train.json 是NeRF blender数据集提供的真实的相机内外参数据,最后两个python文件是后面要用到的脚本。
二、从blender数据构造colmap数据集
这一步是为了读取NeRF的blender相机参数数据,转换成colmap可以使用的数据格式。blender相机参数采用右手坐标系,相机的位姿用于从相机坐标系向世界坐标系转换,以旋转矩阵 R 和平移向量 T 的格式给出;colmap相机参数采用opecv格式的坐标系,相机的位姿用于从世界坐标系向相机坐标系转换,以四元数 Quat 和平移向量 T 的格式给出,因此需要手动进行转换以获得cameras.txt ,images.txt 和 points3D.txt。三个文件各自的格式规定如下:
cameras.txt
# Camera list with one line of data per camera:
# CAMERA_ID, MODEL, WIDTH, HEIGHT, PARAMS[fx,fy,cx,cy]
# Number of cameras: 1
1 PINHOLE 800 800 1111.1110311937682 1111.1110311937682 400.0 400.0
images.txt
# Image list with two lines of data per image:
# IMAGE_ID, QW, QX, QY, QZ, TX, TY, TZ, CAMERA_ID, NAME
# POINTS2D[] as (X, Y, POINT3D_ID)
# Number of images: 100, mean observations per image: 100
1 0.0041 0.0056 -0.8064 0.5919 6.3306e-10 -5.1536e-08 4.0311 1 r_0.png
# Make sure every other line is left empty
2 0.1086 0.15132 -0.7980 0.5729 4.9764e-08 -2.7316e-08 4.0311 1 r_1.png3 0.5450 0.6810 -0.3817 0.3055 -1.2894e-07 -2.6036e-08 4.0311 1 r_10.pngpoints3D.txt
# 3D point list with one line of data per point:
# POINT3D_ID, X, Y, Z, R, G, B, ERROR, TRACK[] as (IMAGE_ID, POINT2D_IDX)
# Number of points: 12888, mean track length: 4.5869025450031033
944 -0.3789 0.5152 -0.1104 58 65 88 0.0692 13 521 49 537 3 446
1054 -0.1167 -0.3606 -0.0849 180 176 187 0.2641 13 1285 49 1440 3 1307
5 -0.1028 -0.4174 0.8981 23 18 7 0.0205 65 33 1 23
完成该转换的 blender_camera2colmap.py 脚本内容如下:
# 该脚本是为了从blender数据集的tranforms_train.json构造colmap的相机参数和图片参数数据集,以便使用指定相机视角的colmap进行重建。
# 参考:https://www.cnblogs.com/li-minghao/p/11865794.html
# 运行方法:python blender_camera2colmap.pyimport numpy as np
import json
import os
import imageio
import math# TODO: change image size
H = 800
W = 800blender2opencv = np.array([[1, 0, 0, 0], [0, -1, 0, 0], [0, 0, -1, 0], [0, 0, 0, 1]])
# 注意:最后输出的图片名字要按自然字典序排列,例:0, 1, 100, 101, 102, 2, 3...因为colmap内部是这么排序的
fnames = list(sorted(os.listdir('images')))
fname2pose = {}with open('transforms_train.json', 'r') as f:meta = json.load(f)fx = 0.5 * W / np.tan(0.5 * meta['camera_angle_x']) # original focal length
if 'camera_angle_y' in meta:fy = 0.5 * H / np.tan(0.5 * meta['camera_angle_y']) # original focal length
else:fy = fx
if 'cx' in meta:cx, cy = meta['cx'], meta['cy']
else:cx = 0.5 * Wcy = 0.5 * H
with open('created/sparse/cameras.txt', 'w') as f:f.write(f'1 PINHOLE {W} {H} {fx} {fy} {cx} {cy}')idx = 1for frame in meta['frames']:fname = frame['file_path'].split('/')[-1]if not (fname.endswith('.png') or fname.endswith('.jpg')):fname += '.png'# blend到opencv的转换:y轴和z轴方向翻转pose = np.array(frame['transform_matrix']) @ blender2opencvfname2pose.update({fname: pose})with open('created/sparse/images.txt', 'w') as f:for fname in fnames:pose = fname2pose[fname]# 参考https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_44120025/article/details/124604229:colmap中相机坐标系和世界坐标系是相反的# blender中:world = R * camera + T; colmap中:camera = R * world + T# 因此转换公式为# R’ = R^-1# t’ = -R^-1 * tR = np.linalg.inv(pose[:3, :3])T = -np.matmul(R, pose[:3, 3])q0 = 0.5 * math.sqrt(1 + R[0, 0] + R[1, 1] + R[2, 2])q1 = (R[2, 1] - R[1, 2]) / (4 * q0)q2 = (R[0, 2] - R[2, 0]) / (4 * q0)q3 = (R[1, 0] - R[0, 1]) / (4 * q0)f.write(f'{idx} {q0} {q1} {q2} {q3} {T[0]} {T[1]} {T[2]} 1 {fname}\n\n')idx += 1with open('created/sparse/points3D.txt', 'w') as f:f.write('')直接在根目录 rootpath 下运行
python blender_camera2colmap.py
即可获得 created/sparse 文件下所需的内容。
三、COLMAP重建流程
1. 抽取图像特征
colmap feature_extractor --database_path database.db --image_path images
终端输出示例如下:
==============================================================================
Feature extraction
==============================================================================Processed file [1/100]Name: r_0.pngDimensions: 800 x 800Camera: #1 - SIMPLE_RADIALFocal Length: 960.00pxFeatures: 2403
Processed file [2/100]Name: r_1.pngDimensions: 800 x 800Camera: #2 - SIMPLE_RADIALFocal Length: 960.00pxFeatures: 2865
Processed file [3/100]
..........
..........
Elapsed time: 0.075 [minutes]
2. 导入指定相机内参
前一步colmap获得了估计的相机内参,但我们有真实的相机内参,所以将colmap估出来的相机内参提环成我们自己的,使用的 transform_colmap_camera.py 脚本内容如下:
# This script is based on an original implementation by True Price.
# 用于手动从database.db中读取相机参数并更改为cameras.txt中的相机参数
# 参考:https://www.cnblogs.com/li-minghao/p/11865794.htmlimport sys
import numpy as np
import sqlite3IS_PYTHON3 = sys.version_info[0] >= 3
MAX_IMAGE_ID = 2**31 - 1CREATE_CAMERAS_TABLE = """CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS cameras (camera_id INTEGER PRIMARY KEY AUTOINCREMENT NOT NULL,model INTEGER NOT NULL,width INTEGER NOT NULL,height INTEGER NOT NULL,params BLOB,prior_focal_length INTEGER NOT NULL)"""CREATE_DESCRIPTORS_TABLE = """CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS descriptors (image_id INTEGER PRIMARY KEY NOT NULL,rows INTEGER NOT NULL,cols INTEGER NOT NULL,data BLOB,FOREIGN KEY(image_id) REFERENCES images(image_id) ON DELETE CASCADE)"""CREATE_IMAGES_TABLE = """CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS images (image_id INTEGER PRIMARY KEY AUTOINCREMENT NOT NULL,name TEXT NOT NULL UNIQUE,camera_id INTEGER NOT NULL,prior_qw REAL,prior_qx REAL,prior_qy REAL,prior_qz REAL,prior_tx REAL,prior_ty REAL,prior_tz REAL,CONSTRAINT image_id_check CHECK(image_id >= 0 and image_id < {}),FOREIGN KEY(camera_id) REFERENCES cameras(camera_id))
""".format(MAX_IMAGE_ID)CREATE_TWO_VIEW_GEOMETRIES_TABLE = """
CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS two_view_geometries (pair_id INTEGER PRIMARY KEY NOT NULL,rows INTEGER NOT NULL,cols INTEGER NOT NULL,data BLOB,config INTEGER NOT NULL,F BLOB,E BLOB,H BLOB,qvec BLOB,tvec BLOB)
"""CREATE_KEYPOINTS_TABLE = """CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS keypoints (image_id INTEGER PRIMARY KEY NOT NULL,rows INTEGER NOT NULL,cols INTEGER NOT NULL,data BLOB,FOREIGN KEY(image_id) REFERENCES images(image_id) ON DELETE CASCADE)
"""CREATE_MATCHES_TABLE = """CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS matches (pair_id INTEGER PRIMARY KEY NOT NULL,rows INTEGER NOT NULL,cols INTEGER NOT NULL,data BLOB)"""CREATE_NAME_INDEX = \"CREATE UNIQUE INDEX IF NOT EXISTS index_name ON images(name)"CREATE_ALL = "; ".join([CREATE_CAMERAS_TABLE,CREATE_IMAGES_TABLE,CREATE_KEYPOINTS_TABLE,CREATE_DESCRIPTORS_TABLE,CREATE_MATCHES_TABLE,CREATE_TWO_VIEW_GEOMETRIES_TABLE,CREATE_NAME_INDEX
])def array_to_blob(array):if IS_PYTHON3:return array.tostring()else:return np.getbuffer(array)def blob_to_array(blob, dtype, shape=(-1,)):if IS_PYTHON3:return np.fromstring(blob, dtype=dtype).reshape(*shape)else:return np.frombuffer(blob, dtype=dtype).reshape(*shape)class COLMAPDatabase(sqlite3.Connection):@staticmethoddef connect(database_path):return sqlite3.connect(database_path, factory=COLMAPDatabase)def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):super(COLMAPDatabase, self).__init__(*args, **kwargs)self.create_tables = lambda: self.executescript(CREATE_ALL)self.create_cameras_table = \lambda: self.executescript(CREATE_CAMERAS_TABLE)self.create_descriptors_table = \lambda: self.executescript(CREATE_DESCRIPTORS_TABLE)self.create_images_table = \lambda: self.executescript(CREATE_IMAGES_TABLE)self.create_two_view_geometries_table = \lambda: self.executescript(CREATE_TWO_VIEW_GEOMETRIES_TABLE)self.create_keypoints_table = \lambda: self.executescript(CREATE_KEYPOINTS_TABLE)self.create_matches_table = \lambda: self.executescript(CREATE_MATCHES_TABLE)self.create_name_index = lambda: self.executescript(CREATE_NAME_INDEX)def update_camera(self, model, width, height, params, camera_id):params = np.asarray(params, np.float64)cursor = self.execute("UPDATE cameras SET model=?, width=?, height=?, params=?, prior_focal_length=1 WHERE camera_id=?",(model, width, height, array_to_blob(params),camera_id))return cursor.lastrowiddef camTodatabase(txtfile):import osimport argparsecamModelDict = {'SIMPLE_PINHOLE': 0,'PINHOLE': 1,'SIMPLE_RADIAL': 2,'RADIAL': 3,'OPENCV': 4,'FULL_OPENCV': 5,'SIMPLE_RADIAL_FISHEYE': 6,'RADIAL_FISHEYE': 7,'OPENCV_FISHEYE': 8,'FOV': 9,'THIN_PRISM_FISHEYE': 10}parser = argparse.ArgumentParser()parser.add_argument("--database_path", default="database.db")args = parser.parse_args()if os.path.exists(args.database_path)==False:print("ERROR: database path dosen't exist -- please check database.db.")return# Open the database.db = COLMAPDatabase.connect(args.database_path)idList=list()modelList=list()widthList=list()heightList=list()paramsList=list()# Update real cameras from .txtwith open(txtfile, "r") as cam:lines = cam.readlines()for i in range(0,len(lines),1):if lines[i][0]!='#':strLists = lines[i].split()cameraId=int(strLists[0])cameraModel=camModelDict[strLists[1]] #SelectCameraModelwidth=int(strLists[2])height=int(strLists[3])paramstr=np.array(strLists[4:12])params = paramstr.astype(np.float64)idList.append(cameraId)modelList.append(cameraModel)widthList.append(width)heightList.append(height)paramsList.append(params)camera_id = db.update_camera(cameraModel, width, height, params, cameraId)# Commit the data to the file.db.commit()# Read and check cameras.rows = db.execute("SELECT * FROM cameras")for i in range(0,len(idList),1):camera_id, model, width, height, params, prior = next(rows)params = blob_to_array(params, np.float64)assert camera_id == idList[i]assert model == modelList[i] and width == widthList[i] and height == heightList[i]assert np.allclose(params, paramsList[i])# Close database.db.db.close()if __name__ == "__main__":camTodatabase("created/sparse/cameras.txt")
直接在根目录 rootpath 下运行
python transform_colmap_camera.py
即可完成database.db中相机内参的替换。
3. 特征匹配
colmap exhaustive_matcher --database_path database.db
终端输出示例如下:
==============================================================================
Exhaustive feature matching
==============================================================================Matching block [1/2, 1/2] in 5.688s
Matching block [1/2, 2/2] in 5.234s
Matching block [2/2, 1/2] in 5.609s
Matching block [2/2, 2/2] in 5.165s
Elapsed time: 0.364 [minutes]
4. 三角测量
colmap point_triangulator --database_path database.db --image_path images --input_path created/sparse --output_path triangulated/sparse
终端输出示例如下:
==============================================================================
Loading model
==============================================================================
==============================================================================
Loading database
==============================================================================
Loading cameras... 100 in 0.000s
Loading matches... 1330 in 0.003s
Loading images... 100 in 0.012s (connected 100)
Building correspondence graph... in 0.025s (ignored 0)
Elapsed time: 0.001 [minutes]==============================================================================
Triangulating image #1 (0)
===============================================================================> Image sees 0 / 465 points=> Triangulated 284 points
..........
..........
Bundle adjustment report
------------------------Residuals : 118254Parameters : 38718Iterations : 3Time : 0.102123 [s]
Initial cost : 0.469918 [px]Final cost : 0.469793 [px]Termination : Convergence=> Completed observations: 2=> Merged observations: 0=> Filtered observations: 1=> Changed observations: 0.000051
==============================================================================
Extracting colors
==============================================================================5. 使用指定相机参数进行稠密重建
运行
colmap gui
在COLMAP图形界面中选择 “File”->“Import Model” ,可以把triangulated/sparse下的内容导入进来看相机视角和稀疏点云重建的如何,以此确定前面的步骤是否执行正确。如果提示“找不到project.ini”可以忽略。我的效果如下:
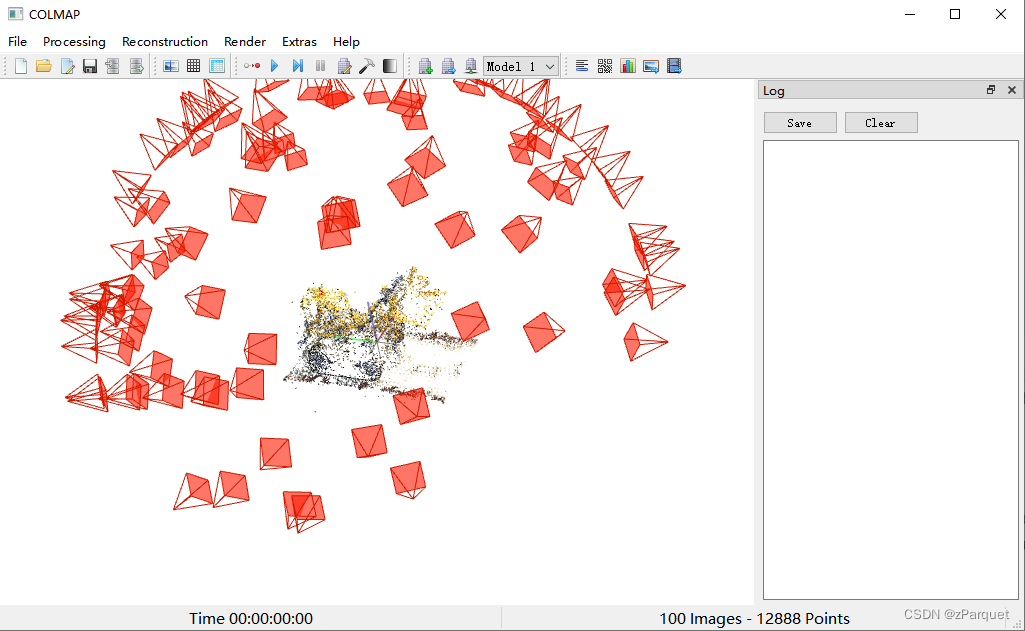
【注意:接下来这一步很重要】
然后选择 “File”->“Export model as txt”,把结果保存在 model 文件夹下,这里包括了colmap稀疏重建估出来的相机内外参和稀疏点云数据。我们把 model/points3D.txt 文件复制到 created/sparse 文件夹下,覆盖掉原来空的 points3D.txt 文件,这是接下来稠密重建需要用到的稀疏点云数据。
接下来运行
colmap image_undistorter --image_path images --input_path created/sparse --output_path dense
终端输出示例如下:
==============================================================================
Reading reconstruction
===============================================================================> Reconstruction with 100 images and 12906 points==============================================================================
Image undistortion
==============================================================================Undistorted image found; copying to location: dense\images\r_0.pngUndistorted image found; copying to location: dense\images\r_10.png
Undistorting image [1/100]
Undistorted image found; copying to location: dense\images\r_13.png
Undistorted image found; copying to location: dense\images\r_14.png
..........
..........
Writing reconstruction...
Writing configuration...
Writing scripts...
Elapsed time: 0.002 [minutes]
6. 立体匹配
colmap patch_match_stereo --workspace_path dense
这一步是最耗时的,如果图片多的话,会花费长达几个小时的时间。在lego数据集上大概花费一个小时。终端输出示例如下:
Reading workspace...
Reading configuration...
Configuration has 100 problems...==============================================================================
Processing view 1 / 100 for r_0.png
==============================================================================Reading inputs...PatchMatch::Problem
-------------------
ref_image_idx: 0
src_image_idxs: 20 36 80 64 37 61 1 73 58 32 47 19 3 46 57 4 77 53 28 33PatchMatchOptions
-----------------
max_image_size: -1
gpu_index: 0
depth_min: 2.2507
depth_max: 6.0306
window_radius: 5
window_step: 1
sigma_spatial: 5
sigma_color: 0.2
num_samples: 15
ncc_sigma: 0.6
min_triangulation_angle: 1
incident_angle_sigma: 0.9
num_iterations: 5
geom_consistency: 0
geom_consistency_regularizer: 0.3
geom_consistency_max_cost: 3
filter: 0
filter_min_ncc: 0.1
filter_min_triangulation_angle: 3
filter_min_num_consistent: 2
filter_geom_consistency_max_cost: 1
write_consistency_graph: 0
allow_missing_files: 0PatchMatch::Run
---------------
Initialization: 0.1131sSweep 1: 0.4373sSweep 2: 0.3998sSweep 3: 0.4118sSweep 4: 0.3944s
Iteration 1: 1.6447sSweep 1: 0.4101sSweep 2: 0.3992s
..........
..........
Writing geometric output for r_99.png
Elapsed time: 61.006 [minutes]
7. 稠密点云融合
colmap stereo_fusion --workspace_path dense --output_path dense/fused.ply
终端输出示例如下:
StereoFusion::Options
---------------------
mask_path:
max_image_size: -1
min_num_pixels: 5
max_num_pixels: 10000
max_traversal_depth: 100
max_reproj_error: 2
max_depth_error: 0.01
max_normal_error: 10
check_num_images: 50
use_cache: 0
cache_size: 32
bbox_min: -3.40282e+38 -3.40282e+38 -3.40282e+38
bbox_max: 3.40282e+38 3.40282e+38 3.40282e+38Reading workspace...
Loading workspace data with 8 threads...
Elapsed time: 0.021 [minutes]
Reading configuration...
Starting fusion with 8 threads
Fusing image [1/100] with index 0 in 2.167s (36527 points)
Fusing image [2/100] with index 36 in 0.655s (50311 points)
Fusing image [3/100] with index 61 in 0.568s (61807 points)
..........
..........
Number of fused points: 493937
Elapsed time: 0.399 [minutes]
Writing output: dense/fused.ply
8. 网格重建
这最后一步COLMAP命令行模式下使用起来比较复杂,建议在meshlab软件中操作。首先用meshlab打开 fused.ply:
选择 “Filters”->“Remeshing, Simplification and Reconstruction”->“Surface Reconstruction: Screened Poisson”,参数可以自行调节。
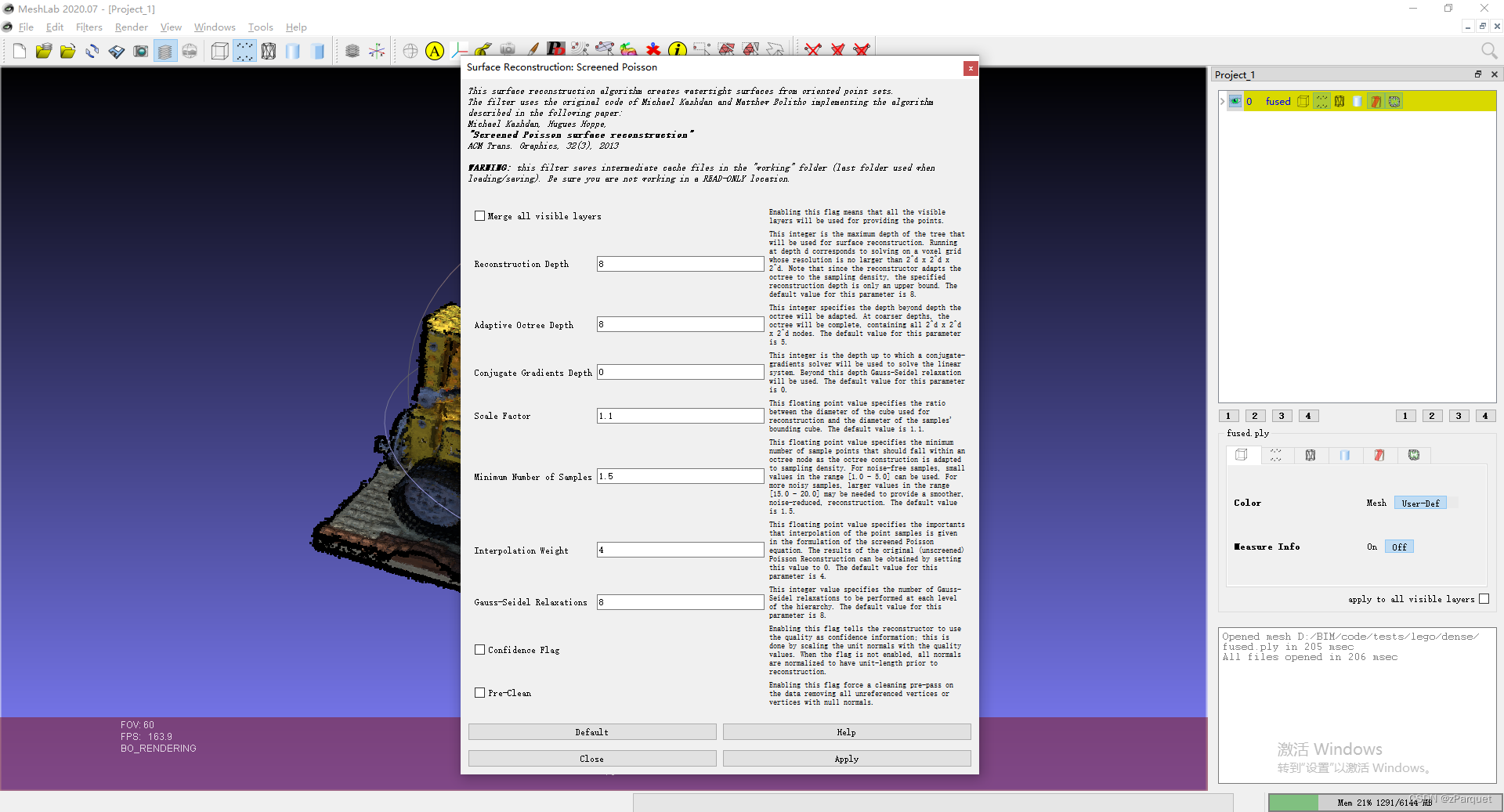
这里建议将 Adaptive Octree Depth 调为和 Reconstruction Depth 一致。该数值为重建网格的分辨率,设置为 8 8 8即为 25 6 3 256^3 2563的分辨率。点击 **“Apply”**开始重建,在meshlab中观察重建好的mesh效果如下:
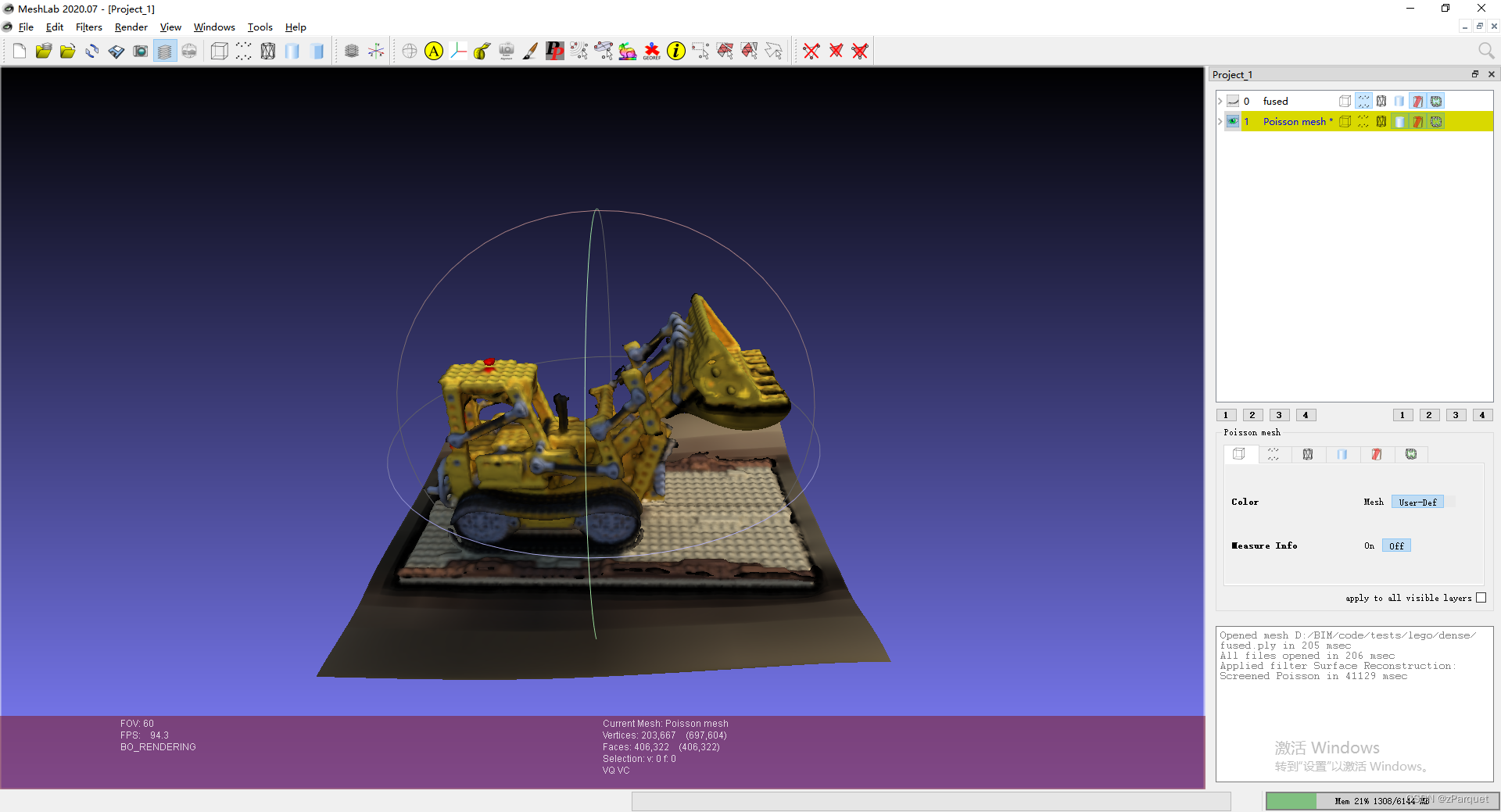
之后选择 “File”->“Export Mesh” 保存重建好的mesh即可。
总结
COLMAP的重建流程比较复杂,最后总结一下所有用到的命令:
0. 构造数据集准备好images里的图片和对应的相机参数文件transforms_train.json,然后
python blender_camera2colmap.py1. 抽取图像特征
colmap feature_extractor --database_path database.db --image_path images2. 自动导入指定相机内参python transform_colmap_camera.py3. 特征匹配colmap exhaustive_matcher --database_path database.db4. 三角测量colmap point_triangulator --database_path database.db --image_path images --input_path created/sparse --output_path triangulated/sparse5. 使用指定相机参数进行稠密重建先在 colmap gui 中导出points3D.txt覆盖到created/sparse里,然后
colmap image_undistorter --image_path images --input_path created/sparse --output_path dense6. 立体匹配colmap patch_match_stereo --workspace_path dense7. 稠密点云融合colmap stereo_fusion --workspace_path dense --output_path dense/fused.ply8. 网格重建在meshlab使用泊松重建这篇关于COLMAP利用已知相机内外参重建NeRF的blender模型的文章就介绍到这儿,希望我们推荐的文章对编程师们有所帮助!








