本文主要是介绍2D碰撞优化 四叉树碰撞检测算法,希望对大家解决编程问题提供一定的参考价值,需要的开发者们随着小编来一起学习吧!
最近公司的小游戏项目贪吃蛇大作战出现了一些优化问题,当游戏玩到后期蛇会变得很长很长,食物也越来越多,游戏就会变得很卡,因为蛇的碰撞使用cocos creator中自带的Collider去检测食物和蛇身体,随着游戏的进行就造成了碰撞体越来越多,变得卡顿,查阅了一些资料,了解到了四叉树碰撞检测算法,所以我将游戏整体的检测进行了一下优化。
代码参考地址 https://github.com/timohausmann/quadtree-js
首先研究一下四叉树算法的原理
QuadTree四叉树顾名思义就是树状的数据结构,其每个节点有四个孩子节点,可将二维平面递归分割子区域。QuadTree常用于空间数据库索引,3D的椎体可见区域裁剪,甚至图片分析处理。QuadTree最常被游戏领域使用到的碰撞检测。采用QuadTree算法将大大减少需要测试碰撞的次数,从而提高游戏刷新性能。
1.就是把一块2d的区域,等分成四个象限
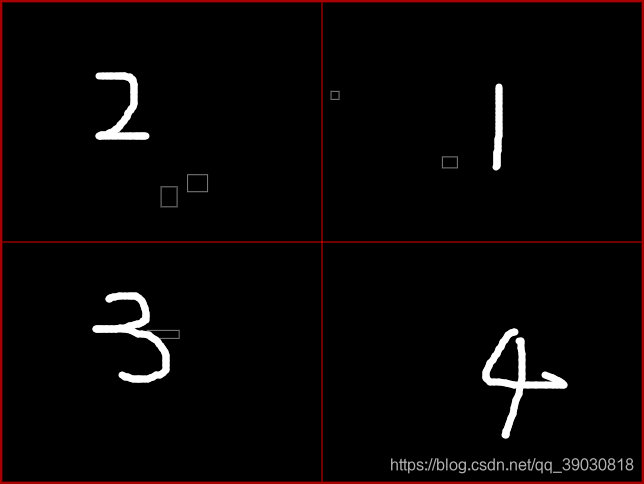
2.当更多的对象被添加到四叉树里时,它们最终会被分为四个子节点。将完全处于某一个象限的物体存储在该象限对应的子节点下,当然,也存在跨越多个象限的物体,我们将它们存在父节点中。如果某个象限内的物体的数量过多,它会同样会分裂成四个子象限,以此类推:

3.上图中右下角区域当蛇(白块表示)处于当前位置,会判断此区域内蛇的矩形所在象限的食物(绿块表示),提取出当前可计算的食物(绿块),进行计算,其他区域的食物(白框格子)不计算。这样就大大减少了计算量
代码如下:
class Quadtree {/** Quadtree Constructor* @param Object bounds bounds of the node { x, y, width, height }* @param Integer max_objects (optional) max objects a node can hold before splitting into 4 subnodes (default: 10)* @param Integer max_levels (optional) total max levels inside root Quadtree (default: 4) * @param Integer level (optional) deepth level, required for subnodes (default: 0)*/constructor (bounds, max_objects, max_levels, level) {this.max_objects = max_objects || 10;this.max_levels = max_levels || 4;this.level = level || 0;this.bounds = bounds;this.objects = [];this.nodes = [];};/** Split the node into 4 subnodes*/split = function() {var nextLevel = this.level + 1,subWidth = this.bounds.width/2,subHeight = this.bounds.height/2,x = this.bounds.x,y = this.bounds.y; //top right nodethis.nodes[0] = new Quadtree({x : x + subWidth, y : y, width : subWidth, height : subHeight}, this.max_objects, this.max_levels, nextLevel);//top left nodethis.nodes[1] = new Quadtree({x : x, y : y, width : subWidth, height : subHeight}, this.max_objects, this.max_levels, nextLevel);//bottom left nodethis.nodes[2] = new Quadtree({x : x, y : y + subHeight, width : subWidth, height : subHeight}, this.max_objects, this.max_levels, nextLevel);//bottom right nodethis.nodes[3] = new Quadtree({x : x + subWidth, y : y + subHeight, width : subWidth, height : subHeight}, this.max_objects, this.max_levels, nextLevel);};/** Determine which node the object belongs to* @param Object pRect bounds of the area to be checked, with x, y, width, height* @return Array an array of indexes of the intersecting subnodes * (0-3 = top-right, top-left, bottom-left, bottom-right / ne, nw, sw, se)*/getIndex = function(pRect) {var indexes = [],verticalMidpoint = this.bounds.x + (this.bounds.width/2),horizontalMidpoint = this.bounds.y + (this.bounds.height/2); var startIsNorth = pRect.y < horizontalMidpoint,startIsWest = pRect.x < verticalMidpoint,endIsEast = pRect.x + pRect.width > verticalMidpoint,endIsSouth = pRect.y + pRect.height > horizontalMidpoint; //top-right quadif(startIsNorth && endIsEast) {indexes.push(0);}//top-left quadif(startIsWest && startIsNorth) {indexes.push(1);}//bottom-left quadif(startIsWest && endIsSouth) {indexes.push(2);}//bottom-right quadif(endIsEast && endIsSouth) {indexes.push(3);}return indexes;};/** Insert the object into the node. If the node* exceeds the capacity, it will split and add all* objects to their corresponding subnodes.* @param Object pRect bounds of the object to be added { x, y, width, height }*/insert = function(pRect) {var i = 0,indexes;//if we have subnodes, call insert on matching subnodesif(this.nodes.length) {indexes = this.getIndex(pRect);for(i=0; i<indexes.length; i++) {this.nodes[indexes[i]].insert(pRect); }return;}//otherwise, store object herethis.objects.push(pRect);//max_objects reachedif(this.objects.length > this.max_objects && this.level < this.max_levels) {//split if we don't already have subnodesif(!this.nodes.length) {this.split();}//add all objects to their corresponding subnodefor(i=0; i<this.objects.length; i++) {indexes = this.getIndex(this.objects[i]);for(var k=0; k<indexes.length; k++) {this.nodes[indexes[k]].insert(this.objects[i]);}}//clean up this nodethis.objects = [];}};/** Return all objects that could collide with the given object* @param Object pRect bounds of the object to be checked { x, y, width, height }* @Return Array array with all detected objects*/retrieve = function(pRect) {var indexes = this.getIndex(pRect),returnObjects = this.objects;//if we have subnodes, retrieve their objectsif(this.nodes.length) {for(var i=0; i<indexes.length; i++) {returnObjects = returnObjects.concat(this.nodes[indexes[i]].retrieve(pRect));}}//remove duplicatesreturnObjects = returnObjects.filter(function(item, index) {return returnObjects.indexOf(item) >= index;});return returnObjects;};/** Clear the quadtree*/clear = function() {this.objects = [];for(var i=0; i < this.nodes.length; i++) {if(this.nodes.length) {this.nodes[i].clear();}}this.nodes = [];};
}使用方法:先创建一个 myFoodTree,再用 insert 方法将所有节点插入到myFoodTree中,通过 retrieve 方法传入蛇头自身的矩形信息,得到相对应的所有食物,在进行计算。
//创建一个quadtree 初始化蛇头的矩形信息
initQuadTree(){this.myFoodTree = new Quadtree({x: 0,y: 0,width: 1136,height: 640});this.snakeHeadRect = {x: 0,y: 0,width: 20,height: 20};this.foodList = [];for(let i = 0; i < 10; i++){this.foodList.push({x : this.random(-1136 / 2,1136 / 2),y : this.random(-1136 / 2,1136 / 2),width : this.random(4, 32),height : this.random(4, 32),})}
},//随机
random: function (min, max) {return Math.floor(Math.random() * (max - min + 1) + min)
},//将所有食物插入
insertFood(){for(let i = 0;i < this.foodList.length;i++){this.myFoodTree.insert({x: foodList[i].x,y: foodList[i].y,width: foodList[i].width,height: foodList[i].height,})}
},//将蛇头的矩形添加参数内 获取可以计算的食物
checkFoodCollision(){var candidates = this.myFoodTree.retrieve(this.snakeHeadRect);//TODO..
},
这篇关于2D碰撞优化 四叉树碰撞检测算法的文章就介绍到这儿,希望我们推荐的文章对编程师们有所帮助!



