本文主要是介绍从APM源码分析GPS、气压计惯导融合,希望对大家解决编程问题提供一定的参考价值,需要的开发者们随着小编来一起学习吧!
最近事多,忙着开源自研飞控,现主要工作基本已经完成,代码最迟下月中旬开放,博客来不及更新,还请各位见谅,后面会抽空多更的咯!!!
自研飞控靓照如下:主控STM32F103RCT6,IMU组合:MPU6050、IST8310(DJI同款磁力计、5883已停产)SPL06_001(歌尔最新高精度气压计),GPS:M8N输出PVT
为方便大家学习,飞控工程支持Keil 、IAR两款编译器,满足不同的使用习惯
支持调试软件有:山外多功能调试助手、APM\Pixhawk\Autoquad原版地面站、ANO地面站等
最新测试视频链接附在本文最后!!!
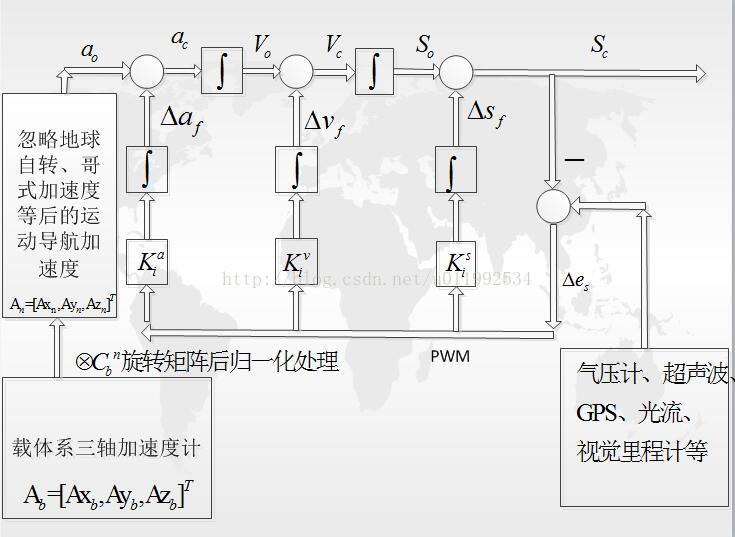
前几篇博客都是讲的无人机惯性导航,气压计、GPS融合问题,算法参考APM的三阶互补滤波方案,也就是经典的回路反馈法。有飞控爱好者和我交流,也想使用该算法,奈何APM整个工程代码量实在太大,新手根本不知道该如何下手,下面我们就直接贴出APM源码里面的AP_InertialNav.c文件出来,逐一分析,相关算法实现步骤。
一、首先解决算法里面三个关键的参数:Ka,Kv,Ks,下面看APM源码里面相关定义:
// update_gains - update gains from time constant (given in seconds)
void AP_InertialNav::update_gains()
{
// X & Y axis time constant
if (_time_constant_xy == 0.0f) {
_k1_xy = _k2_xy = _k3_xy = 0.0f;
}else{
_k1_xy = 3.0f / _time_constant_xy;
_k2_xy = 3.0f / (_time_constant_xy*_time_constant_xy);
_k3_xy = 1.0f / (_time_constant_xy*_time_constant_xy*_time_constant_xy);
}
// Z axis time constant
if (_time_constant_z == 0.0f) {
_k1_z = _k2_z = _k3_z = 0.0f;
}else{
_k1_z = 3.0f / _time_constant_z;
_k2_z = 3.0f / (_time_constant_z*_time_constant_z);
_k3_z = 1.0f / (_time_constant_z*_time_constant_z*_time_constant_z);
}
}
源码里面的_k1为图中Ks,_k2为图中Kv,_k3为图中Ka,代码里面时间常数_time_constant为AP_InertialNav.h里面的宏定义:
#define AP_INTERTIALNAV_TC_XY 2.5f // default time constant for complementary filter's X & Y axis
#define AP_INTERTIALNAV_TC_Z 5.0f // default time constant for complementary filter's Z axis
二、解决第二个问题,惯导观测传感器数据怎么得到
1、气压计相对比较简单,通用的是采用压差法获取相对高度:
// return current scale factor that converts from equivalent to true airspeed
// valid for altitudes up to 10km AMSL
// assumes standard atmosphere lapse rate
float AP_Baro::get_EAS2TAS(void)
{
if ((fabsf(_altitude - _last_altitude_EAS2TAS) < 100.0f) && (_EAS2TAS != 0.0f)) {
// not enough change to require re-calculating
return _EAS2TAS;
}
float tempK = ((float)_ground_temperature) + 273.15f - 0.0065f * _altitude;
_EAS2TAS = safe_sqrt(1.225f / ((float)get_pressure() / (287.26f * tempK)));
_last_altitude_EAS2TAS = _altitude;
return _EAS2TAS;
}
2、GPS利用经纬度得到导航坐标系下相对Home点的正北、正东方向位置偏移量则采用球面投影的方式:
x = (float)(lat - _ahrs.get_home().lat) * LATLON_TO_CM;
y = (float)(lon - _ahrs.get_home().lng) * _lon_to_cm_scaling;
其中:#define LATLON_TO_CM 1.113195f
_lon_to_cm_scaling则根据飞控所处纬度相关,APM为了避免重复计算余弦值,当纬度两次纬度相差0.01度时,此值不更新。
float longitude_scale(Location loc)
{
static int32_t last_lat;
static float scale = 1.0;
//比较两次纬度相差值,避免重复运算余弦函数
if (ABS(last_lat - loc.lat) < 100000) {
// we are within 0.01 degrees (about 1km) of the
// same latitude. We can avoid the cos() and return
// the same scale factor.
return scale;
}
scale = cosf(loc.lat * 1.0e-7f * DEG_TO_RAD);
scale = constrain_float(scale, 0.01f, 1.0f);
last_lat = loc.lat;
return scale;
}
得到的x,y分别表示无人机在导航坐标系下,相对Home点沿着正北、正东方向的位置偏移,单位为CM
3、加速度计得到运动加速度的获取请参考第一篇博客内容:
惯导运动加速度获取
三、结合APM源码,详细说明跟新过程
// update - updates velocities and positions using latest info from ahrs and barometer if new data is available;
void AP_InertialNav::update(float dt)
{
// discard samples where dt is too large
if( dt > 0.1f ) {
return;
}
// decrement ignore error count if required
if (_flags.ignore_error > 0) {
_flags.ignore_error--;
}
// check if new baro readings have arrived and use them to correct vertical accelerometer offsets.
check_baro();
// check if new gps readings have arrived and use them to correct position estimates
check_gps();
Vector3f accel_ef = _ahrs.get_accel_ef();
// remove influence of gravity
accel_ef.z += GRAVITY_MSS;
accel_ef *= 100.0f;
// remove xy if not enabled
if( !_xy_enabled ) {
accel_ef.x = 0.0f;
accel_ef.y = 0.0f;
}
//Convert North-East-Down to North-East-Up
accel_ef.z = -accel_ef.z;
//首先将导航系下正北、正东、天方向上的位置观测误差,旋转机体俯仰与横滚方向上来
// convert ef position error to horizontal body frame
Vector2f position_error_hbf;
position_error_hbf.x = _position_error.x * _ahrs.cos_yaw() + _position_error.y * _ahrs.sin_yaw();
position_error_hbf.y = -_position_error.x * _ahrs.sin_yaw() + _position_error.y * _ahrs.cos_yaw();
//加速度计校正量
float tmp = _k3_xy * dt;
accel_correction_hbf.x += position_error_hbf.x * tmp;
accel_correction_hbf.y += position_error_hbf.y * tmp;
accel_correction_hbf.z += _position_error.z * _k3_z * dt;
//上次速度加校正量
tmp = _k2_xy * dt;
_velocity.x += _position_error.x * tmp;
_velocity.y += _position_error.y * tmp;
_velocity.z += _position_error.z * _k2_z * dt;
//导航坐标系下正北、正东、天方向上位置校正量
tmp = _k1_xy * dt;
_position_correction.x += _position_error.x * tmp;
_position_correction.y += _position_error.y * tmp;
_position_correction.z += _position_error.z * _k1_z * dt;
//将导航系下的沿着载体俯仰、横滚方向的运动加速度计矫正量,旋转到导航坐标系正北、正东方向上
// convert horizontal body frame accel correction to earth frame
Vector2f accel_correction_ef;
accel_correction_ef.x = accel_correction_hbf.x * _ahrs.cos_yaw() - accel_correction_hbf.y * _ahrs.sin_yaw();
accel_correction_ef.y = accel_correction_hbf.x * _ahrs.sin_yaw() + accel_correction_hbf.y * _ahrs.cos_yaw();
//导航坐标系下正北、正东、天方向上,运动的速度增量更新
// calculate velocity increase adding new acceleration from accelerometers
Vector3f velocity_increase;
velocity_increase.x = (accel_ef.x + accel_correction_ef.x) * dt;
velocity_increase.y = (accel_ef.y + accel_correction_ef.y) * dt;
velocity_increase.z = (accel_ef.z + accel_correction_hbf.z) * dt;
//导航坐标系下正北、正东、天方向上,初步位置更新,不包含本次位置校正量
// calculate new estimate of position
_position_base += (_velocity + velocity_increase*0.5) * dt;
//导航坐标系下正北、正东、天方向上,位置校正后更新
// update the corrected position estimate
_position = _position_base + _position_correction;
//导航坐标系下正北、正东、天方向上,速度加增量后更新
// calculate new velocity
_velocity += velocity_increase;
//下面为惯导融合位置缓冲区,用于延时修正处理
// store 3rd order estimate (i.e. estimated vertical position) for future use
_hist_position_estimate_z.push_back(_position_base.z);
/* _histotic_z_counter++;
if (_histotic_z_counter >= 4) {
_histotic_z_counter = 0;
_hist_position_estimate_z.push_back(_position_base.z);
}*/
// store 3rd order estimate (i.e. horizontal position) for future use at 10hz
_historic_xy_counter++;
if( _historic_xy_counter >= AP_INTERTIALNAV_SAVE_POS_AFTER_ITERATIONS ) {
_historic_xy_counter = 0;
_hist_position_estimate_x.push_back(_position_base.x);
_hist_position_estimate_y.push_back(_position_base.y);
}
}
四、延时修正处理,这里仍然看源码即可
观测传感器滞后的主要思想是,由于惯导的主体为加速度计,采样频率与更新实时性要求比较高,而观测传感器(气压计、GPS、超声波、视觉里程计等)更新相对比较慢(或者数据噪声比较大,通常需要低通造成滞后)。在无人机动态条件下,本次采样的得到的带滞后观测量(高度、水平位置)已经不能反映最新状态量(惯导位置),我们认定传感器在通带内的延时时间具有一致性(或者取有效带宽内的平均时延值),即当前观测量只能反映系统N*dt时刻前的状态,所以状态误差(在这里指的是气压计与惯导高度、GPS水平位置与惯导水平位置)采用当前观测量与当前惯导做差的方式不可取,在APM里面采用的处理方式为:将惯导的估计位置用数组存起来,更具气压计和GPS的滞后程度,选取合适的Buffer区与当前观测传感器得到位置做差得到状态误差。
// correct_with_baro - modifies accelerometer offsets using barometer. dt is time since last baro reading
void AP_InertialNav::correct_with_baro(float baro_alt, float dt)
{
static uint8_t first_reads = 0;
static float store_old_alt[8] = {0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0};
static uint8_t now_postion_count = 0;
// discard samples where dt is too large
if( dt > 0.5f ) {
return;
}
// discard first 10 reads but perform some initialisation
if( first_reads <= 10 ) {
set_altitude(baro_alt);
first_reads++;
}
// sanity check the baro position. Relies on the main code calling Baro_Glitch::check_alt() immediatley after a baro update
if (_baro_glitch.glitching()) {
// failed sanity check so degrate position_error to 10% over 2 seconds (assumes 10hz update rate)
_position_error.z *= 0.89715f;
}else{
// if our internal baro glitching flag (from previous iteration) is true we have just recovered from a glitch
// reset the inertial nav alt to baro alt
if (_flags.baro_glitching) {
set_altitude(baro_alt);
_position_error.z = 0.0f;
}else{
// 3rd order samples (i.e. position from baro) are delayed by 150ms (15 iterations at 100hz)
// so we should calculate error using historical estimates
float hist_position_base_z;
if (_hist_position_estimate_z.is_full()) {
hist_position_base_z = _hist_position_estimate_z.front();
} else {
hist_position_base_z = _position_base.z;
}
//**************************//
_params.y = hist_position_base_z;
// hist_position_base_z = _position_base.z;
// calculate error in position from baro with our estimate
_position_error.z = baro_alt - (hist_position_base_z + _position_correction.z);
//*************************************//
/* _position_error.z = baro_alt - store_old_alt[now_postion_count];
store_old_alt[now_postion_count] = hist_position_base_z + _position_correction.z;
now_postion_count++;
if (now_postion_count >= 4) now_postion_count = 0;*/
}
}
// update our internal record of glitching flag so that we can notice a change
_flags.baro_glitching = _baro_glitch.glitching();
}
// correct_with_gps - modifies accelerometer offsets using gps
void AP_InertialNav::correct_with_gps(uint32_t now, int32_t lon, int32_t lat)
{
float dt,x,y;
float hist_position_base_x, hist_position_base_y;
// calculate time since last gps reading
dt = (float)(now - _gps_last_update) * 0.001f;
// update last gps update time
_gps_last_update = now;
// discard samples where dt is too large
if( dt > 1.0f || dt == 0.0f || !_xy_enabled) {
return;
}
// calculate distance from base location
x = (float)(lat - _ahrs.get_home().lat) * LATLON_TO_CM;
y = (float)(lon - _ahrs.get_home().lng) * _lon_to_cm_scaling;
// sanity check the gps position. Relies on the main code calling GPS_Glitch::check_position() immediatley after a GPS update
if (_glitch_detector.glitching()) {
// failed sanity check so degrate position_error to 10% over 2 seconds (assumes 5hz update rate)
_position_error.x *= 0.7943f;
_position_error.y *= 0.7943f;
}else{
// if our internal glitching flag (from previous iteration) is true we have just recovered from a glitch
// reset the inertial nav position and velocity to gps values
if (_flags.gps_glitching) {
set_position_xy(x,y);
_position_error.x = 0.0f;
_position_error.y = 0.0f;
}else{
// ublox gps positions are delayed by 400ms
// we store historical position at 10hz so 4 iterations ago
if( _hist_position_estimate_x.is_full()) {
hist_position_base_x = _hist_position_estimate_x.front();
hist_position_base_y = _hist_position_estimate_y.front();
}else{
hist_position_base_x = _position_base.x;
hist_position_base_y = _position_base.y;
}
// calculate error in position from gps with our historical estimate
_position_error.x = x - (hist_position_base_x + _position_correction.x);
_position_error.y = y - (hist_position_base_y + _position_correction.y);
}
}
// update our internal record of glitching flag so that we can notice a change
_flags.gps_glitching = _glitch_detector.glitching();
}
很明显可以发现:
// ublox gps positions are delayed by 400ms
// 3rd order samples (i.e. position from baro) are delayed by 150ms (15 iterations at 100hz)
// so we should calculate error using historical estimates
关于是否使用,延时修正数据波形对比间上篇博客,链接如下:
四旋翼惯导融合之观测传感器滞后问题汇总与巴特沃斯低通滤波器设计(气压计MS5611、GPS模块M8N、超声波、PX4FLOW等)
下面给出个人飞控参考这部分的代码:
#define TIME_CONTANST_XY 2.5f
#define K_ACC_XY (1.0f / (TIME_CONTANST_XY * TIME_CONTANST_XY * TIME_CONTANST_XY))
#define K_VEL_XY (3.0f / (TIME_CONTANST_XY * TIME_CONTANST_XY))
#define K_POS_XY (3.0f / TIME_CONTANST_XY)
float X_Delta=0,Y_Delta=0;
uint16_t GPS_Save_Period_Cnt=0;
uint16_t GPS_SINS_Delay_Cnt=4;//200ms
Testime SINS_Horizontal_Delta;
void Strapdown_INS_Horizontal()
{
uint16 Cnt=0;
GPSData_Sort();//获取相对home的水平偏移
GPS_Save_Period_Cnt++;
if(GPS_Save_Period_Cnt>=10)//50ms
{
for(Cnt=Num-1;Cnt>0;Cnt--)//100ms滑动一次
{
NamelessQuad.Pos_History[_PITCH][Cnt]=NamelessQuad.Pos_History[_PITCH][Cnt-1];
NamelessQuad.Pos_History[_ROLL][Cnt]=NamelessQuad.Pos_History[_ROLL][Cnt-1];
}
NamelessQuad.Pos_History[_PITCH][0]=NamelessQuad.Position[_PITCH];
NamelessQuad.Pos_History[_ROLL][0]=NamelessQuad.Position[_ROLL];
GPS_Save_Period_Cnt=0;
}
//GPS导航坐标系下,正北、正东方向位置偏移与SINS估计量的差,单位cm
X_Delta=Earth_Frame_To_XYZ.E-NamelessQuad.Pos_History[_PITCH][GPS_SINS_Delay_Cnt];
Y_Delta=Earth_Frame_To_XYZ.N-NamelessQuad.Pos_History[_ROLL][GPS_SINS_Delay_Cnt];
acc_correction[_PITCH] += X_Delta* K_ACC_XY*CNTLCYCLE;//加速度矫正量
acc_correction[_ROLL] += Y_Delta* K_ACC_XY*CNTLCYCLE;//加速度矫正量
vel_correction[_PITCH] += X_Delta* K_VEL_XY*CNTLCYCLE;//速度矫正量
vel_correction[_ROLL] += Y_Delta* K_VEL_XY*CNTLCYCLE;//速度矫正量
pos_correction[_PITCH] += X_Delta* K_POS_XY*CNTLCYCLE;//位置矫正量
pos_correction[_ROLL] += Y_Delta* K_POS_XY*CNTLCYCLE;//位置矫正量
/*************************************************************/
//水平运动加速度计校正
NamelessQuad.Acceleration[_PITCH]=Origion_NamelessQuad.Acceleration[_PITCH]+acc_correction[_PITCH];
//速度增量矫正后更新,用于更新位置
SpeedDealt[_PITCH]=NamelessQuad.Acceleration[_PITCH]*CNTLCYCLE;
//原始位置更新
Origion_NamelessQuad.Position[_PITCH]+=(NamelessQuad.Speed[_PITCH]+0.5*SpeedDealt[_PITCH])*CNTLCYCLE;
//位置矫正后更新
NamelessQuad.Position[_PITCH]=Origion_NamelessQuad.Position[_PITCH]+pos_correction[_PITCH];
//原始速度更新
Origion_NamelessQuad.Speed[_PITCH]+=SpeedDealt[_PITCH];
//速度矫正后更新
NamelessQuad.Speed[_PITCH]=Origion_NamelessQuad.Speed[_PITCH]+vel_correction[_PITCH];
/*************************************************************/
//水平运动加速度计校正
NamelessQuad.Acceleration[_ROLL]=Origion_NamelessQuad.Acceleration[_ROLL]+acc_correction[_ROLL];
//速度增量矫正后更新,用于更新位置
SpeedDealt[_ROLL]=NamelessQuad.Acceleration[_ROLL]*CNTLCYCLE;
//原始位置更新
Origion_NamelessQuad.Position[_ROLL]+=(NamelessQuad.Speed[_ROLL]+0.5*SpeedDealt[_ROLL])*CNTLCYCLE;
//位置矫正后更新
NamelessQuad.Position[_ROLL]=Origion_NamelessQuad.Position[_ROLL]+pos_correction[_ROLL];
//原始速度更新
Origion_NamelessQuad.Speed[_ROLL]+=SpeedDealt[_ROLL];
//速度矫正后更新
NamelessQuad.Speed[_ROLL]=Origion_NamelessQuad.Speed[_ROLL]+vel_correction[_ROLL];
}
void Strapdown_INS_Reset(SINS *Ins,uint8_t Axis,float Pos_Target,float Vel_Target)
{
uint16_t Cnt=0;
Ins->Position[Axis]=Pos_Target;//位置重置
Ins->Speed[Axis]=Vel_Target;//速度重置
Ins->Acceleration[Axis]=0.0f;//加速度清零
Ins->Acce_Bias[Axis]=0.0f;
for(Cnt=Num-1;Cnt>0;Cnt--)//历史位置值,全部装载为当前观测值
{
Ins->Pos_History[Axis][Cnt]=Pos_Target;
}
Ins->Pos_History[Axis][0]=Pos_Target;
for(Cnt=Num-1;Cnt>0;Cnt--)//历史速度值,全部装载为当前观测值
{
Ins->Vel_History[Axis][Cnt]=Vel_Target;
}
Ins->Vel_History[Axis][0]=Vel_Target;
pos_correction[Axis]=0;//清空惯导融合量
acc_correction[Axis]=0;
vel_correction[Axis]=0;
}
个人飞控开源前测试视频,总共有三个:
个人飞控开源前综合测试
个人飞控开源前测试(定钉子)
个人飞控开源前测试(大风定点)
博客会陆续更新,个人主页有联系方式,欢迎大家一起交流,共同进步!!!
这篇关于从APM源码分析GPS、气压计惯导融合的文章就介绍到这儿,希望我们推荐的文章对编程师们有所帮助!