本文主要是介绍【CGAL】圆柱体检测结果后处理,希望对大家解决编程问题提供一定的参考价值,需要的开发者们随着小编来一起学习吧!
文章目录
- 文章说明
- 算法思路
- 代码展示
- 结果展示
文章说明
这篇文章主要介绍,对使用CGAL中的 Region Growing 算法爬取圆柱体的结果进行后处理,以获取位置、轴向量、半径都较为合理的单个圆柱体。
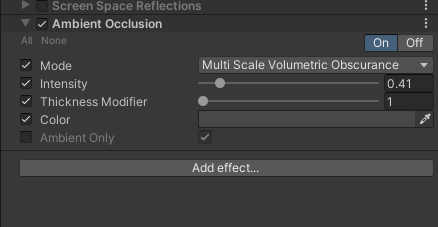
在之前的一篇文章中,使用了open3D生成的标准圆柱体测试了爬取圆柱的代码,结果并不好。结果中标准圆柱体被分了好几部分,也就是说,算法检测到了多个圆柱体,但实际上只有一个。其原因是,CGAL中圆柱体检测只是检测圆柱体的侧面,并不包含上下两个底面。而生成的标准圆柱体是带底面的,这对算法造成了干扰,导致结果不准确。
所以,我基于算法得到的结果,自己写了筛选并合并圆柱体的代码,以得到与真实圆柱体相近的圆柱体及其参数。
用途
这个可以用到物体参数化方面,当我们得到了真实世界类似圆柱体的三维模型,想要将它进行参数化,就可以使用检测圆柱+后处理的方法,来得到模型的参数。
算法思路
1、读取圆柱体结果,包括每个圆柱包含的点个数,半径、中心、轴方向,存储在自定义结构体中。
struct Cylinder_Param {uint32_t m_points_num;double m_radius;Point_3 m_center;DT m_direction;Cylinder_Param() = default;Cylinder_Param(uint32_t points_num, double radius, Point_3& center, DT& direction) :m_points_num(points_num), m_radius(radius), m_center(center), m_direction(direction){}
};
2、计算每个圆柱体的轴向量与其它各个圆柱体轴向量的角度差异,将角度差较小的圆柱体归为一组。在计算角度之前需要调整两个圆柱体的轴向,使其方向保持一致
3、找到包含点数最多的一组圆柱体,合并这一组圆柱体,得到新的单个圆柱体的各个参数。
合并规则
轴向量:各个圆柱体轴向量求平均后归一化
包含点个数:组中的每个圆柱体包含点个数之和
中心:这是可选的,既可以求所有圆柱中心的平均,也可以使用点数最多的圆柱的中心
半径:组中各个圆柱体的平均,或者直接使用包含点数最多的圆柱中心。
规则可以根据自己的实际情况调整。
代码展示
#include <CGAL/Point_set_3.h>
#include <CGAL/Point_set_3/IO.h>
#include <CGAL/Simple_cartesian.h>
#include <CGAL/Shape_detection/Region_growing/Region_growing.h>
#include <CGAL/IO/read_points.h>
#include <CGAL/property_map.h>
#include <CGAL/Shape_detection/Region_growing/Point_set.h>
#include <boost/iterator/function_output_iterator.hpp>
#include <CGAL/utils.h>
#include <fstream>#define src_file_path "cylinder2_dense_normals.ply"#define result_path "cylinder2_dense_all_result.ply"#define param_path "cylinder2_dense_param.txt"#define merge_param_path "cylinder2_dense_merge_param.txt"// Typedefs.
using Kernel = CGAL::Simple_cartesian<double>;
using FT = Kernel::FT;
using Point_3 = Kernel::Point_3;
using Vector_3 = Kernel::Vector_3;
using Line_3 = Kernel::Line_3;
using Point_set = CGAL::Point_set_3<Point_3>;
using Point_map = typename Point_set::Point_map;
//using Normal_map = typename Point_set::Vector_map;
typedef std::pair<Point_3, Vector_3> Point_with_normal;
typedef std::vector<Point_with_normal> Pwn_vector;
using Neighbor_query = CGAL::Shape_detection::Point_set::K_neighbor_query_for_point_set<Point_set>;
using Region_type = CGAL::Shape_detection::Point_set::Least_squares_cylinder_fit_region_for_point_set<Point_set>;
using Region_growing = CGAL::Shape_detection::Region_growing<Neighbor_query, Region_type>;// My
typedef CGAL::Direction_3<Kernel> DT;
typedef std::pair<std::vector<uint32_t>, std::vector<uint32_t>> Cylinders_Group; // first保存该组的圆柱索引,second保存总点数void detec_and_save(Point_set& point_set, Neighbor_query& neighbor_query, Region_type& region_type)
{// Create an instance of the region growing class.Region_growing region_growing(point_set, neighbor_query, region_type);// Add maps to get a colored output.Point_set::Property_map<unsigned char>red = point_set.add_property_map<unsigned char>("red", 0).first,green = point_set.add_property_map<unsigned char>("green", 0).first,blue = point_set.add_property_map<unsigned char>("blue", 0).first;// Run the algorithm.//CGAL::Random random;std::size_t num_cylinders = 0;region_growing.detect(boost::make_function_output_iterator([&](const std::pair< Region_type::Primitive, std::vector<typename Point_set::Index> >& region) {// Assign a random color to each region.const unsigned char r = static_cast<unsigned char>(rand() % 255);const unsigned char g = static_cast<unsigned char>(rand() % 255);const unsigned char b = static_cast<unsigned char>(rand() % 255);for (auto id : region.second) {put(red, id, r);put(green, id, g);put(blue, id, b);}++num_cylinders;}));std::cout << "* number of found cylinders: " << num_cylinders << std::endl;// Save regions to a file.std::ofstream out(result_path);CGAL::IO::set_ascii_mode(out);out << point_set;
}void detec_and_print_param(Point_set& point_set, Neighbor_query& neighbor_query, Region_type& region_type)
{// Create an instance of the region growing class.Region_growing region_growing(point_set, neighbor_query, region_type);std::vector<typename Region_growing::Primitive_and_region> regions;region_growing.detect(std::back_inserter(regions));// 打开输出文件std::ofstream outFile(param_path);for (size_t i = 0; i < regions.size(); i++){const auto& primitive_and_region = regions[i];//const auto& region = primitive_and_region.second;const auto& cylinder_param = primitive_and_region.first;// 获取轴的方向const auto& dx = cylinder_param.axis.direction().dx();const auto& dy = cylinder_param.axis.direction().dy();const auto& dz = cylinder_param.axis.direction().dz();// 获取圆柱中心位置const auto& cx = cylinder_param.axis.point(0).x();const auto& cy = cylinder_param.axis.point(0).y();const auto& cz = cylinder_param.axis.point(0).z();// 获取圆柱半径const auto& r = cylinder_param.radius;outFile << r << " " << dx << " " << dy << " " << dz << " " << cx << " " << cy << " " << cz << "\n";std::cout << "圆柱半径:" << r << std::endl;std::cout << "圆柱轴方向:" << dx << ", " << dy << ", " << dz << std::endl;std::cout << "圆柱轴方向:" << cx << ", " << cy << ", " << cz << std::endl;}outFile.close();
}// 保存合并后的圆柱参数
void save_merge_param(double radius, std::vector<double> center, Eigen::Vector3d direction)
{// 打开输出文件std::ofstream outFile(merge_param_path);outFile << radius << " " << direction[0] << " " << direction[1] << " " << direction[2] << " " << center[0] << " " << center[1] << " " << center[2] << " " << std::endl;outFile.close();
}// 定义一个函数来纠正向量方向
void correctDirection(const Eigen::Vector3d& reference, Eigen::Vector3d& vec) {if (reference.dot(vec) < 0) {vec = -vec;}
}void detec_and_merge(Point_set& point_set, Neighbor_query& neighbor_query, Region_type& region_type)
{struct Cylinder_Param {uint32_t m_points_num;double m_radius;Point_3 m_center;DT m_direction;Cylinder_Param() = default;Cylinder_Param(uint32_t points_num, double radius, Point_3& center, DT& direction) :m_points_num(points_num), m_radius(radius), m_center(center), m_direction(direction){}};// Create an instance of the region growing class.Region_growing region_growing(point_set, neighbor_query, region_type);std::vector<typename Region_growing::Primitive_and_region> regions;region_growing.detect(std::back_inserter(regions));// 获取每个圆柱体参数std::vector<Cylinder_Param> cylinders;for (size_t i = 0; i < regions.size(); i++){const auto& primitive_and_region = regions[i];const auto& region = primitive_and_region.second; // 区域内点索引const auto& cylinder_param = primitive_and_region.first;uint32_t points_num = region.size();double radius = cylinder_param.radius;Point_3 center = primitive_and_region.first.axis.point(0);DT direction = primitive_and_region.first.axis.direction();Cylinder_Param c_p(points_num, radius, center, direction);cylinders.push_back(c_p);}// 将圆柱按照轴向角度差与半径分组std::vector<Cylinders_Group> cylinders_groups;std::vector<bool> region_is_used(regions.size(), false);uint32_t max_points_num(0);uint32_t max_group_idx(0);for (size_t i = 0; i < regions.size(); i++){if (region_is_used[i] == true)continue;region_is_used[i] = true;std::vector<uint32_t> cylinders_idx; // 当前组圆柱索引std::vector<uint32_t> cylinders_points_num;uint32_t points_num = 0; // 当前组总点数cylinders_idx.push_back(i);cylinders_points_num.push_back(cylinders[i].m_points_num);points_num += cylinders[i].m_points_num;Eigen::Vector3d v1(cylinders[i].m_direction.dx(), cylinders[i].m_direction.dy(), cylinders[i].m_direction.dz());for (size_t j = 0; j < regions.size(); j++){if (i == j || region_is_used[j] == true)continue;Eigen::Vector3d v2(cylinders[j].m_direction.dx(), cylinders[j].m_direction.dy(), cylinders[j].m_direction.dz());// 这里只使用了圆柱轴的角度条件,未使用半径条件。auto dot_result = v1.dot(v2);if (abs(dot_result) > 0.87/* diff_angle = 30 */){cylinders_idx.push_back(j);cylinders_points_num.push_back(cylinders[j].m_points_num);points_num += cylinders[j].m_points_num;region_is_used[j] = true;}}// 将得到的圆柱组加入 groupscylinders_groups.emplace_back(cylinders_idx, cylinders_points_num);if (points_num > max_points_num) {max_points_num = points_num;max_group_idx = i;}}// 得到包含点数最多的圆柱组,将其中包含的圆柱纠正方向并计算平均向量和平均半径,以此作为代表圆柱Cylinders_Group real_cylinder_group = cylinders_groups[max_group_idx];// 找到纠正方向所用的参考向量(同组中包含点数最多的圆柱的轴方向)auto maxIt = std::max_element(real_cylinder_group.second.begin(), real_cylinder_group.second.end());int maxIndex = std::distance(real_cylinder_group.second.begin(), maxIt);uint32_t c_id = real_cylinder_group.first[maxIndex];Eigen::Vector3d reference_direction(cylinders[c_id].m_direction.dx(), cylinders[c_id].m_direction.dy(), cylinders[c_id].m_direction.dz());// 初始化平均向量Eigen::Vector3d average_vector = Eigen::Vector3d::Zero();for (size_t i = 0; i < real_cylinder_group.first.size(); i++){uint32_t c_id = real_cylinder_group.first[i];Eigen::Vector3d c_direction(cylinders[c_id].m_direction.dx(), cylinders[c_id].m_direction.dy(), cylinders[c_id].m_direction.dz());Eigen::Vector3d correct_direction = c_direction;correctDirection(reference_direction, correct_direction);average_vector += correct_direction;}// 归一化平均向量average_vector.normalize();// 求真实圆柱组的平均半径与中心double radius_sum(0.0);std::vector<double> center_sum(3, 0);int r_c_size = real_cylinder_group.first.size();for (size_t i = 0; i < real_cylinder_group.first.size(); i++){uint32_t c_id = real_cylinder_group.first[i];radius_sum += cylinders[c_id].m_radius;center_sum[0] += cylinders[c_id].m_center.x();center_sum[1] += cylinders[c_id].m_center.y();center_sum[2] += cylinders[c_id].m_center.z();}// TODO:这里合并后的中心也用了平均值,还有一个选项是用点数最多的圆柱中心for (auto& val : center_sum)val /= static_cast<double>(r_c_size);double average_radius = radius_sum / r_c_size;std::vector<double>& average_center = center_sum;save_merge_param(average_radius, average_center, average_vector);
}int main(int argc, char** argv) {// Load ply data either from a local folder or a user-provided file.const std::string input_file = src_file_path;std::ifstream in(CGAL::data_file_path(input_file));CGAL::IO::set_ascii_mode(in);//CGAL::IO::set_binary_mode(in);if (!in) {std::cerr << "ERROR: cannot read the input file!" << std::endl;return EXIT_FAILURE;}Point_set point_set;in >> point_set;in.close();std::cout << "* number of input points: " << point_set.size() << std::endl;//assert(!is_default_input || point_set.size() == 1813);assert(point_set.has_normal_map()); // input should have normals// Default parameter values for the data file cuble.pwn.const std::size_t k = 10;const FT max_distance = FT(1) / FT(500);const FT max_angle = FT(60);const std::size_t min_region_size = 200;// Create instances of the classes Neighbor_query and Region_type.Neighbor_query neighbor_query = CGAL::Shape_detection::Point_set::make_k_neighbor_query(point_set, CGAL::parameters::k_neighbors(k));Region_type region_type = CGAL::Shape_detection::Point_set::make_least_squares_cylinder_fit_region(point_set,CGAL::parameters::maximum_distance(max_distance).maximum_angle(max_angle).minimum_region_size(min_region_size));// 检测圆柱,对属于不同圆柱的点赋予不同颜色//detec_and_save(point_set, neighbor_query, region_type);// 检测圆柱,输出每个圆柱的参数//detec_and_print_param(point_set, neighbor_query, region_type);// 检测 & 合并detec_and_merge(point_set, neighbor_query, region_type);return EXIT_SUCCESS;
}
如果还没有圆柱的检测结果,需要先运行
detec_and_print_param(point_set, neighbor_query, region_type);
结果展示
说明
初始圆柱是我用open3D生成的,半径为0.1,高度为0.5,轴向量与z轴平行。
在上一篇文章的最后,展示了带底面的圆柱的检测结果。
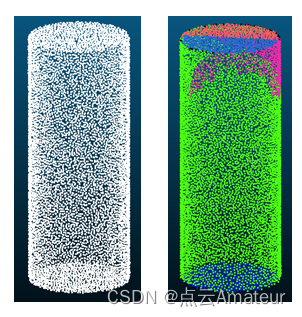
我在blender中使用python脚本画出了检测到的圆柱的真实样貌,检测到的圆柱参数如下:
number of input points: 10000
圆柱半径:0.427617
圆柱轴方向:0.0883206, 0.996081, 0.00471564
圆柱中心:0.0386407, 0.00583636, -0.176611
圆柱半径:0.0984349
圆柱轴方向:0.173551, -0.0677968, 0.982489
圆柱中心:-0.00130926, -0.000494991, 0.2048
圆柱半径:0.08501
圆柱轴方向:0.999531, 0.0304522, -0.00314423
圆柱中心:0.000517605, -0.000217548, -0.179827
圆柱半径:0.0551355
圆柱轴方向:0.133879, 0.989484, 0.0547502
圆柱中心:-0.0453276, -0.00894591, 0.298277
圆柱半径:0.099298
圆柱轴方向:0.00462129, 0.00957155, 0.999944
圆柱中心:-2.68408e-05, 1.09269e-05, -0.0189
将其存放到txt文档中,在blender中新建工程,使用python读取后创建相应圆柱体。
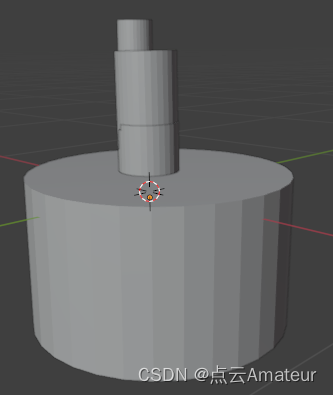
执行圆柱体合并后的结果:
得到的圆柱参数
半径: 0.0988664
轴向量:0.0894765 -0.0292402 0.99556
中心:-0.000668052 -0.000242032 0.0929501
可以看到合并后得到的圆柱,与原始圆柱的参数基本吻合。
其中,半径≈0.01,轴向量与Z轴基本平行
在blender中画出合并后的圆柱
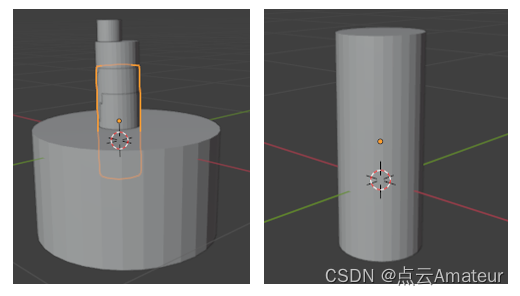
- 左图为合并后的结果与之前检测到的圆柱一起堆放,黄色线为合并结果的轮廓。
- 右图为合并结果单独放置。
这篇关于【CGAL】圆柱体检测结果后处理的文章就介绍到这儿,希望我们推荐的文章对编程师们有所帮助!




![[数据集][目标检测]血细胞检测数据集VOC+YOLO格式2757张4类别](https://i-blog.csdnimg.cn/direct/22c867ab717d44c78b985ed667169b42.png)