noisy专题
Noisy:一款功能强大的DNS和HTTPS网络流量噪声生成工具
关于Noisy Noisy是一款功能强大的DNS和HTTP/S网络流量噪音生成工具,该工具基于Python开发,可以帮助广大研究人员在进行常规网络浏览时,在后台生成随机的HTTP/DNS网络流量噪声,并以此来提升网络通信数据的安全性和隐蔽性。 支持的平台 macOS Ubuntu Raspbian Stretch 支持的环境 Python 2.7 Python 3.6
NLP05_noisy channel model、语言模型、马尔科夫假设
给定一个source,转换成text 通过贝叶斯定理,得到如下的公式 都是将一个信号来转换成文本信息 机器翻译:英译中 根据贝叶斯定理, P(英文|中文)表示的是翻译模型, 指的是中文对应的英文翻译,这个是提供好的,通过翻译模型得到的是英到中的对照翻译,不考虑语法 P(中文)表示语言模型,用他来保证翻译的语法正确。 拼接纠错 P(错误|正确)可以表示编辑距离,也就是正确的 和错误的差异 P
noisy labels and label smothing
我要看懂这个代码!! import numpy as npimport tensorflow as tfimport matplotlib.pyplot as pltnp.random.seed(0) # for reproducibilityX = np.random.randint(0, 3, (32*1100, 10), np.int32) # inputsY = np.equal(
[Machine Learning] Learning with Noisy Labels
文章目录 随机分类噪声 (Random Classification Noise, RCN)类别依赖的标签噪声 (Class-Dependent Noise, CCN)二分类多分类 实例和类别依赖的标签噪声 (Instance and Label-Dependent Noise, ILN) 标签噪声是指分类任务中的标签被错误地标记。这可能是由于各种原因,如数据收集错误、主观偏见
Self-training with Noisy Student
目录 Self-training with Noisy Student improves ImageNet classification1、数据集简介2、性能3、模型策略4、实验策略5、Other Self-training with Noisy Student improves ImageNet classification 该篇论文作者之一 Quoc Le 11.13
论文笔记《Robust Federated Learning with Noisy Labels》
读论文:Robust Federated Learning with Noisy Labels 应用背景(问题与挑战)相关工作Federated learningLearning on noisy data 解决方案的局限性(motivation) 方案介绍Problem definition and notationsLocal updateslocal clean setnaive av
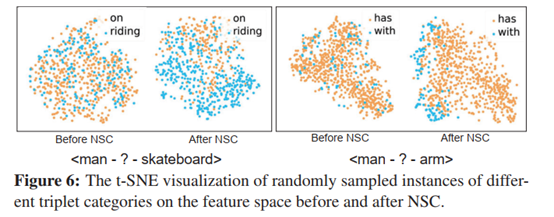
The Devil is in the Labels: Noisy Label Correction forRobust Scene Graph Generation阅读笔记
注:标注、标签、关系的意思相同,指都是的主语宾语间的谓词,样本指 三元组 标题分析 The Devil is inthe Labels:模仿俚语“TheDevil is in the details”概括本文的研究重点:标签。 Noisy LabelCorrection:论文方法,对噪声标签进行修正。 for Robust SceneGraph Generation:论文任务,生成更鲁棒的场景图
《Noisy Activation Function》噪声激活函数
原文:https://arxiv.org/pdf/1603.00391v3.pdf 参考: http://blog.csdn.net/yhl_leo/article/details/51736830 Noisy Activation Functions是ICML 2016年新发表的一篇关于激活函数的论文,其中对以往的激活函数进行了深入的分析,并提出了训练过程中添加噪声的新方法,效果不错,觉得
【论文阅读】learning with noisy correspondence for cross-modal matching ------ 跨模态匹配,噪声对应
注意,本博客非逐字逐句翻译论文,是作者阅读论文后根据自己的理解所写,预知论文详情,请参阅论文原文。 论文标题:Learning with Noisy Correspondence for Cross-modal Matching; 作者:Zhenyu Huang,Guocheng Niu,Xiao Liu,Wenbiao Ding,Xinyan Xiao,Hua Wu,Xi Peng; Co
Streaming Principal Component Analysis in Noisy Settings
论文背景: 面对来袭的数据,连续样本不一定是不相关的,甚至不是同分布的。当前,大部分在线PCA都只关注准确性,而忽视时效性!噪声?数据缺失,观测有偏,重大异常? 论文内容: Section 2 Online Settings Online PCA, 就是在观察到 x 1 , x 2 , x 3 , … , x t − 1 x1, x2, x3, \dots, x_{t-1} x1,x2,
Noisy Channel模型纠正单词拼写错误
本文介绍 Stanford《From Languages to Information》课程中讲到的 单词拼写错误 纠正。背后的数学原理主要是贝叶斯公式。单词拼写错误纠正主要涉及到两个模型:一个是Nosiy Channel模型,它是贝叶斯公式中的似然函数;另一个模型是Language Model,它是贝叶斯公式中的先验概率。 一,问题描述 在这句话中“. . . was called a “
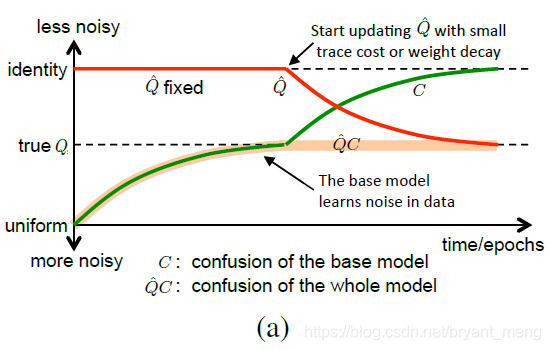
【Noise-Label】《Learning from Noisy Labels with Deep Neural Networks》
arXiv-2014 文章目录 1 Background and Motivation2 Advantages3 Innovations4 Method4.1 Bottom-up Noise Model4.2 Estimating Noise Distribution Using Clean Data4.3 Learning Noise Distribution From Noisy
论文推荐-使用 Noisy Student 进行自训练可以提高 ImageNet 分类的表现
教师学生模型、伪标签、半监督学习和图像分类 使用 Noisy Student 进行自训练改进 ImageNet 分类是一篇由 Google Research、Brain Team 和Carnegie Mellon大学发表在2020 CVPR的论文 Noisy Student在训练时使用相等或更大的学生模型和在学习期间添加噪声(Dropout, Stochastic Depth,和数据增强)扩
深度学习论文: Evaluating You Only Hear Once on noisy audios in the VOICe Dataset及其PyTorch实现
深度学习论文: Evaluating You Only Hear Once on noisy audios in the VOICe Dataset及其PyTorch实现 Evaluating robustness of You Only Hear Once (YOHO) Algorithm on noisy audios in the VOICe Dataset PDF: https://arx
Hybrid attention-based prototypical networks for noisy few-shot relation
Gao [9] 等人提出文本与图像的一大区别在于其多样性和噪音更大,因此提出一种基于混合注意力的原型网络结构,如图 9 所示,首先使用 instance-level 的 attention 从支撑集中选出和 query 更为贴近的实例,同时降低噪声实例所带来的影响。 然后 feature-level 的实例能够衡量特征空间中的哪些维度对分类更为重要,从而为每种不同的关系都生成相适应的距离度量函数



![[Machine Learning] Learning with Noisy Labels](/front/images/it_default2.jpg)