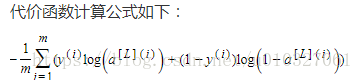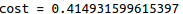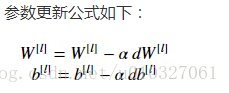本文主要是介绍deeplearning.ai 吴恩达网上课程学习(八)——深层神经网络分类代码实战,希望对大家解决编程问题提供一定的参考价值,需要的开发者们随着小编来一起学习吧!
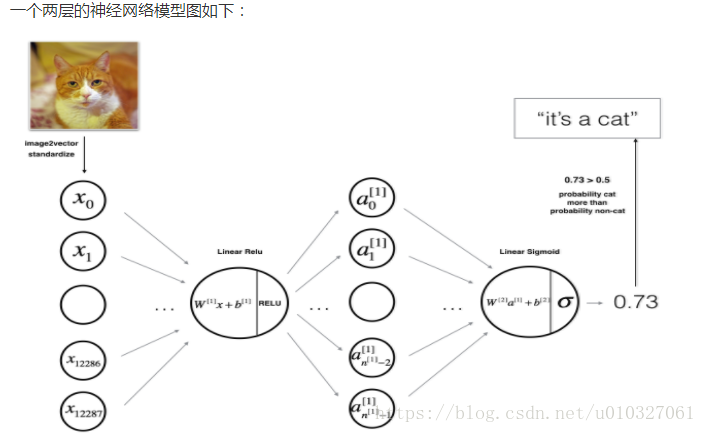
本文将学习如何利用Python的来实现多个隐藏层的图片分类问题:用两层和多层神经网络实现是否是猫图片的分类。
本文的实践平台是Linux,Python3.4,基础库anaconda和spyder,
参考文章的实现平台是jupyter notebook:多层神经网络代码实战
理论知识学习请参看上篇:deeplearning.ai 吴恩达网上课程学习(七)——深层神经网络理论学习
1. 流程概括:
2.引入相关依赖包:
import numpy as np
import time
import h5py
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import scipy
from PIL import Image
from testCases_v2 import * #提供了一些测试函数所有的数据和方法
from dnn_utils_v2 import sigmoid, sigmoid_backward, relu, relu_backward #封装好的方法
from dnn_app_utils_v2 import *plt.rcParams['figure.figsize'] = (5.0, 4.0) # set default size of plots
plt.rcParams['image.interpolation'] = 'nearest'
plt.rcParams['image.cmap'] = 'gray'np.random.seed(1)其中,sigmoid函数如下:(对输入矩阵z进行sigmoid操作,输出操作结果A和输入矩阵cache = z)
def sigmoid(Z):"""Implements the sigmoid activation in numpyArguments:Z -- numpy array of any shapeReturns:A -- output of sigmoid(z), same shape as Zcache -- returns Z as well, useful during backpropagation"""A = 1/(1+np.exp(-Z))cache = Zreturn A, cachesigmoid_backward函数如下:(对单个sigmoid节点反向传播:输入dA代价函数L对a的求导,a表示的是对z的sigmoid结果,z=wx+b,cache是存储的z;输出结果是代价函数L对z的求导)
def sigmoid_backward(dA, cache):"""Implement the backward propagation for a single SIGMOID unit.Arguments:dA -- post-activation gradient, of any shape dL/dacache -- 'Z' where we store for computing backward propagation efficientlyReturns:dZ -- Gradient of the cost with respect to Z"""Z = caches = 1/(1+np.exp(-Z))dZ = dA * s * (1-s) #dL/dz = (dL/da)*(da/ dz) = dA*s'(z)assert (dZ.shape == Z.shape)return dZrelu函数如下:(对输入矩阵z进行relu操作,输出操作结果A和输入矩阵cache = z )
def relu(Z):"""Implement the RELU function.Arguments:Z -- Output of the linear layer, of any shapeReturns:A -- Post-activation parameter, of the same shape as Zcache -- a python dictionary containing "A" ; stored for computing the backward pass efficiently"""A = np.maximum(0,Z)assert(A.shape == Z.shape)cache = Z return A, cacherelu_backward函数如下:(同sigmoid_backward函数)
def relu_backward(dA, cache):"""Implement the backward propagation for a single RELU unit.Arguments:dA -- post-activation gradient, of any shapecache -- 'Z' where we store for computing backward propagation efficientlyReturns:dZ -- Gradient of the cost with respect to Z"""Z = cachedZ = np.array(dA, copy=True) # just converting dz to a correct object.# When z <= 0, you should set dz to 0 as well. dZ[Z <= 0] = 0assert (dZ.shape == Z.shape)return dZ3.初始化:
① 对于一个两层的神经网络结构
模型结构是线性->ReLU->线性->sigmod函数,初始化wi和bi的大小的矩阵
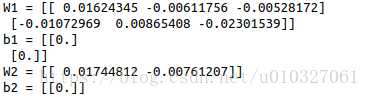
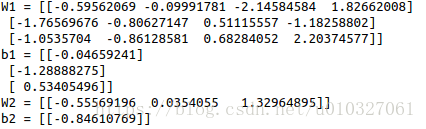
def initialize_parameters(n_x, n_h, n_y):"""Argument:n_x -- size of the input layern_h -- size of the hidden layern_y -- size of the output layerReturns:parameters -- python dictionary containing your parameters:W1 -- weight matrix of shape (n_h, n_x)b1 -- bias vector of shape (n_h, 1)W2 -- weight matrix of shape (n_y, n_h)b2 -- bias vector of shape (n_y, 1)"""np.random.seed(1)### START CODE HERE ### (≈ 4 lines of code)W1 = np.random.randn(n_h, n_x)*0.01b1 = np.zeros((n_h, 1))W2 = np.random.randn(n_y, n_h)*0.01b2 = np.zeros((n_y, 1))### END CODE HERE ###assert(W1.shape == (n_h, n_x))assert(b1.shape == (n_h, 1))assert(W2.shape == (n_y, n_h))assert(b2.shape == (n_y, 1))parameters = {"W1": W1,"b1": b1,"W2": W2,"b2": b2}return parameters parameters = initialize_parameters(3,2,1)
print("W1 = " + str(parameters["W1"]))
print("b1 = " + str(parameters["b1"]))
print("W2 = " + str(parameters["W2"]))
print("b2 = " + str(parameters["b2"]))结果:
② 一个L层的神经网络的初始化:
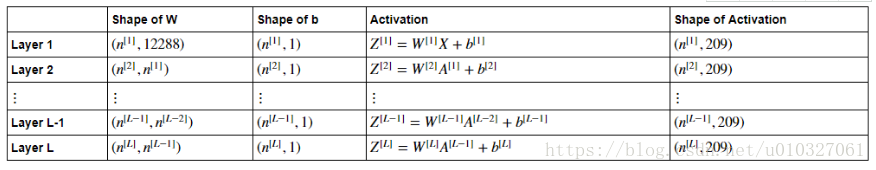
假设X的维度为(12288,209),表示有209个样本,每个样本有12288个特征。n[i]表示第i层神经元数量。
初始化如下:(输入的是包含神经网络每个层神经元个数的一维矩阵)
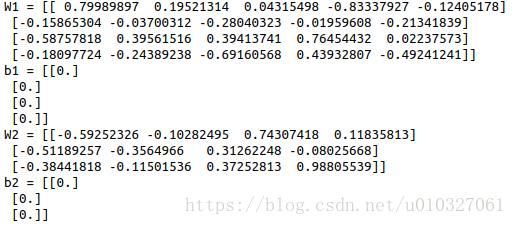
def initialize_parameters_deep(layer_dims):"""Arguments:layer_dims -- python array (list) containing the dimensions of each layer in our networkReturns:parameters -- python dictionary containing your parameters "W1", "b1", ..., "WL", "bL":Wl -- weight matrix of shape (layer_dims[l], layer_dims[l-1])bl -- bias vector of shape (layer_dims[l], 1)"""np.random.seed(3)parameters = {}L = len(layer_dims) # number of layers in the networkfor l in range(1, L):### START CODE HERE ### (≈ 2 lines of code)parameters['W' + str(l)] = np.random.randn(layer_dims[l], layer_dims[l - 1]) / np.sqrt(layer_dims[l - 1])parameters['b' + str(l)] = np.zeros((layer_dims[l], 1))### END CODE HERE ###assert(parameters['W' + str(l)].shape == (layer_dims[l], layer_dims[l-1]))assert(parameters['b' + str(l)].shape == (layer_dims[l], 1))return parameters结果:
为什么关于随机数大家的结果都一样呢?那就是np.random.seed(n)的作用了,方便对随机数的预测,详细的可以参考我的前一篇文章:deeplearning.ai 吴恩达网上课程学习(六)——浅层神经网络分类代码实战Linux,TensorFlow,Python3.4,anaconda和spyder
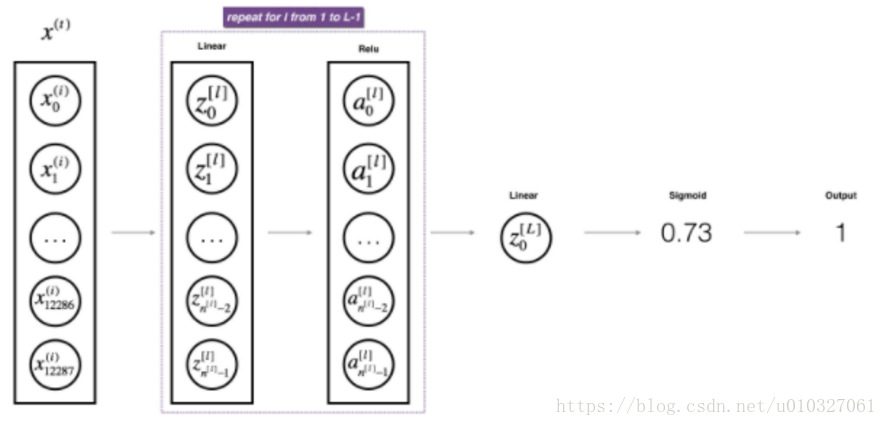
4.前向传播函数:
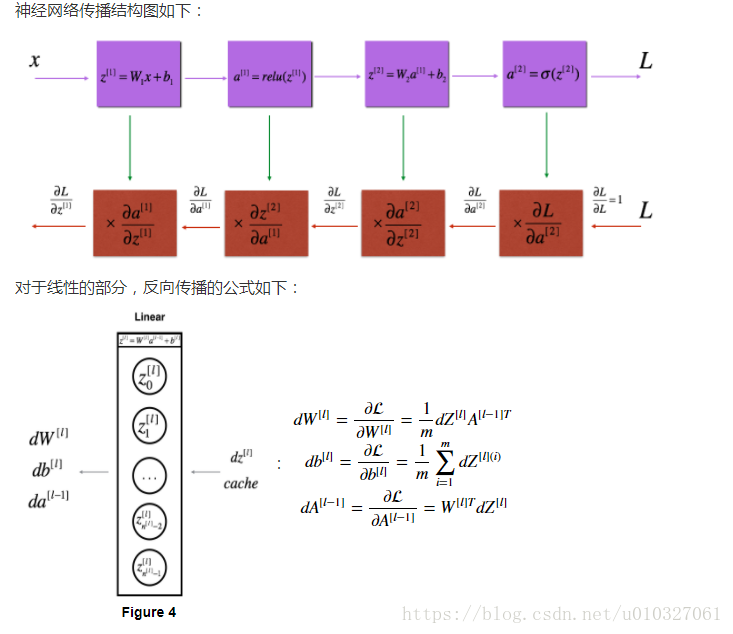
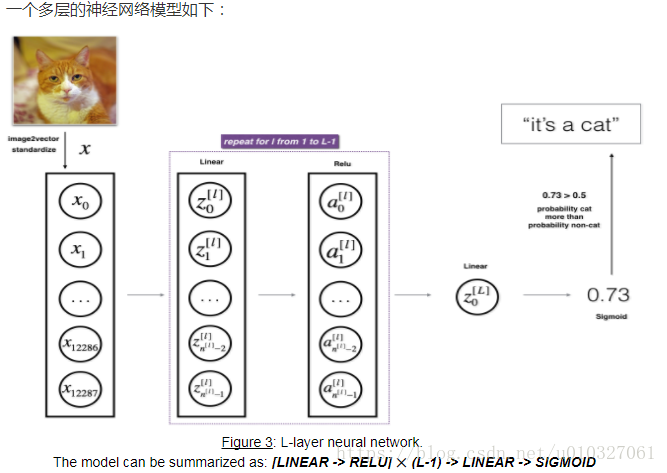
多层模型的前向传播计算模型如下:
①前向传播中,线性部分计算如下:
def linear_forward(A, W, b):"""Implement the linear part of a layer's forward propagation.Arguments:A -- activations from previous layer (or input data): (size of previous layer, number of examples)W -- weights matrix: numpy array of shape (size of current layer, size of previous layer)b -- bias vector, numpy array of shape (size of the current layer, 1)Returns:Z -- the input of the activation function, also called pre-activation parameter cache -- a python dictionary containing "A", "W" and "b" ; stored for computing the backward pass efficiently"""### START CODE HERE ### (≈ 1 line of code)Z = np.dot(W, A) + b### END CODE HERE ###assert(Z.shape == (W.shape[0], A.shape[1]))cache = (A, W, b)return Z, cache测试一下:
A, W, b = linear_forward_test_case()Z, linear_cache = linear_forward(A, W, b)
print("Z = " + str(Z))其中:
def linear_forward_test_case():np.random.seed(1)A = np.random.randn(3,2)W = np.random.randn(1,3)b = np.random.randn(1,1)return A, W, b结果:
Z = [[ 3.26295337 -1.23429987]]
② 线性激活函数如下:
def linear_activation_forward(A_prev, W, b, activation):"""Implement the forward propagation for the LINEAR->ACTIVATION layerArguments:A_prev -- activations from previous layer (or input data): (size of previous layer, number of examples)W -- weights matrix: numpy array of shape (size of current layer, size of previous layer)b -- bias vector, numpy array of shape (size of the current layer, 1)activation -- the activation to be used in this layer, stored as a text string: "sigmoid" or "relu"Returns:A -- the output of the activation function, also called the post-activation value cache -- a python dictionary containing "linear_cache" and "activation_cache";stored for computing the backward pass efficiently"""if activation == "sigmoid":# Inputs: "A_prev, W, b". Outputs: "A, activation_cache".### START CODE HERE ### (≈ 2 lines of code)Z, linear_cache = linear_forward(A_prev, W, b)A, activation_cache = sigmoid(Z)### END CODE HERE ###elif activation == "relu":# Inputs: "A_prev, W, b". Outputs: "A, activation_cache".### START CODE HERE ### (≈ 2 lines of code)Z, linear_cache = linear_forward(A_prev, W, b)A, activation_cache = relu(Z)### END CODE HERE ###assert (A.shape == (W.shape[0], A_prev.shape[1]))cache = (linear_cache, activation_cache)return A, cache测试一下:
A_prev, W, b = linear_activation_forward_test_case()A, linear_activation_cache = linear_activation_forward(A_prev, W, b, activation = "sigmoid")
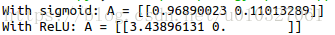
print("With sigmoid: A = " + str(A))A, linear_activation_cache = linear_activation_forward(A_prev, W, b, activation = "relu")
print("With ReLU: A = " + str(A))其中,linear_activation_forward_test_case函数如下:
def linear_activation_forward_test_case():np.random.seed(2)A_prev = np.random.randn(3,2)W = np.random.randn(1,3)b = np.random.randn(1,1)return A_prev, W, b结果:
③ 前向传播函数如下:
def L_model_forward(X, parameters):"""Implement forward propagation for the [LINEAR->RELU]*(L-1)->LINEAR->SIGMOID computationArguments:X -- data, numpy array of shape (input size, number of examples)parameters -- output of initialize_parameters_deep()Returns:AL -- last post-activation valuecaches -- list of caches containing:every cache of linear_relu_forward() (there are L-1 of them, indexed from 0 to L-2)the cache of linear_sigmoid_forward() (there is one, indexed L-1)"""caches = []A = XL = len(parameters) // 2 # number of layers in the neural network# Implement [LINEAR -> RELU]*(L-1). Add "cache" to the "caches" list.for l in range(1, L):A_prev = A A, cache = linear_activation_forward(A_prev, parameters['W' + str(l)], parameters['b' + str(l)], "relu")caches.append(cache)# Implement LINEAR -> SIGMOID. Add "cache" to the "caches" list.AL, cache = linear_activation_forward(A, parameters['W' + str(L)], parameters['b' + str(L)], "sigmoid")caches.append(cache)assert(AL.shape == (1,X.shape[1]))return AL, caches测试一下:
X, parameters = L_model_forward_test_case()
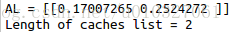
AL, caches = L_model_forward(X, parameters)print("AL = " + str(AL))
print("Length of caches list = " + str(len(caches)))def L_model_forward_test_case():np.random.seed(1)X = np.random.randn(4,2)W1 = np.random.randn(3,4)b1 = np.random.randn(3,1)W2 = np.random.randn(1,3)b2 = np.random.randn(1,1)parameters = {"W1": W1,"b1": b1,"W2": W2,"b2": b2}return X, parameters结果:
5. 计算代价函数:
def compute_cost(AL, Y):"""Implement the cost function defined by equation (7).Arguments:AL -- probability vector corresponding to your label predictions, shape (1, number of examples)Y -- true "label" vector (for example: containing 0 if non-cat, 1 if cat), shape (1, number of examples)Returns:cost -- cross-entropy cost"""m = Y.shape[1]# Compute loss from aL and y.### START CODE HERE ### (≈ 1 lines of code)cost = -np.sum(np.multiply(np.log(AL),Y) + np.multiply(np.log(1 - AL), 1 - Y)) / m### END CODE HERE ###cost = np.squeeze(cost) # To make sure your cost's shape is what we expect (e.g. this turns [[17]] into 17).assert(cost.shape == ())return cost测试一下:
Y, AL = compute_cost_test_case()print("cost = " + str(compute_cost(AL, Y)))def compute_cost_test_case(): Y = np.asarray([[1, 1, 1]]) aL = np.array([[.8,.9,0.4]]) return Y, aL结果:
6.反向传播
实现函数如下:
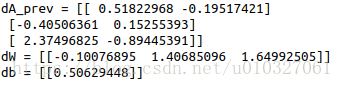
def linear_backward(dZ, cache):"""Implement the linear portion of backward propagation for a single layer (layer l)Arguments:dZ -- Gradient of the cost with respect to the linear output (of current layer l)cache -- tuple of values (A_prev, W, b) coming from the forward propagation in the current layerReturns:dA_prev -- Gradient of the cost with respect to the activation (of the previous layer l-1), same shape as A_prevdW -- Gradient of the cost with respect to W (current layer l), same shape as Wdb -- Gradient of the cost with respect to b (current layer l), same shape as b"""A_prev, W, b = cachem = A_prev.shape[1]### START CODE HERE ### (≈ 3 lines of code)dW = np.dot(dZ, A_prev.T) / mdb = np.sum(dZ, axis=1, keepdims=True) / mdA_prev = np.dot(W.T, dZ)### END CODE HERE ###assert (dA_prev.shape == A_prev.shape)assert (dW.shape == W.shape)assert (db.shape == b.shape)return dA_prev, dW, dbdZ, linear_cache = linear_backward_test_case()dA_prev, dW, db = linear_backward(dZ, linear_cache)
print ("dA_prev = "+ str(dA_prev))
print ("dW = " + str(dW))
print ("db = " + str(db))def linear_backward_test_case():np.random.seed(1)dZ = np.random.randn(1,2)A = np.random.randn(3,2)W = np.random.randn(1,3)b = np.random.randn(1,1)linear_cache = (A, W, b)return dZ, linear_cache结果:
接下来,我们需要计算激活函数的反向传播函数:
def linear_activation_backward(dA, cache, activation):"""Implement the backward propagation for the LINEAR->ACTIVATION layer.Arguments:dA -- post-activation gradient for current layer l cache -- tuple of values (linear_cache, activation_cache) we store for computing backward propagation efficientlyactivation -- the activation to be used in this layer, stored as a text string: "sigmoid" or "relu"Returns:dA_prev -- Gradient of the cost with respect to the activation (of the previous layer l-1), same shape as A_prevdW -- Gradient of the cost with respect to W (current layer l), same shape as Wdb -- Gradient of the cost with respect to b (current layer l), same shape as b"""linear_cache, activation_cache = cacheif activation == "relu":### START CODE HERE ### (≈ 2 lines of code)dZ = relu_backward(dA, activation_cache)dA_prev, dW, db = linear_backward(dZ, linear_cache)### END CODE HERE ###elif activation == "sigmoid":### START CODE HERE ### (≈ 2 lines of code)dZ = sigmoid_backward(dA, activation_cache)dA_prev, dW, db = linear_backward(dZ, linear_cache)### END CODE HERE ###return dA_prev, dW, db验证一下:
AL, linear_activation_cache = linear_activation_backward_test_case()dA_prev, dW, db = linear_activation_backward(AL, linear_activation_cache, activation = "sigmoid")
print ("sigmoid:")
print ("dA_prev = "+ str(dA_prev))
print ("dW = " + str(dW))
print ("db = " + str(db) + "\n")dA_prev, dW, db = linear_activation_backward(AL, linear_activation_cache, activation = "relu")
print ("relu:")
print ("dA_prev = "+ str(dA_prev))
print ("dW = " + str(dW))
print ("db = " + str(db))其中,linear_activation_backward_test_case函数如下:
def linear_activation_backward_test_case():np.random.seed(2)dA = np.random.randn(1,2)A = np.random.randn(3,2)W = np.random.randn(1,3)b = np.random.randn(1,1)Z = np.random.randn(1,2)linear_cache = (A, W, b)activation_cache = Zlinear_activation_cache = (linear_cache, activation_cache)return dA, linear_activation_cache结果:
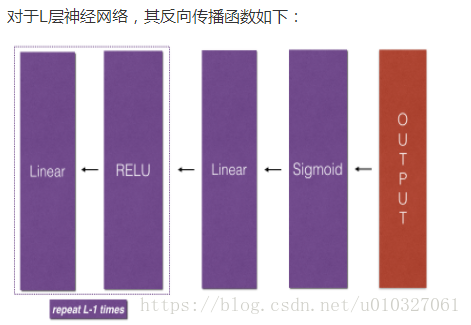
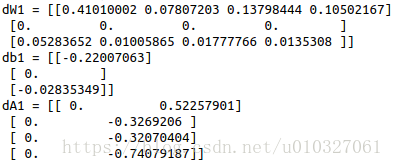
def L_model_backward(AL, Y, caches):"""Implement the backward propagation for the [LINEAR->RELU] * (L-1) -> LINEAR -> SIGMOID groupArguments:AL -- probability vector, output of the forward propagation (L_model_forward())Y -- true "label" vector (containing 0 if non-cat, 1 if cat)caches -- list of caches containing:every cache of linear_activation_forward() with "relu" (it's caches[l], for l in range(L-1) i.e l = 0...L-2)the cache of linear_activation_forward() with "sigmoid" (it's caches[L-1])Returns:grads -- A dictionary with the gradientsgrads["dA" + str(l)] = ... grads["dW" + str(l)] = ...grads["db" + str(l)] = ... """grads = {}L = len(caches) # the number of layersm = AL.shape[1]Y = Y.reshape(AL.shape) # after this line, Y is the same shape as AL# Initializing the backpropagation### START CODE HERE ### (1 line of code)dAL = - (np.divide(Y, AL) - np.divide(1 - Y, 1 - AL))### END CODE HERE #### Lth layer (SIGMOID -> LINEAR) gradients. Inputs: "AL, Y, caches". Outputs: "grads["dAL"], grads["dWL"], grads["dbL"]### START CODE HERE ### (approx. 2 lines)current_cache = caches[L-1]grads["dA" + str(L)], grads["dW" + str(L)], grads["db" + str(L)] = linear_activation_backward(dAL, current_cache, "sigmoid")### END CODE HERE ###for l in reversed(range(L-1)):# lth layer: (RELU -> LINEAR) gradients.# Inputs: "grads["dA" + str(l + 2)], caches". Outputs: "grads["dA" + str(l + 1)] , grads["dW" + str(l + 1)] , grads["db" + str(l + 1)] ### START CODE HERE ### (approx. 5 lines)current_cache = caches[l]dA_prev_temp, dW_temp, db_temp = linear_activation_backward(grads["dA" + str(l + 2)], current_cache, "relu")grads["dA" + str(l + 1)] = dA_prev_tempgrads["dW" + str(l + 1)] = dW_tempgrads["db" + str(l + 1)] = db_temp### END CODE HERE ###return grads测试一下:
AL, Y_assess, caches = L_model_backward_test_case()
grads = L_model_backward(AL, Y_assess, caches)
print ("dW1 = "+ str(grads["dW1"]))
print ("db1 = "+ str(grads["db1"]))
print ("dA1 = "+ str(grads["dA1"]))其中,L_model_backward_test_case函数如下:
def L_model_backward_test_case():np.random.seed(3)AL = np.random.randn(1, 2)Y = np.array([[1, 0]])A1 = np.random.randn(4,2)W1 = np.random.randn(3,4)b1 = np.random.randn(3,1)Z1 = np.random.randn(3,2)linear_cache_activation_1 = ((A1, W1, b1), Z1)A2 = np.random.randn(3,2)W2 = np.random.randn(1,3)b2 = np.random.randn(1,1)Z2 = np.random.randn(1,2)linear_cache_activation_2 = ( (A2, W2, b2), Z2)caches = (linear_cache_activation_1, linear_cache_activation_2)return AL, Y, caches结果:
7.更新参数:
实现过程如下:
def update_parameters(parameters, grads, learning_rate):"""Update parameters using gradient descentArguments:parameters -- python dictionary containing your parameters grads -- python dictionary containing your gradients, output of L_model_backwardReturns:parameters -- python dictionary containing your updated parameters parameters["W" + str(l)] = ... parameters["b" + str(l)] = ..."""L = len(parameters) // 2 # number of layers in the neural network# Update rule for each parameter. Use a for loop.### START CODE HERE ### (≈ 3 lines of code)for l in range(L):parameters["W" + str(l+1)] = parameters["W" + str(l+1)] - learning_rate * grads["dW" + str(l+1)]parameters["b" + str(l+1)] = parameters["b" + str(l+1)] - learning_rate * grads["db" + str(l+1)]### END CODE HERE ###return parameters验证一下:
parameters, grads = update_parameters_test_case()
parameters = update_parameters(parameters, grads, 0.1)print ("W1 = "+ str(parameters["W1"]))
print ("b1 = "+ str(parameters["b1"]))
print ("W2 = "+ str(parameters["W2"]))
print ("b2 = "+ str(parameters["b2"]))其中,update_parameters_test_case函数如下:
def update_parameters_test_case():np.random.seed(2)W1 = np.random.randn(3,4)b1 = np.random.randn(3,1)W2 = np.random.randn(1,3)b2 = np.random.randn(1,1)parameters = {"W1": W1,"b1": b1,"W2": W2,"b2": b2}np.random.seed(3)dW1 = np.random.randn(3,4)db1 = np.random.randn(3,1)dW2 = np.random.randn(1,3)db2 = np.random.randn(1,1)grads = {"dW1": dW1,"db1": db1,"dW2": dW2,"db2": db2}return parameters, grads结果:
至此为止,我们已经实现该神经网络中,所有需要的函数。
接下来,我们将这些方法组合在一起,构成一个神经网络类,可以方便的使用。
8.两层神经网络模型:
定义常量:
n_x = 12288 # num_px * num_px * 3
n_h = 7
n_y = 1
layers_dims = (n_x, n_h, n_y)两层网络模型:
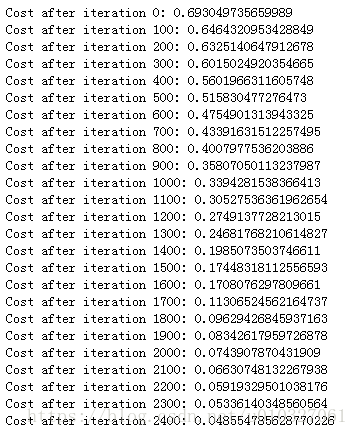
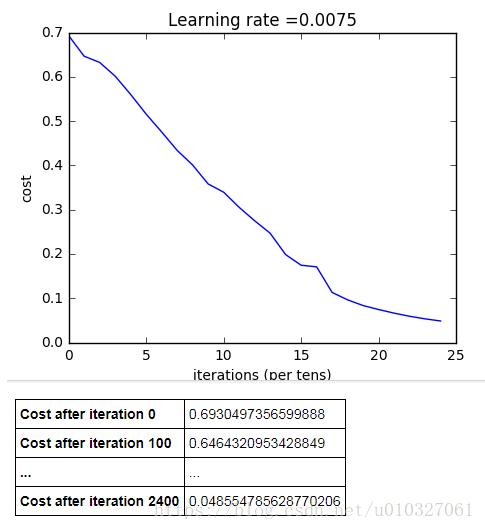
def two_layer_model(X, Y, layers_dims, learning_rate = 0.0075, num_iterations = 3000, print_cost=False):"""Implements a two-layer neural network: LINEAR->RELU->LINEAR->SIGMOID.Arguments:X -- input data, of shape (n_x, number of examples)Y -- true "label" vector (containing 0 if cat, 1 if non-cat), of shape (1, number of examples)layers_dims -- dimensions of the layers (n_x, n_h, n_y)num_iterations -- number of iterations of the optimization looplearning_rate -- learning rate of the gradient descent update ruleprint_cost -- If set to True, this will print the cost every 100 iterations Returns:parameters -- a dictionary containing W1, W2, b1, and b2"""np.random.seed(1)grads = {}costs = [] # to keep track of the costm = X.shape[1] # number of examples(n_x, n_h, n_y) = layers_dims# Initialize parameters dictionary, by calling one of the functions you'd previously implemented### START CODE HERE ### (≈ 1 line of code)parameters = initialize_parameters(n_x, n_h, n_y)### END CODE HERE #### Get W1, b1, W2 and b2 from the dictionary parameters.W1 = parameters["W1"]b1 = parameters["b1"]W2 = parameters["W2"]b2 = parameters["b2"]# Loop (gradient descent)for i in range(0, num_iterations):# Forward propagation: LINEAR -> RELU -> LINEAR -> SIGMOID. Inputs: "X, W1, b1". Output: "A1, cache1, A2, cache2".### START CODE HERE ### (≈ 2 lines of code)A1, cache1 = linear_activation_forward(X, W1, b1, "relu")A2, cache2 = linear_activation_forward(A1, W2, b2, "sigmoid")### END CODE HERE #### Compute cost### START CODE HERE ### (≈ 1 line of code)cost = compute_cost(A2, Y)### END CODE HERE #### Initializing backward propagationdA2 = - (np.divide(Y, A2) - np.divide(1 - Y, 1 - A2))# Backward propagation. Inputs: "dA2, cache2, cache1". Outputs: "dA1, dW2, db2; also dA0 (not used), dW1, db1".### START CODE HERE ### (≈ 2 lines of code)dA1, dW2, db2 = linear_activation_backward(dA2, cache2, "sigmoid")dA0, dW1, db1 = linear_activation_backward(dA1, cache1, "relu")### END CODE HERE #### Set grads['dWl'] to dW1, grads['db1'] to db1, grads['dW2'] to dW2, grads['db2'] to db2grads['dW1'] = dW1grads['db1'] = db1grads['dW2'] = dW2grads['db2'] = db2# Update parameters.### START CODE HERE ### (approx. 1 line of code)parameters = update_parameters(parameters, grads, learning_rate)### END CODE HERE #### Retrieve W1, b1, W2, b2 from parametersW1 = parameters["W1"]b1 = parameters["b1"]W2 = parameters["W2"]b2 = parameters["b2"]# Print the cost every 100 training exampleif print_cost and i % 100 == 0:print("Cost after iteration {}: {}".format(i, np.squeeze(cost)))if print_cost and i % 100 == 0:costs.append(cost)# plot the costplt.plot(np.squeeze(costs))plt.ylabel('cost')plt.xlabel('iterations (per tens)')plt.title("Learning rate =" + str(learning_rate))plt.show()return parameters训练:
parameters = two_layer_model(train_x, train_y, layers_dims = (n_x, n_h, n_y), num_iterations = 2500, print_cost=True)训练结果:
预测准确度:预测函数的实现如下:
def predict(X, y, parameters):"""This function is used to predict the results of a L-layer neural network.Arguments:X -- data set of examples you would like to labelparameters -- parameters of the trained modelReturns:p -- predictions for the given dataset X"""m = X.shape[1]n = len(parameters) // 2 # number of layers in the neural networkp = np.zeros((1,m))# Forward propagationprobas, caches = L_model_forward(X, parameters)# convert probas to 0/1 predictionsfor i in range(0, probas.shape[1]):if probas[0,i] > 0.5:p[0,i] = 1else:p[0,i] = 0print("Accuracy: " + str(float(np.sum((p == y))/m)))return p对于训练集:
predictions_train = predict(train_x, train_y, parameters)结果:
Accuracy:1.0
对于测试集:
predictions_test = predict(test_x, test_y, parameters)结果:
Accuracy:0.72
9.多层神经网络:
常量初始化:
layers_dims = [12288, 20, 7, 5, 1] # 5-layer modelL层神经网络模型:
def L_layer_model(X, Y, layers_dims, learning_rate = 0.0075, num_iterations = 3000, print_cost=False):#lr was 0.009"""Implements a L-layer neural network: [LINEAR->RELU]*(L-1)->LINEAR->SIGMOID.Arguments:X -- data, numpy array of shape (number of examples, num_px * num_px * 3)Y -- true "label" vector (containing 0 if cat, 1 if non-cat), of shape (1, number of examples)layers_dims -- list containing the input size and each layer size, of length (number of layers + 1).learning_rate -- learning rate of the gradient descent update rulenum_iterations -- number of iterations of the optimization loopprint_cost -- if True, it prints the cost every 100 stepsReturns:parameters -- parameters learnt by the model. They can then be used to predict."""np.random.seed(1)costs = [] # keep track of cost# Parameters initialization.### START CODE HERE ###parameters = initialize_parameters_deep(layers_dims)### END CODE HERE #### Loop (gradient descent)for i in range(0, num_iterations):# Forward propagation: [LINEAR -> RELU]*(L-1) -> LINEAR -> SIGMOID.### START CODE HERE ### (≈ 1 line of code)AL, caches = L_model_forward(X, parameters)### END CODE HERE #### Compute cost.### START CODE HERE ### (≈ 1 line of code)cost = compute_cost(AL, Y)### END CODE HERE #### Backward propagation.### START CODE HERE ### (≈ 1 line of code)grads = L_model_backward(AL, Y, caches)### END CODE HERE #### Update parameters.### START CODE HERE ### (≈ 1 line of code)parameters = update_parameters(parameters, grads, learning_rate)### END CODE HERE #### Print the cost every 100 training exampleif print_cost and i % 100 == 0:print ("Cost after iteration %i: %f" %(i, cost))if print_cost and i % 100 == 0:costs.append(cost)# plot the costplt.plot(np.squeeze(costs))plt.ylabel('cost')plt.xlabel('iterations (per tens)')plt.title("Learning rate =" + str(learning_rate))plt.show()return parameters
训练:
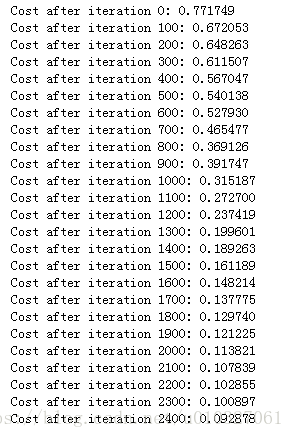
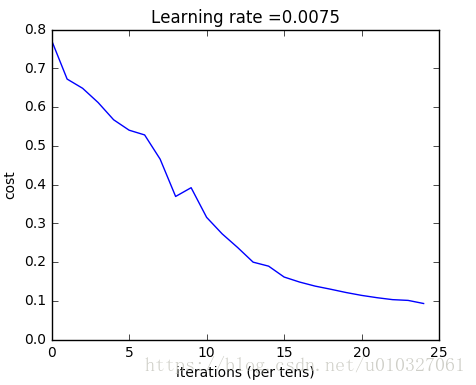
parameters = L_layer_model(train_x, train_y, layers_dims, num_iterations = 2500, print_cost = True)训练结果:
预测准确度:
对于训练集:
pred_train = predict(train_x, train_y, parameters)结果:
Accuracy:0.985645933014
对于测试集:
predictions_test = predict(test_x, test_y, parameters)结果:
Accuracy:0.8
10.结果分析:
print_mislabeled_images(classes, test_x, test_y, pred_test) #显示所有分类错误的图片其中,print_mislabeled_images的实现如下:
def print_mislabeled_images(classes, X, y, p):"""Plots images where predictions and truth were different.X -- datasety -- true labelsp -- predictions"""a = p + ymislabeled_indices = np.asarray(np.where(a == 1))plt.rcParams['figure.figsize'] = (40.0, 40.0) # set default size of plotsnum_images = len(mislabeled_indices[0])for i in range(num_images):index = mislabeled_indices[1][i]plt.subplot(2, num_images, i + 1)plt.imshow(X[:,index].reshape(64,64,3), interpolation='nearest')plt.axis('off')plt.title("Prediction: " + classes[int(p[0,index])].decode("utf-8") + " \n Class: " + classes[y[0,index]].decode("utf-8"))11.用自己的图片试试:
## START CODE HERE ##
my_image = "my_image.jpg" # change this to the name of your image file
my_label_y = [1] # the true class of your image (1 -> cat, 0 -> non-cat)
## END CODE HERE ##fname = "images/" + my_image
image = np.array(ndimage.imread(fname, flatten=False))
my_image = scipy.misc.imresize(image, size=(num_px,num_px)).reshape((num_px*num_px*3,1))
my_predicted_image = predict(my_image, my_label_y, parameters)plt.imshow(image)
print ("y = " + str(np.squeeze(my_predicted_image)) + ", your L-layer model predicts a \"" + classes[int(np.squeeze(my_predicted_image)),].decode("utf-8") + "\" picture.")这篇关于deeplearning.ai 吴恩达网上课程学习(八)——深层神经网络分类代码实战的文章就介绍到这儿,希望我们推荐的文章对编程师们有所帮助!