本文主要是介绍计算方法实验9:Romberg积分求解速度、位移,希望对大家解决编程问题提供一定的参考价值,需要的开发者们随着小编来一起学习吧!
任务

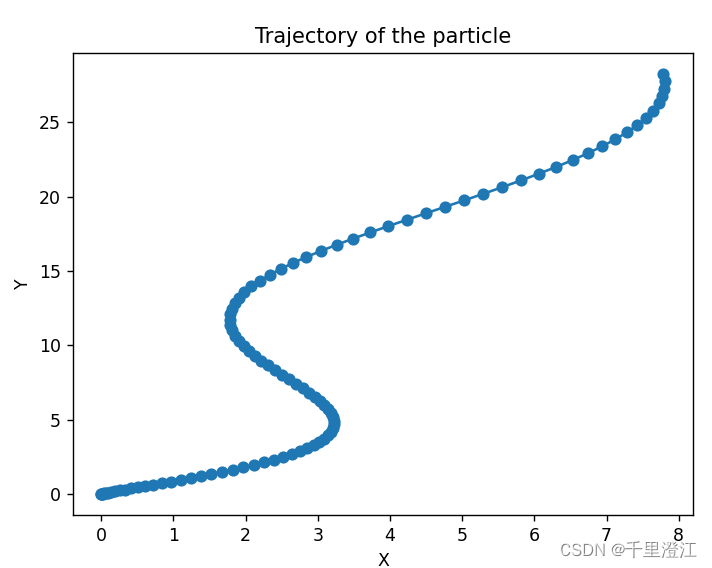
- 输出质点的轨迹 ( x ( t ) , y ( t ) ) , t ∈ { 0.1 , 0.2 , 0.3 , . . . , 10 } (x(t), y(t)), t\in \{0.1, 0.2, 0.3, ..., 10\} (x(t),y(t)),t∈{0.1,0.2,0.3,...,10},并在二维平面中画出该轨迹.
- 请比较M分别取4, 8, 12, 16, 20 时,Romberg积分达到要求精度的比例(达到误差要求的次数/调用总次数),分析该比例随M 的变化。
算法
现在要用数值方法求 ∫ a b f ( x ) d x \int_{a}^{b} f(x) \, dx ∫abf(x)dx,设 h = b − a n h=\frac{b-a}{n} h=nb−a,已知:
复化梯形积分 T n ( f ) = h [ 1 2 f ( a ) + ∑ i = 1 n − 1 f ( a + i h ) + 1 2 f ( b ) ] T_{n}\left(f\right)=h\left[\frac{1}{2}f\left(a\right)+\sum_{i=1}^{n-1}f\left(a+ih\right)+\frac{1}{2}f\left(b\right)\right] Tn(f)=h[21f(a)+∑i=1n−1f(a+ih)+21f(b)]、
复化Simpson积分 S n ( f ) = h 3 [ f ( a ) + 4 ∑ i = 0 m − 1 f ( x 2 i + 1 ) + 2 ∑ i = 1 m − 1 f ( x 2 i ) + f ( b ) ] S_{n}\left(f\right)=\frac{h}{3}\left[f\left(a\right)+4\sum_{i=0}^{m-1}f\left(x_{2i+1}\right)+2\sum_{i=1}^{m-1}f\left(x_{2i}\right)+f\left(b\right)\right] Sn(f)=3h[f(a)+4∑i=0m−1f(x2i+1)+2∑i=1m−1f(x2i)+f(b)].
将 ( T n ( f ) − T 2 n ( f ) ) ( T_n( f) - T_{2n}( f) ) (Tn(f)−T2n(f)) 作 为 T 2 n ( f ) T_{2n}(f) T2n(f)的修正值补充到 I ( f ) I(f) I(f),即
I ( f ) ≈ T 2 n ( f ) + 1 3 ( T 2 n ( f ) − T n ( f ) ) = 4 3 T 2 n − 1 3 T n = S n I(f)\approx T_{2n}(f)+\frac{1}{3}\left(T_{2n}\left(f\right)-T_{n}\left(f\right)\right)=\frac{4}{3}T_{2n}-\frac{1}{3}T_{n}=S_{n} I(f)≈T2n(f)+31(T2n(f)−Tn(f))=34T2n−31Tn=Sn
其结果是将复化梯形求积公式组合成复化 Simpson 求积公式, 截断误差由 O ( h 2 ) O(h^2) O(h2)提高到 O ( h 4 ) O(h^4) O(h4),这种手段称为外推算法,该算法在不增加计算量的前提下提高了误差的精度.不妨对 S 2 n ( f ) , S n ( f ) S_{2n}(f),S_n(f) S2n(f),Sn(f)再作一次线性组合:
I ( f ) − S n ( f ) = − f ( 4 ) ( ξ ) 180 h 4 ( b − a ) ≈ d h 4 I\left(f\right)-S_{n}\left(f\right)=-\frac{f^{\left(4\right)}\left(\xi\right)}{180}h^{4}\left(b-a\right)\approx dh^{4} I(f)−Sn(f)=−180f(4)(ξ)h4(b−a)≈dh4
I ( f ) − S 2 n ( f ) = − f ( 4 ) ( η ) 180 ( h 2 ) 4 ( b − a ) ≈ d ( h 2 ) 4 I(f)-S_{2n}(f)=-\frac{f^{(4)}(\eta)}{180}\left(\frac{h}{2}\right)^{4}(b-a)\approx d\left(\frac{h}{2}\right)^{4} I(f)−S2n(f)=−180f(4)(η)(2h)4(b−a)≈d(2h)4
I ( f ) ≈ S 2 n ( f ) + 1 15 ( S 2 n ( f ) − S n ( f ) ) = C n ( f ) I\left(f\right)\approx S_{2n}\left(f\right)+\frac{1}{15}\left(S_{2n}\left(f\right)-S_{n}\left(f\right)\right)=C_{n}\left(f\right) I(f)≈S2n(f)+151(S2n(f)−Sn(f))=Cn(f)
复化 Simpson 公式组成复化 Cotes 公式,其截断误差是 O ( h 6 ) . O(h^6). O(h6).同理对 Cotes公式进行线性组合:
I ( f ) − C 2 n ( f ) = e ( h 2 ) 6 I ( f ) − C n ( f ) = e h 6 I\left(f\right)-C_{2n}\left(f\right)=e\left(\frac{h}{2}\right)^{6}\\I\left(f\right)-C_{n}\left(f\right)=eh^{6} I(f)−C2n(f)=e(2h)6I(f)−Cn(f)=eh6
得到具有 7 次代数精度和截断误差是 O ( h 8 ) O(h^8) O(h8)的 Romberg 公式:
R n ( f ) = C 2 n ( f ) + 1 63 ( C 2 n ( f ) − C n ( f ) ) R_{n}\left(f\right)=C_{2n}\left(f\right)+\frac{1}{63}\left(C_{2n}\left(f\right)-C_{n}\left(f\right)\right) Rn(f)=C2n(f)+631(C2n(f)−Cn(f))
为了便于在计算机上实现 Romberg 算法,将 T n , S n , C n , R n , ⋯ T_n,S_n,C_n,R_n,\cdots Tn,Sn,Cn,Rn,⋯统一用 R k , j R_{k,j} Rk,j 表示,列标 j = 1 , 2 , 3 , 4 j=1,2,3,4 j=1,2,3,4分别表示梯形、Simpson、Cotes 、Romberg积分,行标 k k k表示步长 h k = h 2 k − 1 h_k=\frac h{2^{k-1}} hk=2k−1h,得到Romberg 计算公式:
R k , j = R k , j − 1 + R k , j − 1 − R k − 1 , j − 1 4 j − 1 − 1 , k = 2 , 3 , ⋯ R_{k,j}=R_{k,j-1}+\frac{R_{k,j-1}-R_{k-1,j-1}}{4^{j-1}-1},k=2,3,\cdots Rk,j=Rk,j−1+4j−1−1Rk,j−1−Rk−1,j−1,k=2,3,⋯
对每一个 k , j k,j k,j从 2 做到 k k k,一直做到 ∣ R k , k − R k − 1 , k − 1 ∣ |R_k,k-R_{k-1,k-1}| ∣Rk,k−Rk−1,k−1∣小于给定控制精度时停止计算.
注:下面代码中数组下标从0开始.
代码
C++实现Romberg积分运算
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;int satisfiedCount;long double ax(long double t);
long double ay(long double t);
long double romberg(function<long double(long double)> f, long double a, long double b, long double eps, int maxIter, bool isX);// Perform the Romberg integrationint main()
{long double eps = 1e-6, proportion;int maxIter;satisfiedCount = 0;maxIter = 4;cout << "maxIter = " << maxIter << endl;for (long double t = 0.1; t <= 10; t += 0.1) { long double vx = romberg(ax, 0, t, eps, maxIter, 0);long double vy = romberg(ay, 0, t, eps, maxIter, 0);long double x = romberg([&](long double t) { return vx; }, 0, t, eps, maxIter, 1);long double y = romberg([&](long double t) { return vy; }, 0, t, eps, maxIter, 0);cout << fixed << setprecision(1) << "At t = " << t << ", vx = " << setprecision(6) << vx << ", vy = " << setprecision(6) << vy << ", " << "(x, y) = (" << setprecision(6) << x << ", " << setprecision(6) << y << ")" << endl;}proportion = (long double)satisfiedCount / 100;cout << "At maxIter = " << maxIter << ", proportion of times the error requirement of x was satisfied: " << proportion << endl;satisfiedCount = 0;maxIter = 8;cout << "maxIter = " << maxIter << endl;ofstream outFile("trajectory.txt");for (long double t = 0.1; t <= 10; t += 0.1) {long double vx = romberg(ax, 0, t, eps, maxIter, 0);long double vy = romberg(ay, 0, t, eps, maxIter, 0);long double x = romberg([&](long double t) { return vx; }, 0, t, eps, maxIter, 1);long double y = romberg([&](long double t) { return vy; }, 0, t, eps, maxIter, 0);cout << fixed << setprecision(1) << "At t = " << t << ", vx = " << setprecision(6) << vx << ", vy = " << setprecision(6) << vy << ", " << "(x, y) = (" << setprecision(6) << x << ", " << setprecision(6) << y << ")" << endl;outFile << fixed << setprecision(6) << x << " " << y << "\n";//把坐标写入文件,方便画轨迹}proportion = (long double)satisfiedCount / 100;cout << "At maxIter = " << maxIter << ", proportion of times the error requirement of x was satisfied: " << proportion << endl;satisfiedCount = 0;maxIter = 12;cout << "maxIter = " << maxIter << endl;for (long double t = 0.1; t <= 10; t += 0.1) {long double vx = romberg(ax, 0, t, eps, maxIter, 0);long double vy = romberg(ay, 0, t, eps, maxIter, 0);long double x = romberg([&](long double t) { return vx; }, 0, t, eps, maxIter, 1);long double y = romberg([&](long double t) { return vy; }, 0, t, eps, maxIter, 0);cout << fixed << setprecision(1) << "At t = " << t << ", vx = " << setprecision(6) << vx << ", vy = " << setprecision(6) << vy << ", " << "(x, y) = (" << setprecision(6) << x << ", " << setprecision(6) << y << ")" << endl;}proportion = (long double)satisfiedCount / 100;cout << "At maxIter = " << maxIter << ", proportion of times the error requirement of x was satisfied: " << proportion << endl;satisfiedCount = 0;maxIter = 16;cout << "maxIter = " << maxIter << endl;for (long double t = 0.1; t <= 10; t += 0.1) {long double vx = romberg(ax, 0, t, eps, maxIter, 0);long double vy = romberg(ay, 0, t, eps, maxIter, 0);long double x = romberg([&](long double t) { return vx; }, 0, t, eps, maxIter, 1);long double y = romberg([&](long double t) { return vy; }, 0, t, eps, maxIter, 0);cout << fixed << setprecision(1) << "At t = " << t << ", vx = " << setprecision(6) << vx << ", vy = " << setprecision(6) << vy << ", " << "(x, y) = (" << setprecision(6) << x << ", " << setprecision(6) << y << ")" << endl;}proportion = (long double)satisfiedCount / 100;cout << "At maxIter = " << maxIter << ", proportion of times the error requirement of x was satisfied: " << proportion << endl;satisfiedCount = 0;maxIter = 20;cout << "maxIter = " << maxIter << endl;for (long double t = 0.1; t < 10.1; t += 0.1) {long double vx = romberg(ax, 0, t, eps, maxIter, 0);long double vy = romberg(ay, 0, t, eps, maxIter, 0);long double x = romberg([&](long double t) { return vx; }, 0, t, eps, maxIter, 1);long double y = romberg([&](long double t) { return vy; }, 0, t, eps, maxIter, 0);cout << fixed << setprecision(1) << "At t = " << t << ", vx = " << setprecision(6) << vx << ", vy = " << setprecision(6) << vy << ", " << "(x, y) = (" << setprecision(6) << x << ", " << setprecision(6) << y << ")" << endl;}proportion = (long double)satisfiedCount / 100;cout << "At maxIter = " << maxIter << ", proportion of times the error requirement of x was satisfied: " << proportion << endl;return 0;
}long double ax(long double t)
{return sin(t) / (1 + sqrt(t));
}long double ay(long double t)
{return log(t + 1) / (t + 1);
}// Perform the Romberg integration
long double romberg(function<long double(long double)> f, long double a, long double b, long double eps, int maxIter, bool isX) {long double h[maxIter], r[maxIter][maxIter];h[0] = b - a;r[0][0] = 0.5 * h[0] * (f(a) + f(b));for (int i = 1; i < maxIter; i++) {h[i] = 0.5 * h[i-1];long double sum = 0;for (int k = 0; k < pow(2, i-1); k++)sum += f(a + (2*k+1) * h[i]);r[i][0] = 0.5 * r[i-1][0] + h[i] * sum;for (int j = 1; j <= i; j++)r[i][j] = r[i][j-1] + (r[i][j-1] - r[i-1][j-1]) / (pow(4, j) - 1);if (i > 1 && fabs(r[i][i] - r[i-1][i-1]) < eps){if(isX)satisfiedCount++;return r[i][i];}}return r[maxIter-1][maxIter-1];
}
python可视化运动轨迹
import matplotlib.pyplot as pltwith open('trajectory.txt', 'r') as file:lines = file.readlines()x, y = zip(*[(float(line.split()[0]), float(line.split()[1])) for line in lines])plt.plot(x, y, 'o-')
plt.xlabel('X')
plt.ylabel('Y')
plt.title('Plot of points with smooth curve')
plt.show()
结果
部分运算结果

轨迹可视化结果
这篇关于计算方法实验9:Romberg积分求解速度、位移的文章就介绍到这儿,希望我们推荐的文章对编程师们有所帮助!