本文主要是介绍【深蓝学院】移动机器人运动规划--第3章 基于采样的路径规划--作业,希望对大家解决编程问题提供一定的参考价值,需要的开发者们随着小编来一起学习吧!
0. Assignment
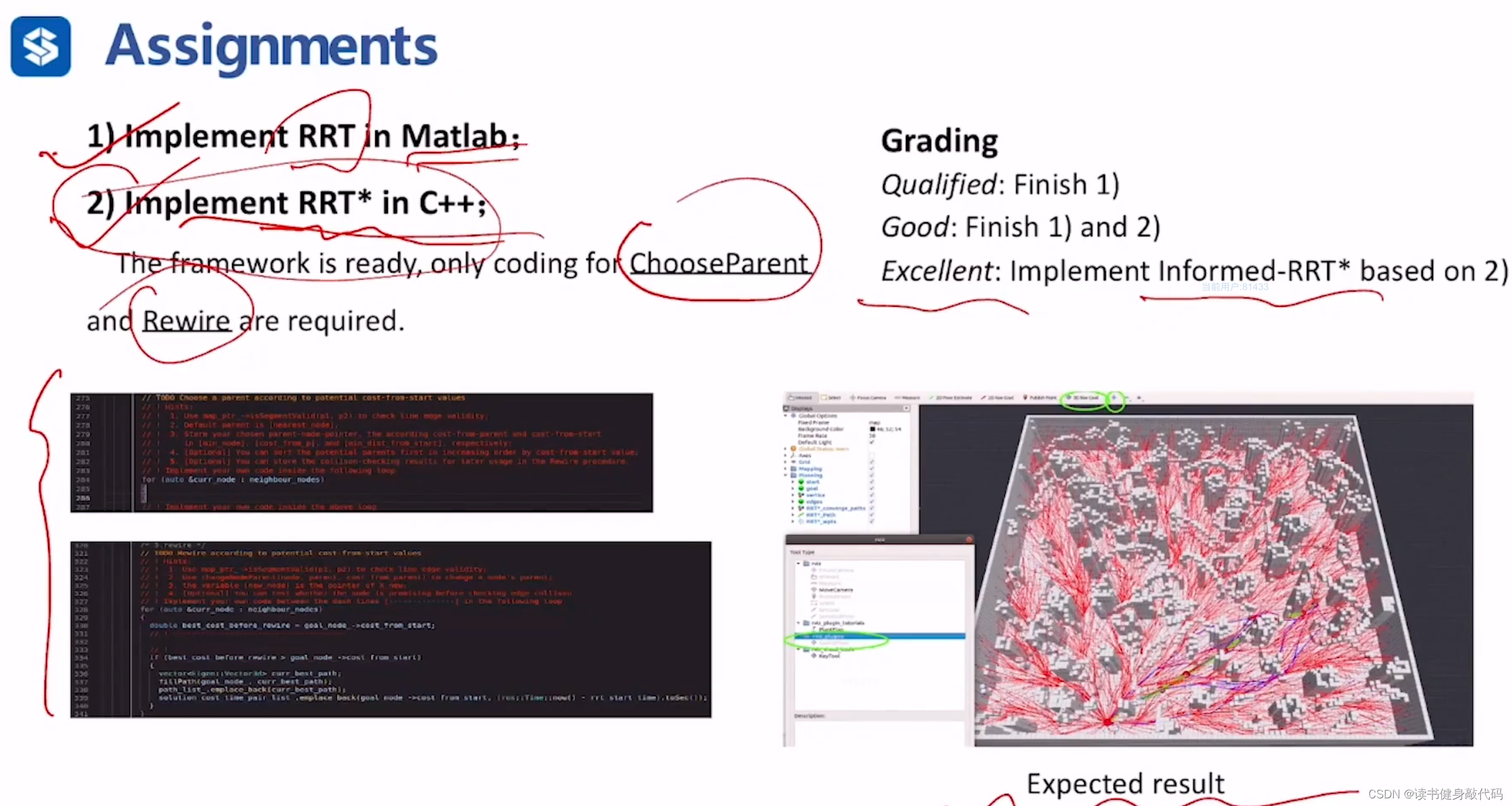
T1. MATLAB实现RRT
1.1 GPT-4任务分析

RRT伪代码:
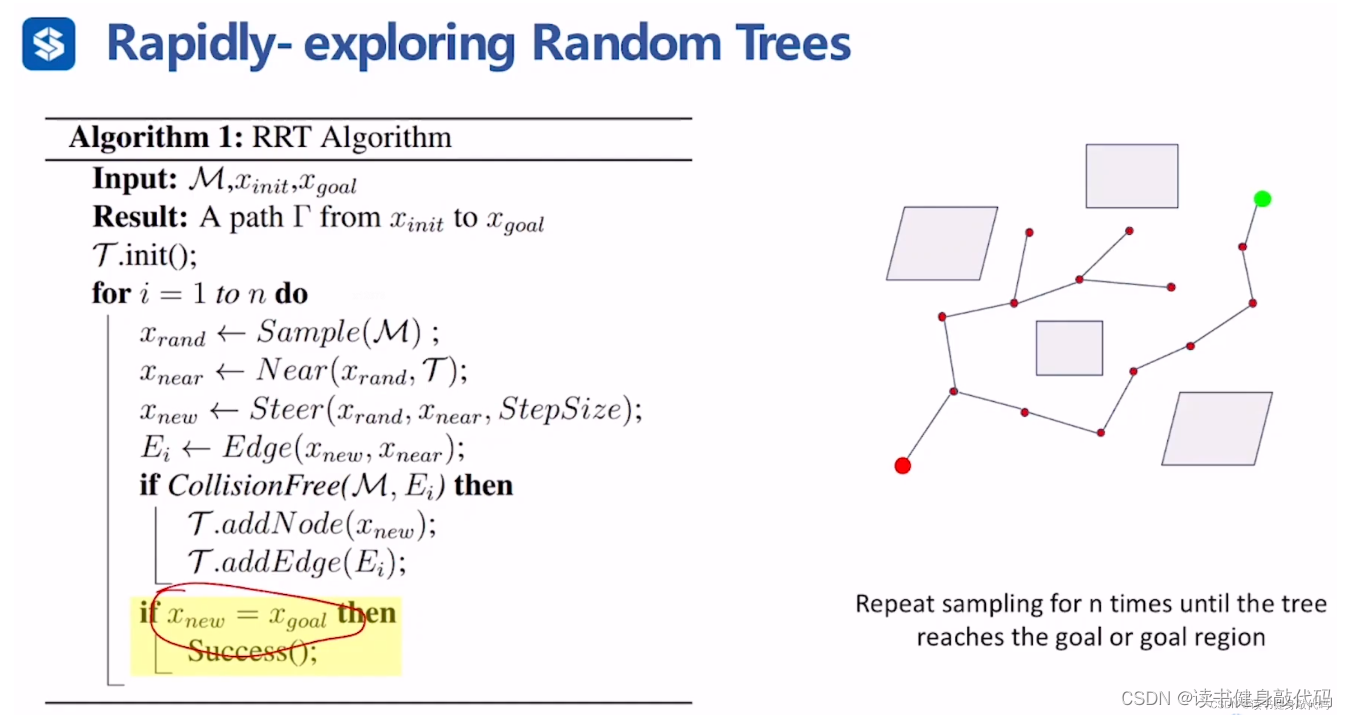
任务1即使用matlab实现RRT,结合作业所给框架,简单梳理,可结合1.2代码理解:
- 设置start,goal,near to goal threshold
Thr,step的步长Delta - Tree初始化,数据结构:2D xy坐标,父节点xy坐标,父节点到该节点距离,父节点的index
- 建树部分需要我们完成:
- step1完成伪代码的
Sample,得到x_rand - step2完成伪代码的
Near,具体操作:遍历树中所有Nodes,计算每个Nodes到x_rand的欧氏距离dst,取最小的,记录dst值和index - step3完成伪代码的
Steer,结合collisionChecking.m中进行collision checking的方法,计算方向并更新x_new - step 4: 将x_new插入树T,对应伪代码Edge,CollisionFree,collision check直接调用函数,不赘述。
- step 5: 检查是否到达目标点附近,计算欧氏距离与
Thr比较。 - step 6:绘图,不赘述。
- step1完成伪代码的
- 反向查询并绘图:
找到goal之后,从goal回溯到父节点为start的节点,依次坐标记录到path中,最后调用MATLAB的end关键字插入一个新的node,即start,并记录start坐标,所以path中按照index顺序实际上是存储的inverse path。
找到的path绘图为蓝色,结束。%已经遍历完path中除了起点外的所有node,end+1表示新增一个元素,所以后面再调用end时就是访问添加后的最后一个元素了 path.pos(end+1).x = x_I; path.pos(end).y = y_I;
1.2 代码
RRT.m代码:
% RRT算法
%% 流程初始化
clc
clear all; close all;
x_I=1; y_I=1; % 设置初始点
x_G=799; y_G=799; % 设置目标点(可尝试修改终点)
Thr=50; % 设置目标点阈值,用法:若当前节点和终点的欧式距离小于Thr,则跳出当前for循环
Delta= 30; % 设置扩展步长 应该是stepsize
%% 建树初始化
T.v(1).x = x_I; % T是我们要做的树,v是节点,这里先把起始点加入到T里面来
T.v(1).y = y_I;
T.v(1).xPrev = x_I; % 起始节点的父节点仍然是其本身
T.v(1).yPrev = y_I;
T.v(1).dist=0; % 从父节点到该节点的距离,这里可取欧氏距离
T.v(1).indPrev = 0; % 这个变量什么意思?根据下面代码来看,indPrev表示indexPrev,父节点的index
%% 开始构建树,作业部分
figure(1);
ImpRgb=imread('generate_RRT.png');
Imp=rgb2gray(ImpRgb); %地图,255为白色,free部分
imshow(Imp)
xL=size(Imp,2);%地图x轴长度 列数
yL=size(Imp,1);%地图y轴长度 行数
hold on
plot(x_I, y_I, 'ro', 'MarkerSize',10, 'MarkerFaceColor','r');
plot(x_G, y_G, 'go', 'MarkerSize',10, 'MarkerFaceColor','g');% 绘制起点和目标点
count=1;%记录树T中节点的个数
bFind = false;for iter = 1:3000x_rand=[];%Step 1: 在地图中随机采样一个点x_rand%提示:用(x_rand(1),x_rand(2))表示环境中采样点的坐标x_rand(1) = rand * (xL-1) +1;%-1是为了保证随机生成的坐标不会超出地图的边界,+1是因为索引是从1开始的x_rand(2) = rand * (yL-1) +1;x_near=[];%Step 2: 遍历树,从树中找到最近邻近点x_near(计算每个节点到 x_rand 的距离,找出最近的一个节点作为 x_near。)%提示:x_near已经在树T里numNodes = length(T.v);nearest_dst = Inf;nearest_idx = 1;for node_idx = 1:numNodestmp_dist = sqrt(sum(([T.v(node_idx).x T.v(node_idx).y]-[x_rand(1) x_rand(2)]).^2));%T中每个节点到x_rand的欧氏距离if tmp_dist < nearest_dstnearest_dst = tmp_dist;nearest_idx = node_idx;endendx_near(1) = T.v(nearest_idx).x;x_near(2) = T.v(nearest_idx).y;%Step 3: 扩展得到x_new节点%提示:注意使用扩展步长Deltadir=atan2(x_rand(1)-x_near(1),x_rand(2)-x_near(2));x_new = x_near + Delta.*[sin(dir) cos(dir)];%检查节点是否是collision-free(即是否feasiable),如果不collision-free,则继续下一次采样if ~collisionChecking(x_near,x_new,Imp) continue;endcount=count+1;%Step 4: 将x_new插入树T %提示:新节点x_new的父节点是x_nearT.v(count).x = x_new(1);T.v(count).y = x_new(2);T.v(count).xPrev = x_I;T.v(count).yPrev = y_I;T.v(count).dist = nearest_dst;T.v(count).indPrev = nearest_idx;%Step 5:检查是否到达目标点附近 %提示:注意使用目标点阈值Thr,若当前节点和终点的欧式距离小于Thr,则跳出当前for循环(退出前需要绘制出x_near和x_new之间的路径)check_dist = calDist(x_new, [x_G y_G]);if check_dist < Thrplot([x_near(1); x_new(1);], [x_near(2); x_new(2)], 'r', 'Linewidth', 3);hold on;bFind = true;break;end%Step 6:将x_near和x_new之间的路径画出来%提示 1:使用plot绘制,因为要多次在同一张图上绘制线段,所以每次使用plot后需要接上hold on命令%提示 2:在判断终点条件弹出for循环前,记得把x_near和x_new之间的路径画出来plot([x_near(1); x_new(1);], [x_near(2); x_new(2)], 'r', 'Linewidth', 3);pause(0.05); %暂停一会,使得RRT扩展过程容易观察
endif T.v(count).x == T.v(end).x && T.v(count).y == T.v(end).yfprintf('T.v(count) == T.v(end), T.v(count): (%f, %f), T.v(end): (%f, %f)\n', T.v(count).x, T.v(count).y,T.v(end).x, T.v(end).y);
elsefprintf('T.v(count) != T.v(end)\n');
end%% 路径已经找到,反向查询
if bFindpath.pos(1).x = x_G; path.pos(1).y = y_G;path.pos(2).x = T.v(end).x; path.pos(2).y = T.v(end).y;%关键字end用于表示pathIndex = T.v(end).indPrev; % 终点加入路径j=0;while 1path.pos(j+3).x = T.v(pathIndex).x;path.pos(j+3).y = T.v(pathIndex).y;pathIndex = T.v(pathIndex).indPrev;if pathIndex == 1breakendj=j+1;end % 沿终点回溯到起点% 起点加入路径path.pos(end+1).x = x_I; %已经遍历完path中除了起点外的所有node,end+1表示新增一个元素,所以后面再调用end时就是访问添加后的最后一个元素了,没毛病path.pos(end).y = y_I;for j = 2:length(path.pos)plot([path.pos(j).x; path.pos(j-1).x;], [path.pos(j).y; path.pos(j-1).y], 'b', 'Linewidth', 3);end
elsedisp('Error, no path found!');
end
calDist.m代码:
function dist=calDist(startPose,goalPose)
dist=sqrt(sum((startPose-goalPose).^2));
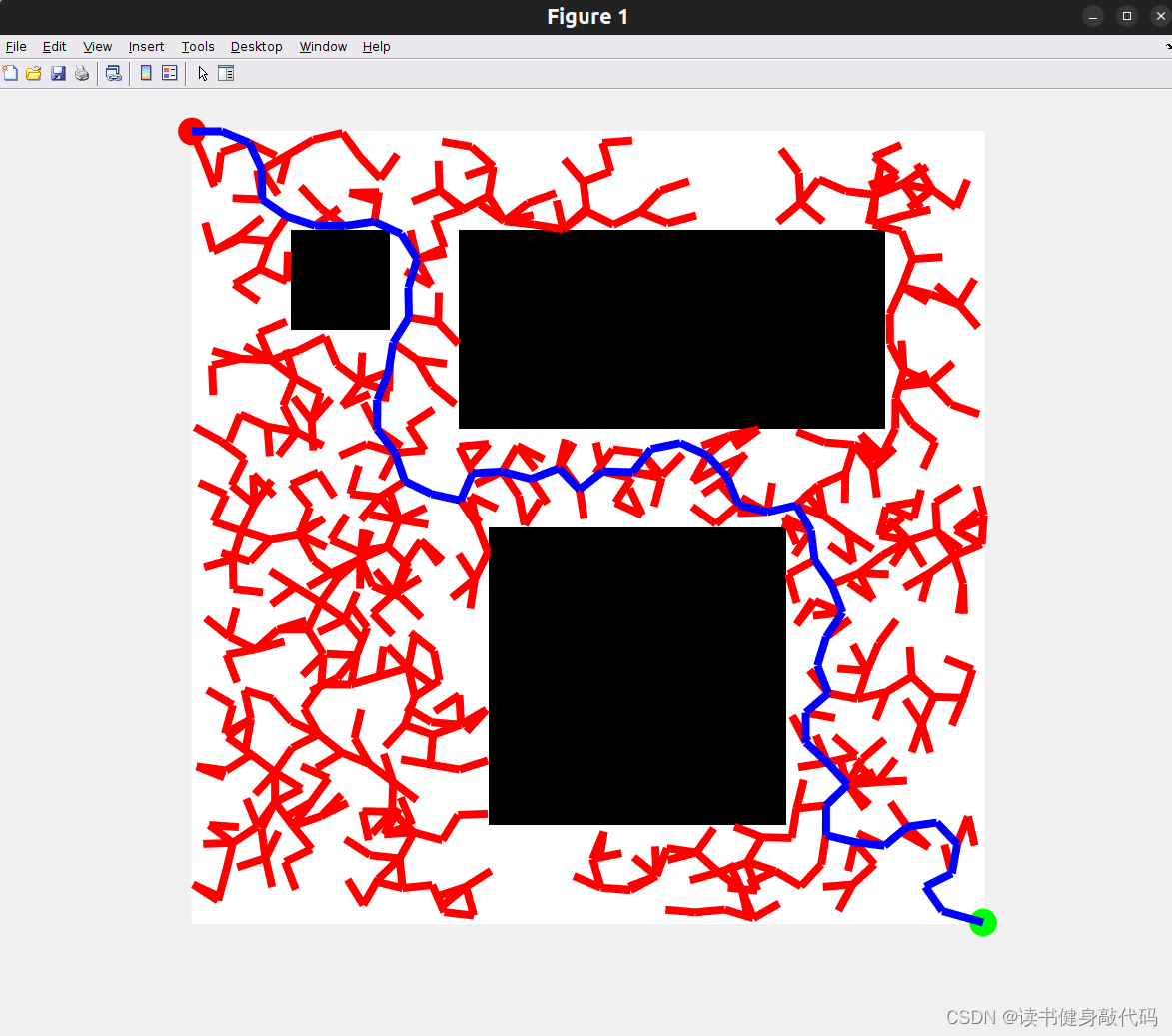
1.3实验结果
如下所示:
1.4 更改Map
根据其中加载的数据,我们可以使用OpenCV生成其他类型的地图,下面是代码,在createRRTMap可以简单更改障碍物形状,上面实验使用的是我自己生成的map。
#include <vector>
#include <stdio.h>
#include<opencv2/opencv.hpp>
using namespace cv;
using namespace std;#include <opencv2/core/core.hpp>
#include <opencv2/highgui.hpp>
using namespace cv;void createRRTMap(Mat &mat)
{mat = cv::Mat(mat.rows, mat.cols, CV_8UC1, cv::Scalar(255)).clone();for(int i = 100; i < 200; ++i)for(int j = 100; j < 200; ++j)mat.at<uint8_t>(i, j) = 0;for(int i = 400; i < 700; ++i)for(int j = 300; j < 600; ++j)mat.at<uint8_t>(i, j) = 0;for(int i = 100; i < 300; ++i)for(int j = 270; j < 700; ++j)mat.at<uint8_t>(i, j) = 0;
}int main( )
{Mat matRRT(800, 800, CV_8UC1);Mat matRRT_rgb(800, 800, CV_8UC1);createRRTMap(matRRT);cv::cvtColor(matRRT, matRRT_rgb, cv::COLOR_GRAY2BGR);vector<int>compression_params;compression_params.push_back(CV_IMWRITE_JPEG_QUALITY);//对于PNG格式的图片,表示压缩级别,值为[0, 9],值越大,尺寸越小,压缩时间越长compression_params.push_back(95);//显示图片try{imwrite("generate_RRT.png", matRRT_rgb, compression_params);imshow("生成的RRT png图",matRRT_rgb);fprintf(stdout,"PNG图片文件的alpha数据保存完毕~\n可以在工程目录下查看由imwrite函数生成的图片\n");waitKey(0);}catch(runtime_error& ex) {fprintf(stderr,"图像转换成PNG格式发生错误:%s\n", ex.what());return 1;}return 0;
}
T2. C++实现RRT*
2.1 关于K-D树的介绍
K-D树(K-Dimensional Tree的简称)是一种用于组织k维空间中的点的数据结构。这种数据结构方便了对多维空间的快速搜索,经常被用于各种数据库和计算机视觉中的快速检索任务。
K-D树是一棵二叉树,其中每个节点都是k维数值点。构造K-D树时,数据会递归地被划分成两个半空间,这个过程类似于二分查找算法。构建树的一个典型方法是选择一个维度,并在这个维度上找到位于中间的值作为划分点,将数据集分为两个子集,然后在子集上重复这个过程,但每次选择不同的维度,直到满足某个终止条件(如每个节点下的点的数量小于一定阈值)。
在K-D树的每个节点上,选择的维度和该维度上的值定义了一个超平面,这个超平面将空间分成两半,每半空间对应树中的一个分支。
搜索时,如果要找的点在划分平面的一边,就进入对应的子树继续搜索。这样可以忽略掉空间中的一大半区域,从而快速缩小搜索范围。不过需要注意的是,最近邻搜索时可能需要检查两边的子树,因为最近的点可能在划分平面的另一侧。
K-D树的优势是在处理多维数据点时提供了比线性搜索更快的查询时间,尤其是在数据点数量很大时。然而,当维数增加时,K-D树的效率会下降,这种现象被称为“维度的诅咒”。在这种情况下,可能需要考虑其他类型的数据结构,如球树或近似最近邻方法。
总结:K-D树是一颗二叉树,其中每个节点都是k维数值点,便于高维查找,当使用最近邻搜索时可能需要检查两边的子树,因为最近的点可能在划分平面的另一侧。维数增加会导致查找效率下降。
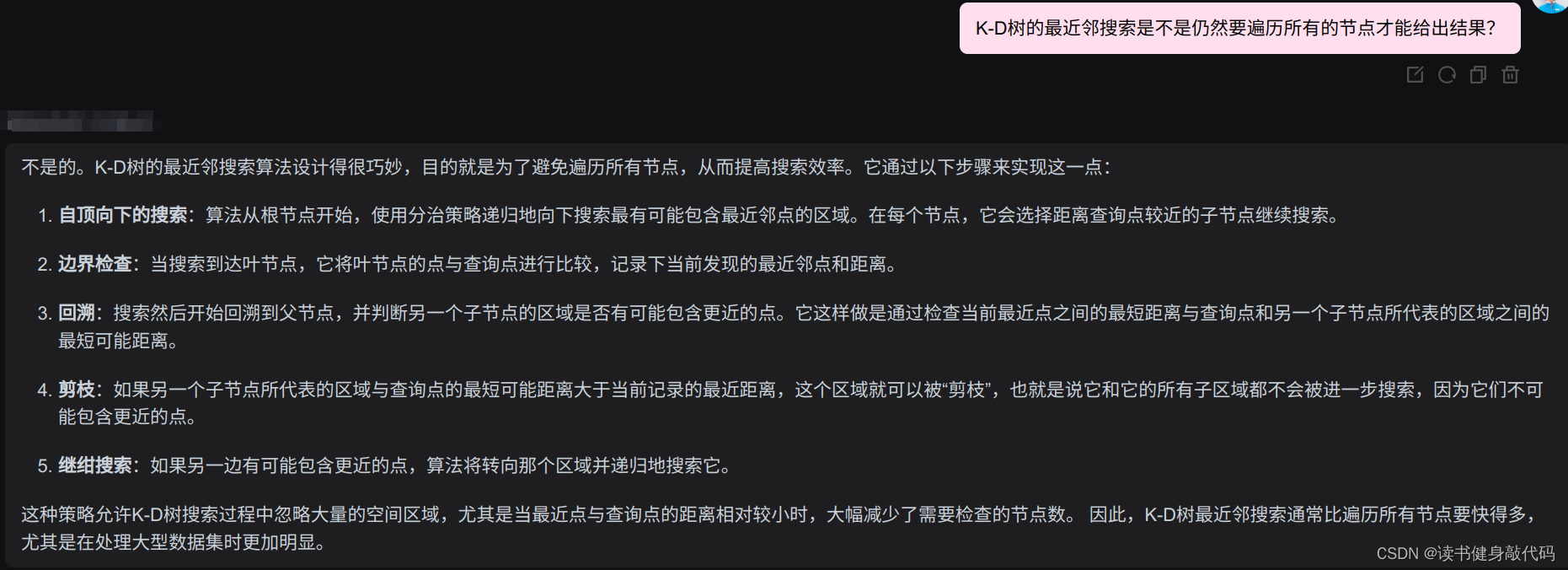
2.2 kd_nearest3 执行K-D树最近邻搜索
kd_nearest_i()具体搜索-
搜索过程,分割不会减小搜索空间维度。
步骤:整个空间,分割空间,子区域,左/右子树的(超)矩形 -
近边界(nearer boundary)和远边界(farther boundary)的更新
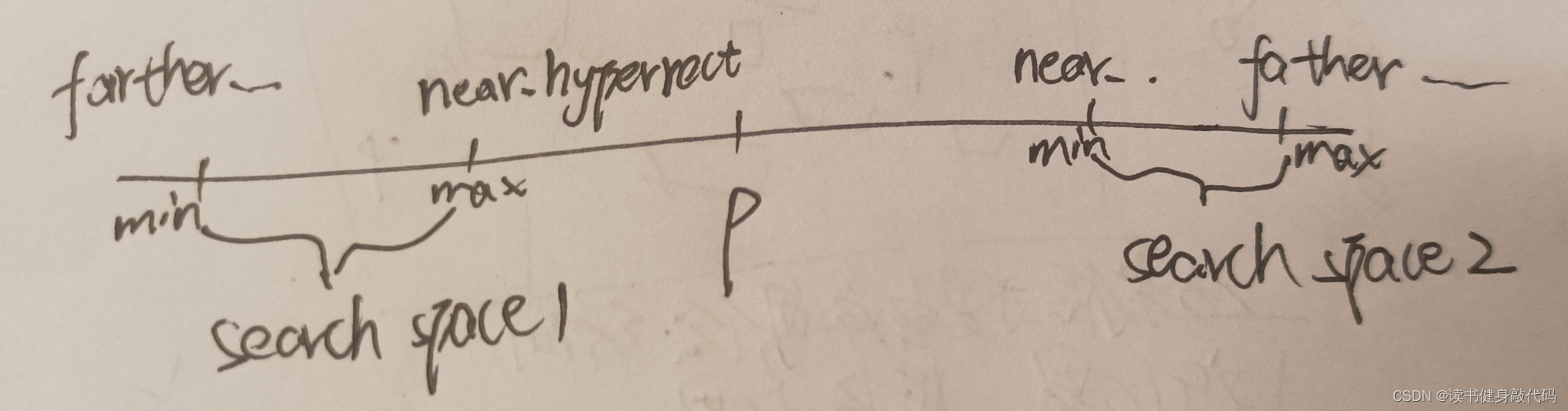
-
K-D树搜索结束条件,效率高,大数据量搜索效率提升明显,随着维度升高,效率下降。
-
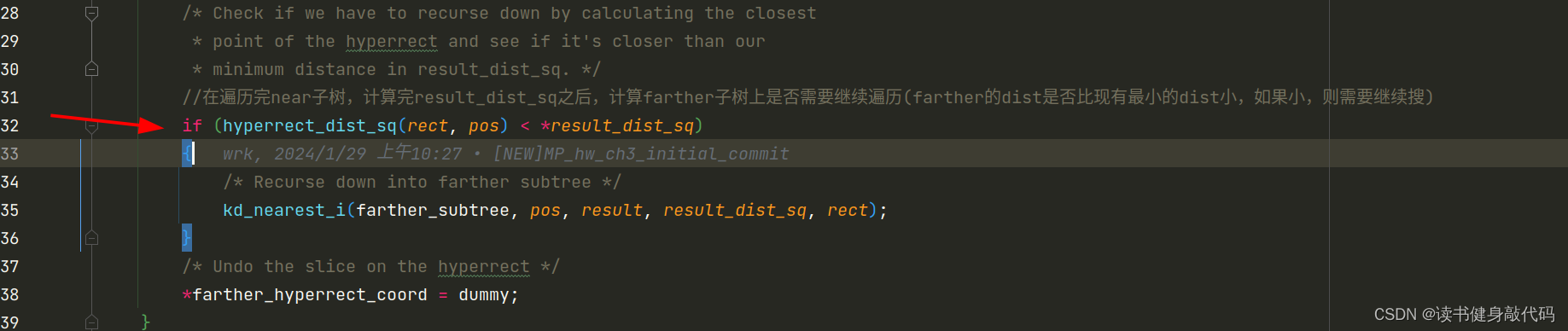
static void kd_nearest_i(struct kdnode *node, const double *pos, struct kdnode **result, double *result_dist_sq, struct kdhyperrect *rect)
{int dir = node->dir;//在第几维上分割搜索空间int i;double dummy, dist_sq;struct kdnode *nearer_subtree, *farther_subtree;double *nearer_hyperrect_coord, *farther_hyperrect_coord;//近边界和远边界/* Decide whether to go left or right in the tree */dummy = pos[dir] - node->pos[dir];if (dummy <= 0) //pos <= node, pos放node左边{nearer_subtree = node->left;farther_subtree = node->right;//在第dir维上更新划分依据:rect->max离node更近,rect->min离node更远,这是指针操作,不是数值加法,//指针指向了新的划分边界,近边界是rect的第dir维max,远边界是dir维minnearer_hyperrect_coord = rect->max + dir;farther_hyperrect_coord = rect->min + dir;}else{nearer_subtree = node->right;farther_subtree = node->left;nearer_hyperrect_coord = rect->min + dir;farther_hyperrect_coord = rect->max + dir;}if (nearer_subtree){/* Slice the hyperrect to get the hyperrect of the nearer subtree */ //递归时其实已经改变了rect的值dummy = *nearer_hyperrect_coord;//备份*nearer_hyperrect_coord = node->pos[dir];//更新rect的judge的维度的值,下一次递归使用这新维度的值来进行judge,新维度上该值为本次root节点上该维度的值(相当于本次用过了这个维度)/* Recurse down into nearer subtree */kd_nearest_i(nearer_subtree, pos, result, result_dist_sq, rect);/* Undo the slice */*nearer_hyperrect_coord = dummy;}/* Check the distance of the point at the current node, compare it* with our best so far */dist_sq = 0;for (i = 0; i < rect->dim; i++){dist_sq += SQ(node->pos[i] - pos[i]);}if (dist_sq < *result_dist_sq){*result = node;*result_dist_sq = dist_sq;}if (farther_subtree){/* Get the hyperrect of the farther subtree */dummy = *farther_hyperrect_coord;*farther_hyperrect_coord = node->pos[dir];/* Check if we have to recurse down by calculating the closest* point of the hyperrect and see if it's closer than our* minimum distance in result_dist_sq. *///在遍历完near子树,计算完result_dist_sq之后,计算farther子树上是否需要继续遍历(farther的dist是否比现有最小的dist小,如果小,则需要继续搜)if (hyperrect_dist_sq(rect, pos) < *result_dist_sq){/* Recurse down into farther subtree */kd_nearest_i(farther_subtree, pos, result, result_dist_sq, rect);}/* Undo the slice on the hyperrect */*farther_hyperrect_coord = dummy;}
}
- 搜索结束后
rlist_insert插入resultnode,插入之后,list->next指向的是itemd所指的kdnode kd_res_rewind使得rset指向result的knode。- void* 类型安全转换为
RRTNode3DPtr类型,即TreeNode*类型。
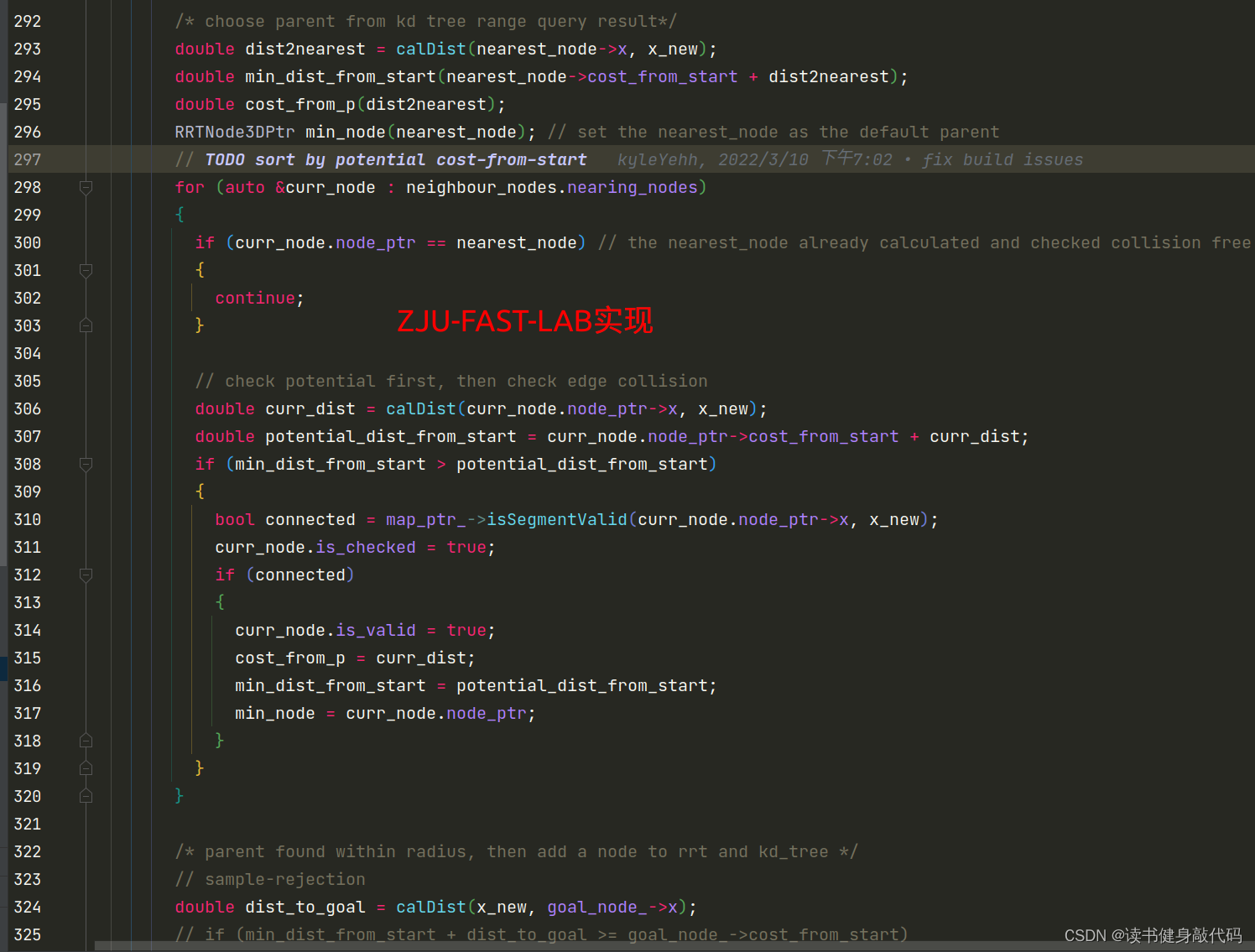
2.3 chooseParent部分实现
该部分作业中的代码和ZJU-FAST-LAB中的代码有所区别,后者主要考虑其他算法的兼容性,在数据结构上有所不同,而作业主要针对RRT*,所以数据结构更简单。
理解了K-D tree的数据结构以及RRT* 的改进点之后,实现该部分代码比较容易,这里使用了std::multimap,先计算所有range内的edge dist并插入std::multimap中,会自动按key升序排序,然后从前到后进行collision checking,找到第一个collision-free的就找到了Parent。
// TODO Choose a parent according to potential cost-from-start values// ! Hints:// ! 1. Use map_ptr_->isSegmentValid(p1, p2) to check line edge validity;// ! 2. Default parent is [nearest_node];// ! 3. Store your chosen parent-node-pointer, the according cost-from-parent and cost-from-start// ! in [min_node], [cost_from_p], and [min_dist_from_start], respectively;// ! 4. [Optional] You can sort the potential parents first in increasing order by cost-from-start value;// ! 5. [Optional] You can store the collison-checking results for later usage in the Rewire procedure.// ! Implement your own code inside the following loopif(use_chooseParent_) {std::multimap<double, std::pair<RRTNode3DPtr, double>> mmp_neighbor_nodes;for (auto &curr_node : neighbour_nodes){double dist2curr_node = calDist(curr_node->x, x_new);double dist_from_start = curr_node->cost_from_start + dist2curr_node;//不同前驱的更新的cost-to-comedouble tmp_cost_from_p = dist2curr_node;//cost-from-parent,即edge_costmmp_neighbor_nodes.insert(std::make_pair(dist_from_start, std::make_pair(curr_node, tmp_cost_from_p)));}int mmp_count = 0;for(auto &each_item : mmp_neighbor_nodes) {++mmp_count;if(map_ptr_->isSegmentValid(x_new, each_item.second.first->x)) {min_dist_from_start = each_item.first;cost_from_p = each_item.second.second;min_node = each_item.second.first;ROS_DEBUG("\nmmp_count: %d, neighbor size: %lu, collision-free, \tcur_dist_from_start: %.10f, cur_cost_from_p: %.10f",mmp_count, neighbour_nodes.size(), each_item.first, each_item.second.second);break;} else {ROS_DEBUG("\nmmp_count: %d, neighbor size: %lu, collisioned, continue, \tcur_dist_from_start: %.10f, cur_cost_from_p: %.10f",mmp_count, neighbour_nodes.size(), each_item.first, each_item.second.second);}}}// ! Implement your own code inside the above loop
2.4 Rewire
该部分代码如下:
/* 3.rewire */// TODO Rewire according to potential cost-from-start values// ! Hints:// ! 1. Use map_ptr_->isSegmentValid(p1, p2) to check line edge validity;// ! 2. Use changeNodeParent(node, parent, cost_from_parent) to change a node's parent;// ! 3. the variable [new_node] is the pointer of X_new;// ! 4. [Optional] You can test whether the node is promising before checking edge collison.// ! Implement your own code between the dash lines [--------------] in the following loop//如果没有rewire,这里的RRT*其实和RRT没有太大区别,唯一的区别就是选取parent时使用K-D树选取了最近邻的node,//而RRT遍历所有现有node,直接选取距离sampling node欧氏距离最近的node作为parentif(use_rewire_) {for (auto &curr_node : neighbour_nodes){double best_cost_before_rewire = goal_node_->cost_from_start;// ! -------------------------------------double cost_new_node_to_neighbor = calDist(new_node->x, curr_node->x);bool is_connected2neighbor = map_ptr_->isSegmentValid(new_node->x, goal_node_->x);bool is_better_path = curr_node->cost_from_start > cost_new_node_to_neighbor + new_node->cost_from_start;if(is_connected2neighbor && is_better_path) {changeNodeParent(curr_node, new_node, cost_new_node_to_neighbor);}// ! -------------------------------------//找到更优的解之后进行更新if (best_cost_before_rewire > goal_node_->cost_from_start){vector<Eigen::Vector3d> curr_best_path;fillPath(goal_node_, curr_best_path);path_list_.emplace_back(curr_best_path);solution_cost_time_pair_list_.emplace_back(goal_node_->cost_from_start, (ros::Time::now() - rrt_start_time).toSec());}}}/* end of rewire */
涉及到changeNodeParent()更改节点A的父节点,以及节点A的子节点的cost_from_start值。
因为改了节点A的父节点,则节点A的子节点的cost_from_start都会改变,需要更新,使用队列,层序遍历,changeNodeParent少量注释:
void changeNodeParent(RRTNode3DPtr &node, RRTNode3DPtr &parent, const double &cost_from_parent)
{//更改node A的parent,首先需要删掉node A与之前parent的edge,再添加新的edge,这里的操作就是remove旧nodeif (node->parent)node->parent->children.remove(node); //DON'T FORGET THIS, remove it form its parent's children list(因为是改变了前驱节点,所以之前的前驱节点要删掉)node->parent = parent;node->cost_from_parent = cost_from_parent;node->cost_from_start = parent->cost_from_start + cost_from_parent;parent->children.push_back(node);// for all its descedants, change the cost_from_start and tau_from_start; 改了节点A的父节点,则节点A的子节点的cost_from_start都会改变,需要更新,使用队列,层序遍历RRTNode3DPtr descendant(node);std::queue<RRTNode3DPtr> Q;Q.push(descendant);while (!Q.empty()){descendant = Q.front();Q.pop();for (const auto &leafptr : descendant->children){leafptr->cost_from_start = leafptr->cost_from_parent + descendant->cost_from_start;//主要是descendant->cost_from_start变了Q.push(leafptr);}}
}
2.5 对比实验
进行以下两组对比实验:
- 相同地图和start,不同goal时,RRT*有无rewire的对比
- 相同地图和start,不同goal时,RRT于RRT* 的对比(使用ZJU-FAST-LAB实验室的公开工作完成,其中RRT与RRT* 数据结构均为K-D tree)
2.5.1 实验1
由于RRT* 相较于RRT的改进主要在chooseParent和Rewire,而其中Rewire起主要作用,因为如果没有rewire,RRT*与RRT区别不大,所以实验1基于课程所给代码,通过是否添加Rewire来对比Rewire的优化效果。
fix地图和start(-15.4994, -20.669, 0.4),由于ramdom sampling存在随机性,所以针对每个fixed goal,每种算法跑5次,最终取均值,共选取4个不同位置的goal,如下图所示
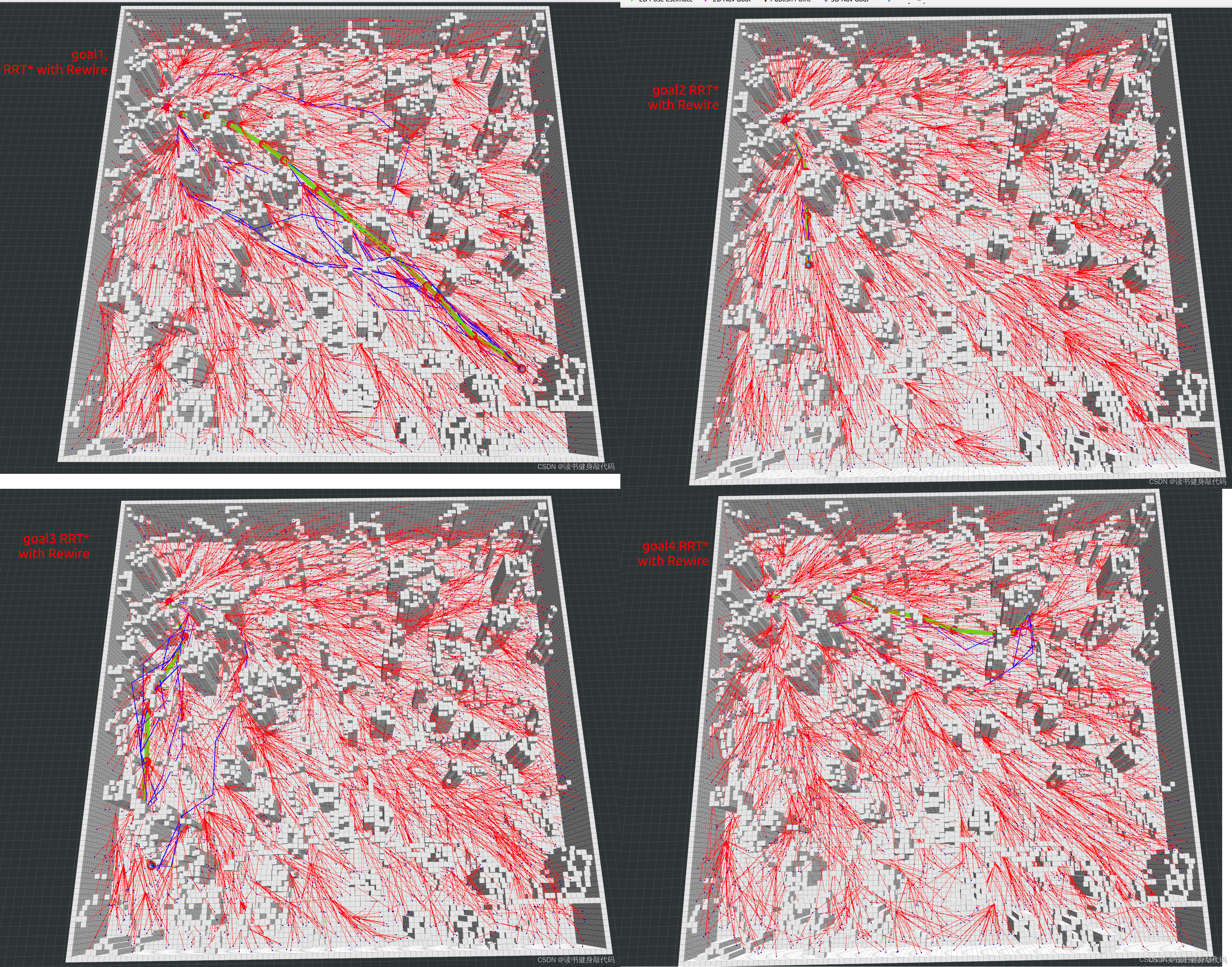
- goal1:16.0521, 20.033, 0.64
RRT* without Rewire
| 组号 | first path time cost(ms) | first path len | final path len |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0.00186324 | 56.4169 | 54.0687 |
| 2 | 0.00213942 | 71.3945 | 55.3649 |
| 3 | 0.00082703 | 60.82 | 54.9993 |
| 4 | 0.000634712 | 56.5303 | 55.5882 |
| 5 | 0.000444331 | 63.243 | 54.713 |
| avg | 0.005908733 | 61.68094 | 54.94682 |
RRT* with Rewire
| 组号 | first path time cost(ms) | first path len | final path len |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0.00129776 | 58.2626 | 53.4338 |
| 2 | 0.00220048 | 60.8224 | 53.6165 |
| 3 | 0.000686174 | 54.2649 | 52.3802 |
| 4 | 0.000682761 | 59.3242 | 53.2708 |
| 5 | 0.000867198 | 58.2678 | 52.2388 |
| avg | 0.0011468 | 58.188 | 52.988 |
goal1 RRT* with Rewire 与 RRT* without Rewire对比,first path time cost无明显差别,有Rewire操作时,final path len更优。
- goal2:2.6292, -16.682, 0.82
RRT* without Rewire
| 组号 | first path time cost(ms) | first path len | final path len |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0.000153107 | 20.2612 | 19.0458 |
| 2 | 0.000514853 | 20.7946 | 18.892 |
| 3 | 0.00013657 | 23.8047 | 19.7088 |
| 4 | 0.00010811 | 20.138 | 19.326 |
| 5 | 0.000312741 | 19.6928 | 19.1867 |
| avg | 0.000245 | 20.9383 | 19.2319 |
RRT* Rewire
| 组号 | first path time cost(ms) | first path len | final path len |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0.00254839 | 21.3555 | 19.0077 |
| 2 | 0.0015859 | 62.134 | 18.8554 |
| 3 | 0.000816326 | 52.7366 | 18.9015 |
| 4 | 5.5032e-05 | 24.2389 | 18.9784 |
| 5 | 0.000101631 | 19.7808 | 19.0004 |
| avg | 0.0010 | 36.0492 | 18.9487 |
goal2 RRT* with Rewire时first path time cost稍长,说明在这项相关性不强,仍然是with Rewire时final path更优。
- goal3:16.0176, -20.1551, 0.32
RRT* without Rewire
| 组号 | first path time cost(ms) | first path len | final path len |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0.00659001 | 42.741 | 32.7316 |
| 2 | 0.00263363 | 53.1167 | 35.0014 |
| 3 | 0.000998615 | 44.2444 | 33.8431 |
| 4 | 0.000316079 | 55.4378 | 33.43 |
| 5 | 0.000968875 | 37.1436 | 34.6206 |
| avg | 0.0023 | 46.5367 | 33.9253 |
RRT* with Rewire
| 组号 | first path time cost(ms) | first path len | final path len |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0.0143187 | 56.0554 | 32.9007 |
| 2 | 0.00205175 | 43.534 | 33.8006 |
| 3 | 0.0043136 | 40.4332 | 33.0486 |
| 4 | 0.000946076 | 41.5242 | 33.6446 |
| 5 | 0.000371171 | 45.0295 | 32.6621 |
| avg | 0.0044 | 45.3153 | 33.2113 |
goal3 with Rewire时path len更优。
- goal4:-12.3907 10.2501 1.74
RRT* without Rewire
| 组号 | first path time cost(ms) | first path len | final path len |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0.000236902 | 52.8212 | 33.3467 |
| 2 | 0.000526351 | 48.6854 | 35.6416 |
| 3 | 0.000134126 | 42.5125 | 34.8541 |
| 4 | 0.00014271 | 45.0459 | 33.6717 |
| 5 | 9.3826e-05 | 35.1948 | 33.7898 |
| avg | 0.0002 | 44.8520 | 34.2608 |
RRT* with Rewire
| 组号 | first path time cost(ms) | first path len | final path len |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0.00728627 | 49.9614 | 34.5846 |
| 2 | 0.000678839 | 41.107 | 34.659 |
| 3 | 0.00379936 | 39.8739 | 34.0933 |
| 4 | 0.0010686 | 41.0364 | 34.6245 |
| 5 | 0.000338409 | 41.3941 | 32.8667 |
| avg | 0.0026 | 42.6746 | 34.1656 |
goal3 with Rewire时path len更优。
整体结论:RRT* with Rewire时final patn len会更优(更短),对于fitst path time cost影响不大。即Rewire有效地提升了feasiable path的optimality。
2.5.2 实验2
其中还跑了RRT#,BRRT,BRRT*,后两种由于没有深入了解方法,就不在此介绍,下面根据实验结果得出初步结论。
结果:
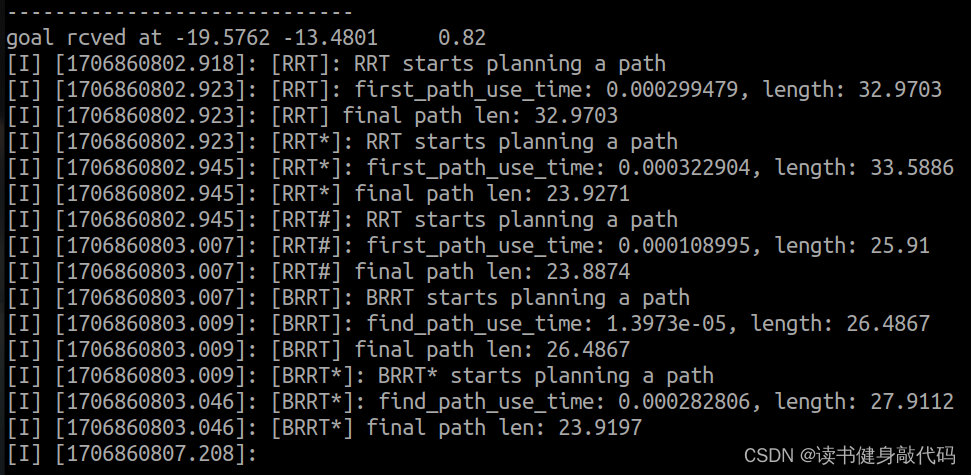
| 组号 | goal | Method | first path use time(ms) | first path len | final path len |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | -19.5762, -13.4801, 0.82 | RRT | 0.000299479 | 32.9703 | 32.9703 |
| 1 | -19.5762, -13.4801, 0.82 | RRT* | 0.000322904 | 33.5886 | 23.9271 |
| 1 | -19.5762, -13.4801, 0.82 | RRT# | 13.205173 | 9.106062 | 23.8874 |
| 2 | 16.4704, 18.2802, 1.56 | RRT | 0.000192407 | 63.1801 | 63.1801 |
| 2 | 16.4704, 18.2802, 1.56 | RRT* | 0.000640923 | 56.572 | 49.0807 |
| 2 | 16.4704, 18.2802, 1.56 | RRT# | 0.0013824 | 67.88 | 48.8112 |
| 3 | 12.1996, -14.5833, 0.6 | RRT | 0.00103743 | 49.0251 | 49.0251 |
| 3 | 12.1996, -14.5833, 0.6 | RRT* | 0.00132163 | 37.7142 | 33.2019 |
| 3 | 12.1996, -14.5833, 0.6 | RRT# | 0.000330199 | 40.8708 | 33.1705 |
结论
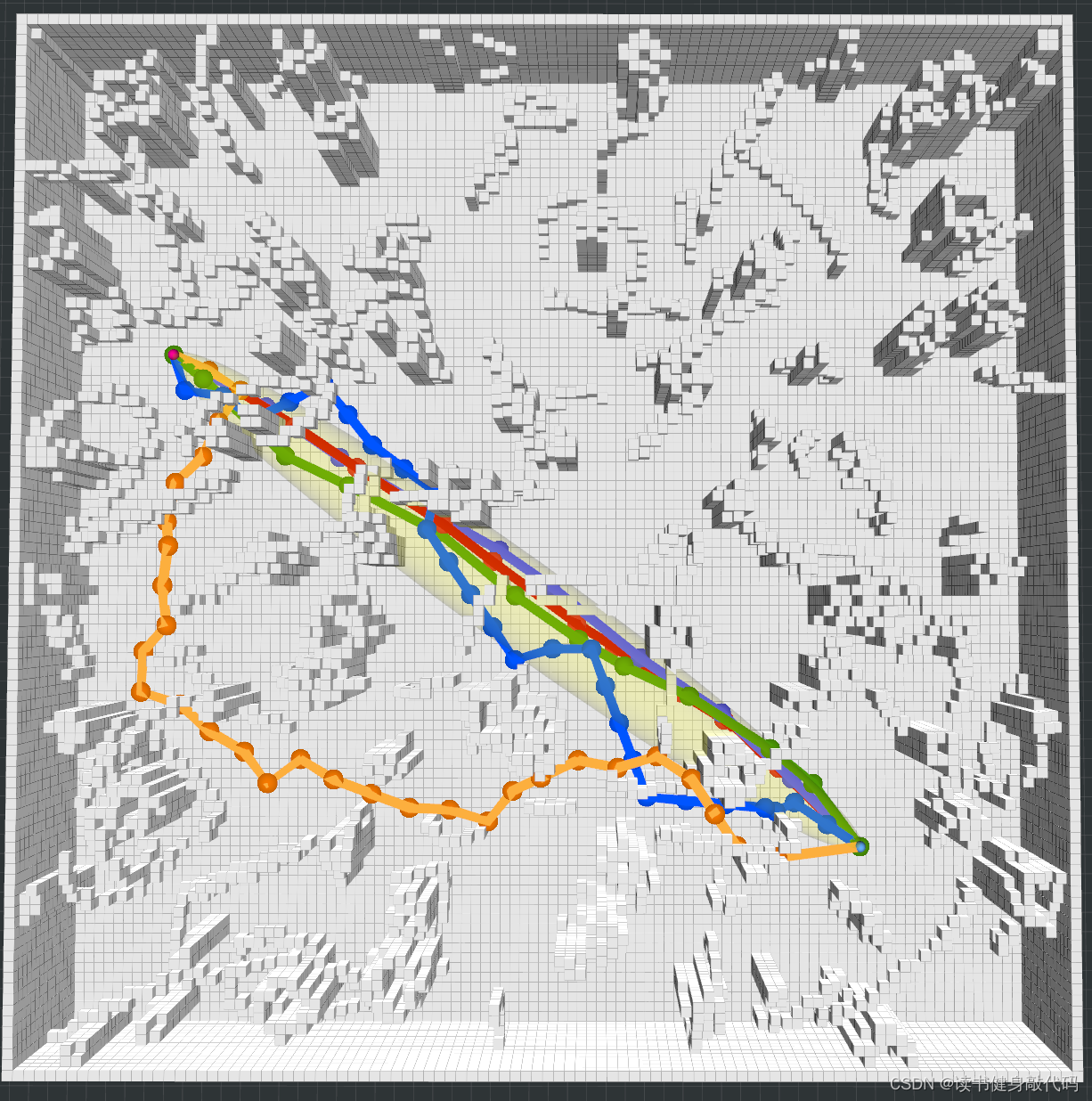
- RRT找到1条feasiable solution之后就不再进行优化,由于数据结构与RRT* 类似,所以找到first path时间与RRT相近,但RRT* first path通常比RRT更优。
- final path cost,RRT* 优于RRT,说明RRT* 的find parent和rewire对path起到了优化的作用。
T3 待做
ZJU-FAST-LAB代码中有Informed sampling和GuILD sampling的实现,都属于Informed RRT*,这个后面有时间再做。
本章完。
这篇关于【深蓝学院】移动机器人运动规划--第3章 基于采样的路径规划--作业的文章就介绍到这儿,希望我们推荐的文章对编程师们有所帮助!





