本文主要是介绍【优化求解】基于Levy飞行的飞蛾扑火优化算法(LMFO)求解单目标优化问题附matlab代码,希望对大家解决编程问题提供一定的参考价值,需要的开发者们随着小编来一起学习吧!
1 简介
由于飞蛾扑火优化 (MFO)算法收敛速度和计算精度还有待提高,提出一种改进的基于 Lévy飞行轨迹的飞蛾扑火优化 (LMFO)算法。增强局部搜索能力,大幅度提升收敛速度和求解精度。对12个无约束基准函数进行实验测试,测试结果表明,改进后的 LMFO 是有效可行的。群智能算法一般来源于对自然界中一些生物群体行为的模仿,因其具有传统优化方法所不具有的优点,已 发展成为优化问题中的研究热点。飞蛾扑火优化 (moth-flameoptimization,MFO算法是由 Mirjalili提出的一种启发式优化算法,此算法的灵感来源于飞蛾在夜间一种奇特的导航方式。夜间飞蛾以月亮为参考物来辨别方向,当 飞 蛾 迷失方向的时候,只需根据月光来自己调整身体的方位,便能找到之前的 方 向。因其与月亮相距甚远,所 以 此 机 制 能确保沿直线运 动。在 现 实 世 界 里,飞蛾常常把人造光误 认为是月亮所发出 的 光,于是飞蛾便会绕着人造光作螺旋状盘旋,这就是时常会看到飞蛾绕着人造光作螺旋形移动的原因,同时也说明了横向定位的低效性。
在基本 MFO 算 法 中,假设飞蛾是候选解,矩 阵 M 表示飞蛾的集合,数组OM 用于存储相应的适应度值。该 算法的另外一个核心组件是火焰,火 焰 矩 阵 用 F 表 示,且 数组 M 和F 的 维 数 相 等,数 组 OF 用来存储相应的适应度值。在这里,飞蛾和火焰都是解。它 们 之 间 不 同 之 处 就 是在每一次迭代过程中对待和更新它们的方式不同。飞 蛾 是在搜索空间里移动的实际搜索主体,而火焰是飞蛾到目前为止获取的 最 佳 位 置。因 此,倘 若 找 到 一 个 更 好 的 解,每只飞蛾便在标记附近搜索并更新它。通 过 此 机 制,飞 蛾 永远不会错过它的最优解。





2 部分代码
%______________________________________________________________________________________________
% Moth-Flame Optimization Algorithm (MFO) toolbox
% Source codes demo version 1.0
%
% Developed in MATLAB R2011b(7.13)
%
% Author and programmer: Seyedali Mirjalili
%
% e-Mail: ali.mirjalili@gmail.com
% seyedali.mirjalili@griffithuni.edu.au
%
% Homepage: http://www.alimirjalili.com
%
% Main paper:
% S. Mirjalili, Moth-Flame Optimization Algorithm: A Novel Nature-inspired Heuristic Paradigm,
% Knowledge-Based Systems, DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.knosys.2015.07.006
%_______________________________________________________________________________________________
% You can simply define your cost in a seperate file and load its handle to fobj
% The initial parameters that you need are:
%__________________________________________
% fobj = @YourCostFunction
% dim = number of your variables
% Max_iteration = maximum number of generations
% SearchAgents_no = number of search agents
% lb=[lb1,lb2,...,lbn] where lbn is the lower bound of variable n
% ub=[ub1,ub2,...,ubn] where ubn is the upper bound of variable n
% If all the variables have equal lower bound you can just
% define lb and ub as two single number numbers
% To run MFO: [Best_score,Best_pos,cg_curve]=MFO(SearchAgents_no,Max_iteration,lb,ub,dim,fobj)
%______________________________________________________________________________________________
function [Best_flame_score,Best_flame_pos,Convergence_curve]=MFO(N,Max_iteration,lb,ub,dim,fobj,handles,value)
display('MFO is optimizing your problem');
%Initialize the positions of moths
Moth_pos=initialization(N,dim,ub,lb);
Convergence_curve=zeros(1,Max_iteration);
Iteration=1;
% Main loop
while Iteration<Max_iteration+1
% Number of flames Eq. (3.14) in the paper
Flame_no=round(N-Iteration*((N-1)/Max_iteration));
for i=1:size(Moth_pos,1)
% Check if moths go out of the search spaceand bring it back
Flag4ub=Moth_pos(i,:)>ub;
Flag4lb=Moth_pos(i,:)<lb;
Moth_pos(i,:)=(Moth_pos(i,:).*(~(Flag4ub+Flag4lb)))+ub.*Flag4ub+lb.*Flag4lb;
% Calculate the fitness of moths
Moth_fitness(1,i)=fobj(Moth_pos(i,:));
All_fitness(1,i)=Moth_fitness(1,i);
end
if Iteration==1
% Sort the first population of moths
[fitness_sorted I]=sort(Moth_fitness);
sorted_population=Moth_pos(I,:);
% Update the flames
best_flames=sorted_population;
best_flame_fitness=fitness_sorted;
else
% Sort the moths
double_population=[previous_population;best_flames];
double_fitness=[previous_fitness best_flame_fitness];
[double_fitness_sorted I]=sort(double_fitness);
double_sorted_population=double_population(I,:);
fitness_sorted=double_fitness_sorted(1:N);
sorted_population=double_sorted_population(1:N,:);
% Update the flames
best_flames=sorted_population;
best_flame_fitness=fitness_sorted;
end
% Update the position best flame obtained so far
Best_flame_score=fitness_sorted(1);
Best_flame_pos=sorted_population(1,:);
previous_population=Moth_pos;
previous_fitness=Moth_fitness;
% a linearly dicreases from -1 to -2 to calculate t in Eq. (3.12)
a=-1+Iteration*((-1)/Max_iteration);
for i=1:size(Moth_pos,1)
for j=1:size(Moth_pos,2)
if i<=Flame_no % Update the position of the moth with respect to its corresponsing flame
% D in Eq. (3.13)
distance_to_flame=abs(sorted_population(i,j)-Moth_pos(i,j));
b=1;
t=(a-1)*rand+1;
% Eq. (3.12)
Moth_pos(i,j)=distance_to_flame*exp(b.*t).*cos(t.*2*pi)+sorted_population(i,j);
end
if i>Flame_no % Upaate the position of the moth with respct to one flame
% Eq. (3.13)
distance_to_flame=abs(sorted_population(i,j)-Moth_pos(i,j));
b=1;
t=(a-1)*rand+1;
% Eq. (3.12)
Moth_pos(i,j)=distance_to_flame*exp(b.*t).*cos(t.*2*pi)+sorted_population(Flame_no,j);
end
end
end
Convergence_curve(Iteration)=Best_flame_score;
if Iteration>2
line([Iteration-1 Iteration], [Convergence_curve(Iteration-1) Convergence_curve(Iteration)],'Color','b')
xlabel('Iteration');
ylabel('Best score obtained so far');
drawnow
end
set(handles.itertext,'String', ['The current iteration is ', num2str(Iteration)])
set(handles.optimumtext,'String', ['The current optimal value is ', num2str(Best_flame_score)])
if value==1
hold on
scatter(Iteration*ones(1,N),All_fitness,'.','k')
end
Iteration=Iteration+1;
end
3 仿真结果
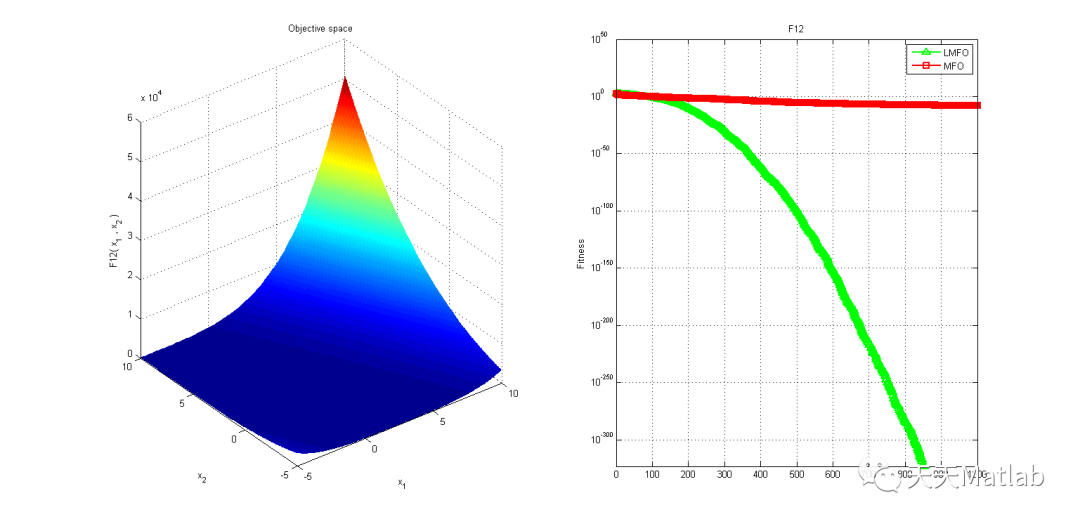
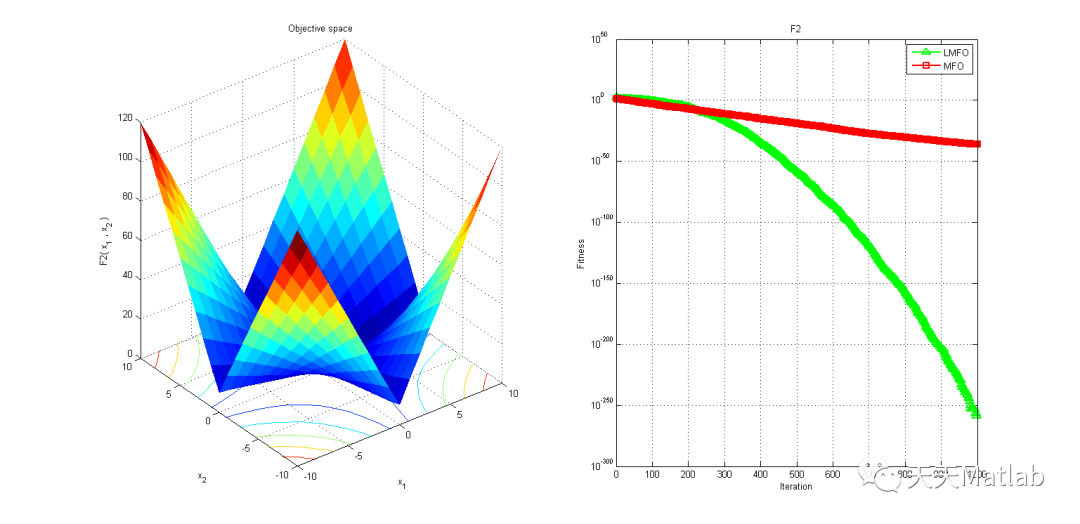
4 参考文献
[1]李志明,莫愿斌.基于Lévy飞行的飞蛾扑火优化算法[J].计算机工程与设计,2017,38(03):807-813.
博主简介:擅长智能优化算法、神经网络预测、信号处理、元胞自动机、图像处理、路径规划、无人机等多种领域的Matlab仿真,相关matlab代码问题可私信交流。
部分理论引用网络文献,若有侵权联系博主删除。

这篇关于【优化求解】基于Levy飞行的飞蛾扑火优化算法(LMFO)求解单目标优化问题附matlab代码的文章就介绍到这儿,希望我们推荐的文章对编程师们有所帮助!





