本文主要是介绍R| Raincloudplots=Scatter+violin+boxplot 云雨图,希望对大家解决编程问题提供一定的参考价值,需要的开发者们随着小编来一起学习吧!
前言
如标题所示,它的实质就是Scatter+Violin+box,在数据点之间加上连线就能很好的展示前测后测,纵向数据。中英文的教程都很多,而且还有不错的shiny应用(https://gabrifc.shinyapps.io/raincloudplots/),功能还比较全面,重点是可获得生成该图的R代码。
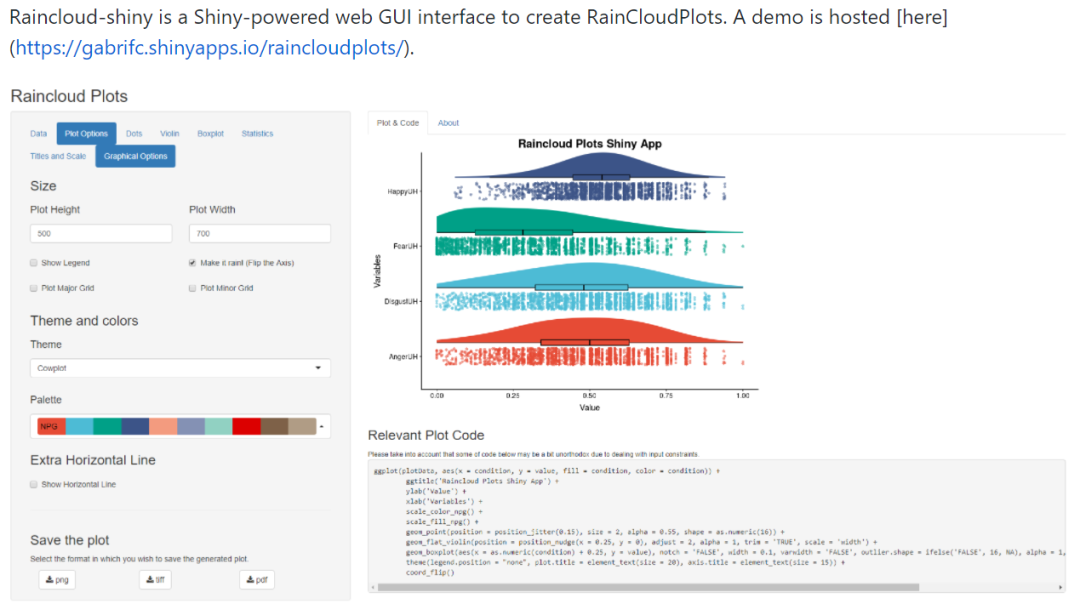
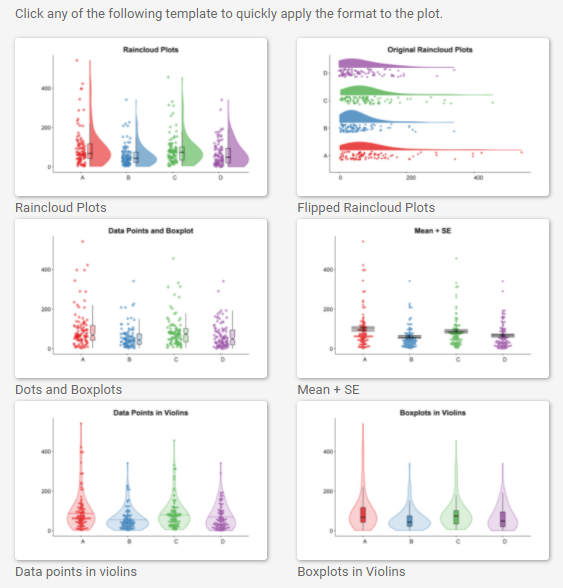
但是可以从该shiny运用提供的模板来看,并不支持多数据点之间的连线。
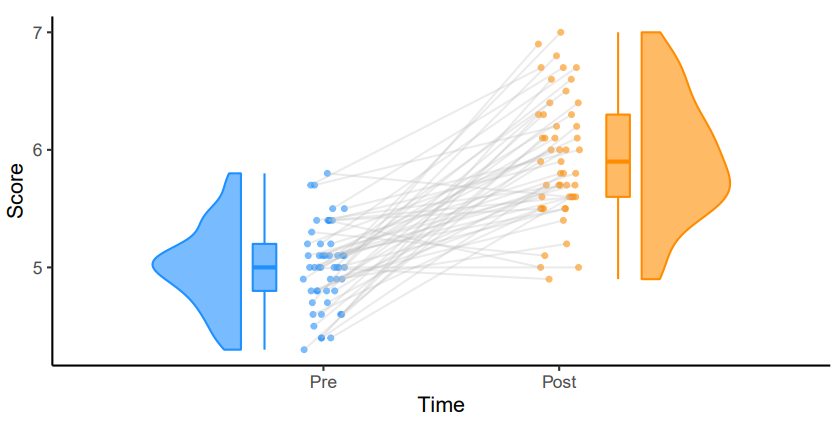
这里推荐的教程在云雨图的基础上增加数据点之间的连线(如下图),以展示不同时间点之间的变化,纵向数据可视化的不二选择。
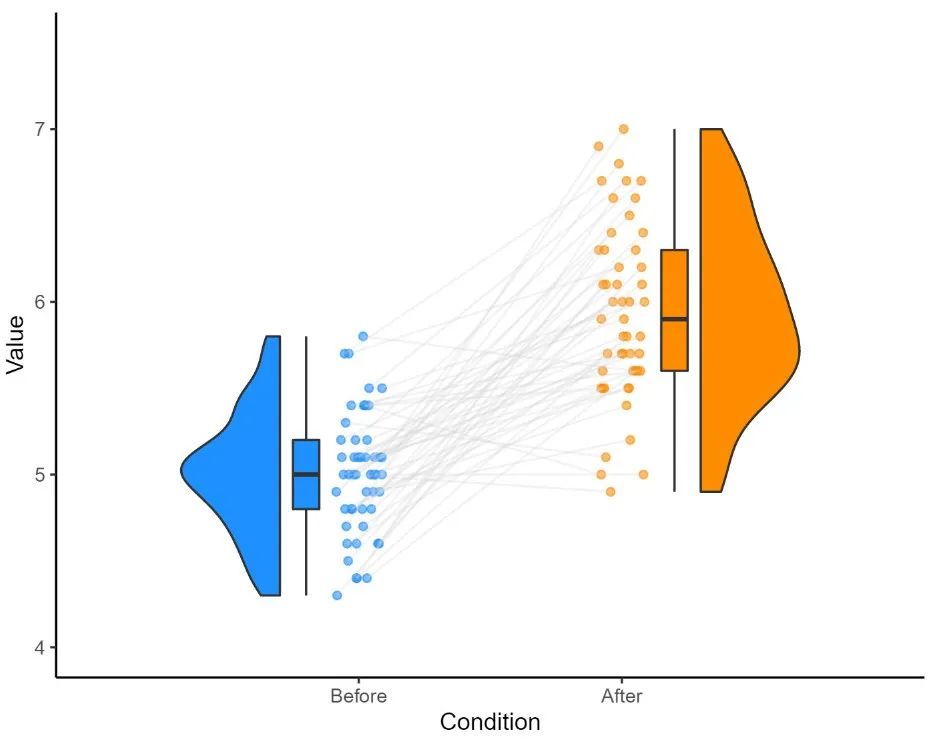
地址:
https://github.com/jorvlan/open-visualizations/blob/master/R/repmes_tutorial_R.pdf
使用了该教程记得给原作者credit(https://github.com/jorvlan/open-visualizations)。教程从最简单的scatter plot开始逐步增加元素和细节,循序渐进的告诉你怎么做这一类图,可以让你更好的了解作图的逻辑,轻松运用到其他的场景。
数据和所需包
载入所需的包:
library("plyr")library("lattice")library("ggplot2")library("dplyr")library("readr")library("rmarkdown")library("Rmisc")library("devtools")library("gghalves")
其中gghalves是用来做一半violin的,可以这么安装:
devtools::install_github(’erocoar/gghalves’)设置2个参数方便之后调用
# Define limits of y-axisy_lim_min = 4y_lim_max = 7.5
生成前后测数据,这里随便找了一组数据(iris),假装是前后测的。
before = iris$Sepal.Length[1:50]after = iris$Sepal.Length[51:100]n <- length(before)d <- data.frame(y = c(before, after),x = rep(c(1,2), each=n),id = factor(rep(1:n,2)))
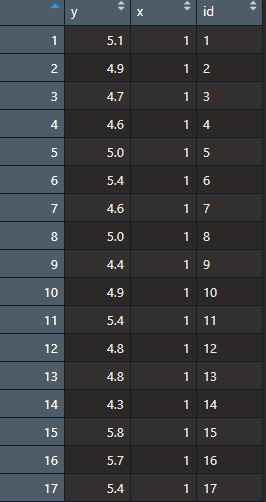
y是数据,x代表前后测,id是可以理解为被试的id。
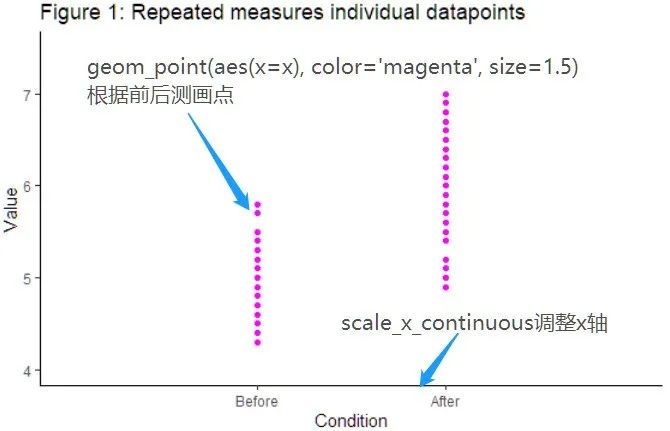
画两组点
使用geom_point,坐标轴x设置为前后测即可,可以顺便看一下怎么调x坐标轴和label。
f1 <- ggplot(data=d, aes(y=y)) +#Add geom_() objectsgeom_point(aes(x=x), color = "magenta", size = 1.5) +#Define additional settingsscale_x_continuous(breaks=c(1,2), labels=c("Before", "After"), limits=c(0, 3)) +xlab("Condition") + ylab("Value") +ggtitle('Figure 1: Repeated measures individual datapoints') +theme_classic() +coord_cartesian(ylim=c(y_lim_min, y_lim_max))f1
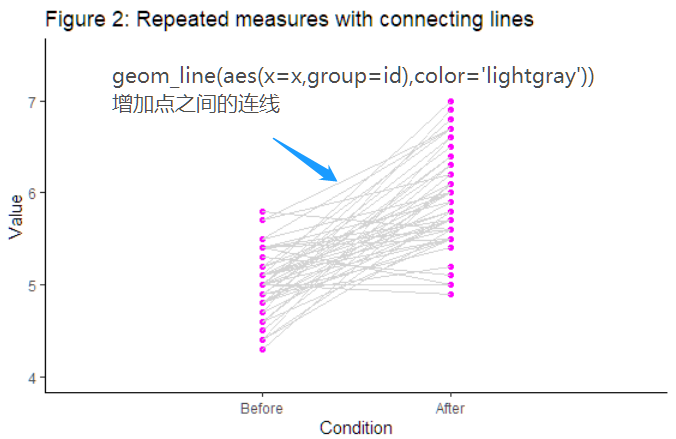
增加连线
f2 <- ggplot(data=d, aes(y=y)) +#Add geom_() objectsgeom_point(aes(x=x), color = "magenta", size = 1.5) +geom_line(aes(x=x, group=id), color = 'lightgray') +#Define additional settingsscale_x_continuous(breaks=c(1,2), labels=c("Before", "After"), limits=c(0, 3)) +xlab("Condition") + ylab("Value") +ggtitle('Figure 2: Repeated measures with connecting lines') +theme_classic()+coord_cartesian(ylim=c(y_lim_min, y_lim_max))f2
增加一点jitter
避免overlap和无聊,使用jitter在x方向增加随机,可以看到这里x需要是numeric。
set.seed(321)d$xj <- jitter(d$x, amount=.09)
其实增加jitter可以直接在geom_point中实现,思考一下为什么不在geom_point中直接增加?(Hint: geom_line)
f3 <- ggplot(data=d, aes(y=y)) +#Add geom_() objectsgeom_point(aes(x=xj), color = "magenta", size = 1.5) +geom_line(aes(x=xj, group=id), color = 'lightgray') +#Define additional settingsscale_x_continuous(breaks=c(1,2), labels=c("Before", "After"), limits=c(0, 3)) +xlab("Condition") + ylab("Value") +ggtitle('Figure 3: Repeated measures with jitter and connections') +theme_classic()+coord_cartesian(ylim=c(y_lim_min, y_lim_max))f3
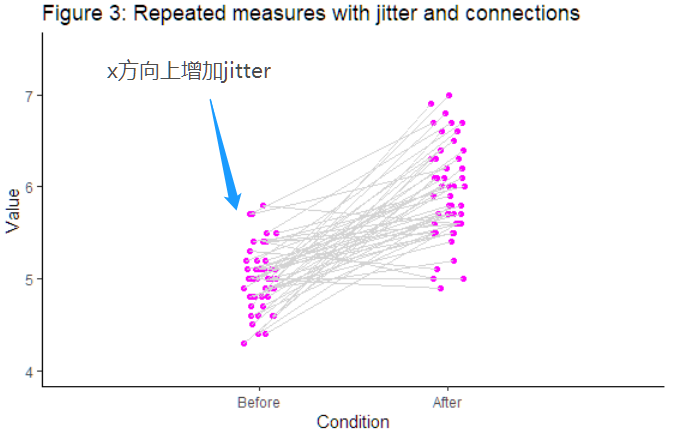
注:如果y方向上有重叠也可以在y方向上增加jitter。在写作中,必须在合适的地方说明加过jitter,否则你的图和数据是对不上的!
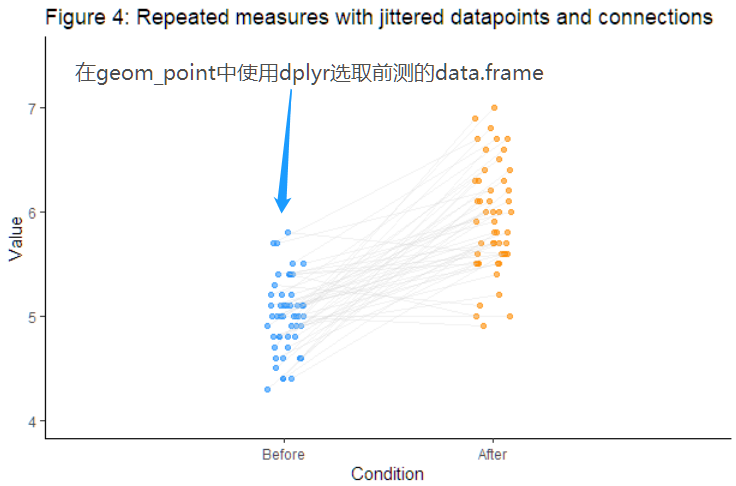
修改点的颜色
同样修改点的颜色也可以在geom_point中实现,但是为了更方便的操作元素和增加box/violin,这里使用的思路是分开画前后测。
使用dplyr选择前后测的data.frame并使用geom_point作图调整颜色。
f4 <- ggplot(data=d, aes(y=y)) +#Add geom_() objectsgeom_point(data = d %>% filter(x=="1"), aes(x=xj), color = 'dodgerblue', size = 1.5,alpha = .6) +geom_point(data = d %>% filter(x=="2"), aes(x=xj), color = 'darkorange', size = 1.5,alpha = .6) +geom_line(aes(x=xj, group=id), color = 'lightgray', alpha = .3) +#Define additional settingsscale_x_continuous(breaks=c(1,2), labels=c("Before", "After"), limits=c(0, 3)) +xlab("Condition") + ylab("Value") +ggtitle('Figure 4: Repeated measures with jittered datapoints and connections') +theme_classic()+coord_cartesian(ylim=c(y_lim_min, y_lim_max)) f4
增加box和violin
同样的思路,选择前后测的data.frame,使用geom_half_boxplot和geom_half_violin增加元素。注意调整它们在x方向的位置,防止重合。
ggplot(rep_data, aes(x = time, y = score, fill = group)) +geom_flat_violin(aes(fill = group),position = position_nudge(x = .1, y = 0), adjust = 1.5, trim = FALSE, alpha = .5, colour = NA)+geom_point(aes(x = as.numeric(time)-.15, y = score, colour = group),position = position_jitter(width = .05, height = 0), size = 1, shape = 20)+geom_boxplot(aes(x = time, y = score, fill = group),outlier.shape = NA, alpha = .5, width = .1, colour = "black")+scale_colour_brewer(palette = "Dark2")+scale_fill_brewer(palette = "Dark2")+ggtitle("Figure 10: Repeated Measures Factorial Rainclouds") + theme_classic()
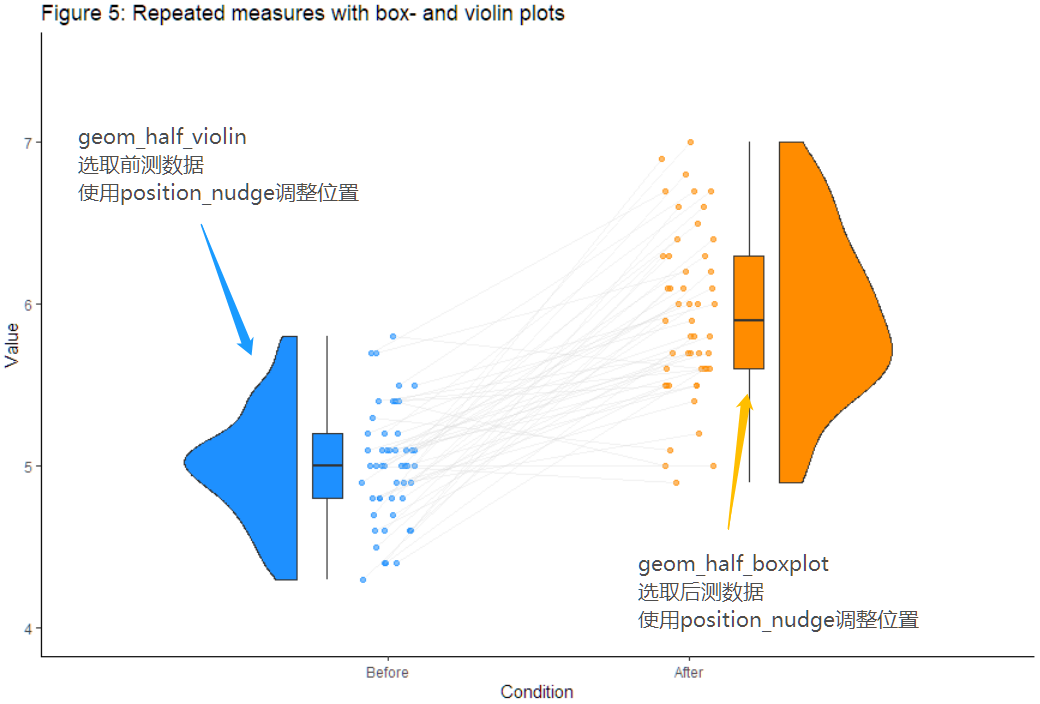
小结
至此基本的操作:
-
画点并加jitter
-
增加连线点之间连线
-
增加violin和box并调整位置
就介绍完了,之后可以根据画图需求调整相应的元素属性,比如位置/颜色/透明度等。也可以参考原教程中的其他原型,按需进行修改。
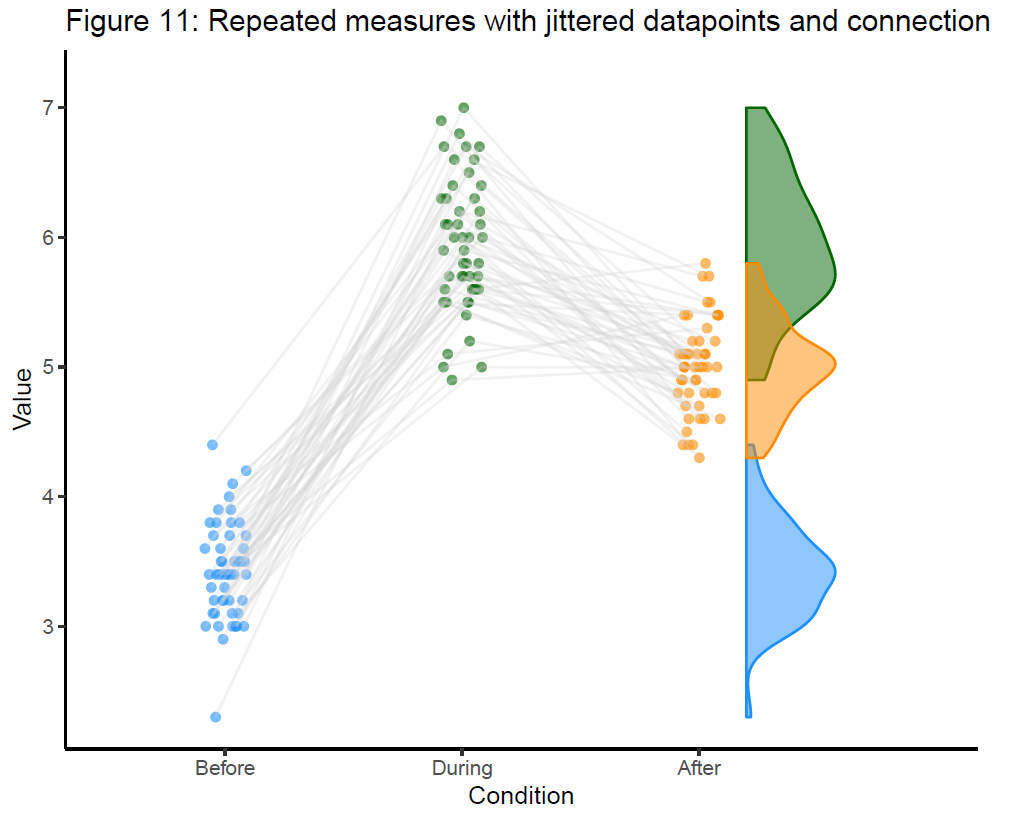
比如三个时间点的图:
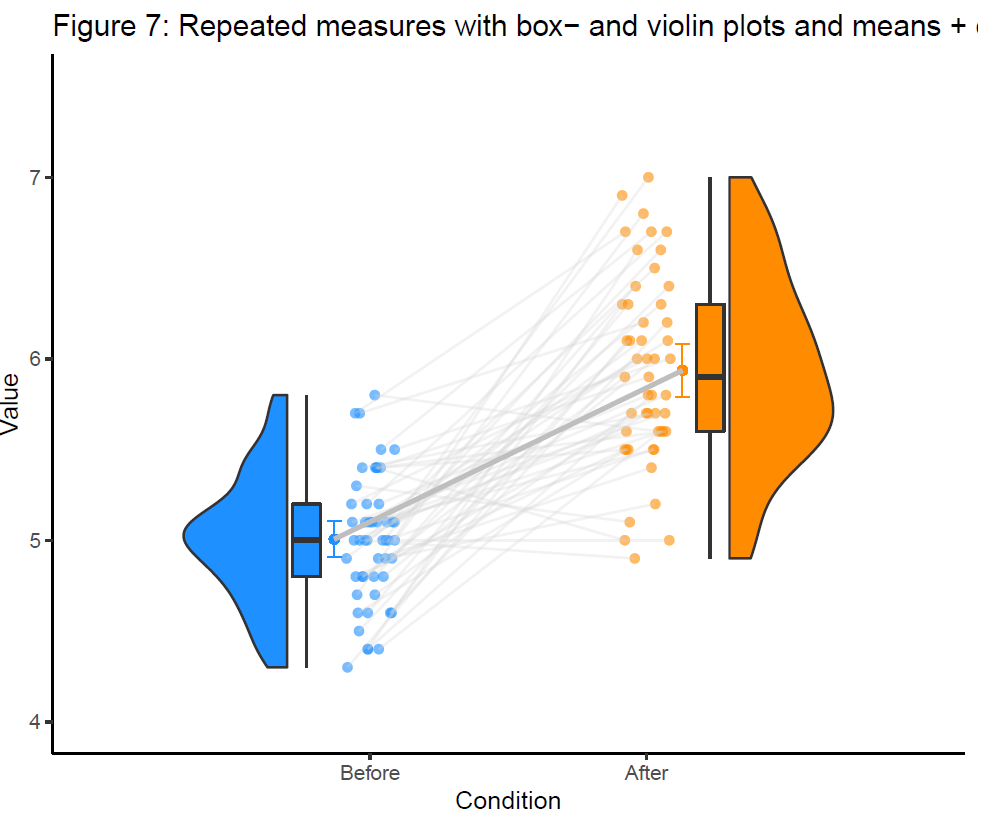
此外,作者的教程中还介绍了如何增加统计量和连线,原理是计算统计量,然后画point+error+line连线,不过似乎让图片看起来有一点冗余。
补充材料
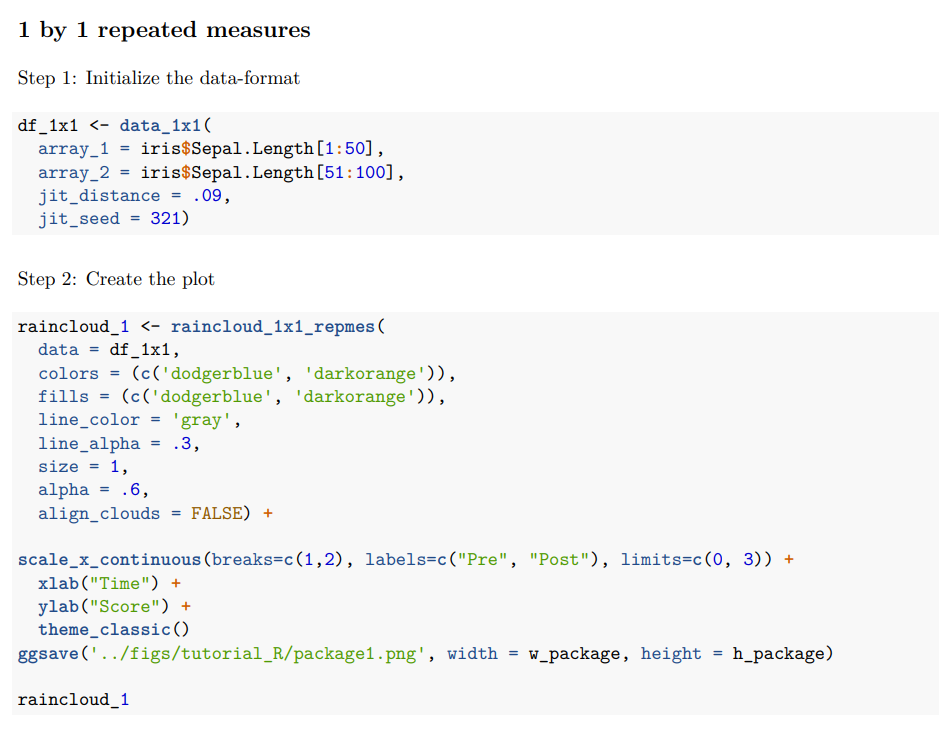
作者将以上代码封装成了raincloud工具包中的函数,以方便直接调用便可直接成图,但是想要更多的灵活度还需要自己写代码。
在另外一份教程中(https://github.com/RainCloudPlots/RainCloudPlots/blob/master/tutorial_R/raincloud_tutorial_r_JVL.pdf),作者还展示了不根据前后测分别选择数据作图的方法,就可以使得代码更简洁(牺牲了部分灵活度)。
(这个例子需要载入另一个示例数据)
ggplot(rep_data, aes(x = time, y = score, fill = group)) + geom_flat_violin(aes(fill = group),position = position_nudge(x = .1, y = 0), adjust = 1.5, trim = FALSE, alpha = .5, colour = NA)+ geom_boxplot(aes(x = time, y = score, fill = group),outlier.shape = NA, alpha = .5, width = .1, colour = "black")+geom_point(aes(x = as.numeric(time)-.15, y = score, colour = group),position = position_jitter(width = .05, height = 0), size = 1, shape = 20)+ scale_colour_brewer(palette = "Dark2")+ scale_fill_brewer(palette = "Dark2")+ ggtitle("Figure 10: Repeated Measures Factorial Rainclouds") + theme_classic()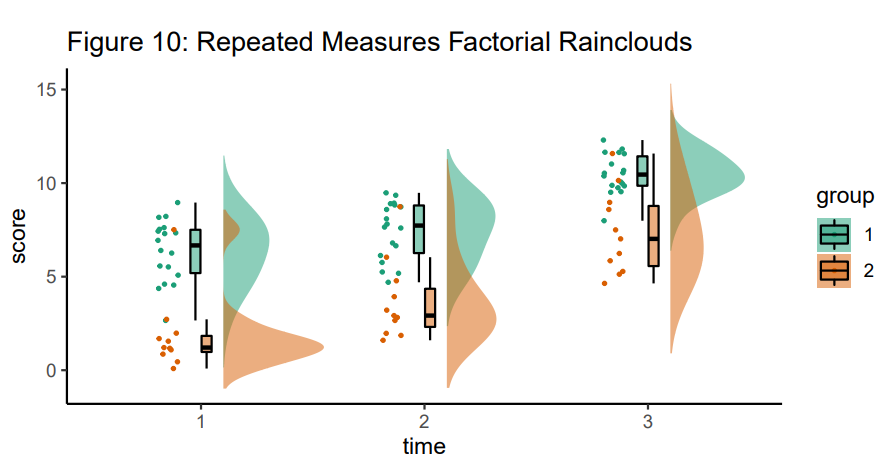
python/matlab同样可以实现,教程见:
https://github.com/RainCloudPlots/RainCloudPlots
在实际的纵向数据中,由于QC和被试的流失,被试数量在时间点之间往往不是平衡的,但是这里使用的代码依然适用于不平衡数据的可视化。数据量大的时候点图会显得有点臃肿。
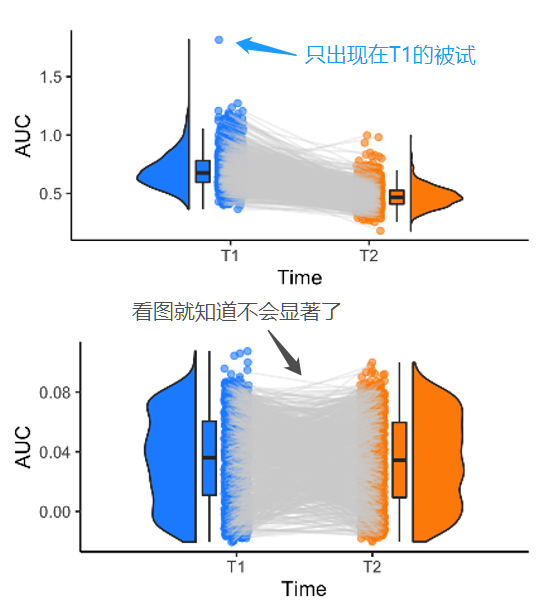
更多的时候,纵向数据的结果都如上图一样,展示出非常复杂的pattern。
END

这篇关于R| Raincloudplots=Scatter+violin+boxplot 云雨图的文章就介绍到这儿,希望我们推荐的文章对编程师们有所帮助!