本文主要是介绍深度学习论文: A YOLO-like Algorithm for Audio Segmentation and Sound Event Detection及其PyTorch实现,希望对大家解决编程问题提供一定的参考价值,需要的开发者们随着小编来一起学习吧!
深度学习论文: A YOLO-like Algorithm for Audio Segmentation and Sound Event Detection及其PyTorch实现
You Only Hear Once: A YOLO-like Algorithm for Audio Segmentation and Sound Event Detection
PDF: https://arxiv.org/pdf/2109.00962.pdf
PyTorch代码: https://github.com/shanglianlm0525/CvPytorch
PyTorch代码: https://github.com/shanglianlm0525/PyTorch-Networks
1 概述
常见的声音分割(audio segmentation)方法可以分为两类:
- distance-based segmentation:通过欧氏距离或者贝叶斯信息准则,通过声音变化的波峰将声音划分为不同的片段,然后检测每个片段的声音类别。
- segmentation-by-classification:将声音划分为10-25ms的帧,然后对帧进行分类。
You Only Hear Once (YOHO) 将声音边界的检测转化为一个基于帧的回归问题,即检测声音的类别以及它的开始和结束点。
2 You Only Hear Once (YOHO)
2-1 网络结构
YOHO的输入特征采用log-mel spectrograms,输入维数依赖于声音序列的长度和mel spectrogram的规格。这里 music-speech 检测的输入包含801 times steps 和 64 frequency bins。在每个time step,第一个神经元二分类来检测是一个声音类别的存在与否,第二和第三个神经元用来回归各自声音类别的开始和结束位置。
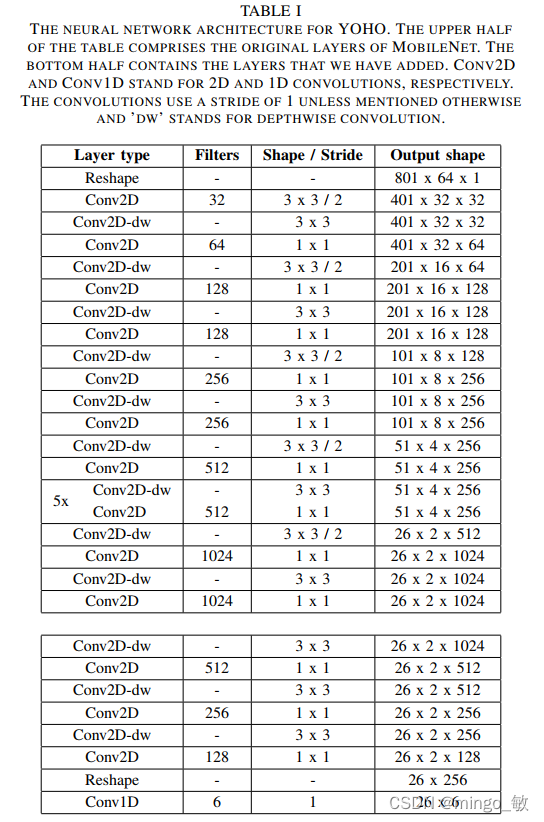
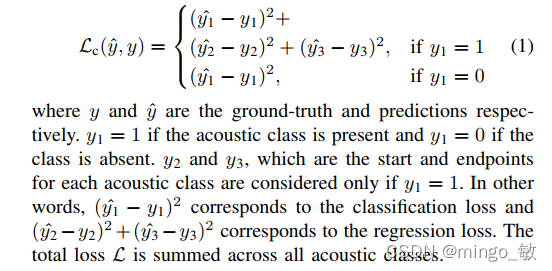
损失函数使用sum squared error
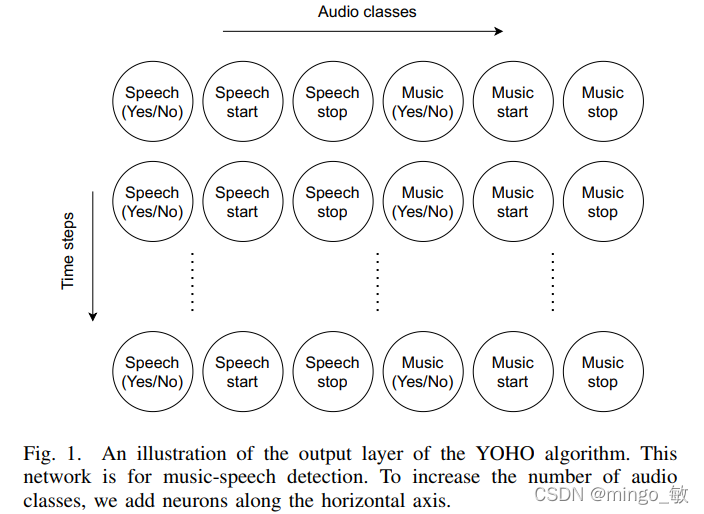
2-2 music-speech detection 输出示例
music-speech detection 输出 music 和 speech 两个示例,因此在每个time step有六个神经元,如长为6s的音频示例,每个输出的time step对应0.307s, 因为有26个分配。输出层的所有神经元后接sigmoid 激活函数,回归的输出归一化到0和1之间。
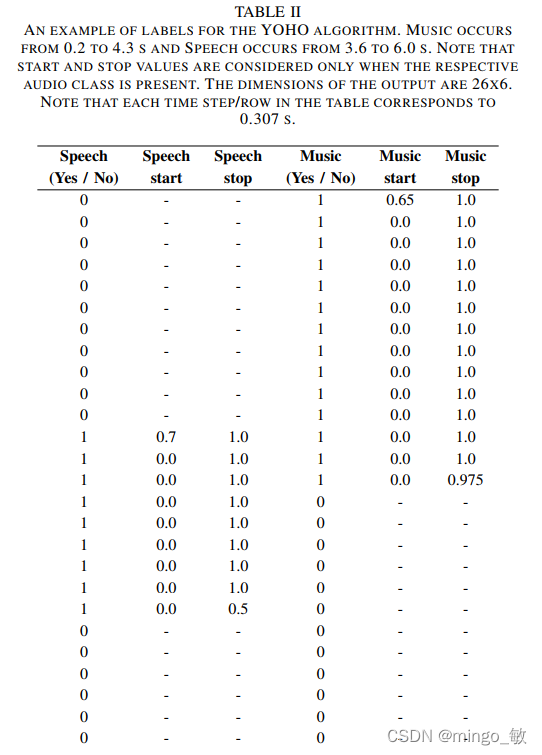
2-3 标签示例
音频总时长8s, 音乐出现在0.2 to 4.3 s ,讲话出现在3.6 to 6.0 s。每一行对应一个 time step,为0.307s。此外回归的值归一化到了0和1之间,因此音乐的开始位置位于 0.2s / 0.307 = 0.65,即第一行。
Post-processing
后处理主要将升级网络的输出转换为人类可读信息。
median filtering 和 threshold-dependent smoothing用于消除虚假(spurious)音频事件的发生,如特别短的声音、相同类别声音中间小的停顿(if the duration of the audio event is too short or if the silence between consecutive events of the same acoustic class is too short, we remove the occurrence.)。
3 Datasets
3-1 Music-Speech Detection
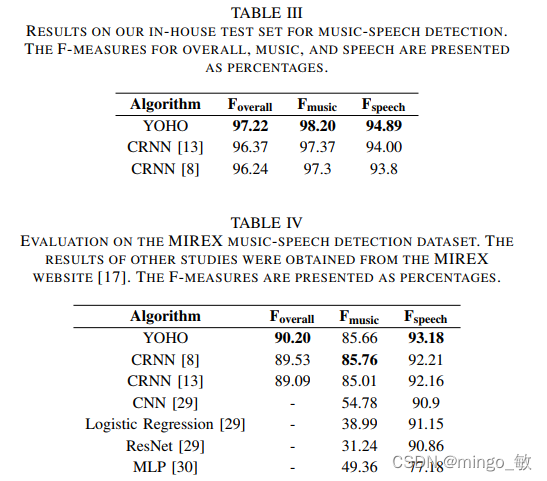
3-2 TUT Sound Event Detection

3-3 Urban-SED
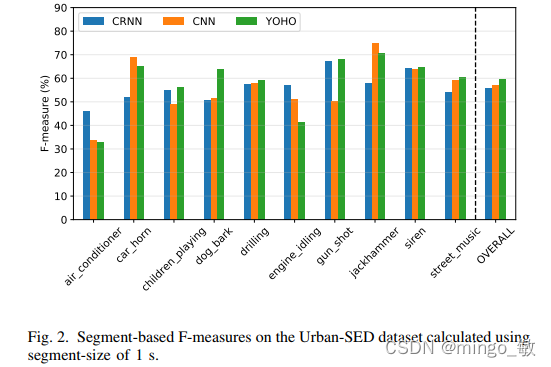
3-4 Speed of Prediction
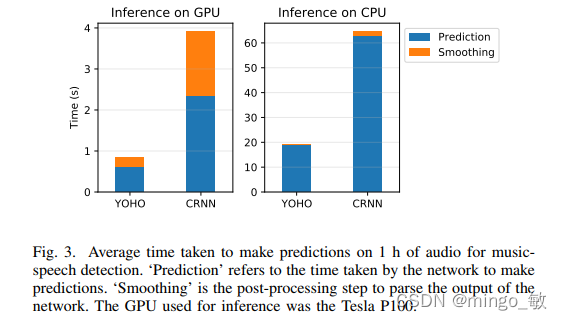
这篇关于深度学习论文: A YOLO-like Algorithm for Audio Segmentation and Sound Event Detection及其PyTorch实现的文章就介绍到这儿,希望我们推荐的文章对编程师们有所帮助!


