本文主要是介绍ChAMP甲基化数据分析:从β值矩阵开始,希望对大家解决编程问题提供一定的参考价值,需要的开发者们随着小编来一起学习吧!
之前的推文详细介绍了ChMAP包从IDAT文件开始的甲基化数据分析流程,今天说一下从β矩阵开始的分析流程。
16.ChAMP分析甲基化数据:标准流程
数据准备
还是用GSE149282这个数据。
suppressMessages(library(GEOquery))
首先获取GSE149282这个数据的β矩阵文件,可以通过getGEO()函数下载,但是由于网络原因经常下载失败,所以我直接去GEO官网下载了这个数据,放到指定文件夹下读取即可。
GSE149282 <- getGEO("GSE149282",destdir = './gse149282',getGPL = F, AnnotGPL = F)
## Found 1 file(s)
## GSE149282_series_matrix.txt.gz
## Using locally cached version: ./gse149282/GSE149282_series_matrix.txt.gz
# 其实你用read.delim()也能读取成功
现在这个GSE149282是一个ExpressionSet对象,在刚学的时候,我不能理解R语言里面的很多对象,但是这并不影响一些操作,只要记住即可,学习不断深入,后面对R语言的各种对象的理解,会逐步明朗。
GSE149282
## $GSE149282_series_matrix.txt.gz
## ExpressionSet (storageMode: lockedEnvironment)
## assayData: 865918 features, 24 samples
## element names: exprs
## protocolData: none
## phenoData
## sampleNames: GSM4495491 GSM4495492 ... GSM4495514 (24 total)
## varLabels: title geo_accession ... tumour stage:ch1 (41 total)
## varMetadata: labelDescription
## featureData: none
## experimentData: use 'experimentData(object)'
## pubMedIds: 32380793
## Annotation: GPL21145
获取β值矩阵非常简单:
beta.m <- exprs(GSE149282[[1]])
dim(beta.m)
## [1] 865918 24beta.m[1:4,1:4]
## GSM4495491 GSM4495492 GSM4495493 GSM4495494
## cg00000029 0.3680475 0.1580980 0.3562024 0.2530871
## cg00000103 0.7357062 0.5472209 0.7322839 0.5866429
## cg00000109 0.8182613 0.8746516 0.7908351 0.8354254
## cg00000155 0.9376374 0.9057370 0.8820246 0.8979353
这个β矩阵可能含有很多缺失值,需要去掉,不然会报错,你可以用各种缺失值插补的方法,这里我们就简单点,直接删除,在实际分析时不建议这么做!
beta.m <- na.omit(beta.m)
dim(beta.m)
## [1] 827476 24
有了这个β值矩阵,下面我们再把样本信息csv文件读取进来,上次推文中已经制作好了,直接读取即可:
pd <- read.csv("./gse149282/GSE149282_RAW/sample_type.csv")
head(pd)
## Sample_Name Sentrix_ID Sentrix_Position Sample_Type
## 1 GSM4495491 GSM4495491_200811050117 R01C01 normal
## 2 GSM4495492 GSM4495492_200811050117 R02C01 cancer
## 3 GSM4495493 GSM4495493_200811050117 R03C01 normal
## 4 GSM4495494 GSM4495494_200811050117 R04C01 cancer
## 5 GSM4495495 GSM4495495_200811050117 R05C01 normal
## 6 GSM4495496 GSM4495496_200811050117 R06C01 cancer
β值矩阵读取
现在有了β值和样本信息csv文件,我们就可以用ChAMP包分析了!
suppressMessages(library(ChAMP))
champ.load()是从IDAT开始的,包括champ.import()和champ.filter(),champ.import()也是从IDAT开始的,现在我们只有β矩阵,可以直接从champ.filter()开始!
myLoad <- champ.filter(beta = beta.m,pd = pd,arraytype = "EPIC")
[===========================]
[<<<< ChAMP.FILTER START >>>>>]
-----------------------------In New version ChAMP, champ.filter() function has been set to do filtering on the result of champ.import(). You can use champ.import() + champ.filter() to do Data Loading, or set "method" parameter in champ.load() as "ChAMP" to get the same effect.This function is provided for user need to do filtering on some beta (or M) matrix, which contained most filtering system in champ.load except beadcount. User need to input beta matrix, pd file themselves. If you want to do filterintg on detP matrix and Bead Count, you also need to input a detected P matrix and Bead Count information.Note that if you want to filter more data matrix, say beta, M, intensity... please make sure they have exactly the same rownames and colnames.[ Section 1: Check Input Start ]You have inputed beta for Analysis.pd file provided, checking if it's in accord with Data Matrix...pd file check success.Parameter filterDetP is TRUE, checking if detP in accord with Data Matrix...!!! Parameter detP is not found, filterDetP is reset FALSE now.Parameter filterBeads is TRUE, checking if beadcount in accord with Data Matrix...!!! Parameter beadcount is not found, filterBeads is reset FALSE now.parameter autoimpute is TRUE. Checking if the conditions are fulfilled...!!! ProbeCutoff is 0, which means you have no needs to do imputation. autoimpute has been reset FALSE.Checking Finished :filterMultiHit,filterSNPs,filterNoCG,filterXY would be done on beta.
[ Section 1: Check Input Done ][ Section 2: Filtering Start >>Filtering NoCG StartOnly Keep CpGs, removing 2792 probes from the analysis.Filtering SNPs StartUsing general EPIC SNP list for filtering.Filtering probes with SNPs as identified in Zhou's Nucleic Acids Research Paper 2016.Removing 94704 probes from the analysis.Filtering MultiHit StartFiltering probes that align to multiple locations as identified in Nordlund et alRemoving 10 probes from the analysis.Filtering XY StartFiltering probes located on X,Y chromosome, removing 16250 probes from the analysis.Updating PD filefilterDetP parameter is FALSE, so no Sample Would be removed.Fixing Outliers StartReplacing all value smaller/equal to 0 with smallest positive value.Replacing all value greater/equal to 1 with largest value below 1..
[ Section 2: Filtering Done ]All filterings are Done, now you have 713720 probes and 24 samples.[<<<<< ChAMP.FILTER END >>>>>>]
[===========================]
[You may want to process champ.QC() next.]
可以和上次直接从IDAT读取的对比一下,可以看到少了很多信息,所以有的过滤不能执行,比如filterDetP、filterBeads。
下面的分析就和上一篇推文一模一样了
# 数据预处理
champ.QC(beta = myLoad$beta,pheno = myLoad$pd$Sample_Type,resultsDir="./CHAMP_QCimages1/")
myNorm <- champ.norm(beta = myLoad$beta,arraytype = "EPIC",#method = "PBC",cores = 8,resultsDir="./CHAMP_Normalization1/")
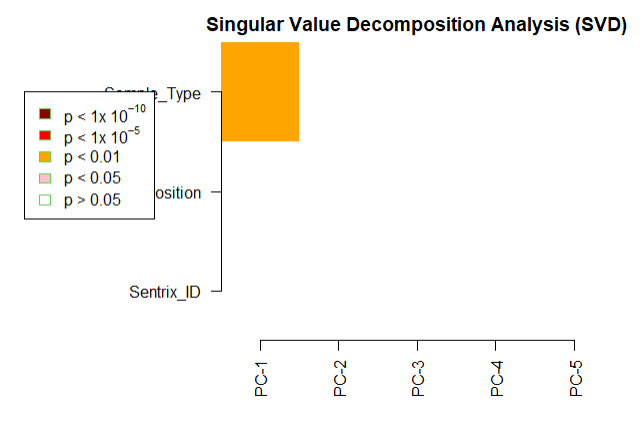
champ.SVD(beta = myNorm |> as.data.frame(), # 这里需要注意pd=myLoad$pd)
[===========================]
[<<<<< ChAMP.SVD START >>>>>]
-----------------------------
champ.SVD Results will be saved in ./CHAMP_SVDimages/ .Your beta parameter is data.frame format. ChAMP is now changing it to matrix.
[SVD analysis will be proceed with 713720 probes and 24 samples.][ champ.SVD() will only check the dimensions between data and pd, instead if checking if Sample_Names are correctly matched (because some user may have no Sample_Names in their pd file),thus please make sure your pd file is in accord with your data sets (beta) and (rgSet).]<Sentrix_ID>(character):GSM4495491, GSM4495492, GSM4495493, GSM4495494, GSM4495495, GSM4495496, GSM4495497, GSM4495498, GSM4495499, GSM4495500, GSM4495501, GSM4495502, GSM4495503, GSM4495504, GSM4495505, GSM4495506, GSM4495507, GSM4495508, GSM4495509, GSM4495510, GSM4495511, GSM4495512, GSM4495513, GSM4495514
<Sentrix_Position>(character):200811050117_R01C01, 200811050117_R02C01, 200811050117_R03C01, 200811050117_R04C01, 200811050117_R05C01, 200811050117_R06C01, 200811050117_R07C01, 200811050117_R08C01, 200811050116_R01C01, 200811050116_R02C01, 200811050116_R03C01, 200811050116_R04C01, 200811050116_R05C01, 200811050116_R06C01, 200811050116_R07C01, 200811050116_R08C01, 202193490061_R01C01, 202193490061_R02C01, 202193490061_R03C01, 202193490061_R04C01, 202193490061_R05C01, 202193490061_R06C01, 202193490061_R07C01, 202193490061_R08C01
<Sample_Type>(character):normal, cancer
[champ.SVD have automatically select ALL factors contain at least two different values from your pd(sample_sheet.csv), if you don't want to analysis some of them, please remove them manually from your pd variable then retry champ.SVD().]<Sample_Name>
[Factors are ignored because they only indicate Name or Project, or they contain ONLY ONE value across all Samples.]Sentrix_ID Sentrix_Position Sample_Type
[1,] 0.4607709 0.4607709 4.146041e-05
[2,] 0.4607709 0.4607709 9.406855e-02
[3,] 0.4607709 0.4607709 4.189234e-01
[4,] 0.4607709 0.4607709 3.263485e-01
[5,] 0.4607709 0.4607709 7.728300e-01
后续的分析和之前推文中介绍的一模一样,就不演示了,大家可以移步之前的推文:
16.ChAMP分析甲基化数据:标准流程
这篇关于ChAMP甲基化数据分析:从β值矩阵开始的文章就介绍到这儿,希望我们推荐的文章对编程师们有所帮助!