本文主要是介绍Yolov8_obb(prob loss) 基于anchor_free的旋转框目标检测,剪枝,跟踪(ByteTracker),希望对大家解决编程问题提供一定的参考价值,需要的开发者们随着小编来一起学习吧!
Yolov8_obb(prob loss) 基于anchor_free的旋转框目标检测,剪枝,跟踪(ByteTracker)
效果好于yolov5,并能在小数据集上大幅度超越v5的结果,不过针对不同的数据集需要进行一些调参.
啊b上测试视频路径,不过效果一般,随便测了下,仅供参考。
https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1wP411Y7RK/?spm_id_from=333.999.0.0&vd_source=e9fe318d5cf880bb21b301822f
算法已上传github,如果对你的工作和学习有所帮助别忘了给博主点一个star
https://github.com/yzqxy/Yolov8_obb_Prune_Track/tree/main

一、 项目地址和运行命令
即将发布
yolov8_obb旋转框检测:训练,评估,测试和导出onnx
#测试
python detect.py --weights yolov8_obb/runs/train/exp/weights/best.pt --source yolov8_obb/dataset/your datafile/images/val/ --img 640 --device 0 --conf-thres 0.25 --iou-thres 0.2
多卡训练
python train.py --data 'data/yolov8obb_demo.yaml' --hyp 'data/hyps/obb/hyp.finetune_dota.yaml' --cfg models/yolov8n.yaml --epochs 300 --batch-size 128 --img 640 -- is_use_DP
单卡训练可指定显卡
#训练
python train.py --data 'data/yolov8obb_demo.yaml' --hyp 'data/hyps/obb/hyp.finetune_dota.yaml' --cfg models/yolov8n.yaml --epochs 300 --batch-size 8 --img 640 --device 1
#评估
python val.py --data data/yolov8obb_demo.yaml --weights yolov8_obb/runs/train/exp/weights/best.pt --task 'val' --img 640
#导出onnx
python export.py --weights yolov8_obb/runs/train/exp/weights/best.pt --batch 1
yolov8_obb剪枝:稀疏训练,剪枝,和微调
#稀疏训练,可选择直接进行稀疏训练,如果直接进行稀疏训练效果不好,可以先进行正常训练到收敛,再进行稀疏训练来微调模型
python train_sparity.py --st --sr 0.0002 --data 'data/yolov8obb_demo.yaml' --hyp 'data/hyps/obb/hyp.finetune_dota.yaml' --cfg models/yolov8n.yaml --epochs 300 --batch-size 8 --img 640 --device 2 --weights yolov8_obb/runs/train/exp/weights/best.pt
#剪枝,percent为剪枝比率,如果传入close_head,则不对输出头部分的卷积层进行剪枝。
python prune.py --percent 0.3 --weights runs/train/exp299/weights/last.pt --data data/yolov5obb_demo.yaml --cfg models/yolov8n.yaml --close_head
#微调
python prune_finetune.py --weights prune/pruned_model.pt --data data/yolov5obb_demo.yaml --epochs 100 --imgsz 640 --batch-size 8
yolov8_obb跟踪:ByteTracker和StrongSort
可选参数
video_path:需要预测的跟踪视频读取路径
video_save_path: 跟踪视频预测完的保存路径
video_fps:需要预测的跟踪视频读取帧数
weights: 旋转框检测模型路径
img_save_path:跟踪视频按照video_fps切分后保存图片的路径
track_type:跟踪类型,可选择bytetracker和strongsort
is_track_img:是否存储画有跟踪框的图片
track_img_path:画有跟踪框的图片的存储文件夹路径
is_track_det_img:是否存储画有检测框的图片
track_det_img_path:画有检测框的图片的存储文件夹路径
#跟踪
python track_predict.py --video_path --video_fps --weights --video_save_path
二、 旋转框的转换和定义
dota的四个角点格式的数据转化成(x, y, w, h, theta)的格式,通过cv2.minAreaRect()获取框的中心点(x,y),宽高(w,h),以及角度angle,angle∈ [0, 90],将角度映射成pi,由于存在w>h和h>w两种形式,统一设置成长边为h,短边为w,旋转的theta角度映射到 [-pi/2, pi/2]范围内。即长边表示法,如下图所示,(代码处理完之后逆时针为正,顺时针为负,跟图里画的相反,请注意,可以自行推导求证)
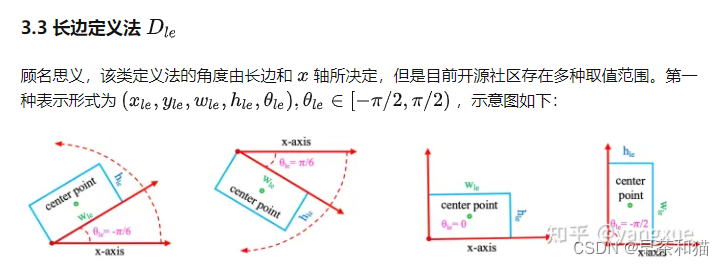
具体角度表示的一些方法请参考https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/459018810
相关代码实现
poly = np.float32(poly.reshape(4, 2))(x, y), (w, h), angle = cv2.minAreaRect(poly) # θ ∈ [0, 90]angle = -angle # θ ∈ [-90, 0]theta = angle / 180 * pi # 转为pi制# trans opencv format to longedge format θ ∈ [-pi/2, pi/2]if w != max(w, h): w, h = h, wtheta += pi/2rboxes.append([x, y, w, h, theta])
将预测的结果重新投影到图片上,需要将(x, y, w, h, theta)格式重新转换成四个角点坐标的格式。
center, w, h, theta = obboxes[:,:, :2], obboxes[:,:, 2:3], obboxes[:,:, 3:4], obboxes[:,:, 4:5]Cos, Sin = torch.cos(theta), torch.sin(theta)vector1 = torch.cat((w/2 * Cos, -w/2 * Sin), dim=-1)vector2 = torch.cat((-h/2 * Sin, -h/2 * Cos), dim=-1)point1 = center + vector1 + vector2point2 = center + vector1 - vector2point3 = center - vector1 - vector2point4 = center - vector1 + vector2order = obboxes.shape[:-1]return torch.cat((point2, point3, point4,point1), dim=-1).reshape(*order, 4,2)
转换过程如图所示:

三、 yolov8_obb旋转框检测
yolov8_obb还是基于上一篇yolov5_obb的基础上进行修改,由于博主技术比较烂,对于在v8源码上进行修改的工作进展会比较困难,所以选择在已有v5_obb的基础上进行修改,只做旋转框的检测,代码量更少,阅读起来也更为轻松。不过可能存在的缺点就是代码性能的优化不及现在的v8框架,毕竟是很多大佬一起维护的,言归正传,下面将介绍整个代码逻辑和细节。
1、 数据格式
1.1、标注软件:roLabelImg
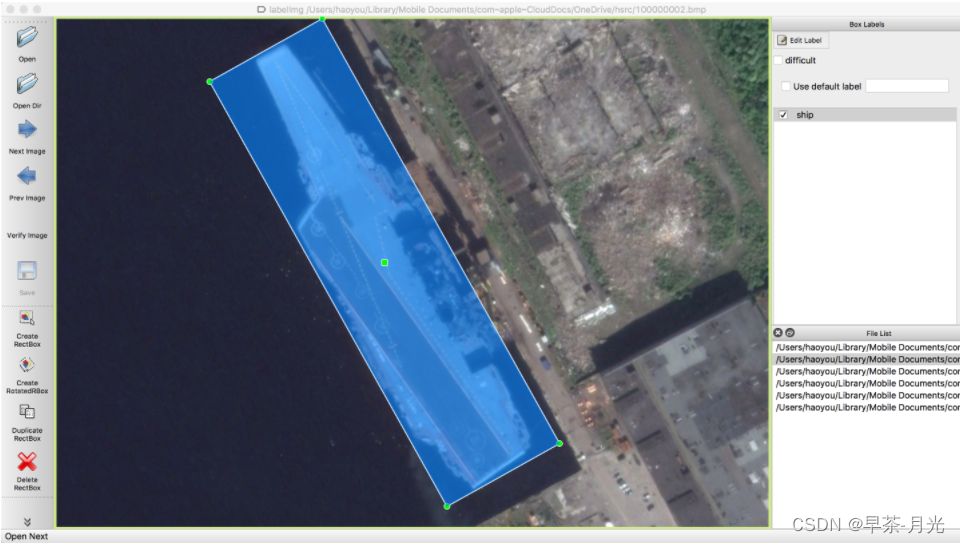
图片来源(https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_38346042/article/details/129314975)
软件快捷键如下:
1) w: 创建水平矩形目标框
2) e: 创建旋转矩形目标框
3) zxcv: 旋转目标框,键z和建x是逆时针旋转,键c和键v是顺时针旋转
1.2、数据格式转换
标注存储xml文件
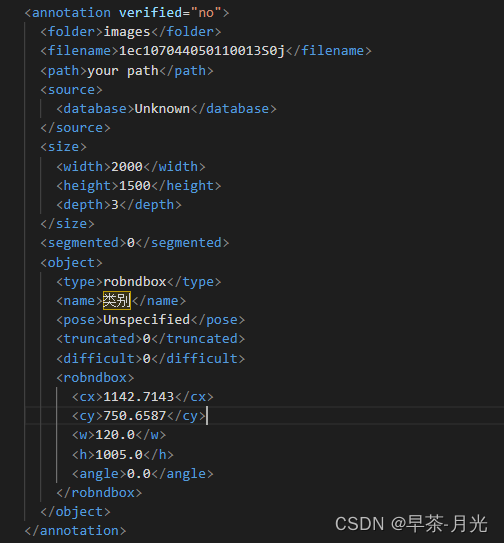
将xml转成yolov5_obb可训练的txt格式------将旋转框的中心点,宽高和角度的存储形式转换成四个角点坐标表现形式
转换代码:
# 文件名称 :roxml_to_dota.py
# 功能描述 :把rolabelimg标注的xml文件转换成dota能识别的xml文件,
# 再转换成dota格式的txt文件
# 把旋转框 cx,cy,w,h,angle,或者矩形框cx,cy,w,h,转换成四点坐标x1,y1,x2,y2,x3,y3,x4,y4
import os
import xml.etree.ElementTree as ET
import mathcls_list=['你的类别']
def edit_xml(xml_file, dotaxml_file):"""修改xml文件:param xml_file:xml文件的路径:return:"""tree = ET.parse(xml_file)objs = tree.findall('object')for ix, obj in enumerate(objs):x0 = ET.Element("x0") # 创建节点y0 = ET.Element("y0")x1 = ET.Element("x1")y1 = ET.Element("y1")x2 = ET.Element("x2")y2 = ET.Element("y2")x3 = ET.Element("x3")y3 = ET.Element("y3")# obj_type = obj.find('bndbox')# type = obj_type.text# print(xml_file)if (obj.find('robndbox') == None):obj_bnd = obj.find('bndbox')obj_xmin = obj_bnd.find('xmin')obj_ymin = obj_bnd.find('ymin')obj_xmax = obj_bnd.find('xmax')obj_ymax = obj_bnd.find('ymax')#以防有负值坐标xmin = max(float(obj_xmin.text),0)ymin = max(float(obj_ymin.text),0)xmax = max(float(obj_xmax.text),0)ymax = max(float(obj_ymax.text),0)obj_bnd.remove(obj_xmin) # 删除节点obj_bnd.remove(obj_ymin)obj_bnd.remove(obj_xmax)obj_bnd.remove(obj_ymax)x0.text = str(xmin)y0.text = str(ymax)x1.text = str(xmax)y1.text = str(ymax)x2.text = str(xmax)y2.text = str(ymin)x3.text = str(xmin)y3.text = str(ymin)else:obj_bnd = obj.find('robndbox')obj_bnd.tag = 'bndbox' # 修改节点名obj_cx = obj_bnd.find('cx')obj_cy = obj_bnd.find('cy')obj_w = obj_bnd.find('w')obj_h = obj_bnd.find('h')obj_angle = obj_bnd.find('angle')cx = float(obj_cx.text)cy = float(obj_cy.text)w = float(obj_w.text)h = float(obj_h.text)angle = float(obj_angle.text)obj_bnd.remove(obj_cx) # 删除节点obj_bnd.remove(obj_cy)obj_bnd.remove(obj_w)obj_bnd.remove(obj_h)obj_bnd.remove(obj_angle)x0.text, y0.text = rotatePoint(cx, cy, cx - w / 2, cy - h / 2, -angle)x1.text, y1.text = rotatePoint(cx, cy, cx + w / 2, cy - h / 2, -angle)x2.text, y2.text = rotatePoint(cx, cy, cx + w / 2, cy + h / 2, -angle)x3.text, y3.text = rotatePoint(cx, cy, cx - w / 2, cy + h / 2, -angle)# obj.remove(obj_type) # 删除节点obj_bnd.append(x0) # 新增节点obj_bnd.append(y0)obj_bnd.append(x1)obj_bnd.append(y1)obj_bnd.append(x2)obj_bnd.append(y2)obj_bnd.append(x3)obj_bnd.append(y3)tree.write(dotaxml_file, method='xml', encoding='utf-8') # 更新xml文件# 转换成四点坐标
def rotatePoint(xc, yc, xp, yp, theta):xoff = xp - xc;yoff = yp - yc;cosTheta = math.cos(theta)sinTheta = math.sin(theta)pResx = cosTheta * xoff + sinTheta * yoffpResy = - sinTheta * xoff + cosTheta * yoffreturn str(int(xc + pResx)), str(int(yc + pResy))def totxt(xml_path, out_path):# 想要生成的txt文件保存的路径,这里可以自己修改files = os.listdir(xml_path)i=0for file in files:tree = ET.parse(xml_path + os.sep + file)root = tree.getroot()name = file.split('.')[0]output = out_path +'\\'+name + '.txt'file = open(output, 'w')i=i+1objs = tree.findall('object')for obj in objs:cls = obj.find('name').textbox = obj.find('bndbox')x0 = int(float(box.find('x0').text))y0 = int(float(box.find('y0').text))x1 = int(float(box.find('x1').text))y1 = int(float(box.find('y1').text))x2 = int(float(box.find('x2').text))y2 = int(float(box.find('y2').text))x3 = int(float(box.find('x3').text))y3 = int(float(box.find('y3').text))if x0<0:x0=0if x1<0:x1=0if x2<0:x2=0if x3<0:x3=0if y0<0:y0=0if y1<0:y1=0if y2<0:y2=0if y3<0:y3=0for cls_index,cls_name in enumerate(cls_list):if cls==cls_name:file.write("{} {} {} {} {} {} {} {} {} {}\n".format(x0, y0, x1, y1, x2, y2, x3, y3, cls,cls_index))file.close()# print(output)print(i)if __name__ == '__main__':# -----**** 第一步:把xml文件统一转换成旋转框的xml文件 ****-----roxml_path = r" 已标注并需要转换的xml文件" dotaxml_path = r'存储dota格式的xml文件的输出路径' #out_path = r'存储data格式yolov5_obb可训练的txt文件的路径' filelist = os.listdir(roxml_path)for file in filelist:edit_xml(os.path.join(roxml_path, file), os.path.join(dotaxml_path, file))# -----**** 第二步:把旋转框xml文件转换成txt格式 ****-----totxt(dotaxml_path, out_path)1.3 数据的分布如下:
path: yolov8_obb/datasets/your data/ # dataset root dir
# path: /home/yuanzhengqian/yolov8_obb/datasets/35kv_tading_230617/ # dataset root dir
train: train.txt #images # train images (relative to 'path')
val: val.txt #images # val images (relative to 'path')
test: val.txt #images # test images (optional)nc: 2 # number of classes
names: ['1','2']
你的数据存放格式
datafile--images--train--val--labelTxt--trian--val
train.txt
val.txt
datafile是你的数据文件夹,train.txt和val.txt存储的是训练和评估的图片路径,可通过tools/mk_train.py来制作
2、 输出头的修改
把v8的输出头copy一下即可,额外增加了new_channle参数,当需要进行剪枝的时候会传进来剪枝之后的通道数,对输出头的卷积层数进行修改,无需剪枝的时候则按初始设置状态进行卷积,下一篇章剪枝部分,再详细介绍如何进行剪枝操作。
class Detect_v8(nn.Module):stride = None # strides computed during buildonnx_dynamic = False # ONNX export parameterdynamic = False # force grid reconstructionanchors = torch.empty(0) # initstrides = torch.empty(0) # initshape = Noneexport = False # export modedef __init__(self, nc=80, ch=(), new_channle=(),inplace=True): # detection layersuper().__init__()self.nc = nc # number of classesself.reg_max = 16 # DFL channels (ch[0] // 16 to scale 4/8/12/16/20 for n/s/m/l/x)#dflself.no_box = nc + self.reg_max * 4 +1 # number of outputs per anchorself.nl = len(ch) # number of detection layersself.na = 3 # number of anchorsself.stride = torch.zeros(self.nl) # strides computed during buildself.theta=1#如果要对输出头的卷积层进行剪枝,这把剪枝后的新的通道数按照卷积的顺序传入if len(new_channle)>0:self.cv2 = nn.ModuleList(nn.Sequential(Conv(ch[x], new_channle[0][x][0], 3), Conv(new_channle[0][x][0], new_channle[0][x][1], 3), nn.Conv2d(new_channle[0][x][1],self.reg_max * 4, 1)) for x in range(len(ch)))self.cv3 = nn.ModuleList(nn.Sequential(Conv(ch[x], new_channle[1][x][0], 3), Conv(new_channle[1][x][0], new_channle[1][x][1], 3), nn.Conv2d(new_channle[1][x][1], self.nc, 1)) for x in range(len(ch)))self.cv4 = nn.ModuleList(nn.Sequential(Conv(ch[x], new_channle[2][x][0], 3), Conv(new_channle[2][x][0], new_channle[2][x][1], 3), nn.Conv2d(new_channle[2][x][1], self.theta, 1)) for x in range(len(ch)))else:c2, c3,c4 = max((16, ch[0] // 4,self.reg_max * 4)), max(ch[0], self.nc),max(ch[0],1) # channelsself.cv2 = nn.ModuleList(nn.Sequential(Conv(x, c2, 3), Conv(c2, c2, 3), nn.Conv2d(c2,self.reg_max * 4, 1)) for x in ch)self.cv3 = nn.ModuleList(nn.Sequential(Conv(x, c3, 3), Conv(c3, c3, 3), nn.Conv2d(c3, self.nc, 1)) for x in ch)self.cv4 = nn.ModuleList(nn.Sequential(Conv(x, c4, 3), Conv(c4, c4, 3), nn.Conv2d(c4, self.theta, 1)) for x in ch)self.inplace = inplace # use in-place ops (e.g. slice assignment)self.dfl = DFL(self.reg_max) if self.reg_max > 1 else nn.Identity()def forward(self, x):shape = x[0].shape # BCHWfor i in range(self.nl):x[i] = torch.cat((self.cv2[i](x[i]),self.cv4[i](x[i]), self.cv3[i](x[i]) ), 1)# print(' x[i]', x[i].shape)if self.training:return xelif self.dynamic or self.shape != shape:self.anchors, self.strides = (x.transpose(0, 1) for x in make_anchors(x, self.stride, 0.5))self.shape = shape#dfl_boxbox,theta, cls = torch.cat([xi.view(shape[0], self.no_box, -1) for xi in x], 2).split((self.reg_max * 4, self.theta ,self.nc), 1)dbox = dist2bbox(self.dfl(box), self.anchors.unsqueeze(0), xywh=True, dim=1) * self.stridesy = torch.cat((dbox,theta, cls.sigmoid()), 1)return y if self.export else (y, x)
对应的DFL,dist2bbox等函数从v8上一并copy过来!
parse_model函数进行搭建模型,将原版输出头修改为Detect_v8
def parse_model(d, ch): # model_dict, input_channels(3)LOGGER.info(f"\n{'':>3}{'from':>20}{'n':>3}{'params':>10} {'module':<40}{'arguments':<30}")# anchors, nc, gd, gw = d['anchors'], d['nc'], d['depth_multiple'], d['width_multiple']nc, gd, gw = d['nc'], d['depth_multiple'], d['width_multiple']# na = (len(anchors[0]) // 2) if isinstance(anchors, list) else anchors # number of anchors# no = na * (nc + 185) # number of outputs = anchors * (classes + 185)print('ch',ch)layers, save, c2 = [], [], ch[-1] # layers, savelist, ch outfor i, (f, n, m, args) in enumerate(d['backbone'] + d['head']): # from, number, module, argsm = eval(m) if isinstance(m, str) else m # eval stringsfor j, a in enumerate(args):try:args[j] = eval(a) if isinstance(a, str) else a # eval stringsexcept NameError:passn = n_ = max(round(n * gd), 1) if n > 1 else n # depth gainif m in [Conv, GhostConv, Bottleneck, GhostBottleneck, SPP, SPPF, DWConv, MixConv2d, Focus, CrossConv,BottleneckCSP, C3, C3TR, C3SPP, C3Ghost,ECA,C2f,SEModel,C2f_SE,CAConv,C2fTR,CBAM,RFCAConv2]:c1, c2 = ch[f], args[0]if c2 != nc: # if not outputc2 = make_divisible(c2 * gw, 8)args = [c1, c2, *args[1:]]if m in [BottleneckCSP, C3,c2f, C3TR, C3Ghost]:args.insert(2, n) # number of repeatsn = 1elif m is nn.BatchNorm2d:args = [ch[f]]elif m is Concat:c2 = sum(ch[x] for x in f)elif m is Detect:args.append([ch[x] for x in f])if isinstance(args[1], int): # number of anchorsargs[1] = [list(range(args[1] * 2))] * len(f)elif m is Detect_v8:args.append([ch[x] for x in f])print('args',args)elif m is Contract:c2 = ch[f] * args[0] ** 2elif m is Expand:c2 = ch[f] // args[0] ** 2else: c2 = ch[f]m_ = nn.Sequential(*(m(*args) for _ in range(n))) if n > 1 else m(*args) # modulet = str(m)[8:-2].replace('__main__.', '') # module typem.np = sum(x.numel() for x in m_.parameters()) # number paramsm_.i, m_.f, m_.type = i, f, t # attach index, 'from' index, typeLOGGER.info(f'{i:>3}{str(f):>20}{n_:>3}{m.np:10.0f} {t:<45}{str(args):<30}') # printsave.extend(x % i for x in ([f] if isinstance(f, int) else f) if x != -1) # append to savelistlayers.append(m_)if i == 0:ch = []ch.append(c2)return nn.Sequential(*layers), sorted(save)
yaml文件的读取格式还是根据v5的版本,检测头换成Detect_v8。读者也可自行修改成v8的形式,不过效果都是一样的。
在models/yaml文件夹下除了常规的n,s,l,x的模型,额外提供了对检测小目标效果更好的yolov8n_small_object.yaml(额外增加了小目标检测层),增加了CBAM注意力机制的yolov8n_cbam.yaml(博主在自己的数据集上可以提高一个点94–>95)
# Parameters
nc: 2 # number of classes
depth_multiple: 0.33 # scales module repeats
width_multiple: 0.25 # scales convolution channels# YOLOv8.0n backbone
backbone:# [from, repeats, module, args][[-1, 1, Conv, [64, 3, 2]], # 0-P1/2[-1, 1, Conv, [128, 3, 2]], # 1-P2/4[-1, 3, C2f, [128, True]],[-1, 1, Conv, [256, 3, 2]], # 3-P3/8[-1, 6, C2f, [256, True]],[-1, 1, Conv, [512, 3, 2]], # 5-P4/16[-1, 6, C2f, [512, True]],[-1, 1, Conv, [1024, 3, 2]], # 7-P5/32[-1, 3, C2f, [1024, True]],[-1, 1, SPPF, [1024, 5]],] # 9
# YOLOv8.0n head
head:[[-1, 1, nn.Upsample, [None, 2, 'nearest']],[[-1, 6], 1, Concat, [1]], # cat backbone P4[-1, 3, C2f, [512]], # 13[-1, 1, nn.Upsample, [None, 2, 'nearest']],[[-1, 4], 1, Concat, [1]], # cat backbone P3[-1, 3, C2f, [256]], # 17 (P3/8-small)[-1, 1, Conv, [256, 3, 2]],[[-1, 12], 1, Concat, [1]], # cat head P4[-1, 3, C2f, [512]], # 20 (P4/16-medium)[-1, 1, Conv, [512, 3, 2]],[[-1, 9], 1, Concat, [1]], # cat head P5[-1, 3, C2f, [1024]], # 23 (P5/32-large)[[15, 18, 21], 1, Detect_v8, [nc]],] # Detect(P3, P4, P5)
3、 计算loss
需要计算的loss有分类loss:lcls_loss ,边框回归loss:box_loss +dfl_loss。原版v8是矩形框边框回归用的是CIOU_loss,我们现在做的是旋转框检测,所以需要将原来的CIOU_loss,替换成旋转框计算loss:probiou_loss或kld_loss。
class ComputeLoss:# Compute lossesdef __init__(self, model, autobalance=False):device = next(model.parameters()).device # get model deviceh = model.hyp # hyperparameters# Define criteriaBCEcls = nn.BCEWithLogitsLoss(pos_weight=torch.tensor([h['cls_pw']], device=device))#边框和角度lossself.kld_loss_n = KLDloss(1,fun='log1p')# Class label smoothing https://arxiv.org/pdf/1902.04103.pdf eqn 3self.cp, self.cn = smooth_BCE(eps=h.get('label_smoothing', 0.0)) # positive, negative BCE targets# Focal lossg = h['fl_gamma'] # focal loss gammaif g > 0:BCEcls= FocalLoss(BCEcls, g)det = model.module.model[-1] if is_parallel(model) else model.model[-1] # Detect() moduleself.no_box=det.no_boxself.nc = det.ncself.assigner = TaskAlignedAssigner(topk=10, num_classes=self.nc, alpha=0.5, beta=6.0)self.device=deviceself.varifocal_loss=VarifocalLoss().to(device)self.reg_max=15self.stride = det.stride # tensor([8., 16., 32., ...])self.balance = {3: [4.0, 1.0, 0.4]}.get(det.nl, [4.0, 1.0, 0.25, 0.06, 0.02]) # P3-P7self.ssi = list(self.stride).index(16) if autobalance else 0 # stride 16 indexself.BCEcls, self.gr, self.hyp, self.autobalance = BCEcls, 1.0, h, autobalancefor k in 'na', 'nc', 'nl':setattr(self, k, getattr(det, k))def __call__(self, p, targets,model_l='l1'): # predictions, targets, model# loss = torch.zeros(2, device=self.device) # box, cls, dfllcls_loss = torch.zeros(1, device=self.device)box_loss = torch.zeros(1, device=self.device)dfl_loss = torch.zeros(1, device=self.device)feats = p[1] if isinstance(p, tuple) else p# print('self.stride',self.stride)anchor_points, stride_tensor = make_anchors(feats, self.stride, 0.5)#dflpred_distri,pred_theta,pred_scores = torch.cat([xi.view(feats[0].shape[0], self.no_box, -1) for xi in feats], 2).split((64, 1,self.nc), 1)pred_scores = pred_scores.permute(0, 2, 1).contiguous() #[16, 8400, n]pred_distri = pred_distri.permute(0, 2, 1).contiguous() #[16, 8400, 64]pred_theta = pred_theta.permute(0, 2, 1).contiguous() #[16, 8400, 1]pred_bboxes = bbox_decode(anchor_points, pred_distri) # xywh, (b, h*w, 4),#[16, 8400, 4]pred_theta = (pred_theta.sigmoid()- 0.5) * math.pipred_bboxes=torch.cat((pred_bboxes, pred_theta), -1)dtype = pred_scores.dtype #torch.float16batch_size = pred_scores.shape[0] #16imgsz = torch.tensor(feats[0].shape[2:], device=self.device, dtype=dtype) * self.stride[0] # image size (h,w)#tensor([640., 640.], device='cuda:0', dtype=torch.float16)#将batch的gt维度进行合并targets = preprocess(targets.to(self.device), batch_size, self.device,scale_tensor=imgsz[[1, 0, 1, 0]]) #torch.Size([16, 2, 6])gt_labels, gt_bboxes = targets.split((1, 5), 2) # cls, xyxy torch.Size([16, 2, 1]),torch.Size([16, 2, 5])mask_gt = gt_bboxes.sum(2, keepdim=True).gt_(0) #torch.Size([16, 2, 1])#TAL动态匹配target_labels, target_bboxes, target_scores, fg_mask, _ = self.assigner(pred_scores.detach().sigmoid(), (pred_bboxes.detach() * stride_tensor).type(gt_bboxes.dtype),anchor_points * stride_tensor, gt_labels, gt_bboxes, mask_gt)target_scores_sum = max(target_scores.sum(), 1)# cls losstarget_labels = torch.where(target_scores > 0 , 1, 0)#分类losslcls_loss += self.varifocal_loss(pred_scores, target_scores, target_labels) / target_scores_sum # VFL #边框+角度lossif fg_mask.sum():#旋转边框值进行下采样,切记不能加入角度target_bboxes[:,:,:4] /= stride_tensorweight = target_scores.sum(-1)[fg_mask].unsqueeze(-1)# weight = target_scores.sum(-1)[fg_mask].unsqueeze(-1).pow(2)probloss = probiou_loss(pred_bboxes[fg_mask], target_bboxes[fg_mask])# probloss = probiou_loss(pred_bboxes[fg_mask], target_bboxes[fg_mask], model_l)box_loss +=(probloss* weight).sum() / target_scores_sum# kldloss = self.kld_loss_n(pred_bboxes[fg_mask], target_bboxes[fg_mask])# box_loss +=kldloss.mean()#DFL losstarget_ltrb = bbox2dist(anchor_points, target_bboxes[:,:,:4], self.reg_max)dfl_loss = df_loss(pred_distri[fg_mask].view(-1, self.reg_max + 1), target_ltrb[fg_mask]) * weightdfl_loss = dfl_loss.sum() / target_scores_sumdfl_loss=dfl_loss.unsqueeze(-1)lcls_loss *= self.hyp['cls']box_loss *= self.hyp['box']dfl_loss *= self.hyp['box']# return ( box_loss + lcls_loss ) * batch_size, torch.cat(( box_loss,lcls_loss)).detach()return ( box_loss + lcls_loss+dfl_loss ) * batch_size, torch.cat(( box_loss,lcls_loss,dfl_loss)).detach()
4、 TAL正负样本匹配机制(旋转框版本)
首先,你需要修改对正样本点筛选的函数,不同于矩形框,我们需要挑选出属于旋转框内部的坐标点。此方法调用的是百度PP-yoloe-r里写好的函数check_points_in_rotated_boxes,感谢大佬们的贡献。
def check_points_in_rotated_boxes(points, boxes):"""Check whether point is in rotated boxesArgs:points (tensor): (1, L, 2) anchor pointsboxes (tensor): [B, N, 5] gt_bboxeseps (float): default 1e-9Returns:is_in_box (tensor): (B, N, L)"""# [B, N, 5] -> [B, N, 4, 2]corners = rbox2poly2(boxes)# [1, L, 2] -> [1, 1, L, 2]points = points.unsqueeze(0)# [B, N, 4, 2] -> [B, N, 1, 2]a, b, c, d = corners.split((1,1,1,1), 2)ab = b - aad = d - a# [B, N, L, 2]ap = points - a# [B, N, L]norm_ab = torch.sum(ab * ab, dim=-1)# [B, N, L]norm_ad = torch.sum(ad * ad, dim=-1)# [B, N, L] dot productap_dot_ab = torch.sum(ap * ab, dim=-1)# [B, N, L] dot productap_dot_ad = torch.sum(ap * ad, dim=-1)# [B, N, L] <A, B> = |A|*|B|*cos(theta) is_in_box = (ap_dot_ab >= 0) & (ap_dot_ab <= norm_ab) & (ap_dot_ad >= 0) & (ap_dot_ad <= norm_ad)return is_in_box
所实现的原理是用向量的定义,即落在旋转框内的点与某一点的连线和该点的临边的点积>=0(两边夹角小于等于90°)。点积小于该边的模长,即该点在此边上的投影要小于等于该边长。有了这两个条件的约束,即可确定该点是否在gt框内。
其次修改的地方是overlap的计算方式,原版是计算矩形框的交并比,我们现在需要修改成计算旋转框的交并比。计算的方法需要调用mmrotate中的box_iou_rotated函数,所以你需要安装mmrotate,环境配置按上一篇v5_obb的装即可。
def rotated_iou_similarity(box1, box2):"""Calculate iou of box1 and box2Args:box1 (Tensor): box with the shape [N, 5]box2 (Tensor): box with the shape [N, 5]Return:iou (Tensor): iou between box1 and box2 with the shape [N]"""rotated_ious = []for b1, b2 in zip(box1, box2):b1=b1.unsqueeze(0)b2=b2.unsqueeze(0)rotated_ious.append(box_iou_rotated(b1, b2).squeeze(0).squeeze(0))return torch.stack(rotated_ious, axis=0)
get_box_metrics函数中得到gt和预测框的交并比overlaps,并通过交并比来选择正负样本。如果数据集分布中存在大框周围有很多小框的情况下,如下图所示,GT2框中的点1位置的预测框P,与GT2的交并比IOU2要小于与GT1的交并比IOU1,这时候只用iou匹配来分配正负样本,则会导致原本再GT2框中的点1分配给了GT1,为了避免这种情况,我选择在交并比overlap的基础上再增加一项距离约束,计算点1到GT1和GT2的欧氏距离L1和L2,尽可能的达到IOU2/L2<(IOU2/L2)的目的。针对此类数据分布,使用此方法可以增加对小目标的召回。

如果是正常的数据分布,则直接使用交并比IOU即可,代码中通过distance_constraint来选择你需要的方法,直接在这里改即可,懒得传参了。
def get_box_metrics(self, pd_scores, pd_bboxes, gt_labels, gt_bboxes, mask_gt):"""Compute alignment metric given predicted and ground truth bounding boxes."""na = pd_bboxes.shape[-2]mask_gt = mask_gt.bool() # b, max_num_obj, h*woverlaps = torch.zeros([self.bs, self.n_max_boxes, na], dtype=pd_bboxes.dtype, device=pd_bboxes.device)bbox_scores = torch.zeros([self.bs, self.n_max_boxes, na], dtype=pd_scores.dtype, device=pd_scores.device)ind = torch.zeros([2, self.bs, self.n_max_boxes], dtype=torch.long) # 2, b, max_num_objind[0] = torch.arange(end=self.bs).view(-1, 1).expand(-1, self.n_max_boxes) # b, max_num_objind[1] = gt_labels.squeeze(-1) # b, max_num_obj# Get the scores of each grid for each gt clsbbox_scores[mask_gt] = pd_scores[ind[0], :, ind[1]][mask_gt] # b, max_num_obj, h*w# (b, max_num_obj, 1, 4), (b, 1, h*w, 4)pd_boxes = pd_bboxes.unsqueeze(1).expand(-1, self.n_max_boxes, -1, -1)[mask_gt]gt_boxes = gt_bboxes.unsqueeze(2).expand(-1, -1, na, -1)[mask_gt]#是否采用欧式距离约束正负样本选择,0 false 1 truedistance_constraint=0if distance_constraint==1:#计算每个anchor中心点与gt中心点之间的欧氏距离Euclidean_distance = torch.zeros([self.bs, self.n_max_boxes, na], dtype=pd_bboxes.dtype, device=pd_bboxes.device)pdist = nn.PairwiseDistance(p=2)Euclidean_distance[mask_gt] = pdist(gt_boxes[:,:2],pd_boxes[:,:2])#归一化欧氏距离eps=0.0001min_score=Euclidean_distance[mask_gt].amin(0)max_score=Euclidean_distance[mask_gt].amax(0)Euclidean_distance[mask_gt]=(Euclidean_distance[mask_gt]-min_score+eps)/(max_score-min_score)Euclidean_distance[mask_gt]=Euclidean_distance[mask_gt].pow(0.1)overlaps_distance = torch.zeros([self.bs, self.n_max_boxes, na], dtype=pd_bboxes.dtype, device=pd_bboxes.device)#计算旋转框iou并除以欧氏距离得到overlaps_distance,距离越小overlaps_distance越大overlaps[mask_gt]=rotated_iou_similarity(gt_boxes,pd_boxes)overlaps_distance[mask_gt]=overlaps[mask_gt]/Euclidean_distance[mask_gt] min_score_overlaps=overlaps_distance[mask_gt].amin(0)max_score_overlaps=overlaps_distance[mask_gt].amax(0)overlaps_distance[mask_gt]=(overlaps_distance[mask_gt]-min_score_overlaps+eps)/(max_score_overlaps-min_score_overlaps)#align_metric得分已overlaps_distance的得分值为主导align_metric = bbox_scores.pow(2) * overlaps_distance.pow(1)return align_metric, overlaps_distanceelse:overlaps[mask_gt]=rotated_iou_similarity(gt_boxes,pd_boxes)align_metric = bbox_scores.pow(2) * overlaps.pow(1)return align_metric, overlaps
总结:

5、 NMS_OBB
v8去除了物体的得分值obj,所以无需再进行obj的得分×cls的得分操作,直接获取分类得分即是该类别得分
# Batched NMSc = x[:, 6:7] * (0 if agnostic else max_wh) # classesrboxes = x[:, :5].clone() rboxes[:, :2] = rboxes[:, :2] + c # rboxes (offset by class)scores = x[:, 5] _, i = obb_nms(rboxes, scores, iou_thres) #dets (tensor/array): (num, [cx cy w h θ]) θ∈[-pi/2, pi/2)# if i.shape[0] > max_det: # limit detectionsi = i[:max_det]
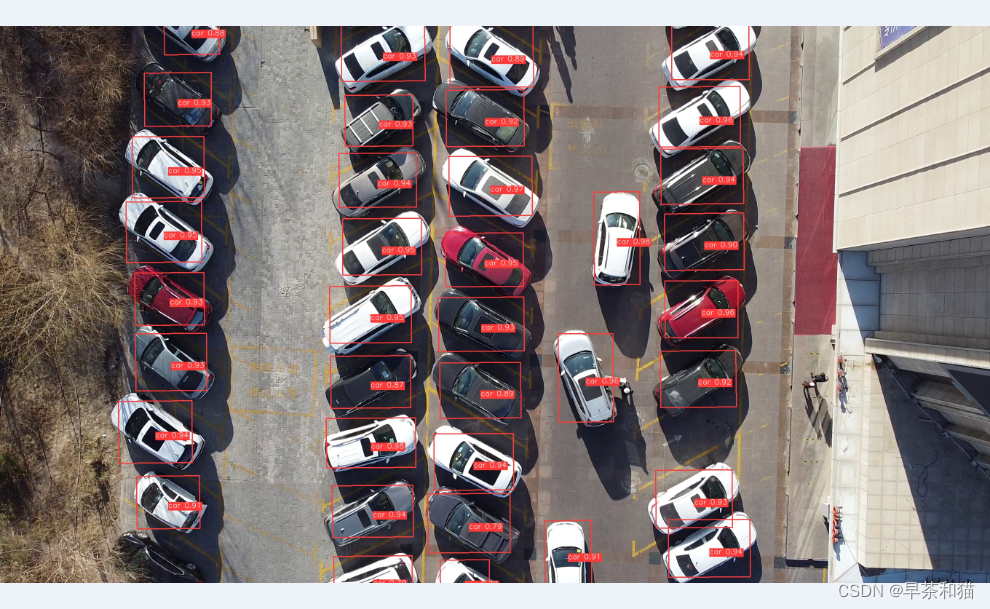
6、 yolov8_obb与yolov5_obb在UAV-ROD数据集上的训练效果对比
yolov5_obb,yolov5s的检测效果,每个目标都能检测到,但是框的回归基本上效果为0

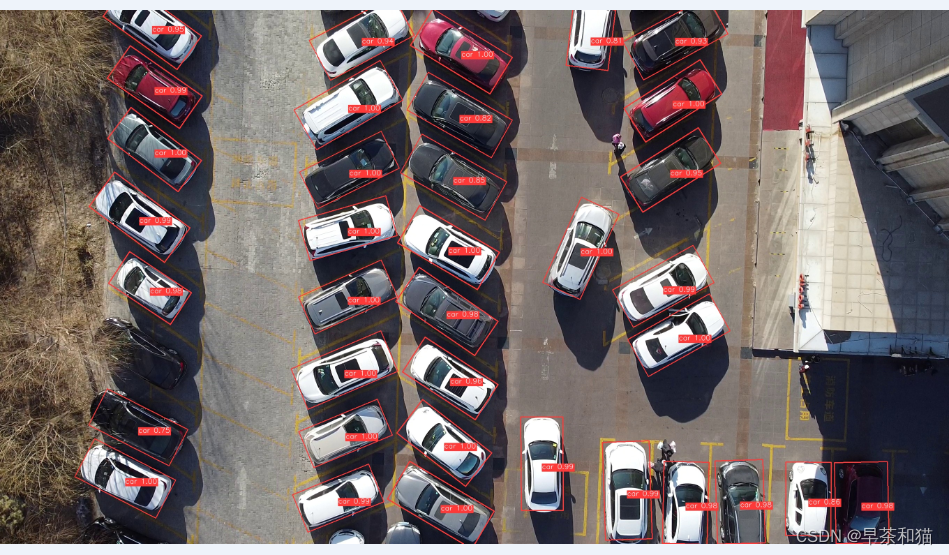
yolov8_obb,yolov8n的收敛效果,完全碾压了v5

四、问题及优化
1、【深度学习】多卡训练__单机多GPU方法详解(torch.nn.DataParallel、torch.distributed)
你的数据里尽量不要有空标签的图片,如果有尽量将你的batch设置大一下,因为再获取gt_box的时候,你的空标签越多,他读取一个batch时可能刚好一整个batch里所有的图片都是空标签,这时候获取的gt_box就为0,会产生空列表导致iou的计算出错。
解决方案就是1、数据里尽量不要有空标签的图片。2、如果有batch_size设置大一点
2、增加save_xml文件功能,可在rolabelimg中打开并调整框,减少标注工作量。
#测试图片并保存对应xml文件
python detcet_save_xml.py --save-xml --xml_save_path_dir your_xml_save_path/ --weights runs/train/exp/weights/best.pt --source dataset/your datafile/images/val/ --img 640 --device 0 --conf-thres 0.25 --iou-thres 0.2
3、剪枝目前只支持剪枝v8n,s以上不支持,有空再优化(此问题已解决,现在都支持–20231016)
五、 yolov8_obb模型剪枝
yolov8_obb模型剪枝
六、 yolov8_obb旋转框跟踪
yolov8_obb旋转框跟踪
七、结语
希望此项目和博文对您的工作和学业有所帮助,祝大家生活愉快,身体健康!
这篇关于Yolov8_obb(prob loss) 基于anchor_free的旋转框目标检测,剪枝,跟踪(ByteTracker)的文章就介绍到这儿,希望我们推荐的文章对编程师们有所帮助!








