本文主要是介绍吴恩达老师机器学习ex3.Multi-class Classification and Neural Networks,希望对大家解决编程问题提供一定的参考价值,需要的开发者们随着小编来一起学习吧!
吴恩达 机器学习 第四周作业 Multi-class Classification and Neural Networks
Octave代码
lrCostFunction.m
function [J, grad] = lrCostFunction(theta, X, y, lambda)
%LRCOSTFUNCTION Compute cost and gradient for logistic regression with
%regularization
% J = LRCOSTFUNCTION(theta, X, y, lambda) computes the cost of using
% theta as the parameter for regularized logistic regression and the
% gradient of the cost w.r.t. to the parameters. % Initialize some useful values
m = length(y); % number of training examples% You need to return the following variables correctly
J = 0;
grad = zeros(size(theta));% ====================== YOUR CODE HERE ======================
% Instructions: Compute the cost of a particular choice of theta.
% You should set J to the cost.
% Compute the partial derivatives and set grad to the partial
% derivatives of the cost w.r.t. each parameter in theta
%
% Hint: The computation of the cost function and gradients can be
% efficiently vectorized. For example, consider the computation
%
% sigmoid(X * theta)
%
% Each row of the resulting matrix will contain the value of the
% prediction for that example. You can make use of this to vectorize
% the cost function and gradient computations.
%
% Hint: When computing the gradient of the regularized cost function,
% there're many possible vectorized solutions, but one solution
% looks like:
% grad = (unregularized gradient for logistic regression)
% temp = theta;
% temp(1) = 0; % because we don't add anything for j = 0
% grad = grad + YOUR_CODE_HERE (using the temp variable)
%
h = 1 ./ (1 + exp(-X * theta));
theta_temp = theta(2 : length(theta), 1);
J = 1 / m * sum(-y .* log(h) - (1 - y) .* log(1 - h)) + 0.5 * lambda / m * sum(theta_temp .^ 2);
grad = 1 / m .* (X' * (h - y)) + lambda / m .* theta;
grad(1) = 1 / m * sum(h - y);% =============================================================grad = grad(:);endoneVsAll.m
function [all_theta] = oneVsAll(X, y, num_labels, lambda)
%ONEVSALL trains multiple logistic regression classifiers and returns all
%the classifiers in a matrix all_theta, where the i-th row of all_theta
%corresponds to the classifier for label i
% [all_theta] = ONEVSALL(X, y, num_labels, lambda) trains num_labels
% logistic regression classifiers and returns each of these classifiers
% in a matrix all_theta, where the i-th row of all_theta corresponds
% to the classifier for label i% Some useful variables
m = size(X, 1);
n = size(X, 2);% You need to return the following variables correctly
all_theta = zeros(num_labels, n + 1);% Add ones to the X data matrix
X = [ones(m, 1) X];% ====================== YOUR CODE HERE ======================
% Instructions: You should complete the following code to train num_labels
% logistic regression classifiers with regularization
% parameter lambda.
%
% Hint: theta(:) will return a column vector.
%
% Hint: You can use y == c to obtain a vector of 1's and 0's that tell you
% whether the ground truth is true/false for this class.
%
% Note: For this assignment, we recommend using fmincg to optimize the cost
% function. It is okay to use a for-loop (for c = 1:num_labels) to
% loop over the different classes.
%
% fmincg works similarly to fminunc, but is more efficient when we
% are dealing with large number of parameters.
%
% Example Code for fmincg:
%
% % Set Initial theta
% initial_theta = zeros(n + 1, 1);
%
% % Set options for fminunc
% options = optimset('GradObj', 'on', 'MaxIter', 50);
%
% % Run fmincg to obtain the optimal theta
% % This function will return theta and the cost
% [theta] = ...
% fmincg (@(t)(lrCostFunction(t, X, (y == c), lambda)), ...
% initial_theta, options);
%for c = 1 : num_labels;initial_theta = zeros(n + 1, 1);
options = optimset('GradObj', 'on', 'MaxIter', 50);
[theta, cost] = fmincg (@(t)(lrCostFunction(t, X, (y == c), lambda)), initial_theta, options);
% fprintf('\ntheta: %f\n', theta);
% fprintf('\nall_theta: %f\n', all_theta);
all_theta(c, :) = theta;end;% =========================================================================end
predictOneVsAll.m
function p = predictOneVsAll(all_theta, X)
%PREDICT Predict the label for a trained one-vs-all classifier. The labels
%are in the range 1..K, where K = size(all_theta, 1).
% p = PREDICTONEVSALL(all_theta, X) will return a vector of predictions
% for each example in the matrix X. Note that X contains the examples in
% rows. all_theta is a matrix where the i-th row is a trained logistic
% regression theta vector for the i-th class. You should set p to a vector
% of values from 1..K (e.g., p = [1; 3; 1; 2] predicts classes 1, 3, 1, 2
% for 4 examples) m = size(X, 1);
num_labels = size(all_theta, 1);% You need to return the following variables correctly
p = zeros(size(X, 1), 1);% Add ones to the X data matrix
X = [ones(m, 1) X];% ====================== YOUR CODE HERE ======================
% Instructions: Complete the following code to make predictions using
% your learned logistic regression parameters (one-vs-all).
% You should set p to a vector of predictions (from 1 to
% num_labels).
%
% Hint: This code can be done all vectorized using the max function.
% In particular, the max function can also return the index of the
% max element, for more information see 'help max'. If your examples
% are in rows, then, you can use max(A, [], 2) to obtain the max
% for each row.
% p_temp = 1 ./ (1 + exp(-X * all_theta'));
[max_value, p] = max(p_temp, [], 2);% =========================================================================end
ex3运行结果
Octave command prompt
octave:33> ex3Loading and Visualizing Data ...
Program paused. Press enter to continue.Testing lrCostFunction() with regularization
Cost: 2.534819
Expected cost: 2.534819
Gradients:0.146561 -0.548558 0.724722 1.398003
Expected gradients:0.146561-0.5485580.7247221.398003
Program paused. Press enter to continue.Training One-vs-All Logistic Regression...
Iteration 50 | Cost: 1.386626e-02
Iteration 50 | Cost: 5.725220e-02
Iteration 50 | Cost: 6.396625e-02
Iteration 50 | Cost: 3.633786e-02
Iteration 50 | Cost: 6.182203e-02
Iteration 50 | Cost: 2.173015e-02
Iteration 50 | Cost: 3.295401e-02
Iteration 50 | Cost: 8.460907e-02
Iteration 50 | Cost: 8.094079e-02
Iteration 50 | Cost: 9.847356e-03
Program paused. Press enter to continue.Training Set Accuracy: 95.100000
octave:34> predict.m
function p = predict(Theta1, Theta2, X)
%PREDICT Predict the label of an input given a trained neural network
% p = PREDICT(Theta1, Theta2, X) outputs the predicted label of X given the
% trained weights of a neural network (Theta1, Theta2)% Useful values
m = size(X, 1);
num_labels = size(Theta2, 1);% You need to return the following variables correctly
p = zeros(size(X, 1), 1);% ====================== YOUR CODE HERE ======================
% Instructions: Complete the following code to make predictions using
% your learned neural network. You should set p to a
% vector containing labels between 1 to num_labels.
%
% Hint: The max function might come in useful. In particular, the max
% function can also return the index of the max element, for more
% information see 'help max'. If your examples are in rows, then, you
% can use max(A, [], 2) to obtain the max for each row.
%X = [ones(m, 1) X];z2 = Theta1 * X';
a2 = 1 ./ (1 + exp(-z2));
units = size(a2, 1);
a2_new = [ones(1, m); a2];z3 = Theta2 * a2_new;
a3 = 1 ./ (1 + exp(-z3));[max_value, p] = max(a3', [], 2);% =========================================================================end
ex3_nn运行结果
Octave command prompt
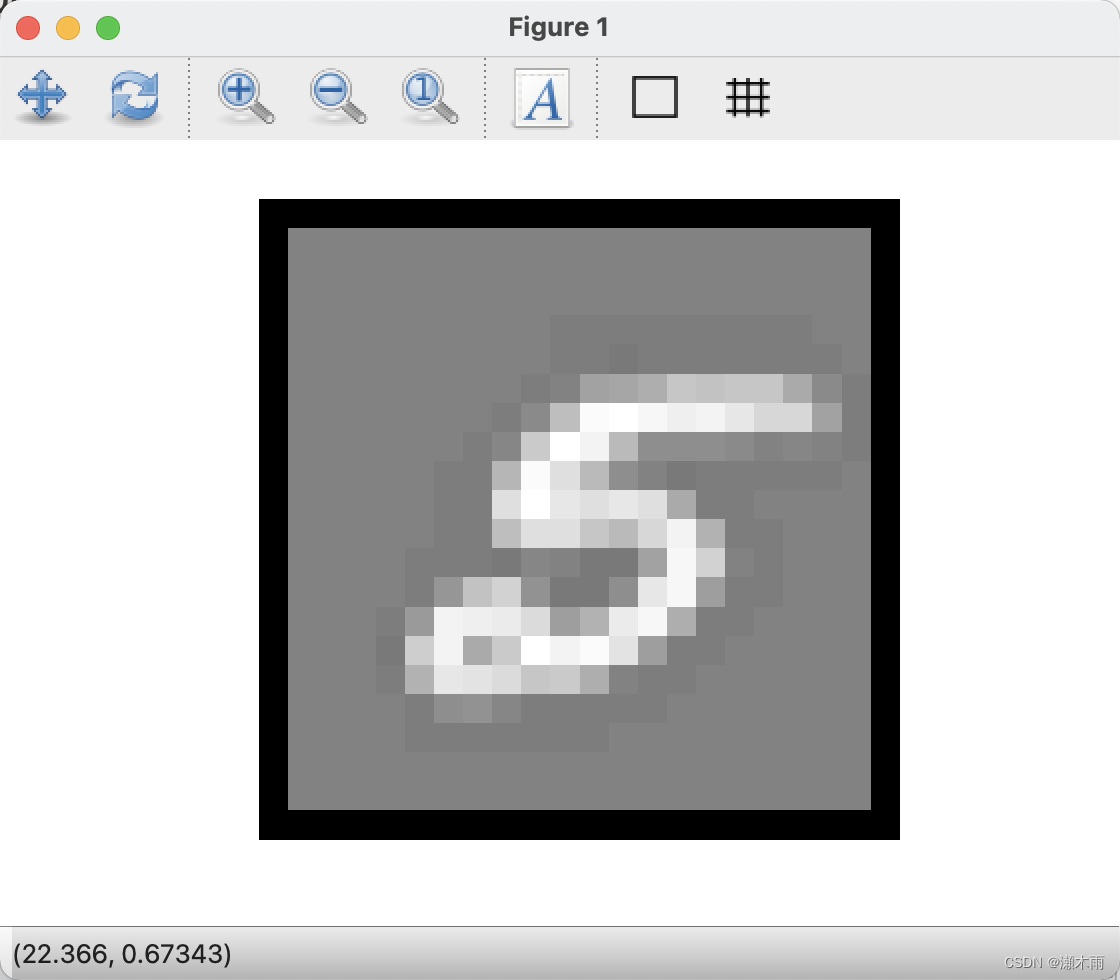
octave:34> ex3_nnLoading and Visualizing Data ...
Program paused. Press enter to continue.Loading Saved Neural Network Parameters ...Training Set Accuracy: 97.520000
Program paused. Press enter to continue.Displaying Example ImageNeural Network Prediction: 5 (digit 5)
Paused - press enter to continue, q to exit:这篇关于吴恩达老师机器学习ex3.Multi-class Classification and Neural Networks的文章就介绍到这儿,希望我们推荐的文章对编程师们有所帮助!






