本文主要是介绍Mplus—随机截距交叉滞后模型(Random Intercepts Cross-Lagged Panel Model, RI-CLPM),希望对大家解决编程问题提供一定的参考价值,需要的开发者们随着小编来一起学习吧!
交叉滞后面板模型(Cross-Lagged Panel Model, CLPM)
说到随机截距交叉滞后模型(Random Intercepts Cross-Lagged Panel Model, RI-CLPM),就不得不提及交叉滞后模型(Cross-Lagged Panel Model, CLPM)
Cross-lagged panel analysis is an analytical strategy used to describe reciprocal relationships, or directional influences, between variables over time (Kearney,2017).
The cross-lagged panel model (CLPM) has been extremely popular inbehavioral and psychological science research (Usami et al., 2019).
CLPM是描述变量之间相互关系的一种纵向数据分析方法。
最基本的CLPM如下图所示,对两个变量在两个时间点分别进行了测量,因此,该模型包括了两个X变量(x1,x2)和两个Y变量(y1,y2)。
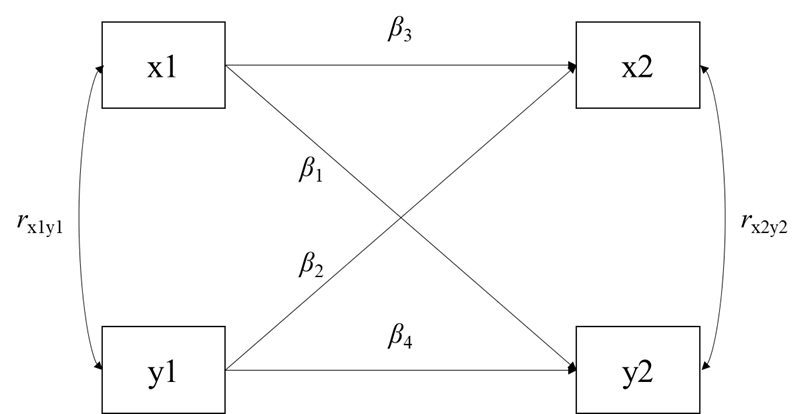
CLPM估计三种类型的关系
1. [Synchronous] Correlations:指同一时间点两个变量之间的关系,在上图中为x1与y1之间的相关,x2与y2之间的相关。
2. Autoregressive effects:指不同时间点同一变量之间的关系,在上图中为x1到x2的效应,y1到y2的效应,即为β3和β4。
Autoregressive effects describe the amount of stability in constructs over time. Smaller autoregressive coefficients (closer to zero) indicate more variance in the construct, meaning less stability or influence from the previous time point. Larger autoregressive coefficients indicate little variance over time, meaning more stability or influence from the previous time point (Kearney, 2017).
3. Cross-Lagged effects:指不同时间点不同变量之间的关系,在上图中为x1到y2的效应,y1到x2的效应,即为β1和β2。
CLPM的优点为:在控制同一时间点内变量之间相关性和变量跨时间稳定性的情况下,探讨一个变量对另一个变量的预测效应。
但Hamaker,Kuiper和Grasman (2015)在A Critique of the Cross-Lagged Panel Model这篇文章中提出:
The CLPM only accounts for temporal stability through the inclusion of autoregressive parameters. This implies that in this model it is implicitly assumed that every person varies over time around the same means μt and πt, and that there are no trait-like individual differences that endure.
CLPM纳入自回归方法只能控制时间稳定性,而没有考虑到变量的稳定性可能存在不同形式,也就是每个个体在同一变量上都围绕相同的均值在变化,不同个体在这一变量上不存在均值差异。
纵向数据是一种多水平的数据,变量变异来源可以自然分类到个体间水平(Between-person level)和个体内水平(Within-person level)。而CLPM混淆了个体间和个体内水平的效应。
A major limitation of the CLPM is that it does not separate between-personeffects from within-person effects. Depending on the between-person and within-person variance structures, CLPM results may reflect mostly between-person effects, mostly within-person effects, or an ambiguous mix of effects, leaving the researcher with an uninterpretable blend of effects (Masselink et al.,2018).
随机截距交叉滞后模型(Random Intercepts Cross-Lagged Panel Model, RI-CLPM)
因此,在CLPM的基础上,Hamaker等人(2015)提出了随机截距的交叉滞后模型(Random Intercepts Cross-Lagged Panel Model, RI-CLPM),区分个体间水平和个体内水平。通过结构方程模型的方法,在CLPM中引入一个随机截距的潜变量,表征个体间稳定、不随时间变化、特征差异,即不同个体在变量上存在不同的截距水平,每个个体不再围绕统一的样本均值变化,而是围绕自己的截距水平而变化。而在个体内水平上,保留了CLPM的基本思想。
RI-CLPM有点类似于实验操纵,在控制个体特质水平的差异后,探讨个体在前一个时间点上一个变量的变化(change)”导致“了后一个时间点上另一个变量的变化。
The random intercept cross-lagged panel model (RI-CLPM) proposed by Hamakeret al. (2015) is an extension of the traditional cross-lagged panel model(CLPM). It was introduced to account for stable, trait-like differences between units (e.g., individuals, dyads, families, etc.), such that the lagged relations pertain exclusively to within-unit fluctuations (Mulder & Hamaker, 2021).
那么CLPM究竟能告诉我们什么呢?
个体间水平可以提示我们”谁在某一变量上具有高风险“、”谁可能需要被干预“
"Who is at risk for heightened X?” and “Who should get an intervention to reduce Y?
个体内水平可以提示我们“干预哪些东西可以帮助个体降低在某一变量上的风险”
At the between-person level, it may be useful to know how adolescents are situated within the group and which individuals are more likely to have higher or lower levels of psychological variables than their peers. Within-person modeling should be considered to explore the development at the individual level (Hudson et al., 2019).
Moreover, within-person associations may help to identify modifiable targets for intervention (between-person associations are helpful in detecting who needs an intervention) (Masselink et al., 2018).
Building up the basic RI-CLPM
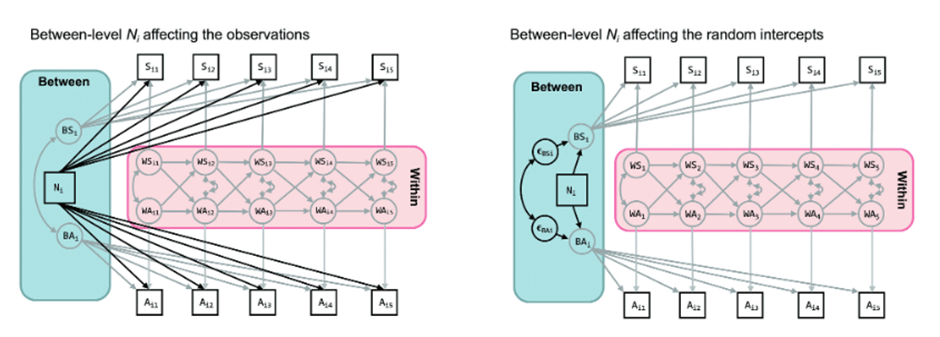
To fit an RI-CLPM, we need to decompose the observed scores into three components: grand means, stable between components, and fluctuating within components.
-
The first components are the grand means, which are the means over all units per occasion t.
-
Second, the between components are the random intercepts. They capture a unit's time-invariant deviation from the grand means and thus represent the stable differences between units.
-
Third, the within components are the differences between a unit's observed measurements and the unit"s expected score based on the grand means and its random intercepts.
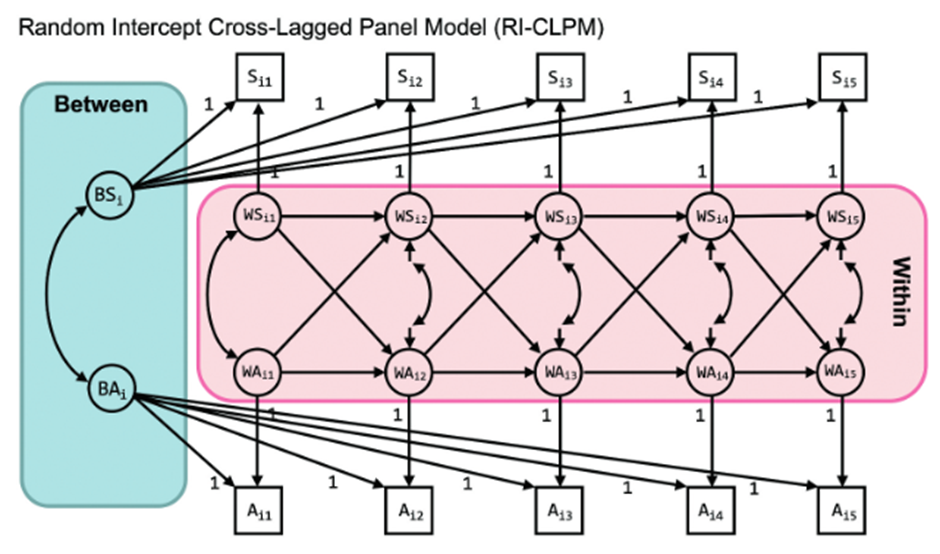
Autoregressive effects
自回归效应代表个体内部的结转效应,或者称之为惯性。
自回归路径系数含义可见下例,代表个体在前一个时间点上一个变量的变化将“导致“其下一个时间点上的变化。
The autoregressive effects (i.e., αt from WSi t-1to WSit and δt from WAi t-1 to WAit) represent the within-person carry-over effects. If αt is positive, this implies that an individual who experiences elevated sleep problems relative to his/her own expected score, is likely to experience elevated sleep problems relative to his/her own expected score atthe next occasion as well.
The within-person autoregressive effects are sometimes referred to as inertia (i.e., the tendency to not move; see Suls etal., 1998).
Cross-lagged effects
交叉滞后效应代表个体在前一个时间点上一个变量的变化/波动会”导致“下一个时间点上另一个变量的变化/波动。
The cross-lagged effects in the model represent the spill-over of the state in one domain into the state of another domain. Here,βt represents the effect of WSi t-1 to WAit and γt the effect of WAi t-1 toWSit. A positive βt implies that a positive (negative) deviation from anindividual"s expected level of sleep problems will likely be followed by apositive (negative) deviation in the individual"s expected level of anxiety atthe next occasion in the same direction.
Random intercepts
某一变量的随机截距的方差显著,表明在这一变量上,个体之间存在显著差异。
不同变量的随机截距之间存在正相关关系,表明在某一群体中,一个变量上得分高的个体往往在另一个变量上得分也高。
We find that both random intercepts have significant variance, which implies that there are stable, trait-like differences between persons on sleep problems and anxiety.
If, in contrast to our findings here, the variance of a random intercept does not significantly differ from 0, this means that there are little to no stable between-unit differences, and that each unit fluctuates around the same grand means over time.
We find a significant positive covariance between the random intercepts of :01 with SE = :001 (the correlation is :59, SE =:050), suggesting that individuals who have more sleep problems, in general, are also more anxious in general.
RI-CLPM和CLPM的关系
CLPM嵌套于RI-CLPM中
即当个体间不存在差异,所有个体围绕相同的样本均值变化时的RI-CLPM等价于CLPM。
If we constrain the variances of all random intercepts (and their covariance) in the RI-CLPM to zero, we obtain a model that is nested under the RI-CLPM, and no longer accounts for stable between-unit differences. This model is actually statistically equivalent to the traditional CLPM (Mulder & Hamaker, 2021).
Mplus语法
最全网址:The RI-CLPM & Extensions (jeroendmulder.github.io)

Basic RI-CLPM
将观察分数/显变量分为个体间和个体内水平,如下图所示。
decomposes each observed score into abetween-person part and a within-person part
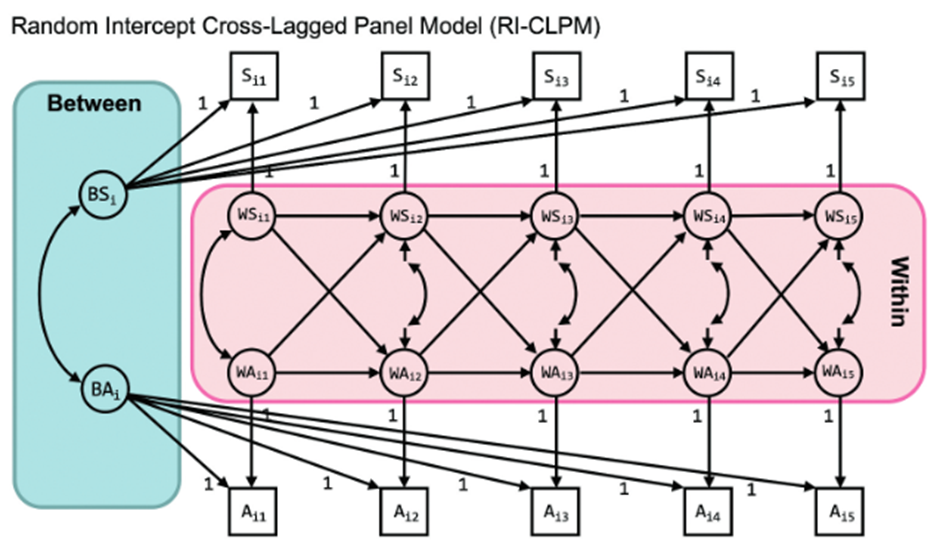
语法可见:ResearchGate-EllenHamaker-How to run the RI-CLPM with Mplus
网址:https://www.researchgate.net/publication/323935149_How_to_run_the_RI-CLPM_with_Mplus
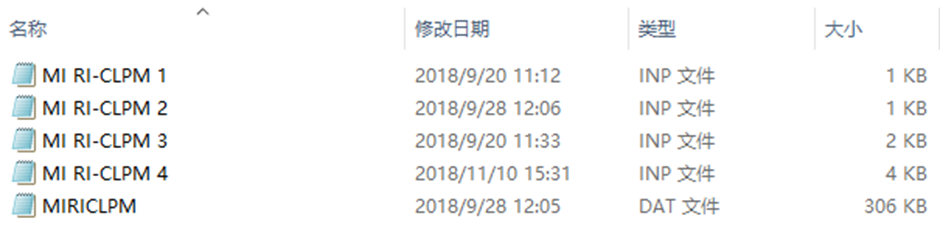
Multiple Indicator RI-CLPM
相当于将潜变量分为个体间和个体内水平,如下图所示。
语法可见:ResearchGate-EllenHamaker-How to run a multipleindicator RI-CLPM in Mplus
网址:https://www.researchgate.net/publication/328095575_How_to_run_a_multiple_indicator_RI-CLPM_in_Mplus
语法可见:ResearchGate-EllenHamaker-Mplus files for the MI RI-CLPM
网址:https://www.researchgate.net/publication/328095732_Mplus_files_for_the_MI_RI-CLPM
RI-CLPM with three (or more) variables
上述的语法,均以两个变量为例,三个或者多个变量的RI-CLPM的语句又如何写呢?答案是将变量分解为个体间和个体内水平,纳入模型即可。

RI-CLPM with covariates
如果想在RI-CLPM模型中纳入协变量,分为两种情况,一种是随时间变化的协变量,一种是时不变协变量。
Time-varying covariates
将这一协变量分为个体间和个体内水平纳入模型中

Time-invariant covariates
Mulder, J. D., & Hamaker, E. L. (2021). ThreeExtensions of the Random Intercept Cross-Lagged Panel Model. StructuralEquation Modeling: A Multidisciplinary Journal, 28(4), 638–648. https://doi.org/10.1080/10705511.2020.1784738
Extension 1: Including time-invariant predictorsand outcomes
上述文章的”Extension 1 “部分有详细阐述,有两种方法,见下图
网址:Using Mplus (jeroendmulder.github.io)
Mediation effect test
三个变量的RI-CLPM中,中介效应的检验可通过Bootstrap法
Mplus语法为: Analysis: Bootstrap = …;
Model Indirect: Y Ind M X;
RI-CLPM with binary/categorical/count outcomes
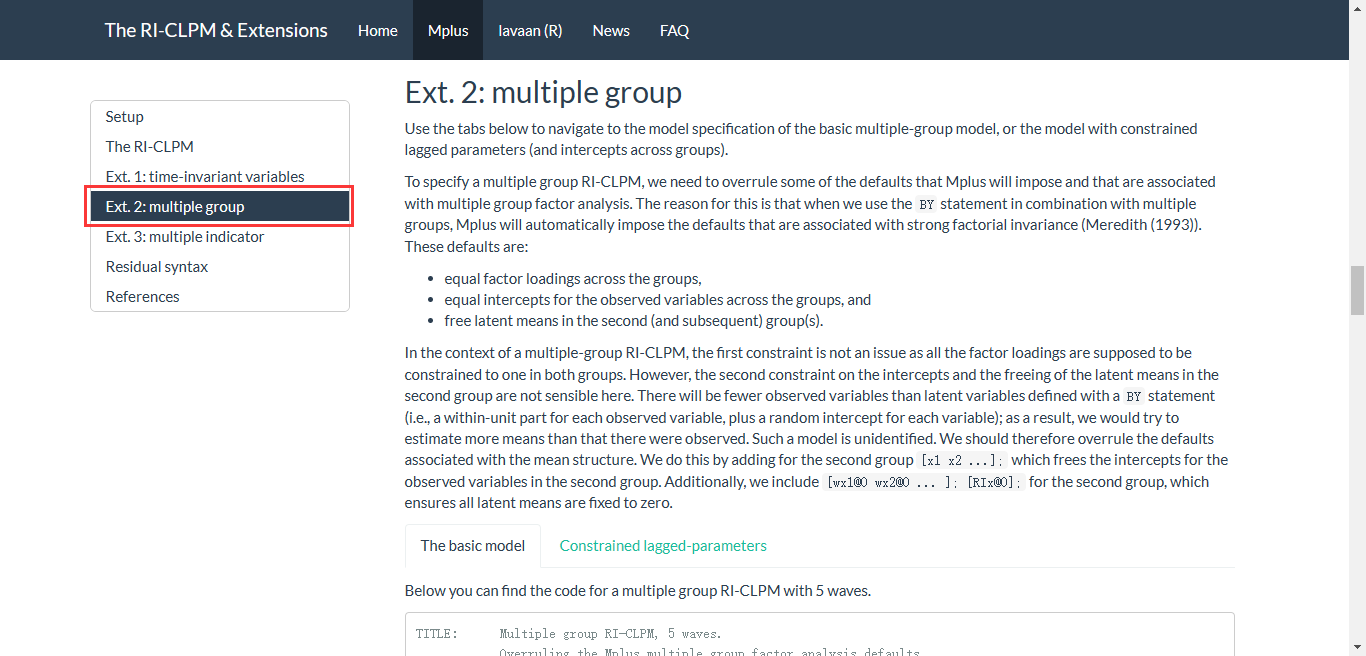
Multiple group RI-CLPM
检验模型是否具有跨组不变性,例如跨性别不变性
探讨变量的调节作用
方法:自由估计模型与限制模型进行比较
网址:Using Mplus (jeroendmulder.github.io)
This can be investigated by comparing a multiple group version of the RI-CLPM in which there are no constraints across the groups, with a model in which the lagged regression coefficients are constrained to be identical across the groups. If the chi-square difference test indicates that this constraint cannot be imposed, this implies that (some of) the lagged coefficients differ across the groups: The lagged effects of the variables on each other depend on the level of the grouping variable. In contrast, when the equality constraints on the lagged parameters across the groups hold, this implies there is no moderation effect (Mulder & Hamaker, 2021).
How do I perform a power analysis for the RI-CLPM?

Effect Size
Orth, U., Meier, L. L., Bühler, J. L., Dapp, L. C.,Krauss, S., Messerli, D., & Robins, R. W. (2022). Effect size guidelines for cross-lagged effects. Psychological Methods. APA PsycNet

这篇关于Mplus—随机截距交叉滞后模型(Random Intercepts Cross-Lagged Panel Model, RI-CLPM)的文章就介绍到这儿,希望我们推荐的文章对编程师们有所帮助!






