本文主要是介绍轻量级超分网络:Edge-oriented Convolution Block for Real-timeMM21_ECBSR 和 eSR,希望对大家解决编程问题提供一定的参考价值,需要的开发者们随着小编来一起学习吧!
文章目录
- ECBSR(Edge-oriented Convolution Block for Real-timeMM21_ECBSR)
- 1. 作者目的是开发一个高效的适合移动端的超分网络。
- 2. 作者决定使用plain net ,但是效果不好,因此利用重参数化方法,丰富特征表示。
- 3. re-parameterization for efficient inference
- 4. 结果
- edge-SR
- 1.转置卷积上采样 和 pixel shuffle的区别
- 2.pooling or downsample 可能有aliasing artifacts
- 3.单层网络eSR-MAX
- 4.eSR-TM, eSR-TR, eSR-CNN
ECBSR(Edge-oriented Convolution Block for Real-timeMM21_ECBSR)
1. 作者目的是开发一个高效的适合移动端的超分网络。
多分支结构,以及dense connections 可以丰富特征提取和表示, 虽然不会引入太多 FLOPs, 但是会牺牲并行化速度,以及受到DDR 低带宽的影响。
另外一些 delite conv等其他卷积方法也有被提出来提高 网络性能,但是在GPU,NPU上可能没有被很好的优化。
因此作者计划 使用平坦 的网络结构 和 常规的卷积方法。
2. 作者决定使用plain net ,但是效果不好,因此利用重参数化方法,丰富特征表示。
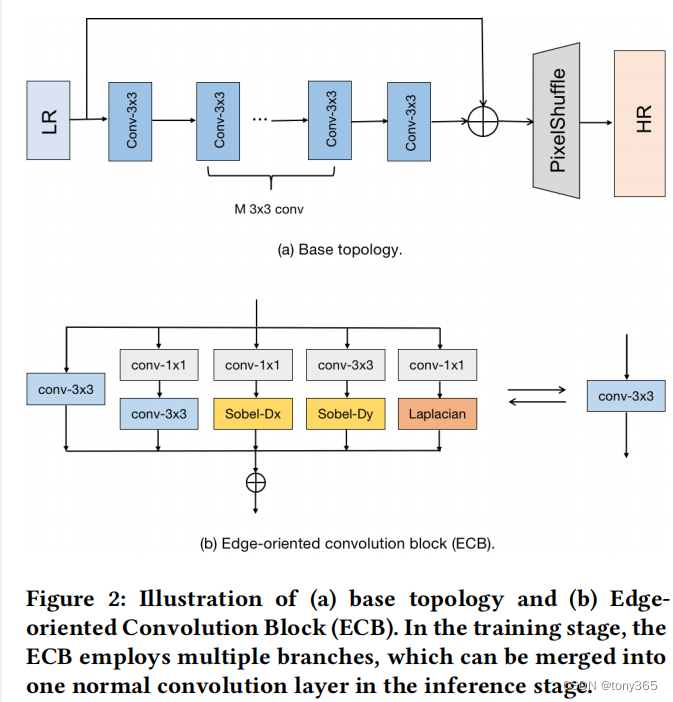
主要结构如下图所示,
-
一个单独的conv-3x3
-
conv-1x1 + conv-3x3: expanding-and-squeezing
-
conv-1x1 + sobelx
-
conv-1x1 + sobely(图中和代码不一致)

-
conv-1x1 + laplasian 显示提取图像的边缘特征

训练的时候网络右五个分支组成,在inference的时候可以利用re-parameteize技术合并为一个conv-3x3,这样推理的速度和效率都得到提高,精度基本上没有损失。
3. re-parameterization for efficient inference
整体网络结构:ecb模块 和 一个pixel shuffle
## parameters for ecbsr
scale: 2
colors: 1
m_ecbsr: 4
c_ecbsr: 16
idt_ecbsr: 0
act_type: 'prelu'
pretrain: null1 + 4 个 conv
1 个 pixel shuffle
class ECBSR(nn.Module):def __init__(self, module_nums, channel_nums, with_idt, act_type, scale, colors):super(ECBSR, self).__init__()self.module_nums = module_numsself.channel_nums = channel_numsself.scale = scaleself.colors = colorsself.with_idt = with_idtself.act_type = act_typeself.backbone = Noneself.upsampler = Nonebackbone = []backbone += [ECB(self.colors, self.channel_nums, depth_multiplier=2.0, act_type=self.act_type, with_idt = self.with_idt)]for i in range(self.module_nums):backbone += [ECB(self.channel_nums, self.channel_nums, depth_multiplier=2.0, act_type=self.act_type, with_idt = self.with_idt)]backbone += [ECB(self.channel_nums, self.colors*self.scale*self.scale, depth_multiplier=2.0, act_type='linear', with_idt = self.with_idt)]self.backbone = nn.Sequential(*backbone)self.upsampler = nn.PixelShuffle(self.scale)def forward(self, x):y = self.backbone(x) + xy = self.upsampler(y)return y
ecb模块:包括五个卷积分支的定义
class ECB(nn.Module):def __init__(self, inp_planes, out_planes, depth_multiplier, act_type='prelu', with_idt = False):super(ECB, self).__init__()self.depth_multiplier = depth_multiplierself.inp_planes = inp_planesself.out_planes = out_planesself.act_type = act_typeif with_idt and (self.inp_planes == self.out_planes):self.with_idt = Trueelse:self.with_idt = Falseself.conv3x3 = torch.nn.Conv2d(self.inp_planes, self.out_planes, kernel_size=3, padding=1)self.conv1x1_3x3 = SeqConv3x3('conv1x1-conv3x3', self.inp_planes, self.out_planes, self.depth_multiplier)self.conv1x1_sbx = SeqConv3x3('conv1x1-sobelx', self.inp_planes, self.out_planes, -1)self.conv1x1_sby = SeqConv3x3('conv1x1-sobely', self.inp_planes, self.out_planes, -1)self.conv1x1_lpl = SeqConv3x3('conv1x1-laplacian', self.inp_planes, self.out_planes, -1)if self.act_type == 'prelu':self.act = nn.PReLU(num_parameters=self.out_planes)elif self.act_type == 'relu':self.act = nn.ReLU(inplace=True)elif self.act_type == 'rrelu':self.act = nn.RReLU(lower=-0.05, upper=0.05)elif self.act_type == 'softplus':self.act = nn.Softplus()elif self.act_type == 'linear':passelse:raise ValueError('The type of activation if not support!')def forward(self, x):if self.training:y = self.conv3x3(x) + \self.conv1x1_3x3(x) + \self.conv1x1_sbx(x) + \self.conv1x1_sby(x) + \self.conv1x1_lpl(x)if self.with_idt:y += xelse:RK, RB = self.rep_params()y = F.conv2d(input=x, weight=RK, bias=RB, stride=1, padding=1) if self.act_type != 'linear':y = self.act(y)return ydef rep_params(self):K0, B0 = self.conv3x3.weight, self.conv3x3.biasK1, B1 = self.conv1x1_3x3.rep_params()K2, B2 = self.conv1x1_sbx.rep_params()K3, B3 = self.conv1x1_sby.rep_params()K4, B4 = self.conv1x1_lpl.rep_params()RK, RB = (K0+K1+K2+K3+K4), (B0+B1+B2+B3+B4)if self.with_idt:device = RK.get_device()if device < 0:device = NoneK_idt = torch.zeros(self.out_planes, self.out_planes, 3, 3, device=device)for i in range(self.out_planes):K_idt[i, i, 1, 1] = 1.0B_idt = 0.0RK, RB = RK + K_idt, RB + B_idtreturn RK, RB
关于重参数化具体实现
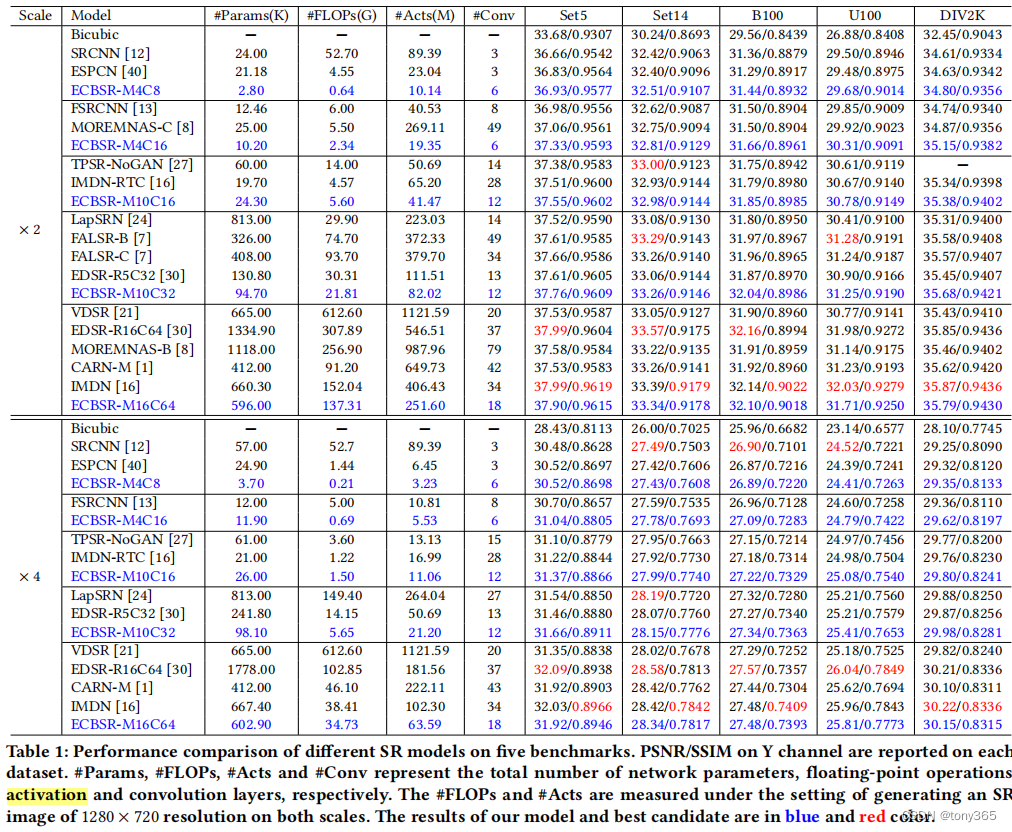
class SeqConv3x3(nn.Module):def __init__(self, seq_type, inp_planes, out_planes, depth_multiplier):super(SeqConv3x3, self).__init__()self.type = seq_typeself.inp_planes = inp_planesself.out_planes = out_planesif self.type == 'conv1x1-conv3x3':self.mid_planes = int(out_planes * depth_multiplier)conv0 = torch.nn.Conv2d(self.inp_planes, self.mid_planes, kernel_size=1, padding=0)self.k0 = conv0.weightself.b0 = conv0.biasconv1 = torch.nn.Conv2d(self.mid_planes, self.out_planes, kernel_size=3)self.k1 = conv1.weightself.b1 = conv1.biaselif self.type == 'conv1x1-sobelx':conv0 = torch.nn.Conv2d(self.inp_planes, self.out_planes, kernel_size=1, padding=0)self.k0 = conv0.weightself.b0 = conv0.bias# init scale & biasscale = torch.randn(size=(self.out_planes, 1, 1, 1)) * 1e-3self.scale = nn.Parameter(scale)# bias = 0.0# bias = [bias for c in range(self.out_planes)]# bias = torch.FloatTensor(bias)bias = torch.randn(self.out_planes) * 1e-3bias = torch.reshape(bias, (self.out_planes,))self.bias = nn.Parameter(bias)# init maskself.mask = torch.zeros((self.out_planes, 1, 3, 3), dtype=torch.float32)for i in range(self.out_planes):self.mask[i, 0, 0, 0] = 1.0self.mask[i, 0, 1, 0] = 2.0self.mask[i, 0, 2, 0] = 1.0self.mask[i, 0, 0, 2] = -1.0self.mask[i, 0, 1, 2] = -2.0self.mask[i, 0, 2, 2] = -1.0self.mask = nn.Parameter(data=self.mask, requires_grad=False)elif self.type == 'conv1x1-sobely':conv0 = torch.nn.Conv2d(self.inp_planes, self.out_planes, kernel_size=1, padding=0)self.k0 = conv0.weightself.b0 = conv0.bias# init scale & biasscale = torch.randn(size=(self.out_planes, 1, 1, 1)) * 1e-3self.scale = nn.Parameter(torch.FloatTensor(scale))# bias = 0.0# bias = [bias for c in range(self.out_planes)]# bias = torch.FloatTensor(bias)bias = torch.randn(self.out_planes) * 1e-3bias = torch.reshape(bias, (self.out_planes,))self.bias = nn.Parameter(torch.FloatTensor(bias))# init maskself.mask = torch.zeros((self.out_planes, 1, 3, 3), dtype=torch.float32)for i in range(self.out_planes):self.mask[i, 0, 0, 0] = 1.0self.mask[i, 0, 0, 1] = 2.0self.mask[i, 0, 0, 2] = 1.0self.mask[i, 0, 2, 0] = -1.0self.mask[i, 0, 2, 1] = -2.0self.mask[i, 0, 2, 2] = -1.0self.mask = nn.Parameter(data=self.mask, requires_grad=False)elif self.type == 'conv1x1-laplacian':conv0 = torch.nn.Conv2d(self.inp_planes, self.out_planes, kernel_size=1, padding=0)self.k0 = conv0.weightself.b0 = conv0.bias# init scale & biasscale = torch.randn(size=(self.out_planes, 1, 1, 1)) * 1e-3self.scale = nn.Parameter(torch.FloatTensor(scale))# bias = 0.0# bias = [bias for c in range(self.out_planes)]# bias = torch.FloatTensor(bias)bias = torch.randn(self.out_planes) * 1e-3bias = torch.reshape(bias, (self.out_planes,))self.bias = nn.Parameter(torch.FloatTensor(bias))# init maskself.mask = torch.zeros((self.out_planes, 1, 3, 3), dtype=torch.float32)for i in range(self.out_planes):self.mask[i, 0, 0, 1] = 1.0self.mask[i, 0, 1, 0] = 1.0self.mask[i, 0, 1, 2] = 1.0self.mask[i, 0, 2, 1] = 1.0self.mask[i, 0, 1, 1] = -4.0self.mask = nn.Parameter(data=self.mask, requires_grad=False)else:raise ValueError('the type of seqconv is not supported!')def forward(self, x):if self.type == 'conv1x1-conv3x3':# conv-1x1y0 = F.conv2d(input=x, weight=self.k0, bias=self.b0, stride=1)# explicitly padding with biasy0 = F.pad(y0, (1, 1, 1, 1), 'constant', 0)b0_pad = self.b0.view(1, -1, 1, 1)y0[:, :, 0:1, :] = b0_pady0[:, :, -1:, :] = b0_pady0[:, :, :, 0:1] = b0_pady0[:, :, :, -1:] = b0_pad# conv-3x3y1 = F.conv2d(input=y0, weight=self.k1, bias=self.b1, stride=1)else:y0 = F.conv2d(input=x, weight=self.k0, bias=self.b0, stride=1)# explicitly padding with biasy0 = F.pad(y0, (1, 1, 1, 1), 'constant', 0)b0_pad = self.b0.view(1, -1, 1, 1)y0[:, :, 0:1, :] = b0_pady0[:, :, -1:, :] = b0_pady0[:, :, :, 0:1] = b0_pady0[:, :, :, -1:] = b0_pad# conv-3x3y1 = F.conv2d(input=y0, weight=self.scale * self.mask, bias=self.bias, stride=1, groups=self.out_planes)return y1def rep_params(self):device = self.k0.get_device()if device < 0:device = Noneif self.type == 'conv1x1-conv3x3':# re-param conv kernelRK = F.conv2d(input=self.k1, weight=self.k0.permute(1, 0, 2, 3))# re-param conv biasRB = torch.ones(1, self.mid_planes, 3, 3, device=device) * self.b0.view(1, -1, 1, 1)RB = F.conv2d(input=RB, weight=self.k1).view(-1,) + self.b1else:tmp = self.scale * self.maskk1 = torch.zeros((self.out_planes, self.out_planes, 3, 3), device=device)for i in range(self.out_planes):k1[i, i, :, :] = tmp[i, 0, :, :]b1 = self.bias# re-param conv kernelRK = F.conv2d(input=k1, weight=self.k0.permute(1, 0, 2, 3))# re-param conv biasRB = torch.ones(1, self.out_planes, 3, 3, device=device) * self.b0.view(1, -1, 1, 1)RB = F.conv2d(input=RB, weight=k1).view(-1,) + b1return RK, RB4. 结果
edge-SR
1.转置卷积上采样 和 pixel shuffle的区别
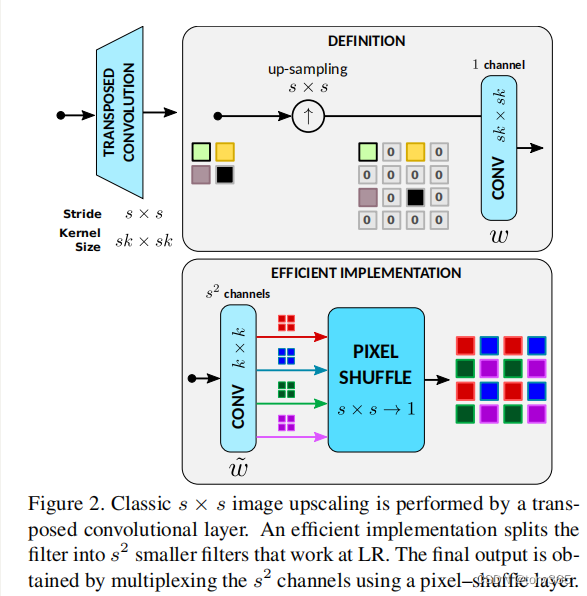
2.pooling or downsample 可能有aliasing artifacts
using an anti–aliasing low–pass filter and then downsamples the image.
This process is implemented in tensor processing frameworks with strided convolutional
layers where the kernel or weight parameters correspond to the low–pass filter coefficients.
3.单层网络eSR-MAX
一个卷积,一个pixel shuffle, 一个max
卷积输出的通道数: sxsxchannel
out_channels=self.stride[0]*self.stride[1]*self.channels,

4.eSR-TM, eSR-TR, eSR-CNN
直接看代码更好理解:
class edgeSR_TM(nn.Module):def __init__(self, model_id):self.model_id = model_idsuper().__init__()assert self.model_id.startswith('eSR-TM_')parse = self.model_id.split('_')self.channels = int([s for s in parse if s.startswith('C')][0][1:])self.kernel_size = (int([s for s in parse if s.startswith('K')][0][1:]), ) * 2self.stride = (int([s for s in parse if s.startswith('s')][0][1:]), ) * 2self.pixel_shuffle = nn.PixelShuffle(self.stride[0])self.softmax = nn.Softmax(dim=1)self.filter = nn.Conv2d(in_channels=1,out_channels=2*self.stride[0]*self.stride[1]*self.channels,kernel_size=self.kernel_size,stride=1,padding=((self.kernel_size[0]-1)//2,(self.kernel_size[1]-1)//2),groups=1,bias=False,dilation=1)nn.init.xavier_normal_(self.filter.weight, gain=1.)self.filter.weight.data[:, 0, self.kernel_size[0]//2, self.kernel_size[0]//2] = 1.def forward(self, input):filtered = self.pixel_shuffle(self.filter(input))value, key = torch.split(filtered, [self.channels, self.channels], dim=1)return torch.sum(value * self.softmax(key),dim=1, keepdim=True)class edgeSR_TR(nn.Module):def __init__(self, model_id):self.model_id = model_idsuper().__init__()assert self.model_id.startswith('eSR-TR_')parse = self.model_id.split('_')self.channels = int([s for s in parse if s.startswith('C')][0][1:])self.kernel_size = (int([s for s in parse if s.startswith('K')][0][1:]), ) * 2self.stride = (int([s for s in parse if s.startswith('s')][0][1:]), ) * 2self.pixel_shuffle = nn.PixelShuffle(self.stride[0])self.softmax = nn.Softmax(dim=1)self.filter = nn.Conv2d(in_channels=1,out_channels=3*self.stride[0]*self.stride[1]*self.channels,kernel_size=self.kernel_size,stride=1,padding=((self.kernel_size[0]-1)//2,(self.kernel_size[1]-1)//2),groups=1,bias=False,dilation=1)nn.init.xavier_normal_(self.filter.weight, gain=1.)self.filter.weight.data[:, 0, self.kernel_size[0]//2, self.kernel_size[0]//2] = 1.def forward(self, input):filtered = self.pixel_shuffle(self.filter(input))value, query, key = torch.split(filtered, [self.channels, self.channels, self.channels], dim=1)return torch.sum(value * self.softmax(query*key),dim=1, keepdim=True)
这篇关于轻量级超分网络:Edge-oriented Convolution Block for Real-timeMM21_ECBSR 和 eSR的文章就介绍到这儿,希望我们推荐的文章对编程师们有所帮助!






