本文主要是介绍【Derivation】Convex Optimization,希望对大家解决编程问题提供一定的参考价值,需要的开发者们随着小编来一起学习吧!
Separation theorems and supporting hyperplanes(分离定理与支撑超平面)
Inner and outer polyhedral approximations.(内部与外部多面体逼近)
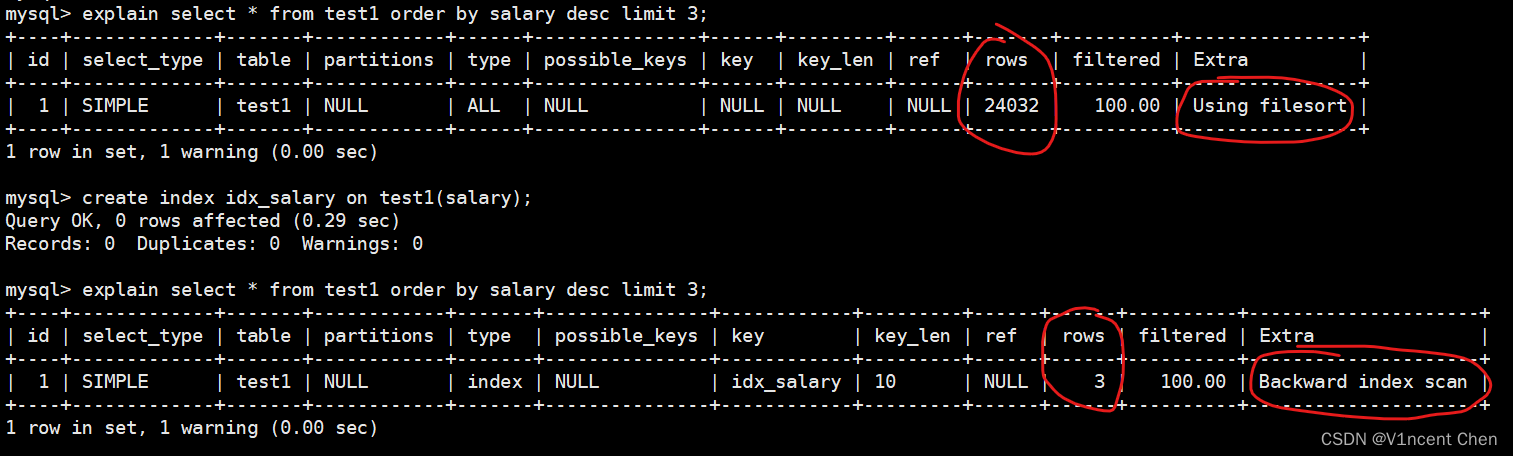
Let C belongs to Rn be a closed convex set.and suppose that x1,...xk are on the boundary of C.Suppose that for each i,Ati(x-xi)=0 defines a supporting hyperplane for C at xi,.e.,C belongs to {x|aAti(x-xi)<=0}.consider the two polyhedra
Pinner = conv{ x1,...xk }, Pouter = { x | Ati(x-xi)<=0 , i=1,...,K}.
Show that Pinner belongs to C belongs to Pouter.Draw a picture illustrating this.
令C包含于Rn 为闭凸集,并设x1,...xk 在C的边界上。设对于每个i,Ati(x-xi)=0定义了C在xi处的一个支撑超平面,即C包含于 {x|aAti(x-xi)<=0}。考虑两个多面体
Pinner = conv{ x1,...xk }, Pouter = { x | Ati(x-xi)<=0 , i=1,...,K}.
证明Pinner 包含于 C 包含于 Pouter 并画出图像进行说明。
Solution.
The points xi are in C because C is closed.Any point in Pinner = conv{x1,...xk }, is also in C because C is convex .Therefore Pinner belongs to C. If x belongs to C then Ati(x-xi)<=0 for i=1,...,K,i.e,x belongs to pouter.therefore C belongs to Pouter.
Pinner = conv(x1,...,xk).
C = { x | Ati(x-xi)<=0 }.
Pouter = { x | Ati(x-xi)<=0 , i=1,...,K}.
The figure shows an example with k=4.
解:
由于C是闭的所以xi都在C中。由于C为凸集, 所以Pinner = conv{x1,...xk } 中的任意点也在C中,因此Pinner包含于C。如果x包含于C 及 Ati(x-xi)<=0 for i=1,...,K,即x包含于Pouter, 因此C包含于Pouter。
这篇关于【Derivation】Convex Optimization的文章就介绍到这儿,希望我们推荐的文章对编程师们有所帮助!

![[论文笔记]Circle Loss: A Unified Perspective of Pair Similarity Optimization](/front/images/it_default.gif)