本文主要是介绍基于大模型 Gemma-7B 和 llama_index,轻松实现 NL2SQL,希望对大家解决编程问题提供一定的参考价值,需要的开发者们随着小编来一起学习吧!
节前,我们星球组织了一场算法岗技术&面试讨论会,邀请了一些互联网大厂朋友、参加社招和校招面试的同学.
针对算法岗技术趋势、大模型落地项目经验分享、新手如何入门算法岗、该如何准备、面试常考点分享等热门话题进行了深入的讨论。
汇总合集:《大模型面试宝典》(2024版) 发布!
本文将会介绍Text to SQL相关的概念,如何使用大模型SFT实现Text to SQL,最后介绍Text to SQL的应用场景。
引言
Text to SQL,又被称为Natural Language to SQL(简称NL2SQL),指的是将自然语言描述转化为数据库的SQL查询语句。由于数据库在我们日常工作生活中随处可见,因此Text to SQL技术也获得业界和学术界的不少研究与关注。
举个例子,比如在问题“What’s the population of New York city?”,那么我们在相关的某张表格(比如city表)中,对应的SQL语句应当为“SELECT POPULATION FROM city WHERE name = “New York””,此时数据库应当能执行该SQL语句。
常见的Text to SQL数据集有WIKISQL, Spider, ATIS, GeoQuery。以往已经有不少的NLP或者机器学习相关的技术涉及Text to SQL,但效果都比较一般。
接下来,我们将会介绍如何使用大模型SFT技术来实现Text to SQL,看看大模型的表现。
技术交流群
前沿技术资讯、算法交流、求职内推、算法竞赛、面试交流(校招、社招、实习)等、与 10000+来自港科大、北大、清华、中科院、CMU、腾讯、百度等名校名企开发者互动交流~
我们建了大模型算法岗技术与面试交流群, 想要交流、需要源码&资料、提升技术的同学,可以直接加微信号:mlc2060。加的时候备注一下:研究方向 +学校/公司+CSDN,即可。然后就可以拉你进群了。
方式①、微信搜索公众号:机器学习社区,后台回复:加群
方式②、添加微信号:mlc2060,备注:CSDN + 技术交流
SFT
我们使用HuggingFace上的b-mc2/sql-create-context数据集,该数据集只有78,577条训练数据,无测试集数据,字段为answer, question, context,其中answer为最终产生的SQL语句,question为用户问题,context为数据库表格创建语句。
比如其中在一个样本中,question为How many heads of the departments are older than 56 ?, context为CREATE TABLE head (age INTEGER), answer为SELECT COUNT(*) FROM head WHERE age > 56。
我们使用谷歌开源的Gemma-7B模型对改数据集进行指令微调。以上述样本为例,对应的指令格式为:
\nBelow is an instruction that describes a task.Write a response that appropriately completes the request.\n### Instruction: How many heads of the departments are older than 56 ?\n### Database Schema:\nCREATE TABLE head (age INTEGER)\n### Response:\nSELECT COUNT(*) FROM head WHERE age > 56\n<eos>\n
其中为Gemma-7B模型的结束标志符。
使用trl可以很方面地对Gemma-7B模型进行SFT,代码如下:
from datasets import load_dataset
import torch
from peft import LoraConfig
from trl import SFTTrainer
from transformers import TrainingArguments
from transformers import AutoTokenizer, AutoModelForCausalLM, BitsAndBytesConfig# Hugging Face model id
model_id = "./models/gemma-7b"# BitsAndBytesConfig int-4 config
bnb_config = BitsAndBytesConfig(load_in_4bit=True, bnb_4bit_use_double_quant=True, bnb_4bit_quant_type="nf4", bnb_4bit_compute_dtype=torch.bfloat16
)# Load model and tokenizer
model = AutoModelForCausalLM.from_pretrained(model_id,device_map="auto",torch_dtype=torch.bfloat16,quantization_config=bnb_config
)
tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained(model_id)
tokenizer.padding_side = 'right'train_dataset = load_dataset("json", data_files="sql-create-context.json")['train']
print(train_dataset[0])
print(f"train size: {len(train_dataset)}")# LoRA config based on QLoRA paper & Sebastian Raschka experiment
peft_config = LoraConfig(lora_alpha=16,lora_dropout=0.05,r=64,bias="none",target_modules=["q_proj", "k_proj", "v_proj", "o_proj","gate_proj"],task_type="CAUSAL_LM",
)args = TrainingArguments(output_dir="output", # directory to save and repository idnum_train_epochs=2, # number of training epochsper_device_train_batch_size=8, # batch size per device during traininggradient_accumulation_steps=4, # number of steps before performing a backward/update passgradient_checkpointing=True, # use gradient checkpointing to save memoryoptim="paged_adamw_8bit", save_strategy="epoch",logging_strategy="steps",logging_steps=10, # log every 10 stepsbf16=True, # use bfloat16 precisionlearning_rate=1e-4, # learning rate, based on QLoRA papermax_grad_norm=0.3, # max gradient norm based on QLoRA paperwarmup_ratio=0.1, # warmup ratio based on QLoRA paperlr_scheduler_type="constant", # use constant learning rate schedulerpush_to_hub=False, # push model to hubreport_to="tensorboard", # report metrics to tensorboard
)max_seq_length = 1024trainer = SFTTrainer(model=model,args=args,train_dataset=train_dataset,peft_config=peft_config,max_seq_length=max_seq_length,tokenizer=tokenizer,packing=False,dataset_text_field="text"
)trainer.train()
trainer.save_model()
训练完后,我们使用下面的脚本进行新样本的预测,代码如下:
from transformers import AutoModelForCausalLM, AutoTokenizerpeft_model_id = "./output/checkpoint-4911"
model = AutoModelForCausalLM.from_pretrained(peft_model_id, device_map="cuda")
tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained("./models/gemma-7b")while True:question = input("enter a question: ")context = input("enter database schema: ")input_text = f"""
Below is an instruction that describes a task.Write a response that appropriately completes the request.
### Instruction: {question}
### Database Schema:
{context}
### Response:
"""encoding = tokenizer(input_text, return_tensors="pt").to("cuda")outputs = model.generate(**encoding, max_new_tokens=100, temperature=0.1, do_sample=True)generated_ids = outputs[:, encoding.input_ids.shape[1]:]generated_texts = tokenizer.batch_decode(generated_ids, skip_special_tokens=True)print("Instruction: ", input_text)print("SQL: ", generated_texts[0].strip())
为了验证改模型的效果,我们在新样本进行测试。
- 例子1
直接从SQL测验网站进行测试,第一个例子为:

测试题例子1
模型生成的SQL语句为:SELECT * FROM CITY WHERE COUNTRYCODE = "USA" AND POPULATION > 100000,成功运行!

生成的SQL语句执行成功1
- 例子2
第二个例子为:

生成的SQL语句为SELECT CITY, STATE FROM STATION,也能执行成功!
- 例子3
上述的两个较为简单,我们再来看个复杂点的例子。第三个例子为:

生成的SQL语句为SELECT CITY FROM STATION WHERE SUBSTR(CITY, -1) NOT IN ('A', 'E', 'I', 'O', 'U') GROUP BY CITY,竟然能执行成功!
- 例子4
第四例子为两个表格,需要对表格进行join,如下:

生成的SQL语句为SELECT T1.NAME FROM CITY AS T1 JOIN COUNTRY AS T2 ON T1.COUNTRYCODE = T2.CODE WHERE T2.CONTINENT = 'Africa',竟然能执行成功!
以上只是找了几个比较好的例子,实际上还是有很多生成的SQL语句无法通过测试的。
在实际的Text to SQL应用场景中,需要调整system prompt,对指令进行更加详细的描述,比较加入表格、字段描述。同时,还需要质量更高、更贴近业务场景的训练数据,以及合适的大模型等,需要保证生成的SQL语句的可执行准确率。
表格问答应用
我们举个例子,来说明Text to SQL和大模型结合起来使用,在表格问答场景中能有更好的表现。
Mysql中的users表的描述:
+-------------+--------------+------+-----+---------+----------------+
| Field | Type | Null | Key | Default | Extra |
+-------------+--------------+------+-----+---------+----------------+
| id | int | NO | PRI | NULL | auto_increment |
| name | varchar(256) | NO | | NULL | |
| age | int | YES | | NULL | |
| place | varchar(256) | NO | | NULL | |
| insert_time | datetime | YES | | NULL | |
+-------------+--------------+------+-----+---------+----------------+
表格中的所有数据:
+----+---------------+------+-------+---------------------+
| id | name | age | place | insert_time |
+----+---------------+------+-------+---------------------+
| 1 | Jack | 25 | USA | 2023-12-23 23:48:48 |
| 2 | Green | 26 | UK | 2023-12-23 23:48:58 |
| 3 | Alex | 31 | GER | 2023-12-23 23:49:03 |
| 4 | Chen | 52 | CHN | 2023-12-23 23:49:08 |
| 5 | Zhang | 42 | CHN | 2023-12-23 23:49:13 |
| 6 | ElasticSearch | 12 | USA | 2023-12-24 00:41:20 |
| 7 | Kibana | 24 | USA | 2023-12-24 00:41:37 |
| 8 | Logstash | 36 | USA | 2023-12-24 00:42:41 |
+----+---------------+------+-------+---------------------+
我们考虑以下四个问题:
-
How old is Chen?
-
Who is the oldest person and its age and place?
-
How many persons come from USA and what are their names and age?
-
Return the top 5 oldest person in descending order with their name and age.
-
what are the names that begins with J or E?
使用LlamaIndex工具中的Text-to-SQL QueryEngine对上述四个问题进行问答。代码如下:
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
# @file: nl2sql_test.py
# llama-index == 0.9.30
# SQLAlchemy==2.0.20
# PyMySQL == 1.1.0
from sqlalchemy import create_engine, textfrom llama_index import SQLDatabase, ServiceContext
from llama_index.llms import OpenAI
from llama_index.indices.struct_store.sql_query import NLSQLTableQueryEnginefrom llama_index.indices.struct_store.sql_query import (SQLTableRetrieverQueryEngine,
)
from llama_index.objects import (SQLTableNodeMapping,ObjectIndex,SQLTableSchema,
)
from llama_index import VectorStoreIndex
from llama_index.retrievers import NLSQLRetriever
from llama_index.query_engine import RetrieverQueryEnginellm = OpenAI(temperature=0.1, model="gpt-3.5-turbo")
service_context = ServiceContext.from_defaults(llm=llm)engine = create_engine("mysql+pymysql://root:root@localhost:3306/orm_test")
sql_database = SQLDatabase(engine, include_tables=["users"])# text-to-sql query engine, simple example
query_engine = NLSQLTableQueryEngine(sql_database=sql_database,tables=["users"]
)
query_str = "How old is Chen?"
response = query_engine.query(query_str)
print(response)
print('*' * 30, end='\n\n')# total size of table schema overflows context window size
# then use SQLTableNodeMapping
# set Logging to DEBUG for more detailed outputs
table_node_mapping = SQLTableNodeMapping(sql_database)
table_schema_objs = [(SQLTableSchema(table_name="users"))
] # add a SQLTableSchema for each tableobj_index = ObjectIndex.from_objects(table_schema_objs,table_node_mapping,VectorStoreIndex,
)
query_engine = SQLTableRetrieverQueryEngine(sql_database, obj_index.as_retriever(similarity_top_k=1)
)response = query_engine.query("Who is the oldest person and its age and place?")
print(response)
print('*' * 30, end='\n\n')response = query_engine.query("How many persons come from USA and what are their names and age?")
print(response.metadata)
print(response.metadata['result'])
print(response)
print('*' * 30, end='\n\n')# manually set context text
city_stats_text = ("This table gives information regarding the persons and their age and place.\n""The insert time means when the record was inserted into this table."
)table_node_mapping = SQLTableNodeMapping(sql_database)
table_schema_objs = [(SQLTableSchema(table_name="users", context_str=city_stats_text))
]# text-to-sql retriever
# SQL Retriever
# default retrieval (return_raw=True)
nl_sql_retriever = NLSQLRetriever(sql_database, tables=["users"], return_raw=True
)results = nl_sql_retriever.retrieve("Return the top 5 oldest person in descending order with their name and age."
)for n in results:print(n)
print('*' * 30, end='\n\n')# default retrieval (return_raw=False)
nl_sql_retriever = NLSQLRetriever(sql_database, tables=["users"], return_raw=False
)
results = nl_sql_retriever.retrieve("Return the top 5 oldest person in descending order with their name and age."
)# NOTE: all the content is in the metadata
for n in results:print(n, n.metadata)
print('*' * 30, end='\n\n')# compose SQL Retriever with RetrieverQueryEngine to synthesize a response
nl_sql_retriever = NLSQLRetriever(sql_database, tables=["users"], return_raw=True
)
query_engine = RetrieverQueryEngine.from_args(nl_sql_retriever)
queries = ["Return the top 5 oldest person in descending order with their name and age.","what are the names that begins with J or E?"]
for query in queries:response = query_engine.query(query)print(response)
print('*' * 30, end='\n\n')
对应的输出答案为(中间有部分省略):
Chen is 52 years old.
******************************
The oldest person is Chen, who is 52 years old and is from China.
******************************
There are four persons from the USA in the database. Their names are Jack, ElasticSearch, Kibana, and Logstash, and their ages are 25, 12, 24, and 36 respectively.
******************************
The top 5 oldest people in descending order with their names and ages are:
1. Chen, 52
2. Zhang, 42
3. Logstash, 36
4. Alex, 31
5. Green, 26
******************************
The names that begin with J or E are ElasticSearch and Jack.
看来Text to SQL对于表格问答场景有很大帮助。
补充
对于上述表格问答应用中的5个问题,我们使用Gemma-7B微调的Text to SQL模型进行回答,生成的SQL语句如下:
-
SELECT age FROM users WHERE place = ‘Chen’
-
SELECT id, name, age, place FROM users ORDER BY age DESC LIMIT 1
-
SELECT id, name, age FROM users WHERE place = ‘USA’ ORDER BY insert_time
-
SELECT id, name, age FROM users ORDER BY age DESC LIMIT 5
-
SELECT name FROM users WHERE name LIKE ‘J%’ OR name LIKE ‘E%’
将它们在MySQL中进行执行,结果如下:
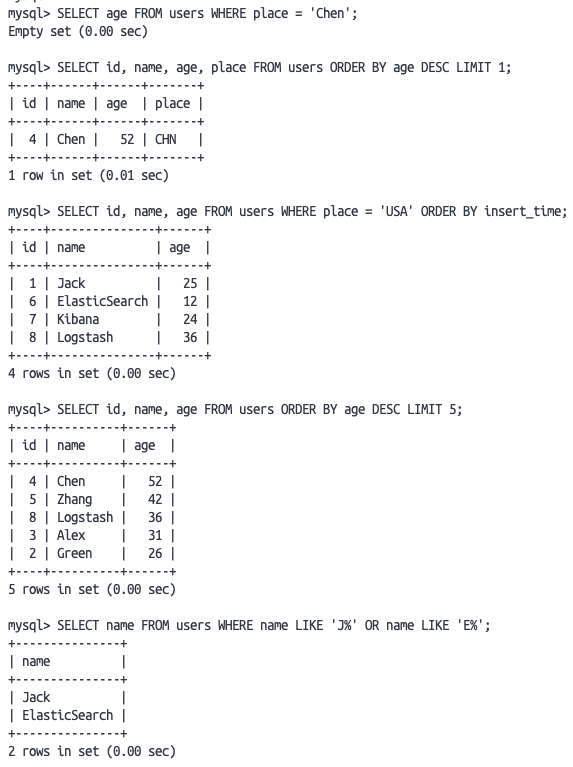
MySQL执行结果
所有的语句都可以执行,但第一条语句是错误的,不过只需将place改成name即可执行成功。
有了上述的SQL执行结果,我们将上述表格问答中的第三个例子进行Prompt Engineer,如下:
<The background information follows>:table `users` in Mysql:+-------------+--------------+------+-----+---------+----------------+
| Field | Type | Null | Key | Default | Extra |
+-------------+--------------+------+-----+---------+----------------+
| id | int | NO | PRI | NULL | auto_increment |
| name | varchar(256) | NO | | NULL | |
| age | int | YES | | NULL | |
| place | varchar(256) | NO | | NULL | |
| insert_time | datetime | YES | | NULL | |
+-------------+--------------+------+-----+---------+----------------+SQL execution result:mysql> SELECT id, name, age FROM users WHERE place = 'USA' ORDER BY insert_time;+----+---------------+------+
| id | name | age |
+----+---------------+------+
| 1 | Jack | 25 |
| 6 | ElasticSearch | 12 |
| 7 | Kibana | 24 |
| 8 | Logstash | 36 |
+----+---------------+------+Based on the background information, Answer the question: How many persons come from USA and what are their names and age?
看看GPT3.5模型的回答:

回答正确!
以上仅仅是对LlamaIndex中使用Text to SQL技术的一种可能的实现方式的思考,故在此作为补充。
这篇关于基于大模型 Gemma-7B 和 llama_index,轻松实现 NL2SQL的文章就介绍到这儿,希望我们推荐的文章对编程师们有所帮助!





