本文主要是介绍椭圆轨道的周期性运动轨道,希望对大家解决编程问题提供一定的参考价值,需要的开发者们随着小编来一起学习吧!
一、背景介绍
本节将从轨道六根数的角度,探究目标星为椭圆轨道,追踪星周期性环绕目标的必要条件。根据航天动力学的原理,对于一个椭圆轨道,其轨道能量为
对于能够不产生漂移的情况,绕飞编队的能量。对于追踪星到目标星的能量差,可以写
因此,对于零能量差的形式可以写为
通过使用下列离心率的关系
式中:为轨道近地点位置,所以离心率偏差
可以写为近地点角的偏差
,即
通过对上式修改,可以得到
上述是微分能量的精确表达式,注意到和
存在复杂的耦合关系。最后的表达式近似表达为
假设且
。在这里
是给定半长轴圆轨道的速度
所以,对于任意
,等式被写为
根据运动学关系,在线性化的框架中,对于给定的几何形状,可以计算按到底层中心的参考的微分速度,在绝对惯性坐标系下,目标星在近地点的角速度
在目标星的相对坐标系,追踪星的速度可以写为
在VVLH坐标系下,初始条件满足关系式即为
二、STK仿真验证
下面这段代码,在之前TH方程的基础上,在STK添加VVLH报表后,进行仿真得到的结果
% 使用STK验证VVLH坐标系
clc;clear
uiApplication = actxGetRunningServer('STK12.application');
root = uiApplication.Personality2;
checkempty = root.Children.Count;
if checkempty ~= 0root.CurrentScenario.Unloadroot.CloseScenario;
end
root.NewScenario('VVLH');
StartTime = '26 Jan 2024 04:00:00.000'; % 场景开始时间
StopTime = '10 Feb 2024 04:00:00.000'; % 场景结束时间
root.ExecuteCommand(['SetAnalysisTimePeriod * "',StartTime,'" "',StopTime,'"']);
root.ExecuteCommand(' Animate * Reset');
SatName = 'Target'; % SAR_ GX_ Sat_ GX_1_ SAR_1_
satellite = root.CurrentScenario.Children.New('eSatellite', SatName);
satellite.SetPropagatorType('ePropagatorAstrogator'); % 不设置的时候默认为二体模型 ePropagatorJ4Perturbation
satellite.Propagator;
Perigee=6378.137+500;
Ecc=0.1;
sma=Perigee/(1-Ecc);
Inc=30;
w=0;
RAAN=0;
TA=0;
root.ExecuteCommand(['Astrogator */Satellite/',SatName,' SetValue MainSequence.SegmentList Initial_State Propagate']);
InitialState=satellite.Propagator.MainSequence.Item(0);
%% 初始化卫星参数
root.ExecuteCommand(['Astrogator */Satellite/',SatName,' SetValue MainSequence.SegmentList.Initial_State.CoordinateType Modified Keplerian']);
root.ExecuteCommand(['Astrogator */Satellite/',SatName,' SetValue MainSequence.SegmentList.Initial_State.InitialState.Epoch ',StartTime,' UTCG']);
root.ExecuteCommand(['Astrogator */Satellite/',SatName,' SetValue MainSequence.SegmentList.Initial_State.InitialState.Keplerian.sma ',num2str(sma),' km']);
root.ExecuteCommand(['Astrogator */Satellite/',SatName,' SetValue MainSequence.SegmentList.Initial_State.InitialState.Keplerian.ecc ',num2str(Ecc)]);
root.ExecuteCommand(['Astrogator */Satellite/',SatName,' SetValue MainSequence.SegmentList.Initial_State.InitialState.Keplerian.inc ',num2str(Inc),' deg']);
root.ExecuteCommand(['Astrogator */Satellite/',SatName,' SetValue MainSequence.SegmentList.Initial_State.InitialState.Keplerian.w ',num2str(w),' deg']);
root.ExecuteCommand(['Astrogator */Satellite/',SatName,' SetValue MainSequence.SegmentList.Initial_State.InitialState.Keplerian.RAAN ',num2str(RAAN),' deg']);
root.ExecuteCommand(['Astrogator */Satellite/',SatName,' SetValue MainSequence.SegmentList.Initial_State.InitialState.Keplerian.TA ',num2str(TA),' deg']);
%% 二体传播
Propagate=satellite.Propagator.MainSequence.Item(1);
Propagate.PropagatorName='Earth Point Mass';
root.ExecuteCommand(['Astrogator */Satellite/',SatName,' RunMCS']);% 插入目标星
SatName2 = 'Chaser'; % SAR_ GX_ Sat_ GX_1_ SAR_1_
satellite2 = root.CurrentScenario.Children.New('eSatellite', SatName2);
satellite2.SetPropagatorType('ePropagatorAstrogator'); % 不设置的时候默认为二体模型 ePropagatorJ4Perturbation
satellite2.Propagator;
InitialState2=satellite2.Propagator.MainSequence.Item(0);
InitialState2.CoordSystemName='Satellite/Target VVLH';
Z=0.1;
n=sqrt(3.986e5/sma^3);
Vx1 = n*(2+Ecc);
Vx2 = (1+Ecc)^(1/2)*(1-Ecc)^(3/2);
Vx = Vx1/Vx2 * Z;InitialState2.Element.X=0;
InitialState2.Element.Y=0;
InitialState2.Element.Z=Z;
InitialState2.Element.Vx=Vx;
InitialState2.Element.Vy=0;
InitialState2.Element.Vz=0;
Propagate2=satellite2.Propagator.MainSequence.Item(1);
Propagate2.PropagatorName='Earth Point Mass';
root.ExecuteCommand(['Astrogator */Satellite/',SatName2,' RunMCS']);% 报告二颗卫星的三维关系
satellite.VO.OrbitSystems.InertialByWindow.IsVisible=0;
satellite2.VO.OrbitSystems.InertialByWindow.IsVisible=0;
satellite2.VO.OrbitSystems.Add('Satellite/Target VVLH System')
satellite.VO.Vector.RefCrdns.Item(2).Visible=1;targetdata=root.ExecuteCommand(['Report_RM */Satellite/Target Style "VVLH" TimePeriod "26 Jan 2024 04:00:00.000" "26 Jan 2024 16:00:00.000" TimeStep 60']);
Num=targetdata.Count;
for j=1:Num-2struct=regexp(targetdata.Item(j),',','split');Tar_x(j)=str2double(struct{2});Tar_y(j)=str2double(struct{3});Tar_z(j)=str2double(struct{4});
end
%
figure(1)
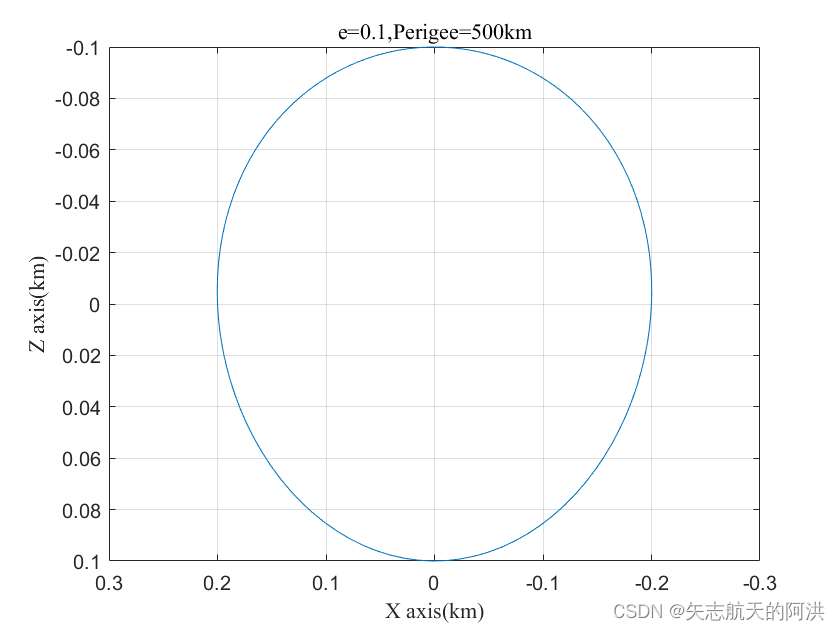
plot(Tar_x(1:220),Tar_z(1:220));set(gca,'XDir','reverse');
set(gca,'YDir','reverse');
xlabel('X axis(km)','FontName','Times New Roman')
ylabel('Z axis(km)','FontName','Times New Roman')
title('e=0.1,Perigee=500km','FontName','Times New Roman')figure(2)
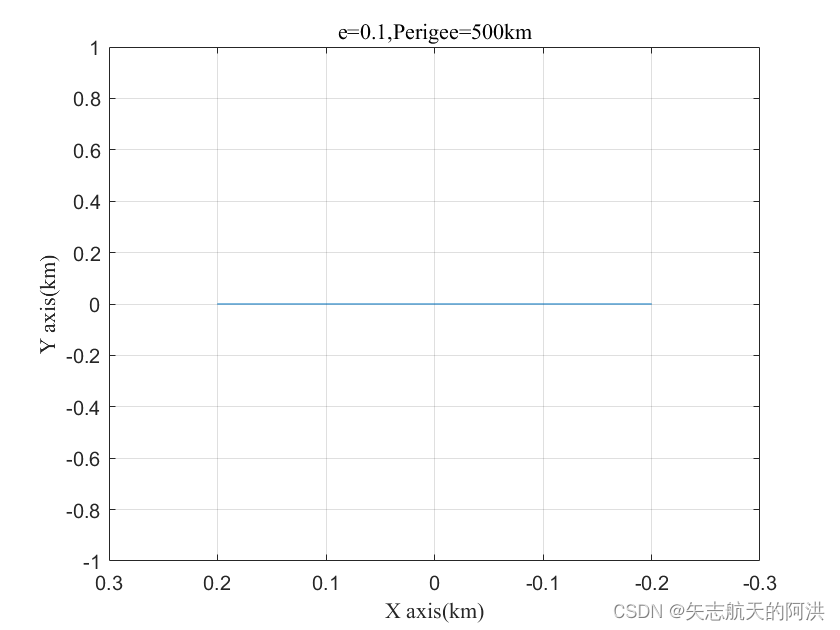
plot(Tar_x(1:220),Tar_y(1:220));set(gca,'XDir','reverse');
xlabel('X axis(km)','FontName','Times New Roman')
ylabel('Y axis(km)','FontName','Times New Roman')
title('e=0.1,Perigee=500km','FontName','Times New Roman')
grid on
这篇关于椭圆轨道的周期性运动轨道的文章就介绍到这儿,希望我们推荐的文章对编程师们有所帮助!









