本文主要是介绍41_经典卷积网络、LeNet、AlexNet、VGG、GoogleNet、ResNet、NIN、DenseNet、EfficientNet、MobileNetV1/2/3、SENet等,希望对大家解决编程问题提供一定的参考价值,需要的开发者们随着小编来一起学习吧!
1.38.经典卷积网络
1.38.1.LeNet
1.38.1.1.介绍
1.38.1.2.网络结构
1.38.1.3.代码实现
1.38.2.AlexNet
1.38.2.1.介绍
1.38.2.2.网络结构
1.38.2.3.代码实现
1.38.3.VGG
1.38.3.1.介绍
1.38.3.2.网络结构 VGG-16
1.38.3.3.代码实现
1.38.4.GoogleNet
1.38.4.1.介绍
1.38.4.2.网络结构
1.38.4.3.代码实现
1.38.5.ResNet
1.38.5.1.介绍
1.38.5.2.网络结构
1.38.5.3.代码实现
1.38.6.NIN
1.38.6.1.局部块
1.38.6.2.替代FC,使用全局平均池化层求分类
1.38.6.3.代码案例
1.38.7.DenseNet
1.38.7.1.稠密块
1.38.7.2.过滤层
1.38.7.3.模型结构
1.38.7.4.代码案例
1.38.7.5.总结
1.38.8.EfficientNet
1.38.9.MobileNetV1
1.38.10.MobileNetV2
1.38.11.MobileNetV3
1.38.12.SENet
1.38.13.ShuffleNetV1
1.38.14.ShuffleNetV2
1.38.15.参考博文
1.38.经典卷积网络
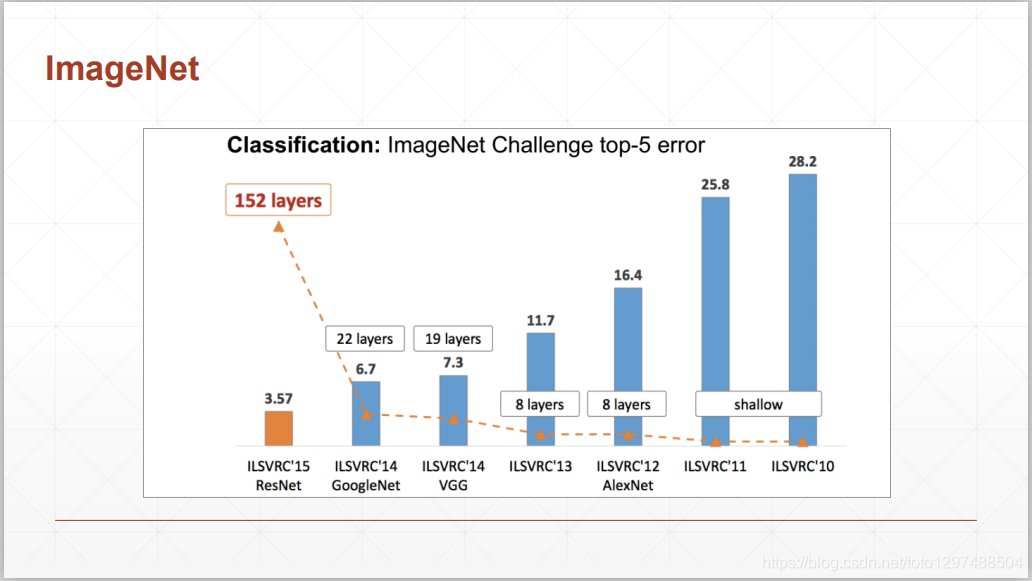
网络的精确度为:

ImageNet上前5个误差最小的网络
1.38.1.LeNet
LeNet-5第一个神经网络,用于手写字体识别
1.38.1.1.介绍
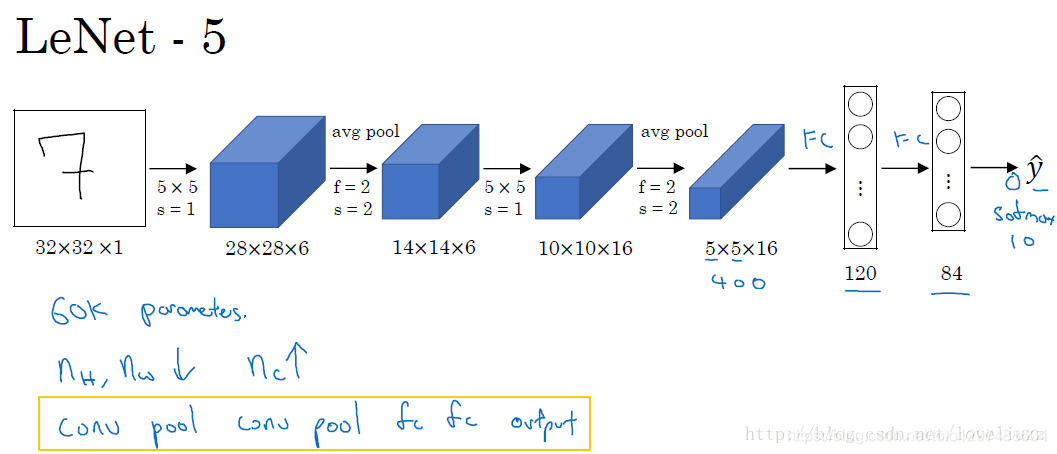
LeNet是卷积神经网络的祖师爷LeCun在1998年提出,用于解决手写数字识别的视觉任务。一共有7层,其中2层卷积和2层池化层交替出现,最后输出3层全连接层得到整体的结果。没有添加激活层。
随后CNN的最基本的架构就定下来了:卷积层、池化层、全连接层。如今各大深度学习框架中所使用的LeNet都是简化改进过的LeNet-5(-5表示具有5个层),和原始的LeNet有些许不同,比如把激活函数改为了现在很常用的ReLu。
LeNet-5跟现有的conv->pool->ReLU的套路不同,它使用的方式是conv1->pool->conv2->pool2再接全连接层,但是不变的是,卷积层后紧接池化层的模式。
99.2% acc
5/6 layers
1.38.1.2.网络结构
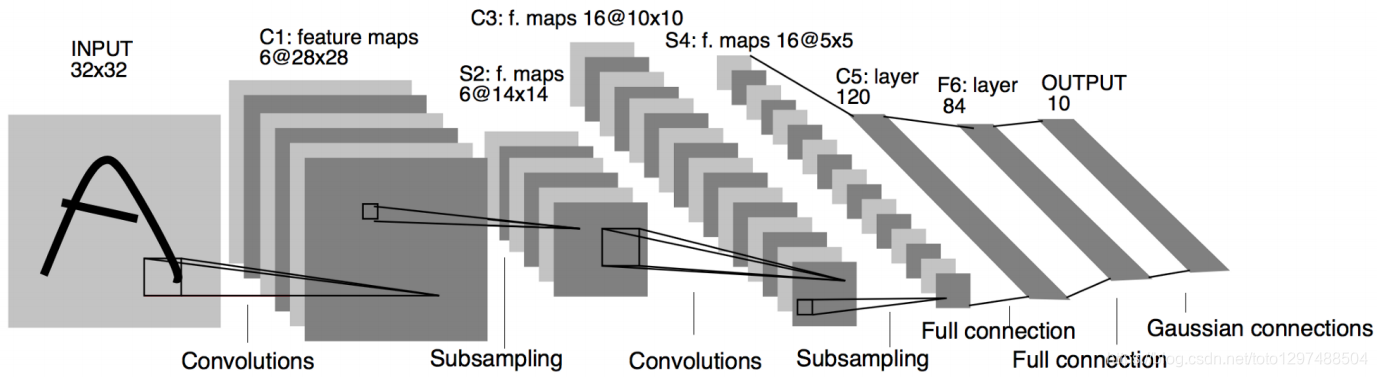
LeNet-5网络
LeNet-5网络是针对灰度图进行训练的,输入图像大小为32 * 32 * 1
1.38.1.3.代码实现
# -*- coding: UTF-8 -*-import torch
import torch.nn as nnclass Lenet(nn.Module):def __init__(self):super(Lenet, self).__init__()layer1 = nn.Sequential()layer1.add_module('conv1', nn.Conv2d(3, 6, 5, padding=1))layer1.add_module('pool1', nn.MaxPool2d(2, 2))self.layer1 = layer1layer2 = nn.Sequential()layer2.add_module('conv2', nn.Conv2d(6, 16, 5))layer2.add_module('pool2', nn.MaxPool2d(2, 2))self.layer2 = layer2layer3 = nn.Sequential()layer3.add_module('fc1', nn.Linear(400, 120))layer3.add_module('fc2', nn.Linear(120, 84))layer3.add_module('fc3', nn.Linear(84, 10))self.layer3 = layer3def forward(self, x):assert x.size(-1) == 32x = self.layer1(x)x = self.layer2(x)x = x.view(x.size(0), -1)x = self.layer3(x)return xdef main():net = Lenet()x = torch.randn(1, 3, 32, 32)print(net(x))if __name__ == '__main__':main()
输出结果:
tensor([[-0.0687, 0.1565, 0.0494, -0.1422, 0.0449, -0.0102, -0.0630, -0.0782,0.1001, -0.2641]], grad_fn=<AddmmBackward>)
1.38.2.AlexNet
AlexNet,8层网络,2012年ImageNet冠军,引起了对神经网络的关注
提出了max pooling,ReLU函数,使用dropout,采集卷积核比较大。
1.38.2.1.介绍
2012年AlexNet框架在ImageNet竞赛上面大放异彩的,它以领先第二名10%的准确度夺得冠军。掀起了卷积神经网络在图像领域的热潮。AlexNet相比于LeNet层数更深,第一次引入了激活层ReLU,并且在全连接层加入了Dropout防止过拟合。
1.38.2.2.网络结构
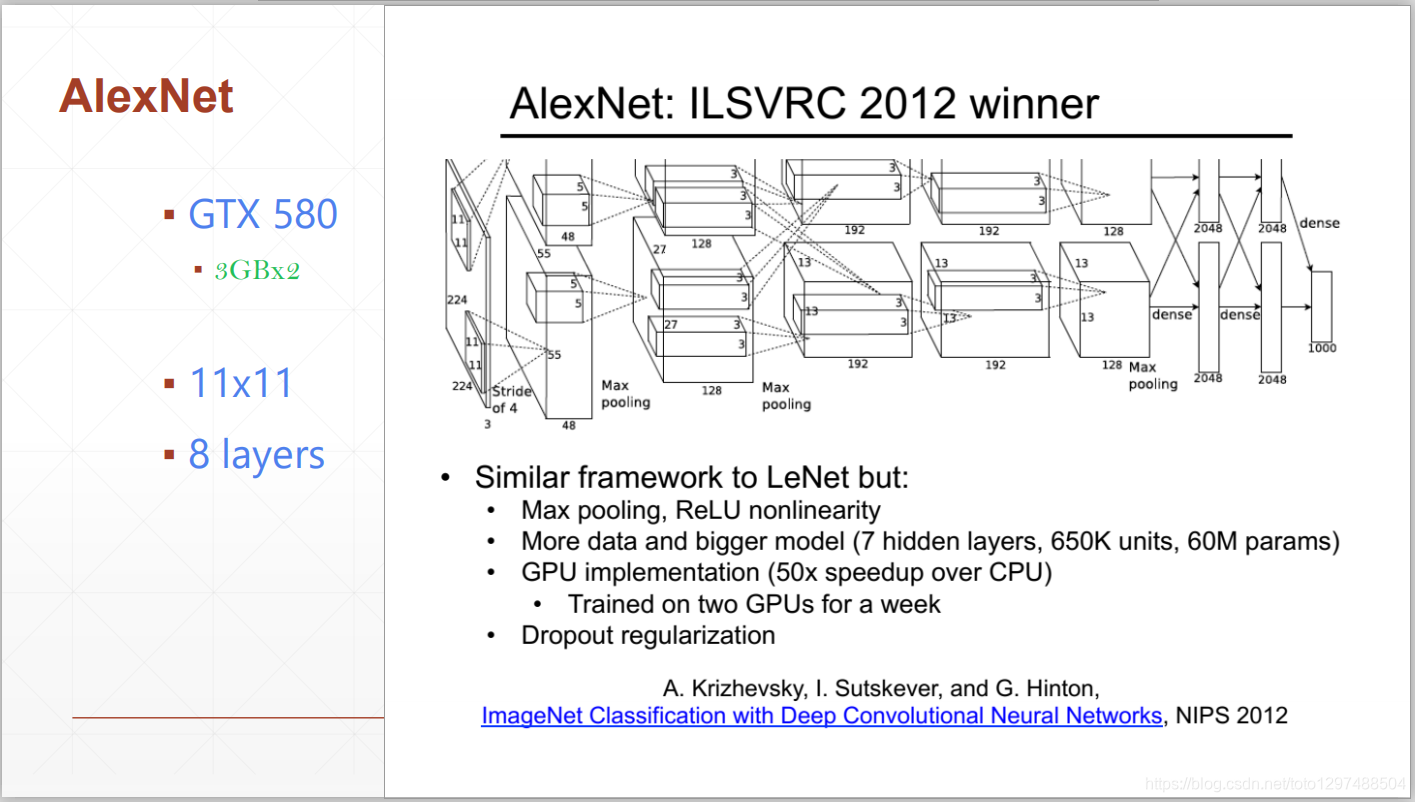
网友画的图有:
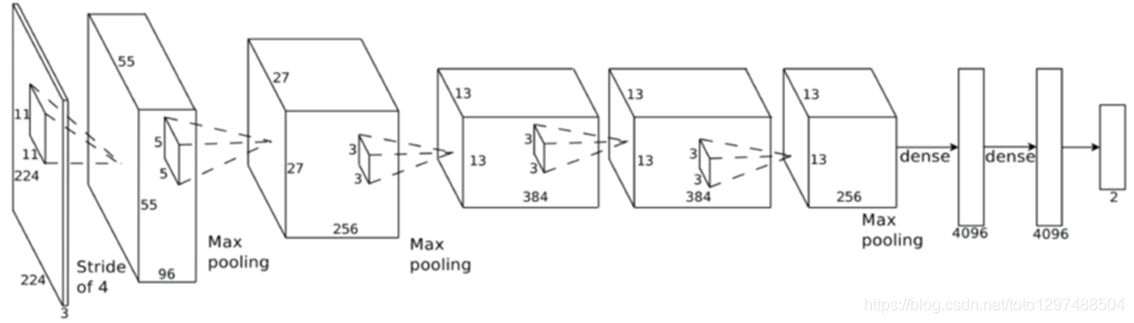
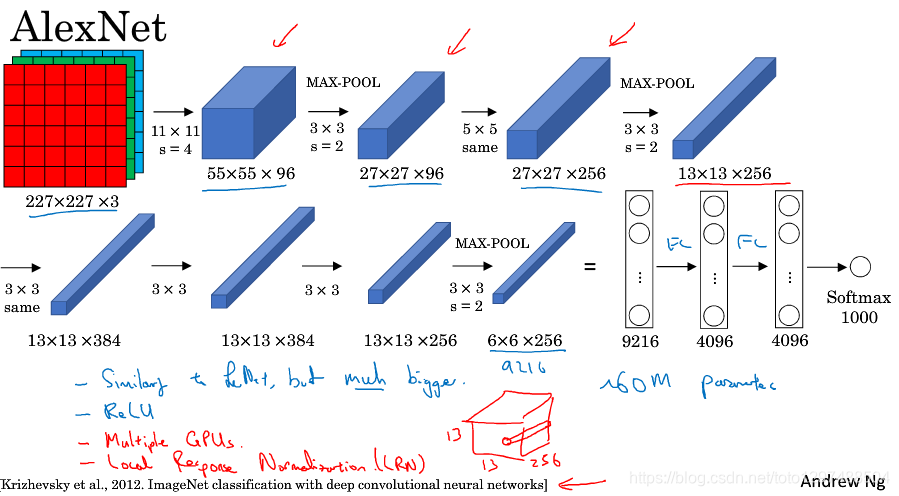
1.贡献: ILSVRC2012冠军,展现出了深度CNN在图像任务上的惊人表现,掀起CNN研究的热潮,是如今深度学习和AI迅猛发展的重要原因。ImageNet比赛为一直研究神经网络的Hinton提供了施展平台,AlexNet就是由hinton和他的两位学生发表的,在AlexNet之前,深度学习已经沉寂了很久。
2.网络结构:如下图所示,8层网络,参数大约有60 million,使用了relu函数,头两个全连接层使用了0.5的dropout。使用了LRN和重叠的池化,现在LRN都不用了,一般用BN作Normalization。当时使用了多GPU训练。
3.预处理:先down-sample成最短边为256的图像,然后剪出中间的256x256图像,再减均值做归一化(over training set)。 训练时,做数据增强,对每张图像,随机提取出227x227以及水平镜像版本的图像。除了数据增强,还使用了PCA对RGB像素降维的方式来缓和过拟合问题。
4.预测:对每张图像提取出5张(四个角落以及中间)以及水平镜像版本,总共10张,平均10个预测作为最终预测。
5.超参数:SGD,学习率0.01,batch size是128,momentum为0.9,weight decay为0.0005(论文有个权重更新公式),每当validation error不再下降时,学习率除以10。权重初始化用(0,0.01)的高斯分布,二四五卷积层和全连接层的bias初始化为1(给relu提供正值利于加速前期训练),其余bias初始化为0。
AlexNet Architecture
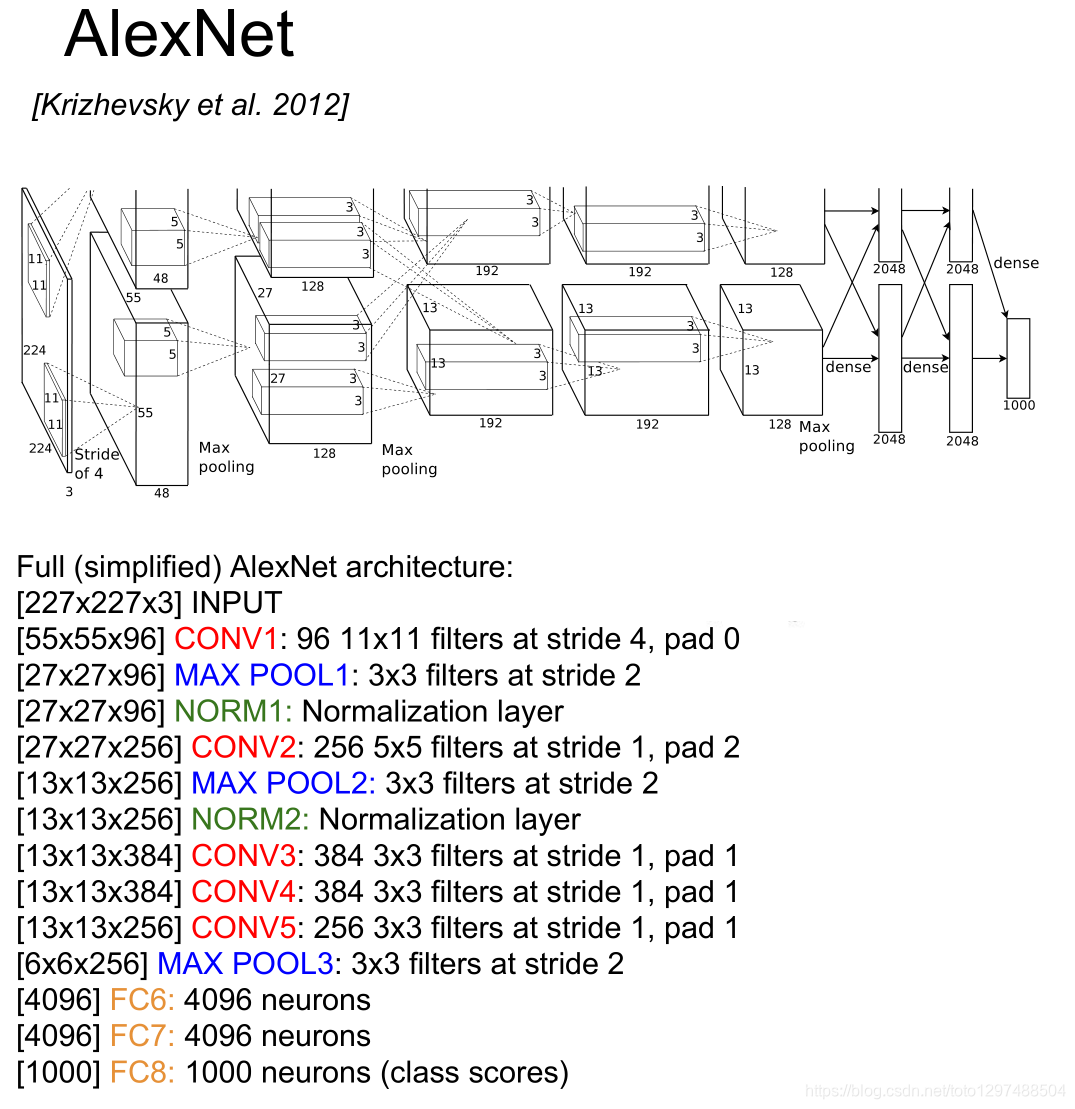
AlexNet 每层的超参数及参数数量
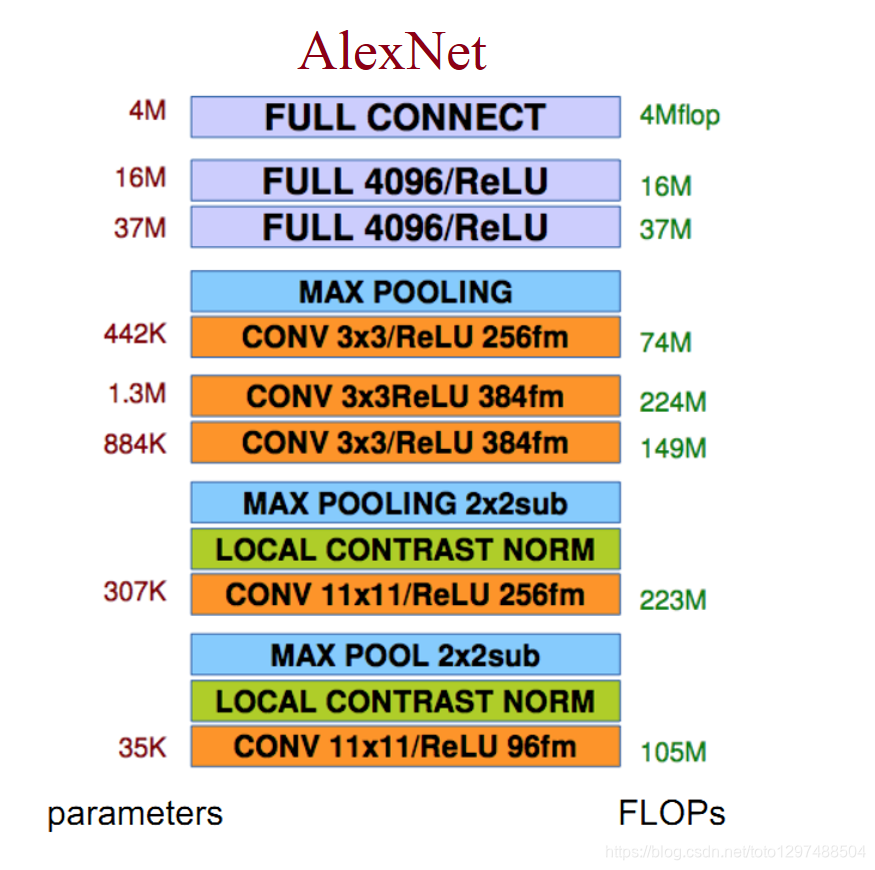
1.38.2.3.代码实现
# -*- coding: UTF-8 -*-import torch
import torch.nn as nnclass Alexnet(nn.Module):def __init__(self, n_classes):super(Alexnet, self).__init__()self.features = nn.Sequential(nn.Conv2d(3, 64, kernel_size=11, stride=4, padding=2),nn.ReLU(inplace=True),nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=3, stride=2),nn.Conv2d(64, 192, kernel_size=5, padding=2),nn.ReLU(inplace=True),nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=3, stride=2),nn.Conv2d(192, 384, kernel_size=3, padding=1),nn.ReLU(inplace=True),nn.Conv2d(384, 256, kernel_size=3, padding=1),nn.ReLU(inplace=True),nn.Conv2d(256, 256, kernel_size=3, padding=1),nn.ReLU(inplace=True),nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=3, stride=2),)self.classifier = nn.Sequential(nn.Dropout(p=0.1),nn.Linear(256 * 6 * 6, 4096),nn.ReLU(inplace=True),nn.Dropout(p=0.1),nn.Linear(4096, 4096),nn.ReLU(inplace=True),nn.Linear(4096, n_classes),)def forward(self, x):assert x.size(-1) == 224x = self.features(x)x = x.view(x.size(0), -1)x = self.classifier(x)return xdef main():x = torch.randn(1, 3, 224, 224)net = Alexnet(10)print(net(x))if __name__ == '__main__':main()
输出结果:
tensor([[-0.0016, 0.0054, -0.0021, -0.0123, 0.0113, 0.0088, 0.0171, 0.0032,-0.0075, 0.0074]], grad_fn=<AddmmBackward>)
1.38.3.VGG
VGG 网络层数更新,提出1 * 1, 3 * 3卷积核会使参数更少,效果更好。
1.38.3.1.介绍
VGGNe是ImageNet 2014年的亚军,它使用了更小的滤波器,同时使用的更深的网络结构。VGG只是对网络层进行不断的堆叠,并没有进行太多的创新,但增加深度确实可以一定程度改善模型效果。
AlexNet只有8层网络,而VGGNet有16和19层网络。AlexNet使用1111的大滤波器,而VGGNet使用33的卷积滤波器和22的大池化层。AlexNet和VGGNet对比图:
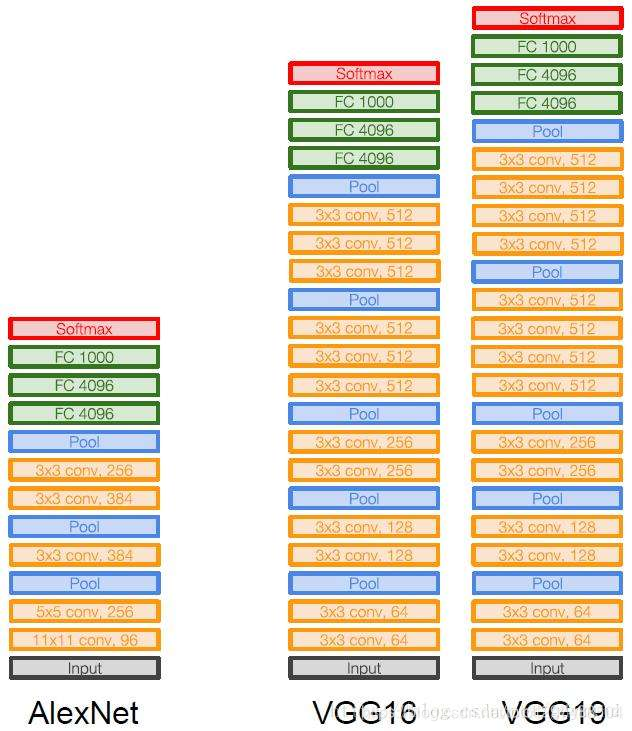
1.38.3.2.网络结构 VGG-16
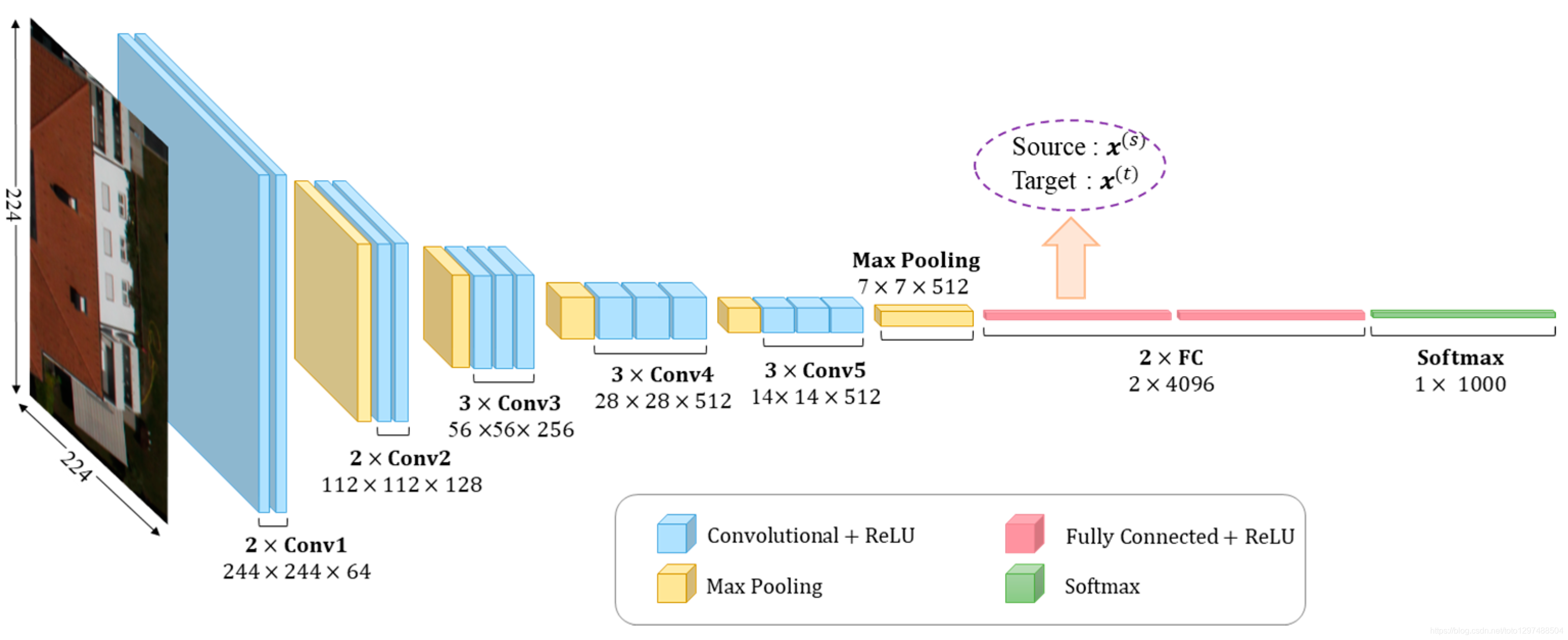
从网络模型可以看出,VGG16相比AlexNet类的模型具有较深的深度,通过反复堆叠33的卷积层和22的池化层,VGG16构建了较深层次的网络结构,整个网络的卷积核使用了一致的33的尺寸,最大池化层尺寸也一致为22。与AlexNet主要有以下不同:
VGG16有16层网络,AlexNet只有8层
在训练和测试时使用了多尺度做数据增强。
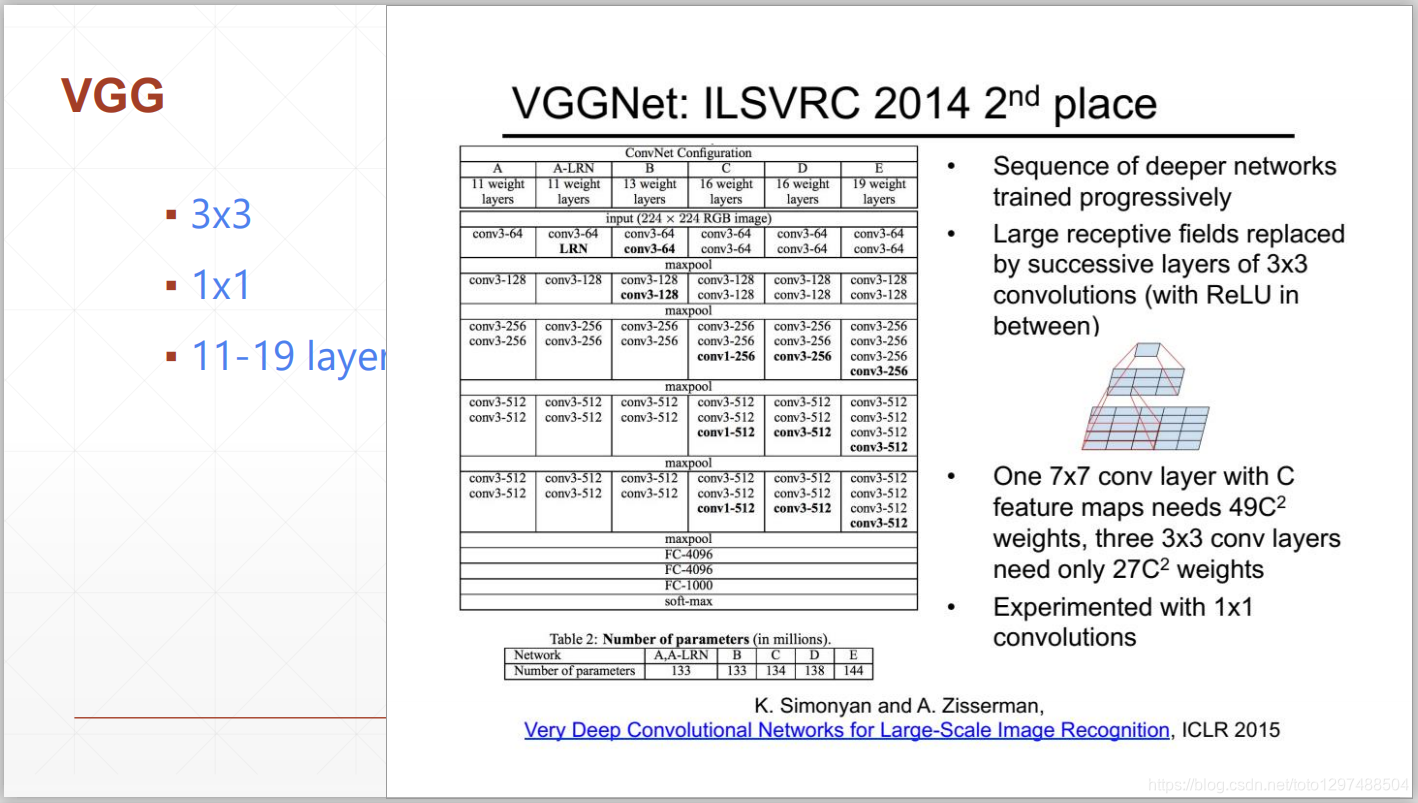
1.38.3.3.代码实现
# -*- coding: UTF-8 -*-import torch
import torch.nn as nnclass VGGNet(nn.Module):def __init__(self, n_classes, n_layers, in_channels=3):super(VGGNet, self).__init__()self.architecture = {16: [64, 64, 'Pooling', 128, 128, 'Pooling', 256, 256, 256,'Pooling', 512, 512, 512, 'Pooling', 512, 512, 512, 'Pooling'],19: [64, 64, 'Pooling', 128, 128, 'Pooling', 256, 256, 256, 256,'Pooling', 512, 512, 512, 512, 'Pooling', 512, 512, 512, 512, 'Pooling'],}self.features = self._constructNet(self.architecture[n_layers], in_channels)self.classifier = nn.Linear(512, n_classes)def _constructNet(self, arch, in_channels):net = []for out_channels in arch:if out_channels == 'Pooling':net += [nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=2, stride=2)]else:net += [nn.Conv2d(in_channels, out_channels, kernel_size=3, padding=1),nn.BatchNorm2d(out_channels),nn.ReLU(inplace=True)]in_channels = out_channelsnet += [nn.AvgPool2d(kernel_size=1, stride=1)]return nn.Sequential(*net)def forward(self, x):assert x.size(-1) == 32x = self.features(x)x = x.view(x.size(0), -1)x = self.classifier(x)return xdef main():x = torch.randn(1, 3, 32, 32)net = VGGNet(10, 19)print(net(x))if __name__ == '__main__':main()
1.38.4.GoogleNet
1.38.4.1.介绍
GoogLeNet 也叫InceptionNet,是在 2014 年被提出的。GoogLeNet 采取了比 VGGNet 更深的网络结构, 一共有 22 层,但是它的参数却比 A1exNet少了12倍。同时有很高的计算效率 ,因为它采用了一种很有效的Inception模块,而且它也没有全连接层,是 2014 年比赛的冠军。
1.38.4.2.网络结构
简单版Inception模块:
该结构将CNN中常用的卷积(1x1,3x3,5x5)、池化操作(3x3)堆叠在一起(卷积、池化后的尺寸相同,将通道相加),一方面增加了网络的宽度,另一方面也增加了网络对尺度的适应性。
网络卷积层中的网络能够提取输入的每一个细节信息,同时5x5的滤波器也能够覆盖大部分接受层的的输入。还可以进行一个池化操作,以减少空间大小,降低过度拟合。在这些层之上,在每一个卷积层后都要做一个ReLU操作,以增加网络的非线性特征。然而这个Inception原始版本,所有的卷积核都在上一层的所有输出上来做,而那个5x5的卷积核所需的计算量就太大了,造成了特征图的厚度很大。
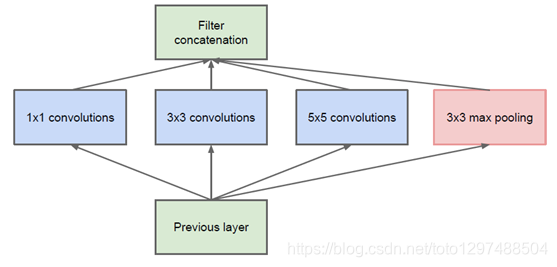
优化版Inception模型:为了避免上述情况,在3x3前、5x5前、max pooling后分别加上了1x1的卷积核,以起到了降低特征图厚度的作用,这也就形成了Inception v1的网络结构,如下图所示:
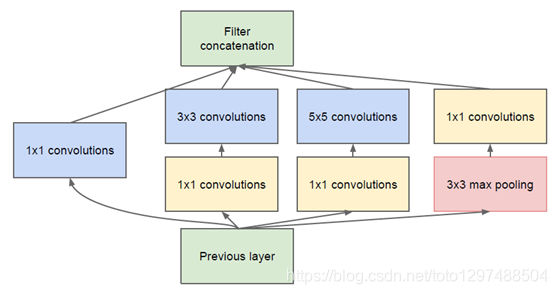
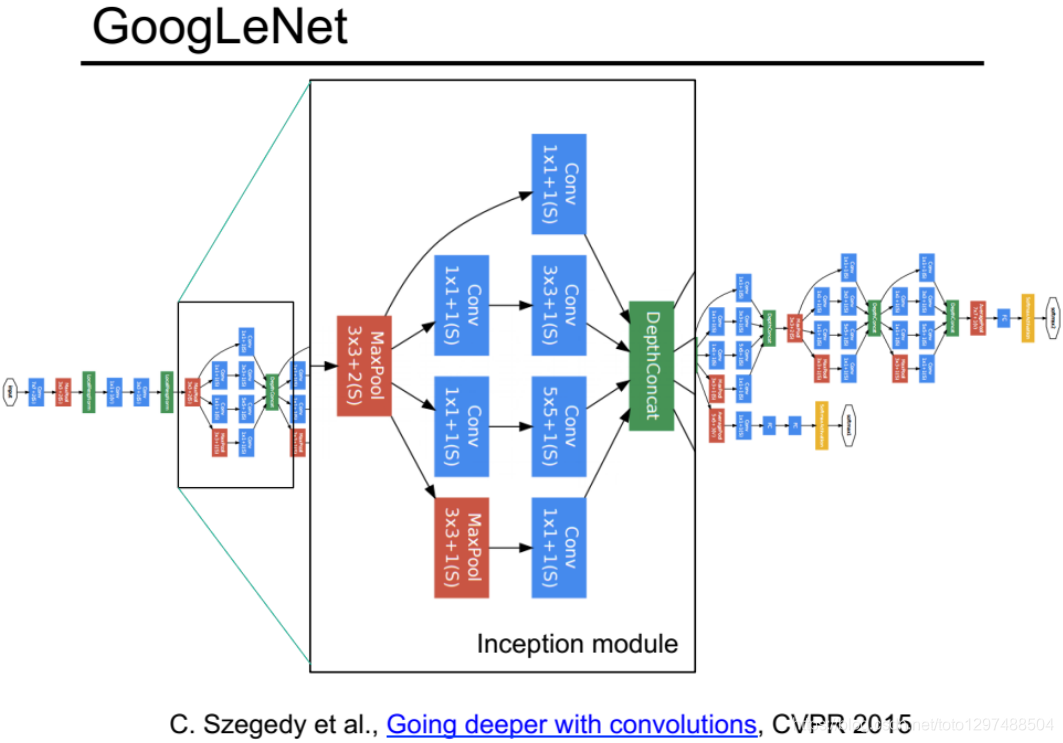
1.38.4.3.代码实现
整个GoogLeNet都是由这些Inception模块组成的。首先定义一个最基础的卷积模块、然后根据这个模块定义了1x1 ,3x3和5x5的模块和一个池化层,最后使用 torch.cat()将它们按深度拼接起来,得到输出结果。
# -*- coding: UTF-8 -*-import torch
import torch.nn as nnclass Inception(nn.Module):def __init__(self, in_channels, out_1x1, out_3x3_1, out_n3x3_2, out_5x5_1, out_5x5_2, pool_size):super(Inception, self).__init__()# 1x1 conv branchself.b1 = nn.Sequential(nn.Conv2d(in_channels, out_1x1, kernel_size=1),nn.BatchNorm2d(out_1x1),nn.ReLU(True),)# 1x1 conv -> 3x3 conv branchself.b2 = nn.Sequential(nn.Conv2d(in_channels, out_3x3_1, kernel_size=1),nn.BatchNorm2d(out_3x3_1),nn.ReLU(True),nn.Conv2d(out_3x3_1, out_n3x3_2, kernel_size=3, padding=1),nn.BatchNorm2d(out_n3x3_2),nn.ReLU(True),)# 1x1 conv -> 5x5 conv branchself.b3 = nn.Sequential(nn.Conv2d(in_channels, out_5x5_1, kernel_size=1),nn.BatchNorm2d(out_5x5_1),nn.ReLU(True),nn.Conv2d(out_5x5_1, out_5x5_2, kernel_size=3, padding=1),nn.BatchNorm2d(out_5x5_2),nn.ReLU(True),nn.Conv2d(out_5x5_2, out_5x5_2, kernel_size=3, padding=1),nn.BatchNorm2d(out_5x5_2),nn.ReLU(True),)# 3x3 pool -> 1x1 conv branchself.b4 = nn.Sequential(nn.MaxPool2d(3, stride=1, padding=1),nn.Conv2d(in_channels, pool_size, kernel_size=1),nn.BatchNorm2d(pool_size),nn.ReLU(True),)def forward(self, x):y1 = self.b1(x)y2 = self.b2(x)y3 = self.b3(x)y4 = self.b4(x)return torch.cat([y1,y2,y3,y4], 1)class Googlenet(nn.Module):def __init__(self):super(Googlenet, self).__init__()self.pre_layers = nn.Sequential(nn.Conv2d(3, 192, kernel_size=3, padding=1),nn.BatchNorm2d(192),nn.ReLU(True),)self.a3 = Inception(192, 64, 96, 128, 16, 32, 32)self.b3 = Inception(256, 128, 128, 192, 32, 96, 64)self.maxpool = nn.MaxPool2d(3, stride=2, padding=1)self.a4 = Inception(480, 192, 96, 208, 16, 48, 64)self.b4 = Inception(512, 160, 112, 224, 24, 64, 64)self.c4 = Inception(512, 128, 128, 256, 24, 64, 64)self.d4 = Inception(512, 112, 144, 288, 32, 64, 64)self.e4 = Inception(528, 256, 160, 320, 32, 128, 128)self.a5 = Inception(832, 256, 160, 320, 32, 128, 128)self.b5 = Inception(832, 384, 192, 384, 48, 128, 128)self.avgpool = nn.AvgPool2d(8, stride=1)self.linear = nn.Linear(1024, 10)def forward(self, x):x = self.pre_layers(x)x = self.a3(x)x = self.b3(x)x = self.maxpool(x)x = self.a4(x)x = self.b4(x)x = self.c4(x)x = self.d4(x)x = self.e4(x)x = self.maxpool(x)x = self.a5(x)x = self.b5(x)x = self.avgpool(x)x = x.view(x.size(0), -1)x = self.linear(x)return xdef main():x = torch.randn(1, 3, 32, 32)net = Googlenet()print(net(x))if __name__ == '__main__':main()
1.38.5.ResNet
1.38.5.1.介绍
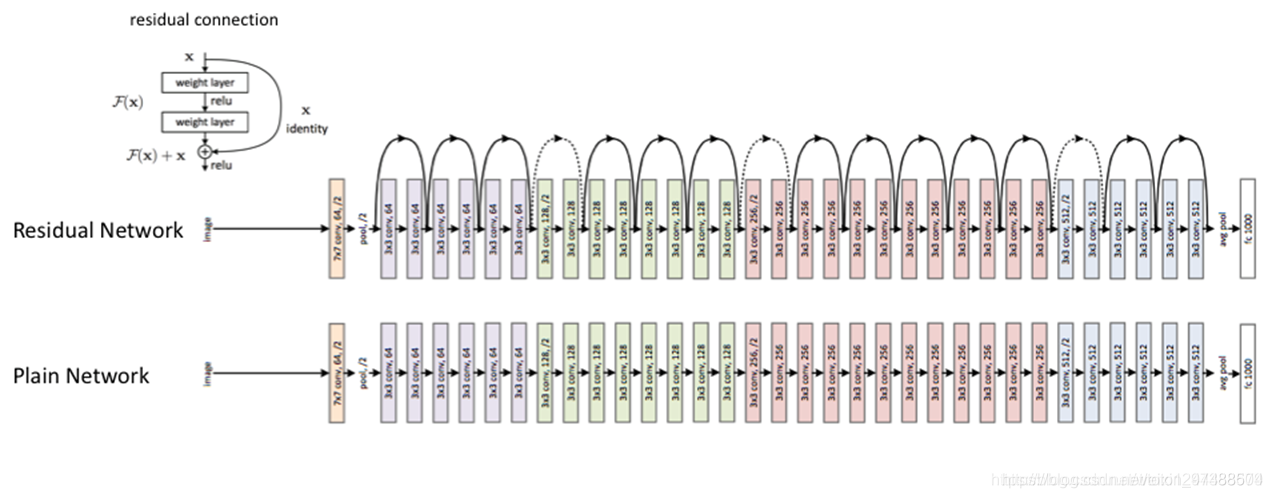
ResNet是2015年ImageNet竞赛的冠军。由微软研究院提出,不再是简单的堆积层数,通过残差模块能够成功地训练高达152层深的神经网络。ResNet 最初的设计灵感来自这个问题:
随着网络深度增加,网络的准确度应该同步增加,当然要注意过拟合问题。但是网络深度增加的一个问题在于这些增加的层是参数更新的信号,因为梯度是从后向前传播的,增加网络深度后,比较靠前的层梯度会很小。这意味着这些层基本上学习停滞了,这就是梯度消失问题。
深度网络的第二个问题在于训练,当网络更深时意味着参数空间更大,优化问题变得更难,因此简单地去增加网络深度反而出现更高的训练误差。在不断加深度神经网络的时候,会出现一个Degradation,即准确率会先上开然后达到饱和,再持续增加深度则会导致模型准确率下降。比如下图,一个56层的网络的性能却不如20层的性能好,这不是因为过拟合(训练集训练误差依然很高),这就是退化问题。残差网络ResNet设计一种残差模块让我们可以训练更深的网络。
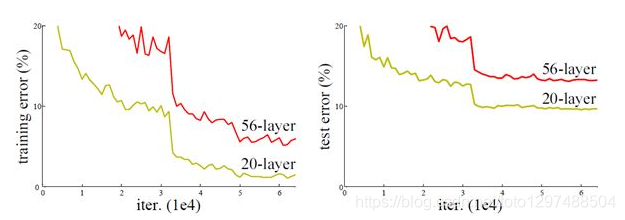
这里详细分析一下残差单元来理解ResNet的精髓。
从下图可以看出,数据经过了两条路线,一条是常规路线,另一条则是捷(shortcut),直接实现单位映射的直接连接的路线,这有点类似与电路中的“短路”。通过实验,这种带有shortcut的结构确实可以很好地应对退化问题。我们把网络中的一个模块的输入和输出关系看作是y=H(x),那么直接通过梯度方法求H(x)就会遇到上面提到的退化问题,如果使用了这种带shortcut的结构,那么可变参数部分的优化目标就不再是H(x),若用F(x)来代表需要优化的部分的话,则H(x)=F(x)+x,也就是F(x)=H(x)-x。因为在单位映射的假设中y=x就相当于观测值,所以F(x)就对应着残差,因而叫残差网络。为啥要这样做,因为作者认为学习残差F(X)比直接学习H(X)简单!设想下,现在根据我们只需要去学习输入和输出的差值就可以了,绝对量变为相对量(H(x)-x 就是输出相对于输入变化了多少),优化起来简单很多。
考虑到x的维度与F(X)维度可能不匹配情况,需进行维度匹配。这里论文中采用两种方法解决这一问题(其实是三种,但通过实验发现第三种方法会使performance急剧下降,故不采用):
zero_padding:对恒等层进行0填充的方式将维度补充完整。这种方法不会增加额外的参数
projection:在恒等层采用1x1的卷积核来增加维度。这种方法会增加额外的参数
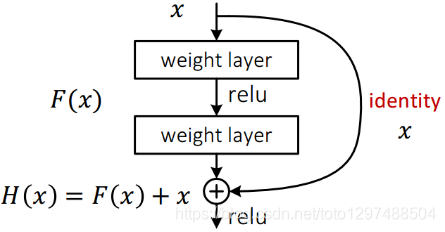
1.38.5.2.网络结构
下图展示了两种形态的残差模块,左图是常规残差模块,有两个3×3卷积核卷积核组成,但是随着网络进一步加深,这种残差结构在实践中并不是十分有效。针对这问题,右图的“瓶颈残差模块”(bottleneck residual block)可以有更好的效果,它依次由1×1、3×3、1×1这三个卷积层堆积而成,这里的1×1的卷积能够起降维或升维的作用,从而令3×3的卷积可以在相对较低维度的输入上进行,以达到提高计算效率的目的。
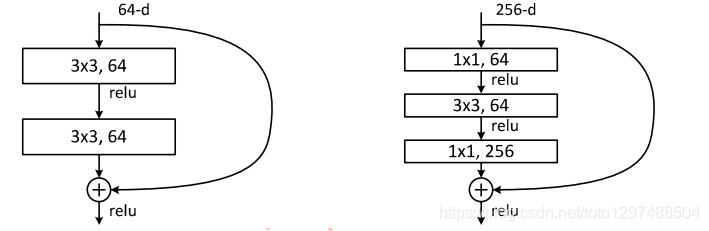
1.38.5.3.代码实现
# -*- coding: UTF-8 -*-import torch
import torch.nn as nn
import torch.nn.functional as Fclass basicBlock(nn.Module):expansion = 1def __init__(self, in_channels, out_channels, stride=1):super(basicBlock, self).__init__()self.conv1 = nn.Conv2d(in_channels, out_channels, kernel_size=3, padding=1, bias=False)self.bn1 = nn.BatchNorm2d(out_channels)self.conv2 = nn.Conv2d(out_channels, out_channels, kernel_size=3, stride=stride, padding=1, bias=False)self.bn2 = nn.BatchNorm2d(out_channels)# shortcut is a convolution layer with BatchNormalizationself.shortcut = nn.Sequential()if stride != 1 or in_channels != self.expansion * in_channels:self.shortcut = nn.Sequential(nn.Conv2d(in_channels, self.expansion * out_channels, kernel_size=1, stride=stride, bias=False),nn.BatchNorm2d(self.expansion * out_channels))def forward(self, input):x = F.relu(self.bn1(self.conv1(input)))x = self.bn2(self.conv2(x))x += self.shortcut(input)x = F.relu(x)return xclass bottleneckBlock(nn.Module):expansion = 4def __init__(self, in_channels, out_channels, stride=1):super(bottleneckBlock, self).__init__()self.conv1 = nn.Conv2d(in_channels, out_channels, kernel_size=1, stride=stride, bias=False)self.bn1 = nn.BatchNorm2d(out_channels)self.conv2 = nn.Conv2d(out_channels, out_channels, kernel_size=3, stride=stride, bias=False)self.bn2 = nn.BatchNorm2d(out_channels)self.conv3 = nn.Conv2d(out_channels, self.expansion * out_channels, kernel_size=1, bias=False)self.bn3 = nn.BatchNorm2d(self.expansion * out_channels)if stride != 1 or in_channels != self.expansion * out_channels:self.shortcut = nn.Sequential(nn.Conv2d(in_channels, self.expansion * out_channels, kernel_size=1, stride=stride, bias=False),nn.BatchNorm2d(self.expansion * out_channels))def forward(self, input):x = F.relu(self.bn1(self.conv1(input)))x = F.relu(self.bn2(self.conv2(x)))x = self.bn3(self.conv3(x))x += self.shortcut(input)x = F.relu(x)return xclass Resnet(nn.Module):def __init__(self, block, num_blocks, num_classes=10):super(Resnet, self).__init__()self.in_channels = 64self.conv1 = nn.Conv2d(3, 64, kernel_size=3, stride=1, padding=1, bias=False)self.bn1 = nn.BatchNorm2d(64)self.layer1 = self._make_layer(block, 64, num_blocks[0], stride=1)self.layer2 = self._make_layer(block, 128, num_blocks[1], stride=2)self.layer3 = self._make_layer(block, 256, num_blocks[2], stride=2)self.layer4 = self._make_layer(block, 512, num_blocks[3], stride=2)self.linear = nn.Linear(512 * block.expansion, num_classes)def _make_layer(self, block, out_channels, num_blocks, stride):strides = [stride] + [1] * (num_blocks - 1)layers = []for stride in strides:layers.append(block(self.in_channels, out_channels, stride))self.in_channels = out_channels * block.expansionreturn nn.Sequential(*layers)def forward(self, x):x = F.relu(self.bn1(self.conv1(x)))x = self.layer1(x)x = self.layer2(x)x = self.layer3(x)x = self.layer4(x)x = F.avg_pool2d(x, 4)x = x.view(x.size(0), -1)x = self.linear(x)return xdef ResNet18():return Resnet(basicBlock, [2, 2, 2, 2])def ResNet152():return Resnet(bottleneckBlock, [3, 8, 36, 3])def main():x = torch.randn(1, 3, 32, 32)net = ResNet18()print(net(x))if __name__ == '__main__':main()
1.38.6.NIN
全称Network in network,顾名思义,该网络的目的就是用某种方式堆叠小的网络。
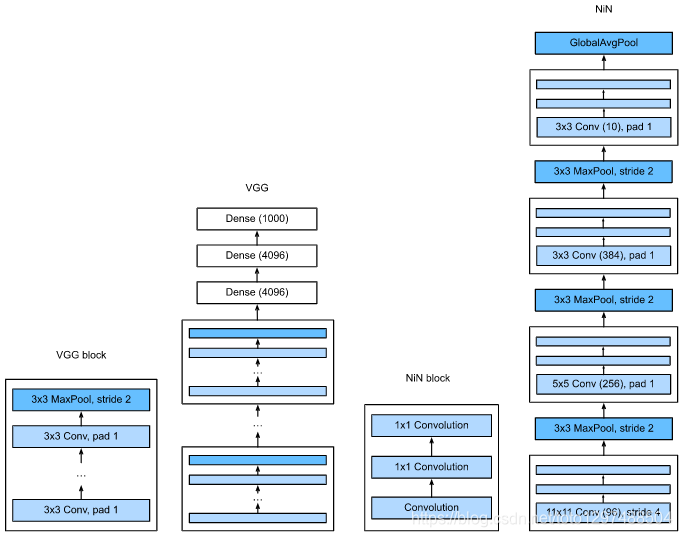
左图展示了AlexNet和VGG的网络结构,右图展示了NiN的网络结构。
1.38.6.1.局部块
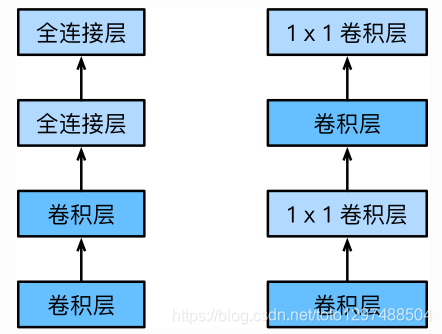
左图是AlexNet和VGG的网络结构局部,右图是NiN的网络结构局部
左图是AlexNet和VGG的网络结构局部,右图是NiN的网络结构局部
NiN块是NiN中的基础块。它由一个卷积层加两个充当全连接层的卷积层串联而成。其中第一个卷积层的超参数可以自行设置,而而第二和第三个卷积层的超参数一般是固定的。
如果要堆叠小模型,那么就无法避免全连接层,而将卷积结果的特征图转为全连接的维度转换,将耗费大量的资源。而使用1x1的卷积层正好可以完成这一替换。1x1的卷积层,可以看成全连接层,其中空间维度(高和宽)上的每个元素相当于样本,通道相当于特征。因此,NIN使用1x1卷积层来替代全连接层,从而使空间信息能够自然传递到后面的层。
1.38.6.2.替代FC,使用全局平均池化层求分类
NiN还有一个设计与AlexNet显著不不同:NiN去掉了了AlexNet最后的3个全连接层,取而代之地,NiN使用用了输出通道数等于标签类别数的NiN块,然后使用全局平均池化层对每个通道中所有元素求平均并直接用于分类。
这里的全局平均池化层即窗口形状等于输入空间维形状的平均池化层。
NiN的这个设计的好处是可以显著减小模型参数尺寸,从而缓解过拟合。然而,该设计有时会造成获得有效模型的训练时间的增加。
1.38.6.3.代码案例
class GlobalAvgPool2d(nn.Module):def __init__(self):super(GlobalAvgPool2d, self).__init__()def forward(self, x):return F.avg_pool2d(x, kernel_size=x.size()[2:])class FlattenLayer(nn.Module):def __init__(self):super(FlattenLayer, self).__init__()def forward(self, X):return X.view(X.shape[0], -1)class NIN(nn.Module):def __init__(self, classes):self.classes = classessuper(NIN, self).__init__()self.net = nn.Sequential(self.nin_block(3, 96, kernel_size=11, stride=4, padding=0),nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=3, stride=2),self.nin_block(96, 256, kernel_size=5, stride=1, padding=2),nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=3, stride=2),self.nin_block(256, 384, kernel_size=3, stride=1, padding=1),nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=3, stride=2),nn.Dropout(0.5),self.nin_block(384, self.classes, kernel_size=3, stride=1, padding=1),GlobalAvgPool2d(),FlattenLayer())def nin_block(self, in_channels, out_channels, kernel_size, stride, padding):block = nn.Sequential(nn.Conv2d(in_channels, out_channels, kernel_size, stride, padding),nn.ReLU(),nn.Conv2d(out_channels, out_channels, kernel_size=1),nn.ReLU(),nn.Conv2d(out_channels, out_channels, kernel_size=1),nn.ReLU())return blockdef forward(self, img):return self.net(img)
1.38.7.DenseNet
DenseNet与ResNet区别主要在于它将ResNet的残差块中的相加变为了channel的连结。
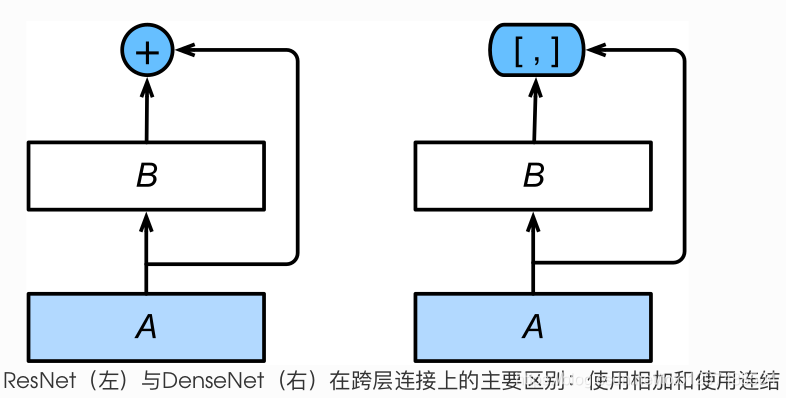
1.38.7.1.稠密块
DenseNet使用了ResNet改良版的“BN->relu->conv”结构,它组成了基本的卷积块 conv_block。
稠密块由多个 conv_block 组成,每块使用相同的输出通道数。但在前向计算时,我们将每块的输入和输出在通道维上连结。
1.38.7.2.过滤层
由于每个稠密块都会带来通道数的增加,使用用过多则会带来过于复杂的模型。过渡层用来控制模型复杂度。它通过卷积层来减小通道数,并使用步幅为2的平均池化层减半高和宽,从而进一步降低模型复杂度。
1.38.7.3.模型结构
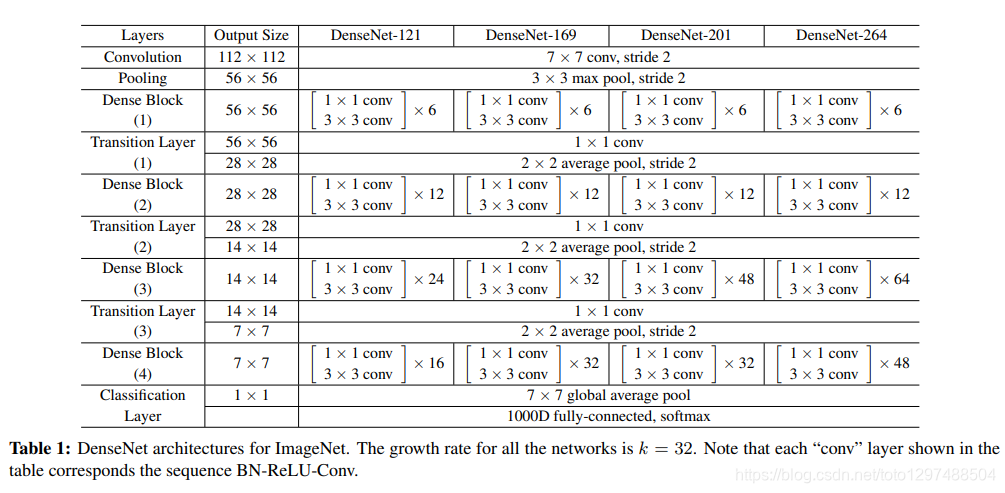
1.38.7.4.代码案例
class FlattenLayer(nn.Module):def __init__(self):super(FlattenLayer, self).__init__()def forward(self, X):return X.view(X.shape[0], -1)class GlobalAvgPool2d(nn.Module):def __init__(self):super(GlobalAvgPool2d, self).__init__()def forward(self, x):return F.avg_pool2d(x, kernel_size=x.size()[2:])class DenseBlock(nn.Module):def __init__(self, in_channels, out_channels, num_conv):super(DenseBlock, self).__init__()self.out_channels = out_channelslayers = []for i in range(num_conv):in_c = in_channels + i * self.out_channelslayers.append(self.conv_block(in_c, self.out_channels))self.net = nn.ModuleList(layers)self.out_channels = in_channels + num_conv * out_channelsdef conv_block(self, in_channels, out_channels):block = nn.Sequential(nn.BatchNorm2d(in_channels),nn.ReLU(),nn.Conv2d(in_channels, out_channels, kernel_size=3, padding=1))return blockdef forward(self, X):for layer in self.net:Y = layer(X)X = torch.cat((X, Y), dim=1)return Xclass DenseNet(nn.Module):def __init__(self, classes):super(DenseNet, self).__init__()self.classes = classesself.net = nn.Sequential(nn.Conv2d(3, 64, kernel_size=7, stride=2, padding=3),nn.BatchNorm2d(64),nn.ReLU(),nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=3, stride=2))num_channels, growth_rate = 64, 32 # 当前通道数64,每层增加32通道(即每层卷积输出通道为32)num_convs_in_dense_block = [4, 4, 4, 4] # 每个dense block 卷积数for i, num_convs in enumerate(num_convs_in_dense_block):block = DenseBlock(num_channels, growth_rate, num_convs)self.net.add_module("dense_block_%d" % i, block)num_channels = block.out_channels # 上一个块的输出通道数if i != len(num_convs_in_dense_block) - 1:self.net.add_module("trainsition_block_%d" % i, self.transition_block(num_channels, num_channels // 2))num_channels = num_channels // 2self.net.add_module("BN", nn.BatchNorm2d(num_channels))self.net.add_module("relu", nn.ReLU())self.net.add_module("global_avg_pool", GlobalAvgPool2d())self.net.add_module("flatten", FlattenLayer())self.net.add_module("fc", nn.Linear(num_channels, self.classes))def forward(self, X):return self.net(X)def transition_block(self, in_channels, out_channels):block = nn.Sequential(nn.BatchNorm2d(in_channels),nn.ReLU(),nn.Conv2d(in_channels, out_channels, kernel_size=1),nn.AvgPool2d(kernel_size=2, stride=2))return block
1.38.7.5.总结
在跨层连接上,不同于ResNet中将输入与输出相加,DenseNet在通道维上连结输入与输出。
DenseNet的主要构建模块是稠密块和过渡层。
1.38.8.EfficientNet
代码:
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
import torch.nn.functional as F
import numpy as npdef conv_bn_act(in_, out_, kernel_size,stride=1, groups=1, bias=True,eps=1e-3, momentum=0.01):return nn.Sequential(SamePadConv2d(in_, out_, kernel_size, stride, groups=groups, bias=bias),nn.BatchNorm2d(out_, eps, momentum),Swish())class SamePadConv2d(nn.Conv2d):def __init__(self, in_channels, out_channels, kernel_size, stride=1, dilation=1, groups=1, bias=True):super(SamePadConv2d, self).__init__(in_channels, out_channels, kernel_size, stride, 0, dilation, groups, bias)def get_pad_odd(self, in_, weight, stride, dilation):effective_filter_size_rows = (weight - 1) * dilation + 1out_rows = (in_ + stride - 1) // stridepadding_needed = max(0, (out_rows - 1) * stride + effective_filter_size_rows - in_)padding_rows = max(0, (out_rows - 1) * stride + (weight - 1) * dilation + 1 - in_)rows_odd = (padding_rows % 2 != 0)return padding_rows, rows_odddef forward(self, x):padding_rows, rows_odd = self.get_pad_odd(x.shape[2], self.weight.shape[2], self.stride[0], self.dilation[0])padding_cols, cols_odd = self.get_pad_odd(x.shape[3], self.weight.shape[3], self.stride[1], self.dilation[1])if rows_odd or cols_odd:x = F.pad(x, [0, int(cols_odd), 0, int(rows_odd)])return F.conv2d(x, self.weight, self.bias, self.stride,padding=(padding_rows // 2, padding_cols // 2),dilation=self.dilation, groups=self.groups)class Swish(nn.Module):def forward(self, x):return x * torch.sigmoid(x)class Flatten(nn.Module):def forward(self, x):return x.view(x.shape[0], -1)class SEModule(nn.Module):def __init__(self, in_, squeeze_ch):super(SEModule, self).__init__()self.se = nn.Sequential(nn.AdaptiveAvgPool2d(1),nn.Conv2d(in_, squeeze_ch, kernel_size=1, stride=1, padding=0, bias=True),Swish(),nn.Conv2d(squeeze_ch, in_, kernel_size=1, stride=1, padding=0, bias=True),)def forward(self, x):return x * torch.sigmoid(self.se(x))class DropConnect(nn.Module):def __init__(self, ratio):super().__init__()self.ratio = 1.0 - ratiodef forward(self, x):if not self.training:return xrandom_tensor = self.ratiorandom_tensor += torch.rand([x.shape[0], 1, 1, 1], dtype=torch.float, device=x.device)random_tensor.requires_grad_(False)return x / self.ratio * random_tensor.floor()class MBConv(nn.Module):def __init__(self, in_, out_, expand,kernel_size, stride, skip,se_ratio, dc_ratio=0.2):super().__init__()mid_ = in_ * expandself.expand_conv = conv_bn_act(in_, mid_, kernel_size=1, bias=False) if expand != 1 else nn.Identity()self.depth_wise_conv = conv_bn_act(mid_, mid_,kernel_size=kernel_size, stride=stride,groups=mid_, bias=False)self.se = SEModule(mid_, int(in_ * se_ratio)) if se_ratio > 0 else nn.Identity()self.project_conv = nn.Sequential(SamePadConv2d(mid_, out_, kernel_size=1, stride=1, bias=False),nn.BatchNorm2d(out_, 1e-3, 0.01))# if _block_args.id_skip:# and all(s == 1 for s in self._block_args.strides)# and self._block_args.input_filters == self._block_args.output_filters:self.skip = skip and (stride == 1) and (in_ == out_)# DropConnect# self.dropconnect = DropConnect(dc_ratio) if dc_ratio > 0 else nn.Identity()# Original TF Repo not using drop_rate# https://github.com/tensorflow/tpu/blob/05f7b15cdf0ae36bac84beb4aef0a09983ce8f66/models/official/efficientnet/efficientnet_model.py#L408self.dropconnect = nn.Identity()def forward(self, inputs):expand = self.expand_conv(inputs)x = self.depth_wise_conv(expand)x = self.se(x)x = self.project_conv(x)if self.skip:x = self.dropconnect(x)x = x + inputsreturn xclass MBBlock(nn.Module):def __init__(self, in_, out_, expand, kernel, stride, num_repeat, skip, se_ratio, drop_connect_ratio=0.2):super().__init__()layers = [MBConv(in_, out_, expand, kernel, stride, skip, se_ratio, drop_connect_ratio)]for i in range(1, num_repeat):layers.append(MBConv(out_, out_, expand, kernel, 1, skip, se_ratio, drop_connect_ratio))self.layers = nn.Sequential(*layers)def forward(self, x):return self.layers(x)class EfficientNet(nn.Module):def __init__(self, width_coeff, depth_coeff,depth_div=8, min_depth=None,dropout_rate=0.2, drop_connect_rate=0.2,num_classes=1000):super().__init__()min_depth = min_depth or depth_divself.stem = conv_bn_act(3, 32, kernel_size=3, stride=2, bias=False)def renew_ch(x):if not width_coeff:return xx *= width_coeffnew_x = max(min_depth, int(x + depth_div / 2) // depth_div * depth_div)if new_x < 0.9 * x:new_x += depth_divreturn int(new_x)def renew_repeat(x):return int(np.ceil(x * depth_coeff))self.blocks = nn.Sequential(# input channel output expand k s skip seMBBlock(renew_ch(32), renew_ch(16), 1, 3, 1, renew_repeat(1), True, 0.25, drop_connect_rate),MBBlock(renew_ch(16), renew_ch(24), 6, 3, 2, renew_repeat(2), True, 0.25, drop_connect_rate),MBBlock(renew_ch(24), renew_ch(40), 6, 5, 2, renew_repeat(2), True, 0.25, drop_connect_rate),MBBlock(renew_ch(40), renew_ch(80), 6, 3, 2, renew_repeat(3), True, 0.25, drop_connect_rate),MBBlock(renew_ch(80), renew_ch(112), 6, 5, 1, renew_repeat(3), True, 0.25, drop_connect_rate),MBBlock(renew_ch(112), renew_ch(192), 6, 5, 2, renew_repeat(4), True, 0.25, drop_connect_rate),MBBlock(renew_ch(192), renew_ch(320), 6, 3, 1, renew_repeat(1), True, 0.25, drop_connect_rate))self.head = nn.Sequential(*conv_bn_act(renew_ch(320), renew_ch(1280), kernel_size=1, bias=False),nn.AdaptiveAvgPool2d(1),nn.Dropout2d(dropout_rate, True) if dropout_rate > 0 else nn.Identity(),Flatten(),nn.Linear(renew_ch(1280), num_classes))self.init_weights()def init_weights(self):for m in self.modules():if isinstance(m, SamePadConv2d):nn.init.kaiming_normal_(m.weight, mode="fan_out")elif isinstance(m, nn.Linear):init_range = 1.0 / np.sqrt(m.weight.shape[1])nn.init.uniform_(m.weight, -init_range, init_range)def forward(self, inputs):stem = self.stem(inputs)x = self.blocks(stem)head = self.head(x)return headdef main():x = torch.randn(1, 3, 224, 224)net = EfficientNet(1, 1)print(net(x))if __name__ == '__main__':main()
1.38.9.MobileNetV1
import time
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
import torchvision.models as models
from torch.autograd import Variableclass MobileNet(nn.Module):def __init__(self):super(MobileNet, self).__init__()def conv_bn(inp, oup, stride):return nn.Sequential(nn.Conv2d(inp, oup, 3, stride, 1, bias=False),nn.BatchNorm2d(oup),nn.ReLU(inplace=True))def conv_dw(inp, oup, stride):return nn.Sequential(nn.Conv2d(inp, inp, 3, stride, 1, groups=inp, bias=False),nn.BatchNorm2d(inp),nn.ReLU(inplace=True),nn.Conv2d(inp, oup, 1, 1, 0, bias=False),nn.BatchNorm2d(oup),nn.ReLU(inplace=True))self.feature = nn.Sequential(conv_bn(3, 32, 2),conv_dw(32, 64, 1),conv_dw(64, 128, 2),conv_dw(128, 128, 1),conv_dw(128, 256, 2),conv_dw(256, 256, 1),conv_dw(256, 512, 2),conv_dw(512, 512, 1),conv_dw(512, 512, 1),conv_dw(512, 512, 1),conv_dw(512, 512, 1),conv_dw(512, 512, 1),conv_dw(512, 1024, 2),conv_dw(1024, 1024, 1),nn.AvgPool2d(7) )self.fc = nn.Linear(1024, 1000)def forward(self, x):x = self.feature(x)x = x.view(x.size(0), -1)x = self.fc(x)return xdef main():x = torch.randn(1, 3, 224, 224)net = MobileNet()print(net(x))if __name__ == '__main__':main()
1.38.10.MobileNetV2
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
import numpy as npclass InvertedResidual(nn.Module):def __init__(self, inp, oup, stride, expand_ratio):super(InvertedResidual, self).__init__()self.stride = strideassert stride in [1, 2]hidden_dim = int(inp * expand_ratio)self.use_res_connect = self.stride == 1 and inp == oupif expand_ratio == 1:self.conv = nn.Sequential(# dwnn.Conv2d(hidden_dim, hidden_dim, 3, stride, 1, groups=hidden_dim, bias=False),nn.BatchNorm2d(hidden_dim),nn.ReLU6(inplace=True),# pw-linearnn.Conv2d(hidden_dim, oup, 1, 1, 0, bias=False),nn.BatchNorm2d(oup),)else:self.conv = nn.Sequential(# pwnn.Conv2d(inp, hidden_dim, 1, 1, 0, bias=False),nn.BatchNorm2d(hidden_dim),nn.ReLU6(inplace=True),# dwnn.Conv2d(hidden_dim, hidden_dim, 3, stride, 1, groups=hidden_dim, bias=False),nn.BatchNorm2d(hidden_dim),nn.ReLU6(inplace=True),# pw-linearnn.Conv2d(hidden_dim, oup, 1, 1, 0, bias=False),nn.BatchNorm2d(oup),)def forward(self, x):if self.use_res_connect:return x + self.conv(x)else:return self.conv(x)class MobileNet(nn.Module):def __init__(self, n_class=15, input_size=224, width_mult=1.):super(MobileNet, self).__init__()block = InvertedResidualinput_channel = 32last_channel = 1280interverted_residual_setting = [# t, c, n, s[1, 16, 1, 1],[6, 24, 2, 2],[6, 32, 3, 2],[6, 64, 4, 2],[6, 96, 3, 1],[6, 160, 3, 2],[6, 320, 1, 1],]# building first layerassert input_size % 32 == 0# input_channel = make_divisible(input_channel * width_mult) # first channel is always 32!self.last_channel = self.make_divisible(last_channel * width_mult) if width_mult > 1.0 else last_channelself.features = [self.conv_bn(3, input_channel, 2)]# building inverted residual blocksfor t, c, n, s in interverted_residual_setting:output_channel = self.make_divisible(c * width_mult) if t > 1 else cfor i in range(n):if i == 0:self.features.append(block(input_channel, output_channel, s, expand_ratio=t))else:self.features.append(block(input_channel, output_channel, 1, expand_ratio=t))input_channel = output_channel# building last several layersself.features.append(self.conv_1x1_bn(input_channel, self.last_channel))# make it nn.Sequentialself.features = nn.Sequential(*self.features)# building classifierself.classifier = nn.Linear(self.last_channel, n_class)self._initialize_weights()def make_divisible(self, x, divisible_by=8):import numpy as npreturn int(np.ceil(x * 1. / divisible_by) * divisible_by)def conv_bn(self, inp, oup, stride):return nn.Sequential(nn.Conv2d(inp, oup, 3, stride, 1, bias=False),nn.BatchNorm2d(oup),nn.ReLU6(inplace=True))def conv_1x1_bn(self, inp, oup):return nn.Sequential(nn.Conv2d(inp, oup, 1, 1, 0, bias=False),nn.BatchNorm2d(oup),nn.ReLU6(inplace=True))def forward(self, x):x = self.features(x)x = x.mean(3).mean(2)x = self.classifier(x)return xdef _initialize_weights(self):for m in self.modules():if isinstance(m, nn.Conv2d):n = m.kernel_size[0] * m.kernel_size[1] * m.out_channelsm.weight.data.normal_(0, np.sqrt(2. / n))if m.bias is not None:m.bias.data.zero_()elif isinstance(m, nn.BatchNorm2d):m.weight.data.fill_(1)m.bias.data.zero_()elif isinstance(m, nn.Linear):n = m.weight.size(1)m.weight.data.normal_(0, 0.01)m.bias.data.zero_()def main():x = torch.randn(1, 3, 224, 224)net = MobileNet()print(net)print(net(x))if __name__ == '__main__':main()
1.38.11.MobileNetV3
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
import torch.nn.functional as F
import numpy as npdef get_model_parameters(model):total_parameters = 0for layer in list(model.parameters()):layer_parameter = 1for l in list(layer.size()):layer_parameter *= ltotal_parameters += layer_parameterreturn total_parametersclass h_sigmoid(nn.Module):def __init__(self, inplace=True):super(h_sigmoid, self).__init__()self.inplace = inplacedef forward(self, x):return F.relu6(x + 3., inplace=self.inplace) / 6.class h_swish(nn.Module):def __init__(self, inplace=True):super(h_swish, self).__init__()self.inplace = inplacedef forward(self, x):out = F.relu6(x + 3., inplace=self.inplace) / 6.return out * xclass SqueezeBlock(nn.Module):def __init__(self, exp_size, divide=4):super(SqueezeBlock, self).__init__()self.dense = nn.Sequential(nn.Linear(exp_size, exp_size // divide),nn.ReLU(inplace=True),nn.Linear(exp_size // divide, exp_size),h_sigmoid())def forward(self, x):batch, channels, height, width = x.size()out = F.avg_pool2d(x, kernel_size=[height, width]).view(batch, -1)out = self.dense(out)out = out.view(batch, channels, 1, 1)# out = hard_sigmoid(out)return out * xclass MobileBlock(nn.Module):def __init__(self, in_channels, out_channels, kernal_size, stride, nonLinear, SE, exp_size):super(MobileBlock, self).__init__()self.out_channels = out_channelsself.nonLinear = nonLinearself.SE = SEpadding = (kernal_size - 1) // 2self.use_connect = stride == 1 and in_channels == out_channelsif self.nonLinear == "RE":activation = nn.ReLUelse:activation = h_swishself.conv = nn.Sequential(nn.Conv2d(in_channels, exp_size, kernel_size=1, stride=1, padding=0, bias=False),nn.BatchNorm2d(exp_size),activation(inplace=True))self.depth_conv = nn.Sequential(nn.Conv2d(exp_size, exp_size, kernel_size=kernal_size, stride=stride, padding=padding, groups=exp_size),nn.BatchNorm2d(exp_size),)if self.SE:self.squeeze_block = SqueezeBlock(exp_size)self.point_conv = nn.Sequential(nn.Conv2d(exp_size, out_channels, kernel_size=1, stride=1, padding=0),nn.BatchNorm2d(out_channels),activation(inplace=True))def forward(self, x):# MobileNetV2out = self.conv(x)out = self.depth_conv(out)# Squeeze and Exciteif self.SE:out = self.squeeze_block(out)# point-wise convout = self.point_conv(out)# connectionif self.use_connect:return x + outelse:return outclass MobileNet(nn.Module):def __init__(self, model_mode="SMALL", num_classes=1000, multiplier=1.0, dropout_rate=0.0):super(MobileNet, self).__init__()self.num_classes = num_classesif model_mode == "LARGE":layers = [[16, 16, 3, 1, "RE", False, 16],[16, 24, 3, 2, "RE", False, 64],[24, 24, 3, 1, "RE", False, 72],[24, 40, 5, 2, "RE", True, 72],[40, 40, 5, 1, "RE", True, 120],[40, 40, 5, 1, "RE", True, 120],[40, 80, 3, 2, "HS", False, 240],[80, 80, 3, 1, "HS", False, 200],[80, 80, 3, 1, "HS", False, 184],[80, 80, 3, 1, "HS", False, 184],[80, 112, 3, 1, "HS", True, 480],[112, 112, 3, 1, "HS", True, 672],[112, 160, 5, 1, "HS", True, 672],[160, 160, 5, 2, "HS", True, 672],[160, 160, 5, 1, "HS", True, 960],]init_conv_out = self._make_divisible(16 * multiplier)self.init_conv = nn.Sequential(nn.Conv2d(in_channels=3, out_channels=init_conv_out, kernel_size=3, stride=2, padding=1),nn.BatchNorm2d(init_conv_out),h_swish(inplace=True),)self.block = []for in_channels, out_channels, kernal_size, stride, nonlinear, se, exp_size in layers:in_channels = self._make_divisible(in_channels * multiplier)out_channels = self._make_divisible(out_channels * multiplier)exp_size = self._make_divisible(exp_size * multiplier)self.block.append(MobileBlock(in_channels, out_channels, kernal_size, stride, nonlinear, se, exp_size))self.block = nn.Sequential(*self.block)out_conv1_in = self._make_divisible(160 * multiplier)out_conv1_out = self._make_divisible(960 * multiplier)self.out_conv1 = nn.Sequential(nn.Conv2d(out_conv1_in, out_conv1_out, kernel_size=1, stride=1),nn.BatchNorm2d(out_conv1_out),h_swish(inplace=True),)out_conv2_in = self._make_divisible(960 * multiplier)out_conv2_out = self._make_divisible(1280 * multiplier)self.out_conv2 = nn.Sequential(nn.Conv2d(out_conv2_in, out_conv2_out, kernel_size=1, stride=1),h_swish(inplace=True),nn.Dropout(dropout_rate),nn.Conv2d(out_conv2_out, self.num_classes, kernel_size=1, stride=1),)elif model_mode == "SMALL":layers = [[16, 16, 3, 2, "RE", True, 16],[16, 24, 3, 2, "RE", False, 72],[24, 24, 3, 1, "RE", False, 88],[24, 40, 5, 2, "RE", True, 96],[40, 40, 5, 1, "RE", True, 240],[40, 40, 5, 1, "RE", True, 240],[40, 48, 5, 1, "HS", True, 120],[48, 48, 5, 1, "HS", True, 144],[48, 96, 5, 2, "HS", True, 288],[96, 96, 5, 1, "HS", True, 576],[96, 96, 5, 1, "HS", True, 576],]init_conv_out = self._make_divisible(16 * multiplier)self.init_conv = nn.Sequential(nn.Conv2d(in_channels=3, out_channels=init_conv_out, kernel_size=3, stride=2, padding=1),nn.BatchNorm2d(init_conv_out),h_swish(inplace=True),)self.block = []for in_channels, out_channels, kernal_size, stride, nonlinear, se, exp_size in layers:in_channels = self._make_divisible(in_channels * multiplier)out_channels = self._make_divisible(out_channels * multiplier)exp_size = self._make_divisible(exp_size * multiplier)self.block.append(MobileBlock(in_channels, out_channels, kernal_size, stride, nonlinear, se, exp_size))self.block = nn.Sequential(*self.block)out_conv1_in = self._make_divisible(96 * multiplier)out_conv1_out = self._make_divisible(576 * multiplier)self.out_conv1 = nn.Sequential(nn.Conv2d(out_conv1_in, out_conv1_out, kernel_size=1, stride=1),SqueezeBlock(out_conv1_out),nn.BatchNorm2d(out_conv1_out),h_swish(inplace=True),)out_conv2_in = self._make_divisible(576 * multiplier)out_conv2_out = self._make_divisible(1280 * multiplier)self.out_conv2 = nn.Sequential(nn.Conv2d(out_conv2_in, out_conv2_out, kernel_size=1, stride=1),h_swish(inplace=True),nn.Dropout(dropout_rate),nn.Conv2d(out_conv2_out, self.num_classes, kernel_size=1, stride=1),)self._initialize_weights()def _initialize_weights(self):for m in self.modules():if isinstance(m, nn.Conv2d):n = m.kernel_size[0] * m.kernel_size[1] * m.out_channelsm.weight.data.normal_(0, np.sqrt(2. / n))if m.bias is not None:m.bias.data.zero_()elif isinstance(m, nn.BatchNorm2d):m.weight.data.fill_(1)m.bias.data.zero_()elif isinstance(m, nn.Linear):n = m.weight.size(1)m.weight.data.normal_(0, 0.01)m.bias.data.zero_()def _make_divisible(self, v, divisor=8, min_value=None):if min_value is None:min_value = divisornew_v = max(min_value, int(v + divisor / 2) // divisor * divisor)# Make sure that round down does not go down by more than 10%.if new_v < 0.9 * v:new_v += divisorreturn new_vdef forward(self, x):out = self.init_conv(x)out = self.block(out)out = self.out_conv1(out)batch, channels, height, width = out.size()out = F.avg_pool2d(out, kernel_size=[height, width])out = self.out_conv2(out).view(batch, -1)return outdef main():x = torch.randn(1, 3, 224, 224)net = MobileNet()print(net(x))if __name__ == '__main__':main()
1.38.12.SENet
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
import torch.nn.functional as Fclass SEBlock(nn.Module):def __init__(self, in_planes, planes, stride=1):super(SEBlock, self).__init__()self.conv1 = nn.Conv2d(in_planes, planes, kernel_size=3, stride=stride, padding=1, bias=False)self.bn1 = nn.BatchNorm2d(planes)self.conv2 = nn.Conv2d(planes, planes, kernel_size=3, stride=1, padding=1, bias=False)self.bn2 = nn.BatchNorm2d(planes)self.shortcut = nn.Sequential()if stride != 1 or in_planes != planes:self.shortcut = nn.Sequential(nn.Conv2d(in_planes, planes, kernel_size=1, stride=stride, bias=False),nn.BatchNorm2d(planes))# SE layersself.fc1 = nn.Conv2d(planes, planes//16, kernel_size=1) # Use nn.Conv2d instead of nn.Linearself.fc2 = nn.Conv2d(planes//16, planes, kernel_size=1)def forward(self, x):out = F.relu(self.bn1(self.conv1(x)))out = self.bn2(self.conv2(out))# Squeezew = F.avg_pool2d(out, out.size(2))w = F.relu(self.fc1(w))w = F.sigmoid(self.fc2(w))# Excitationout = out * w # New broadcasting feature from v0.2!out += self.shortcut(x)out = F.relu(out)return outclass PreActBlock(nn.Module):def __init__(self, in_planes, planes, stride=1):super(PreActBlock, self).__init__()self.bn1 = nn.BatchNorm2d(in_planes)self.conv1 = nn.Conv2d(in_planes, planes, kernel_size=3, stride=stride, padding=1, bias=False)self.bn2 = nn.BatchNorm2d(planes)self.conv2 = nn.Conv2d(planes, planes, kernel_size=3, stride=1, padding=1, bias=False)if stride != 1 or in_planes != planes:self.shortcut = nn.Sequential(nn.Conv2d(in_planes, planes, kernel_size=1, stride=stride, bias=False))# SE layersself.fc1 = nn.Conv2d(planes, planes//16, kernel_size=1)self.fc2 = nn.Conv2d(planes//16, planes, kernel_size=1)def forward(self, x):out = F.relu(self.bn1(x))shortcut = self.shortcut(out) if hasattr(self, 'shortcut') else xout = self.conv1(out)out = self.conv2(F.relu(self.bn2(out)))# Squeezew = F.avg_pool2d(out, out.size(2))w = F.relu(self.fc1(w))w = F.sigmoid(self.fc2(w))# Excitationout = out * wout += shortcutreturn outclass SqueezeExcitationNet(nn.Module):def __init__(self, block, num_blocks, num_classes=1000):super(SqueezeExcitationNet, self).__init__()self.in_planes = 64self.conv1 = nn.Conv2d(3, 64, kernel_size=3, stride=1, padding=1, bias=False)self.bn1 = nn.BatchNorm2d(64)self.layer1 = self._make_layer(block, 64, num_blocks[0], stride=1)self.layer2 = self._make_layer(block, 128, num_blocks[1], stride=2)self.layer3 = self._make_layer(block, 256, num_blocks[2], stride=2)self.layer4 = self._make_layer(block, 512, num_blocks[3], stride=2)self.linear = nn.Linear(25088, num_classes)def _make_layer(self, block, planes, num_blocks, stride):strides = [stride] + [1]*(num_blocks-1)layers = []for stride in strides:layers.append(block(self.in_planes, planes, stride))self.in_planes = planesreturn nn.Sequential(*layers)def forward(self, x):out = F.relu(self.bn1(self.conv1(x)))out = self.layer1(out)out = self.layer2(out)out = self.layer3(out)out = self.layer4(out)out = F.avg_pool2d(out, 4)out = out.view(out.size(0), -1)out = self.linear(out)return outdef SENet18():return SqueezeExcitationNet(PreActBlock, [2,2,2,2])def main():x = torch.randn(1, 3, 224, 224)net = SENet18()print(net(x))if __name__ == '__main__':main()
1.38.13.ShuffleNetV1
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
import torch.nn.functional as F
from torch.autograd import Variable
from collections import OrderedDict
from torch.nn import initdef channel_shuffle(x, groups):batchsize, num_channels, height, width = x.data.size()channels_per_group = num_channels // groups# reshapex = x.view(batchsize, groups,channels_per_group, height, width)# transpose# - contiguous() required if transpose() is used before view().# See https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/issues/764x = torch.transpose(x, 1, 2).contiguous()# flattenx = x.view(batchsize, -1, height, width)return xclass ShuffleUnit(nn.Module):def __init__(self, in_channels, out_channels, groups=3,grouped_conv=True, combine='add'):super(ShuffleUnit, self).__init__()self.in_channels = in_channelsself.out_channels = out_channelsself.grouped_conv = grouped_convself.combine = combineself.groups = groupsself.bottleneck_channels = self.out_channels // 4# define the type of ShuffleUnitif self.combine == 'add':# ShuffleUnit Figure 2bself.depthwise_stride = 1self._combine_func = self._addelif self.combine == 'concat':# ShuffleUnit Figure 2cself.depthwise_stride = 2self._combine_func = self._concat# ensure output of concat has the same channels as# original output channels.self.out_channels -= self.in_channelselse:raise ValueError("Cannot combine tensors with \"{}\"" \"Only \"add\" and \"concat\" are" \"supported".format(self.combine))# Use a 1x1 grouped or non-grouped convolution to reduce input channels# to bottleneck channels, as in a ResNet bottleneck module.# NOTE: Do not use group convolution for the first conv1x1 in Stage 2.self.first_1x1_groups = self.groups if grouped_conv else 1self.g_conv_1x1_compress = self._make_grouped_conv1x1(self.in_channels,self.bottleneck_channels,self.first_1x1_groups,batch_norm=True,relu=True)# 3x3 depthwise convolution followed by batch normalizationself.depthwise_conv3x3 = nn.Conv2d(self.bottleneck_channels, self.bottleneck_channels, kernel_size=3, padding=1,stride=self.depthwise_stride, groups=self.bottleneck_channels, bias=False)self.bn_after_depthwise = nn.BatchNorm2d(self.bottleneck_channels)# Use 1x1 grouped convolution to expand from# bottleneck_channels to out_channelsself.g_conv_1x1_expand = self._make_grouped_conv1x1(self.bottleneck_channels,self.out_channels,self.groups,batch_norm=True,relu=False)@staticmethoddef _add(x, out):# residual connectionreturn x + out@staticmethoddef _concat(x, out):# concatenate along channel axisreturn torch.cat((x, out), 1)def _make_grouped_conv1x1(self, in_channels, out_channels, groups,batch_norm=True, relu=False):modules = OrderedDict()conv = nn.Conv2d(in_channels, out_channels, kernel_size=1, groups=groups)modules['conv1x1'] = convif batch_norm:modules['batch_norm'] = nn.BatchNorm2d(out_channels)if relu:modules['relu'] = nn.ReLU()if len(modules) > 1:return nn.Sequential(modules)else:return convdef forward(self, x):# save for combining later with outputresidual = xif self.combine == 'concat':residual = F.avg_pool2d(residual, kernel_size=3,stride=2, padding=1)out = self.g_conv_1x1_compress(x)out = channel_shuffle(out, self.groups)out = self.depthwise_conv3x3(out)out = self.bn_after_depthwise(out)out = self.g_conv_1x1_expand(out)out = self._combine_func(residual, out)return F.relu(out)class ShuffleNet(nn.Module):"""ShuffleNet implementation."""def __init__(self, groups=3, in_channels=3, num_classes=1000):"""ShuffleNet constructor.Arguments:groups (int, optional): number of groups to be used in grouped1x1 convolutions in each ShuffleUnit. Default is 3 for bestperformance according to original paper.in_channels (int, optional): number of channels in the input tensor.Default is 3 for RGB image inputs.num_classes (int, optional): number of classes to predict. Defaultis 1000 for ImageNet."""super(ShuffleNet, self).__init__()self.groups = groupsself.stage_repeats = [3, 7, 3]self.in_channels = in_channelsself.num_classes = num_classes# index 0 is invalid and should never be called.# only used for indexing convenience.if groups == 1:self.stage_out_channels = [-1, 24, 144, 288, 567]elif groups == 2:self.stage_out_channels = [-1, 24, 200, 400, 800]elif groups == 3:self.stage_out_channels = [-1, 24, 240, 480, 960]elif groups == 4:self.stage_out_channels = [-1, 24, 272, 544, 1088]elif groups == 8:self.stage_out_channels = [-1, 24, 384, 768, 1536]else:raise ValueError("""{} groups is not supported for1x1 Grouped Convolutions""".format(self.groups))# Stage 1 always has 24 output channelsself.conv1 = nn.Conv2d(self.in_channels, self.stage_out_channels[1], kernel_size=3, padding=1, groups=1, stride=2)self.maxpool = nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=3, stride=2, padding=1)# Stage 2self.stage2 = self._make_stage(2)# Stage 3self.stage3 = self._make_stage(3)# Stage 4self.stage4 = self._make_stage(4)# Global pooling:# Undefined as PyTorch's functional API can be used for on-the-fly# shape inference if input size is not ImageNet's 224x224# Fully-connected classification layernum_inputs = self.stage_out_channels[-1]self.fc = nn.Linear(num_inputs, self.num_classes)self.init_params()def init_params(self):for m in self.modules():if isinstance(m, nn.Conv2d):init.kaiming_normal_(m.weight, mode='fan_out')if m.bias is not None:init.constant_(m.bias, 0)elif isinstance(m, nn.BatchNorm2d):init.constant_(m.weight, 1)init.constant_(m.bias, 0)elif isinstance(m, nn.Linear):init.normal_(m.weight, std=0.001)if m.bias is not None:init.constant_(m.bias, 0)def _make_stage(self, stage):modules = OrderedDict()stage_name = "ShuffleUnit_Stage{}".format(stage)# First ShuffleUnit in the stage# 1. non-grouped 1x1 convolution (i.e. pointwise convolution)# is used in Stage 2. Group convolutions used everywhere else.grouped_conv = stage > 2# 2. concatenation unit is always used.first_module = ShuffleUnit(self.stage_out_channels[stage - 1],self.stage_out_channels[stage],groups=self.groups,grouped_conv=grouped_conv,combine='concat')modules[stage_name + "_0"] = first_module# add more ShuffleUnits depending on pre-defined number of repeatsfor i in range(self.stage_repeats[stage - 2]):name = stage_name + "_{}".format(i + 1)module = ShuffleUnit(self.stage_out_channels[stage],self.stage_out_channels[stage],groups=self.groups,grouped_conv=True,combine='add')modules[name] = modulereturn nn.Sequential(modules)def forward(self, x):x = self.conv1(x)x = self.maxpool(x)x = self.stage2(x)x = self.stage3(x)x = self.stage4(x)# global average pooling layerx = F.avg_pool2d(x, x.data.size()[-2:])# flatten for input to fully-connected layerx = x.view(x.size(0), -1)x = self.fc(x)return F.log_softmax(x, dim=1)def main():x = torch.randn(1, 3, 224, 224)net = ShuffleNet()print(net(x))if __name__ == '__main__':main()
1.38.14.ShuffleNetV2
import torch
import torch.nn as nndef channel_shuffle(x, groups):batchsize, num_channels, height, width = x.data.size()channels_per_group = num_channels // groups# reshapex = x.view(batchsize, groups,channels_per_group, height, width)x = torch.transpose(x, 1, 2).contiguous()# flattenx = x.view(batchsize, -1, height, width)return xclass InvertedResidual(nn.Module):def __init__(self, inp, oup, stride, benchmodel):super(InvertedResidual, self).__init__()self.benchmodel = benchmodelself.stride = strideassert stride in [1, 2]oup_inc = oup // 2if self.benchmodel == 1:# assert inp == oup_incself.banch2 = nn.Sequential(# pwnn.Conv2d(oup_inc, oup_inc, 1, 1, 0, bias=False),nn.BatchNorm2d(oup_inc),nn.ReLU(inplace=True),# dwnn.Conv2d(oup_inc, oup_inc, 3, stride, 1, groups=oup_inc, bias=False),nn.BatchNorm2d(oup_inc),# pw-linearnn.Conv2d(oup_inc, oup_inc, 1, 1, 0, bias=False),nn.BatchNorm2d(oup_inc),nn.ReLU(inplace=True),)else:self.banch1 = nn.Sequential(# dwnn.Conv2d(inp, inp, 3, stride, 1, groups=inp, bias=False),nn.BatchNorm2d(inp),# pw-linearnn.Conv2d(inp, oup_inc, 1, 1, 0, bias=False),nn.BatchNorm2d(oup_inc),nn.ReLU(inplace=True),)self.banch2 = nn.Sequential(# pwnn.Conv2d(inp, oup_inc, 1, 1, 0, bias=False),nn.BatchNorm2d(oup_inc),nn.ReLU(inplace=True),# dwnn.Conv2d(oup_inc, oup_inc, 3, stride, 1, groups=oup_inc, bias=False),nn.BatchNorm2d(oup_inc),# pw-linearnn.Conv2d(oup_inc, oup_inc, 1, 1, 0, bias=False),nn.BatchNorm2d(oup_inc),nn.ReLU(inplace=True),)@staticmethoddef _concat(x, out):# concatenate along channel axisreturn torch.cat((x, out), 1)def forward(self, x):if 1 == self.benchmodel:x1 = x[:, :(x.shape[1] // 2), :, :]x2 = x[:, (x.shape[1] // 2):, :, :]out = self._concat(x1, self.banch2(x2))elif 2 == self.benchmodel:out = self._concat(self.banch1(x), self.banch2(x))else:returnreturn channel_shuffle(out, 2)class ShuffleNetV2(nn.Module):def __init__(self, n_class=1000, input_size=224, width_mult=1.):super(ShuffleNetV2, self).__init__()assert input_size % 32 == 0self.stage_repeats = [4, 8, 4]# index 0 is invalid and should never be called.# only used for indexing convenience.if width_mult == 0.5:self.stage_out_channels = [-1, 24, 48, 96, 192, 1024]elif width_mult == 1.0:self.stage_out_channels = [-1, 24, 116, 232, 464, 1024]elif width_mult == 1.5:self.stage_out_channels = [-1, 24, 176, 352, 704, 1024]elif width_mult == 2.0:self.stage_out_channels = [-1, 24, 224, 488, 976, 2048]else:raise ValueError("""{} groups is not supported for1x1 Grouped Convolutions""".format(self.groups))# building first layerinput_channel = self.stage_out_channels[1]self.conv1 = self._conv_bn(3, input_channel, 2)self.maxpool = nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=3, stride=2, padding=1)self.features = []# building inverted residual blocksfor idxstage in range(len(self.stage_repeats)):numrepeat = self.stage_repeats[idxstage]output_channel = self.stage_out_channels[idxstage + 2]for i in range(numrepeat):if i == 0:# inp, oup, stride, benchmodel):self.features.append(InvertedResidual(input_channel, output_channel, 2, 2))else:self.features.append(InvertedResidual(input_channel, output_channel, 1, 1))input_channel = output_channel# make it nn.Sequentialself.features = nn.Sequential(*self.features)# building last several layersself.conv_last = self._conv_1x1_bn(input_channel, self.stage_out_channels[-1])self.globalpool = nn.Sequential(nn.AvgPool2d(int(input_size / 32)))# building classifierself.classifier = nn.Sequential(nn.Linear(self.stage_out_channels[-1], n_class))def _conv_1x1_bn(self, inp, oup):return nn.Sequential(nn.Conv2d(inp, oup, 1, 1, 0, bias=False),nn.BatchNorm2d(oup),nn.ReLU(inplace=True))def _conv_bn(self, inp, oup, stride):return nn.Sequential(nn.Conv2d(inp, oup, 3, stride, 1, bias=False),nn.BatchNorm2d(oup),nn.ReLU(inplace=True))def forward(self, x):x = self.conv1(x)x = self.maxpool(x)x = self.features(x)x = self.conv_last(x)x = self.globalpool(x)x = x.view(-1, self.stage_out_channels[-1])x = self.classifier(x)return xdef main():x = torch.randn(1, 3, 224, 224)net = ShuffleNetV2()print(net)if __name__ == '__main__':main()

1.38.15.参考博文
https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_44388679/article/details/103059143
http://ishero.net/CNN%E7%B3%BB%E5%88%97%E4%B9%8B%E5%9B%BE%E5%83%8F%E5%88%86%E7%B1%BB.html
这篇关于41_经典卷积网络、LeNet、AlexNet、VGG、GoogleNet、ResNet、NIN、DenseNet、EfficientNet、MobileNetV1/2/3、SENet等的文章就介绍到这儿,希望我们推荐的文章对编程师们有所帮助!







