本文主要是介绍【论文阅读】RS-Mamba for Large Remote Sensing Image Dense Prediction(附Code),希望对大家解决编程问题提供一定的参考价值,需要的开发者们随着小编来一起学习吧!
论文作者提出了RS-Mamba(RSM)用于高分辨率遥感图像遥感的密集预测任务。RSM设计用于模拟具有线性复杂性的遥感图像的全局特征,使其能够有效地处理大型VHR图像。它采用全向选择性扫描模块,从多个方向对图像进行全局建模,从多个方向捕捉大的空间特征。
论文链接:https://arxiv.org/abs/2404.02668
code链接:https://github.com/walking-shadow/Official_Remote_Sensing_Mamba
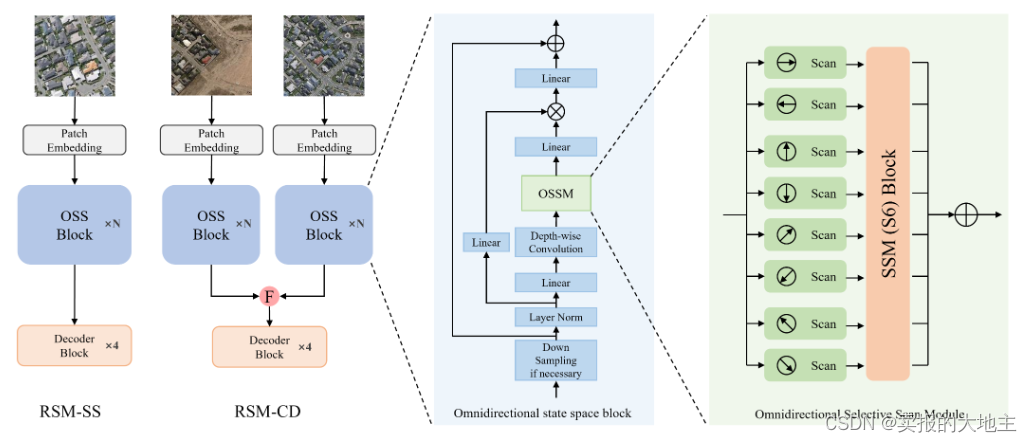
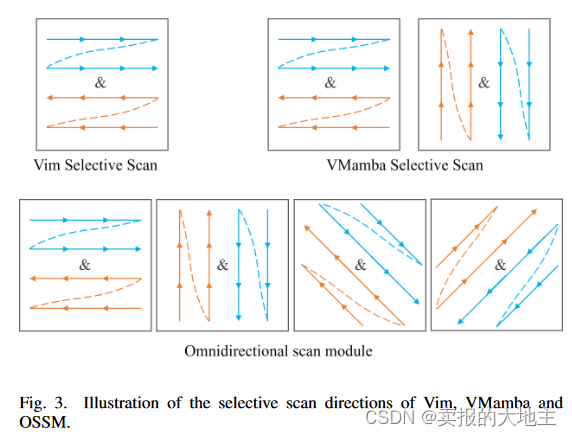
2D全向扫描机制是本研究的主要创新点。作者考虑到遥感影像地物多方向的特点,在VMamba2D双向扫描机制的基础上增加了斜向扫描机制。
以下是作者针对该部分进行改进的代码:
def antidiagonal_gather(tensor):# 取出矩阵所有反斜向的元素并拼接B, C, H, W = tensor.size()shift = torch.arange(H, device=tensor.device).unsqueeze(1) # 创建一个列向量[H, 1]index = (torch.arange(W, device=tensor.device) - shift) % W # 利用广播创建索引矩阵[H, W]# 扩展索引以适应B和C维度expanded_index = index.unsqueeze(0).unsqueeze(0).expand(B, C, -1, -1)# 使用gather进行索引选择return tensor.gather(3, expanded_index).transpose(-1,-2).reshape(B, C, H*W)def diagonal_gather(tensor):# 取出矩阵所有反斜向的元素并拼接B, C, H, W = tensor.size()shift = torch.arange(H, device=tensor.device).unsqueeze(1) # 创建一个列向量[H, 1]index = (shift + torch.arange(W, device=tensor.device)) % W # 利用广播创建索引矩阵[H, W]# 扩展索引以适应B和C维度expanded_index = index.unsqueeze(0).unsqueeze(0).expand(B, C, -1, -1)# 使用gather进行索引选择return tensor.gather(3, expanded_index).transpose(-1,-2).reshape(B, C, H*W)def diagonal_scatter(tensor_flat, original_shape):# 把斜向元素拼接起来的一维向量还原为最初的矩阵形式B, C, H, W = original_shapeshift = torch.arange(H, device=tensor_flat.device).unsqueeze(1) # 创建一个列向量[H, 1]index = (shift + torch.arange(W, device=tensor_flat.device)) % W # 利用广播创建索引矩阵[H, W]# 扩展索引以适应B和C维度expanded_index = index.unsqueeze(0).unsqueeze(0).expand(B, C, -1, -1)# 创建一个空的张量来存储反向散布的结果result_tensor = torch.zeros(B, C, H, W, device=tensor_flat.device, dtype=tensor_flat.dtype)# 将平铺的张量重新变形为[B, C, H, W],考虑到需要使用transpose将H和W调换tensor_reshaped = tensor_flat.reshape(B, C, W, H).transpose(-1, -2)# 使用scatter_根据expanded_index将元素放回原位result_tensor.scatter_(3, expanded_index, tensor_reshaped)return result_tensordef antidiagonal_scatter(tensor_flat, original_shape):# 把反斜向元素拼接起来的一维向量还原为最初的矩阵形式B, C, H, W = original_shapeshift = torch.arange(H, device=tensor_flat.device).unsqueeze(1) # 创建一个列向量[H, 1]index = (torch.arange(W, device=tensor_flat.device) - shift) % W # 利用广播创建索引矩阵[H, W]expanded_index = index.unsqueeze(0).unsqueeze(0).expand(B, C, -1, -1)# 初始化一个与原始张量形状相同、元素全为0的张量result_tensor = torch.zeros(B, C, H, W, device=tensor_flat.device, dtype=tensor_flat.dtype)# 将平铺的张量重新变形为[B, C, W, H],因为操作是沿最后一个维度收集的,需要调整形状并交换维度tensor_reshaped = tensor_flat.reshape(B, C, W, H).transpose(-1, -2)# 使用scatter_将元素根据索引放回原位result_tensor.scatter_(3, expanded_index, tensor_reshaped)return result_tensorclass CrossScan(torch.autograd.Function):# ZSJ 这里是把图像按照特定方向展平的地方,改变扫描方向可以在这里修改@staticmethoddef forward(ctx, x: torch.Tensor):B, C, H, W = x.shapectx.shape = (B, C, H, W)# xs = x.new_empty((B, 4, C, H * W))xs = x.new_empty((B, 8, C, H * W))# 添加横向和竖向的扫描xs[:, 0] = x.flatten(2, 3)xs[:, 1] = x.transpose(dim0=2, dim1=3).flatten(2, 3)xs[:, 2:4] = torch.flip(xs[:, 0:2], dims=[-1])# 提供斜向和反斜向的扫描xs[:, 4] = diagonal_gather(x)xs[:, 5] = antidiagonal_gather(x)xs[:, 6:8] = torch.flip(xs[:, 4:6], dims=[-1])return xs@staticmethoddef backward(ctx, ys: torch.Tensor):# out: (b, k, d, l)B, C, H, W = ctx.shapeL = H * W# 把横向和竖向的反向部分再反向回来,并和原来的横向和竖向相加# ys = ys[:, 0:2] + ys[:, 2:4].flip(dims=[-1]).view(B, 2, -1, L)y_rb = ys[:, 0:2] + ys[:, 2:4].flip(dims=[-1]).view(B, 2, -1, L)# 把竖向的部分转成横向,然后再相加,再转回最初是的矩阵形式# y = ys[:, 0] + ys[:, 1].view(B, -1, W, H).transpose(dim0=2, dim1=3).contiguous().view(B, -1, L)y_rb = y_rb[:, 0] + y_rb[:, 1].view(B, -1, W, H).transpose(dim0=2, dim1=3).contiguous().view(B, -1, L)y_rb = y_rb.view(B, -1, H, W)# 把斜向和反斜向的反向部分再反向回来,并和原来的斜向和反斜向相加y_da = ys[:, 4:6] + ys[:, 6:8].flip(dims=[-1]).view(B, 2, -1, L)# 把斜向和反斜向的部分都转成原来的最初的矩阵形式,再相加y_da = diagonal_scatter(y_da[:, 0], (B,C,H,W)) + antidiagonal_scatter(y_da[:, 1], (B,C,H,W))y_res = y_rb + y_da# return y.view(B, -1, H, W)return y_resclass CrossMerge(torch.autograd.Function):@staticmethoddef forward(ctx, ys: torch.Tensor):B, K, D, H, W = ys.shapectx.shape = (H, W)ys = ys.view(B, K, D, -1)# ys = ys[:, 0:2] + ys[:, 2:4].flip(dims=[-1]).view(B, 2, D, -1)# y = ys[:, 0] + ys[:, 1].view(B, -1, W, H).transpose(dim0=2, dim1=3).contiguous().view(B, D, -1)y_rb = ys[:, 0:2] + ys[:, 2:4].flip(dims=[-1]).view(B, 2, D, -1)# 把竖向的部分转成横向,然后再相加,再转回最初是的矩阵形式y_rb = y_rb[:, 0] + y_rb[:, 1].view(B, -1, W, H).transpose(dim0=2, dim1=3).contiguous().view(B, D, -1)y_rb = y_rb.view(B, -1, H, W)# 把斜向和反斜向的反向部分再反向回来,并和原来的斜向和反斜向相加y_da = ys[:, 4:6] + ys[:, 6:8].flip(dims=[-1]).view(B, 2, D, -1)# 把斜向和反斜向的部分都转成原来的最初的矩阵形式,再相加y_da = diagonal_scatter(y_da[:, 0], (B,D,H,W)) + antidiagonal_scatter(y_da[:, 1], (B,D,H,W))y_res = y_rb + y_dareturn y_res.view(B, D, -1)# return y@staticmethoddef backward(ctx, x: torch.Tensor):# B, D, L = x.shape# out: (b, k, d, l)H, W = ctx.shapeB, C, L = x.shape# xs = x.new_empty((B, 4, C, L))xs = x.new_empty((B, 8, C, L))# 横向和竖向扫描xs[:, 0] = xxs[:, 1] = x.view(B, C, H, W).transpose(dim0=2, dim1=3).flatten(2, 3)xs[:, 2:4] = torch.flip(xs[:, 0:2], dims=[-1])# xs = xs.view(B, 4, C, H, W)# 提供斜向和反斜向的扫描xs[:, 4] = diagonal_gather(x.view(B,C,H,W))xs[:, 5] = antidiagonal_gather(x.view(B,C,H,W))xs[:, 6:8] = torch.flip(xs[:, 4:6], dims=[-1])# return xsreturn xs.view(B, 8, C, H, W)这篇关于【论文阅读】RS-Mamba for Large Remote Sensing Image Dense Prediction(附Code)的文章就介绍到这儿,希望我们推荐的文章对编程师们有所帮助!







![[论文笔记]LLM.int8(): 8-bit Matrix Multiplication for Transformers at Scale](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/img_convert/172ed0ed26123345e1773ba0e0505cb3.png)