本文主要是介绍Transformer学习: Transformer小模块学习--位置编码,多头自注意力,掩码矩阵,希望对大家解决编程问题提供一定的参考价值,需要的开发者们随着小编来一起学习吧!
提示:文章写完后,目录可以自动生成,如何生成可参考右边的帮助文档
Transformer学习
- 1 位置编码模块
- 1.1 PE代码
- 1.2 测试PE
- 2 多头自注意力模块
- 2.1 多头自注意力代码
- 2.2 测试多头注意力
- 3 未来序列掩码矩阵
1 位置编码模块
P E ( p o s , 2 i ) = sin ( p o s / 1000 0 2 i / d m o d e l ) PE(pos,2i)=\sin(pos/10000^{2i/d_{\mathrm{model}}}) PE(pos,2i)=sin(pos/100002i/dmodel)
P E ( p o s , 2 i + 1 ) = cos ( p o s / 1000 0 2 i / d m o d e l ) PE(pos,2i+1)=\cos(pos/10000^{2i/d_\mathrm{model}}) PE(pos,2i+1)=cos(pos/100002i/dmodel)
pos 是序列中每个对象的索引, p o s ∈ [ 0 , m a x s e q l e n ] pos\in [0,max_seq_len] pos∈[0,maxseqlen], i i i 向量维度序号, i ∈ [ 0 , e m b e d d i m / 2 ] i\in [0,embed_dim/2] i∈[0,embeddim/2], d m o d e l d_{model} dmodel是模型的embedding维度
1.1 PE代码
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import math
import torch
import seaborn as snsdef get_pos_ecoding(max_seq_len,embed_dim):# 初始化位置矩阵 [max_seq_len,embed_dim]pe = torch.zeros(max_seq_len,embed_dim])position = torch.arange(0,max_seq_len).unsqueeze(1) # [max_seq_len,1]print("位置:", position,position.shape)div_term = torch.exp(torch.arange(0,embed_dim,2)*-(math.log(10000.0)/embed_dim)) # 除项维度为embed_dim的一半,因为对矩阵分奇数和偶数位置进行填充。pe[:,0::2] = torch.sin(position/div_term)pe[:,1::2] = torch.cos(position/div_term)return pe
1.2 测试PE
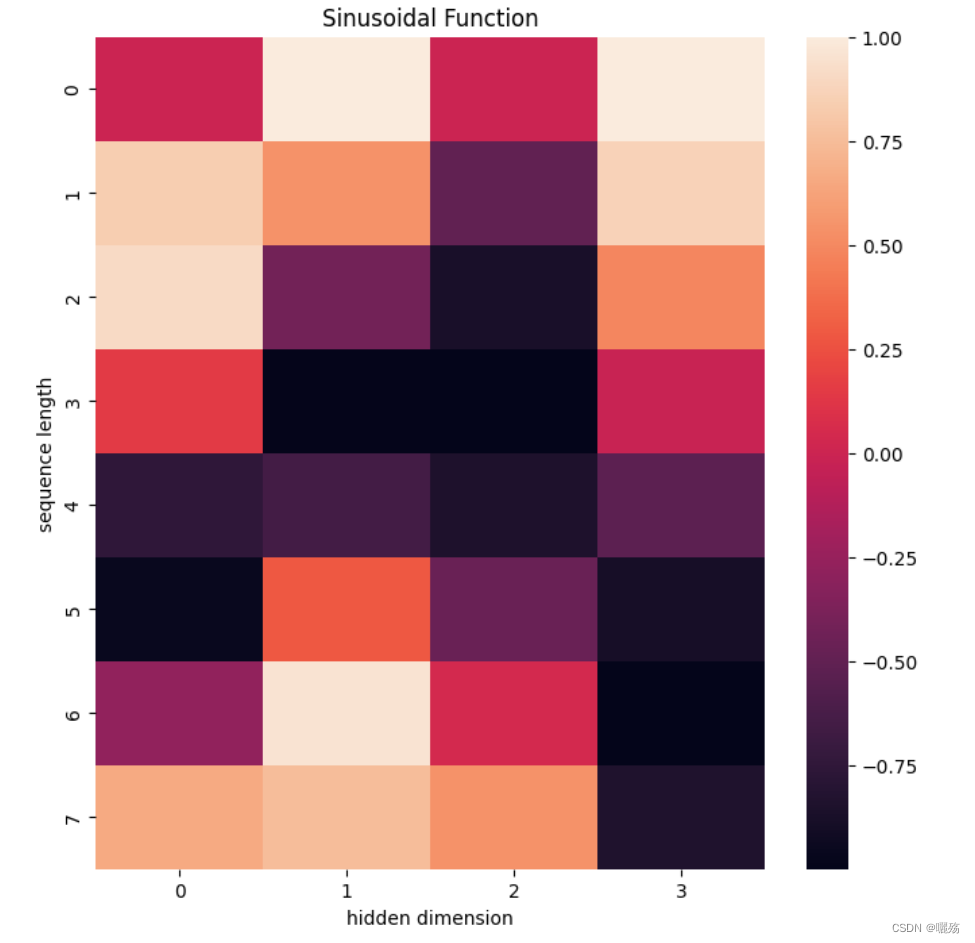
pe = get_pos_ecoding(8,4)
plt.figure(figsize=(8,8))
sns.heatmap(pe)
plt.title("Sinusoidal Function")
plt.xlabel("hidden dimension")
plt.ylabel("sequence length")
输出:
位置: tensor([[0],
[1],
[2],
[3],
[4],
[5],
[6],
[7]]) torch.Size([8, 1])
除项: tensor([1.0000, 0.0100]) torch.Size([2])
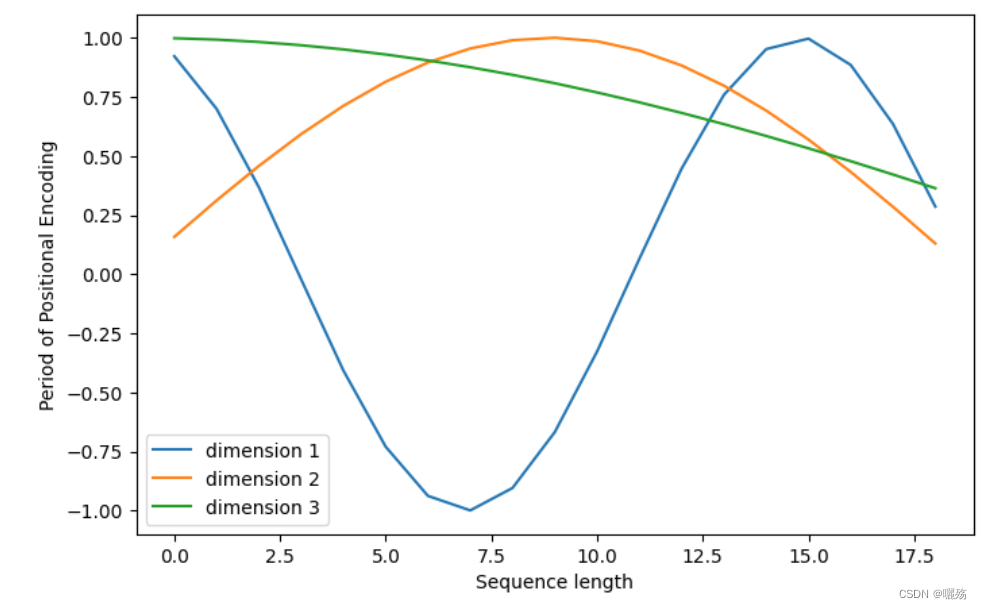
plt.figure(figsize=(8, 5))
plt.plot(positional_encoding[1:, 1], label="dimension 1")
plt.plot(positional_encoding[1:, 2], label="dimension 2")
plt.plot(positional_encoding[1:, 3], label="dimension 3")
plt.legend()
plt.xlabel("Sequence length")
plt.ylabel("Period of Positional Encoding")
2 多头自注意力模块
2.1 多头自注意力代码
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
import torch.nn.functional as F
import copy# 复制网络,即使用几层网络就改变N的数量
# 如 4层线性层 clones(nn.Linear(model_dim,model_dim),4)
def clones(module, N):"Produce N identical layers."return nn.ModuleList([copy.deepcopy(module) for _ in range(N)])# 计算注意力
def attention(q, k, v, mask=None, dropout=None):d_k = q.size(-1)scores = torch.matmul(q, k.transpose(-2, -1)) / math.sqrt(d_k)if mask is not None:scores = scores.masked_fill(mask == 0, -1e9)p_attn = F.softmax(scores, dim = -1)if dropout is not None:p_attn = dropout(p_attn)return torch.matmul(p_attn, v), p_attn# 计算多头注意力
class Multi_Head_Self_Att(nn.Module):def __init__(self,head,model_dim,dropout=0.1):super(Multi_Head_Self_Att,self).__init__()+assert model_dim % head == 0self.d_k = model_dim/headself.head = headself.linears = clones(nn.Linear(model_dim,model_dim),4)self.att = Noneself.dropout = nn.Dropout(p=dropout)def forward(self,q,k,v,mask=None):if mask is not None:mask = mask.unsqueeze(1)nbatches = q.size(0)# zip函数 将线性层与q,k,v分别对应(self.linears,q),(self.linears,k),(self.linears,v)# q,k,v [bs,-1,head,embed_dim/head]q,k,v = [l(x).view(nbatches,-1,int(self.head),int(self.d_k)).transpose(1,2) for l,x in zip(self.linears,(q,k,v))] # 返回计算注意力之后的值作为x和注意力分数x, self.attn = attention(q, k, v, mask=mask, dropout=self.dropout)x = x.transpose(1, 2).contiguous().view(nbatches, -1, int(self.head * self.d_k))return self.linears[-1](x),self.attn
2.2 测试多头注意力
# 模型参数
head = 4
model_dim = 128
seq_len = 10
dropout = 0.1# 生成示例输入
q = torch.randn(seq_len, model_dim)
k = torch.randn(seq_len, model_dim)
v = torch.randn(seq_len, model_dim)# 创建多头自注意力模块
att = Multi_Head_Self_Att(head, model_dim, dropout=dropout)# 运行模块
output,att = att(q, k, v)# 输出形状
print("Output shape:", output.shape)
print(att.shape())
sns.heatmap(att.squeeze().detach().cpu())
输出
Output shape: torch.Size([10, 1, 128])
torch.Size([10, 4, 1, 1])
3 未来序列掩码矩阵
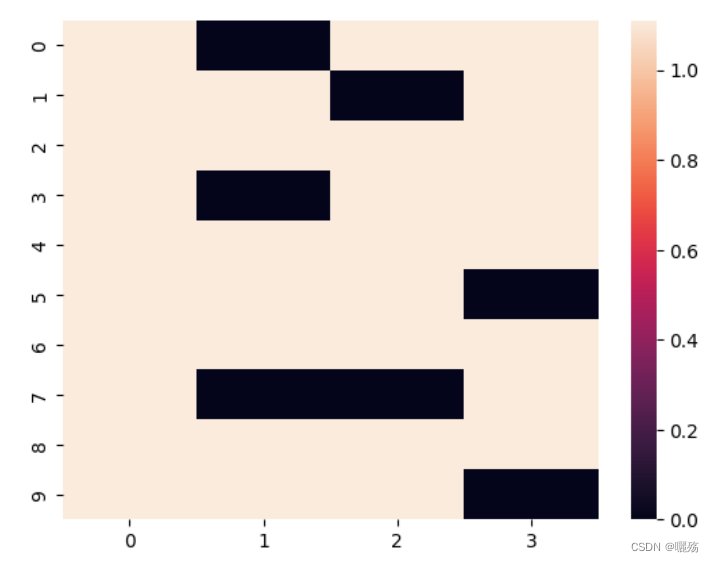
作用: 防止泄露未来要预测的部分,掩码矩阵是一个除对角线的上三角矩阵
3.1 代码
def subsequent_mask(size):"Mask out subsequent positions."attn_shape = (1, size, size)subsequent_mask = np.triu(np.ones(attn_shape), k=1).astype('uint8')print("掩码矩阵:",subsequent_mask)return torch.from_numpy(subsequent_mask) == 0
测试掩码
plt.figure(figsize=(5,5))
print(subsequent_mask(8),subsequent_mask(8).shape)
plt.imshow(subsequent_mask(8)[0])
掩码矩阵:
[[[0 1 1 1 1 1 1 1]
[0 0 1 1 1 1 1 1]
[0 0 0 1 1 1 1 1]
[0 0 0 0 1 1 1 1]
[0 0 0 0 0 1 1 1]
[0 0 0 0 0 0 1 1]
[0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1]
[0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0]]]
tensor([[[ True, False, False, False, False, False, False, False],
[ True, True, False, False, False, False, False, False],
[ True, True, True, False, False, False, False, False],
[ True, True, True, True, False, False, False, False],
[ True, True, True, True, True, False, False, False],
[ True, True, True, True, True, True, False, False],
[ True, True, True, True, True, True, True, False],
[ True, True, True, True, True, True, True, True]]]) torch.Size([1, 8, 8])
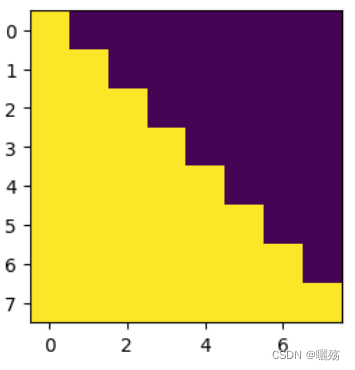
紫色部分为添加掩码的部分
这篇关于Transformer学习: Transformer小模块学习--位置编码,多头自注意力,掩码矩阵的文章就介绍到这儿,希望我们推荐的文章对编程师们有所帮助!






