本文主要是介绍LLM之RAG实战(三十五)| 使用LangChain的3种query扩展来优化RAG,希望对大家解决编程问题提供一定的参考价值,需要的开发者们随着小编来一起学习吧!
RAG有时无法从矢量数据库中检索到正确的文档。比如我们问如下问题:
从1980年到1990年,国际象棋的规则是什么?
RAG在矢量数据库中进行相似性搜索,来查询与国际象棋规则问题相关的相关文档。然而,在某些情况下,我们的向量数据库没有存储完整的信息,例如,我们的矢量数据库没有存储不同年份的规则。这样,数据库可以返回与国际象棋规则相关但与特定问题不直接相关的文档。
针对上述情况,我们可以采用查询扩展技术,该技术可以对用户的原始查询生成更全面、信息更丰富的搜索。这个新生成的查询将从矢量数据库中获取更多相关文档。
本文,我们将介绍三种查询扩展方法:
一、后退提示(Step Back Prompting)
Step back prompting来自论文《Take A Step Back: Evoking Reasoning Via Abstraction In Large Language Models》[1]
Step back prompting是谷歌deepmind开发的一种方法,它首先使用LLM创建用户查询的抽象(从用户具体查询到通用查询的转换,因此称为后退提示),然后根据生成的通用查询来生成答案。
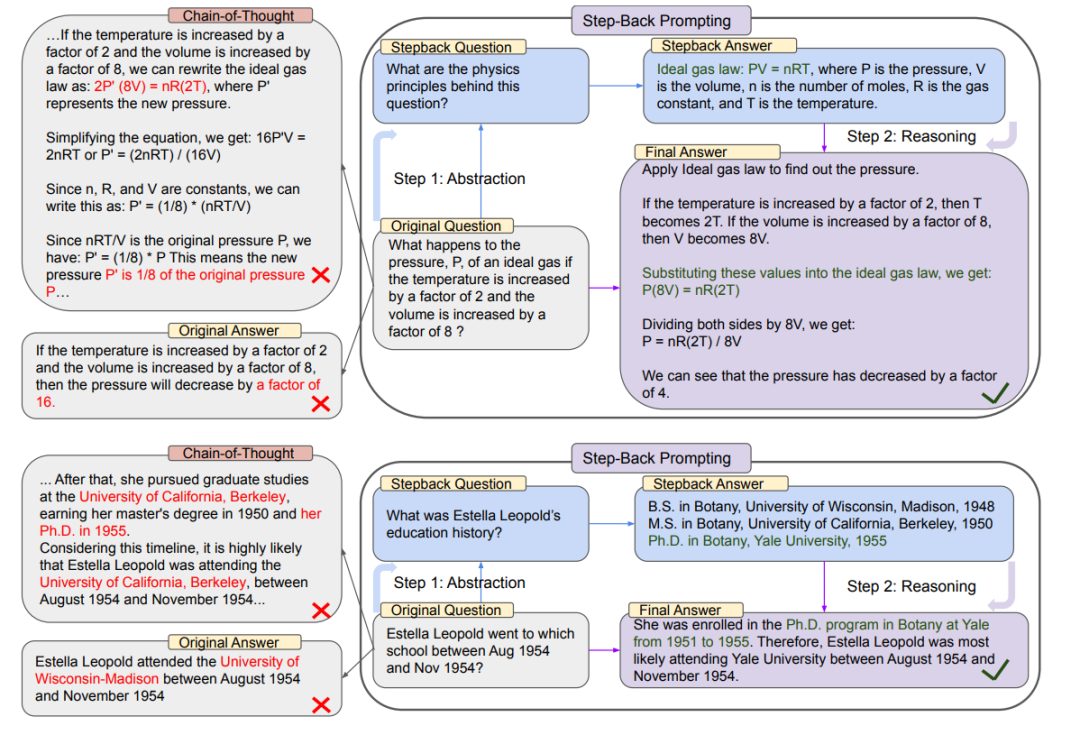
以下是“原始查询”和“后退查询”的示例:
{"Original_Query": "Could the members of The Police perform lawful arrests?","Step_Back_Query": "what can the members of The Police do?",},{"Original_Query": "Jan Sindel’s was born in what country?","Step_Back_Query": "what is Jan Sindel’s personal history?",}
#---------------------Prepare VectorDB-----------------------------------# Build a sample vectorDBfrom langchain.text_splitter import RecursiveCharacterTextSplitterfrom langchain_community.document_loaders import WebBaseLoaderfrom langchain_community.vectorstores import Chromafrom langchain.embeddings import OpenAIEmbeddingsimport osos.environ["OPENAI_API_KEY"] = "Your OpenAI KEY"# Load blog postloader = WebBaseLoader("https://lilianweng.github.io/posts/2023-06-23-agent/")data = loader.load()# Splittext_splitter = RecursiveCharacterTextSplitter(chunk_size=100, chunk_overlap=0)splits = text_splitter.split_documents(data)# VectorDBembedding = OpenAIEmbeddings()vectordb = Chroma.from_documents(documents=splits, embedding=embedding)#-------------------Prepare Step Back Prompt Pipeline------------------------from langchain_core.output_parsers import StrOutputParserfrom langchain_core.prompts import ChatPromptTemplate, FewShotChatMessagePromptTemplatefrom langchain_core.runnables import RunnableLambdafrom langchain.chat_models import ChatOpenAIretriever = vectordb.as_retriever()llm = ChatOpenAI()# Few Shot Examplesexamples = [{"input": "Could the members of The Police perform lawful arrests?","output": "what can the members of The Police do?",},{"input": "Jan Sindel’s was born in what country?","output": "what is Jan Sindel’s personal history?",},]# We now transform these to example messagesexample_prompt = ChatPromptTemplate.from_messages([("human", "{input}"),("ai", "{output}"),])few_shot_prompt = FewShotChatMessagePromptTemplate(example_prompt=example_prompt,examples=examples,)prompt = ChatPromptTemplate.from_messages([("system","""You are an expert at world knowledge. Your task is to step back and paraphrase a question to a more generic step-back question, which is easier to answer. Here are a few examples:""",),# Few shot examplesfew_shot_prompt,# New question("user", "{question}"),])question_gen = prompt | llm | StrOutputParser()#--------------------------QnA using Back Prompt Technique-----------------from langchain import hubdef format_docs(docs):doc_strings = [doc.page_content for doc in docs]return "\n\n".join(doc_strings)response_prompt = hub.pull("langchain-ai/stepback-answer")chain = ({# Retrieve context using the normal question"normal_context": RunnableLambda(lambda x: x["question"]) | retriever | format_docs,# Retrieve context using the step-back question"step_back_context": question_gen | retriever | format_docs,# Pass on the question"question": lambda x: x["question"],}| response_prompt| llm| StrOutputParser())result = chain.invoke({"question": "What Task Decomposition that work in 2022?"})
上面的代码是使用后退提示技术运行QnA的langchain脚本。需要注意的是:使用OPENAI_API_KEY并准备自己的向量数据库。
# Load blog post# You can use different loader to load different type fileloader = WebBaseLoader("https://lilianweng.github.io/posts/2023-06-23-agent/")data = loader.load()# Splittext_splitter = RecursiveCharacterTextSplitter(chunk_size=100, chunk_overlap=0)splits = text_splitter.split_documents(data)
我们尝试如下问题:
Original Query: What Task Decomposition that work in 2022?后退查询结果如下:
Step Back Query: What are some examples of task decomposition in the current year?这两个查询将用于提取相关文档,我们将这些文档组合在一起作为上下文,并在下面的这一部分中提供给您的LLM。
{# Retrieve context using the normal question"normal_context": RunnableLambda(lambda x: x["question"]) | retriever | format_docs,# Retrieve context using the step-back question"step_back_context": question_gen | retriever | format_docs,# Pass on the question"question": lambda x: x["question"],}
二、Multi Query(多查询)[2]

多查询是一种使用LLM从第一个查询生成更多查询的技术。这种技术试图回答一些用户提示没有那么具体的情况,这些生成的查询将用于在矢量数据库中查找文档。目标是细化查询,使其与主题更加相关,从而从数据库中检索更多相关的文档。
细节可以参考:LLM之RAG实战(三十四)| 使用LangChain的三个函数来优化RAG
三、Cross Encoding Re-Ranking(交叉编码器重排序)
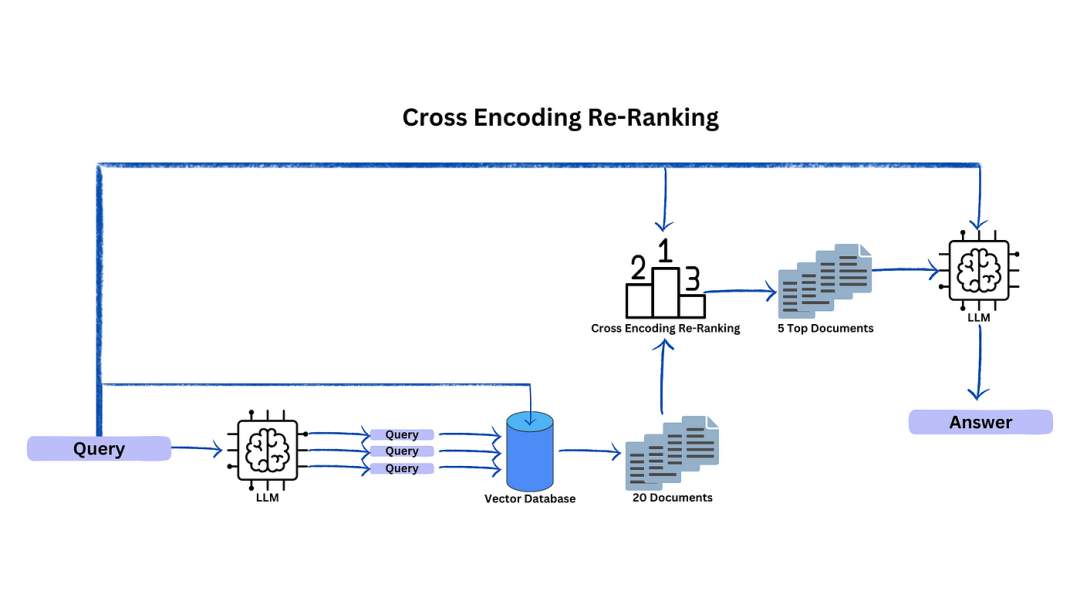
交叉编码是多查询和交叉编码器重新排序的结合,因为用户能够使用LLM生成更多的问题,每个生成的查询都能够从矢量数据库中提取出几个文档。这些提取的文档必须通过交叉编码器,以获得与初始查询的相似性分数。现在我们可以对相关文档进行重新排序,并选择前5名作为LLM摘要的上下文。
为什么我们需要选择前5个文档?在这种情况下,我们试图避免从矢量数据库中检索到不相关的文档,这种选择确保了交叉编码器专注于最相似和最有意义的文档,从而生成更准确、更简洁的摘要。
#------------------------Prepare Vector Database--------------------------# Build a sample vectorDBfrom langchain.text_splitter import RecursiveCharacterTextSplitterfrom langchain_community.document_loaders import WebBaseLoaderfrom langchain_community.vectorstores import Chromafrom langchain.embeddings import OpenAIEmbeddingsfrom langchain.chat_models import ChatOpenAIimport osos.environ["OPENAI_API_KEY"] = "Your API KEY"# Load blog postloader = WebBaseLoader("https://lilianweng.github.io/posts/2023-06-23-agent/")data = loader.load()llm = ChatOpenAI()# Splittext_splitter = RecursiveCharacterTextSplitter(chunk_size=100, chunk_overlap=0)splits = text_splitter.split_documents(data)# VectorDBembedding = OpenAIEmbeddings()vectordb = Chroma.from_documents(documents=splits, embedding=embedding)#--------------------Generate More Question----------------------------------#This function use to generate queries using LLMdef create_original_query(original_query):query = original_query["question"]qa_system_prompt = """You are an AI language model assistant. Your task is to generate fivedifferent versions of the given user question to retrieve relevant documents from a vectordatabase. By generating multiple perspectives on the user question, your goal is to helpthe user overcome some of the limitations of the distance-based similarity search.Provide these alternative questions separated by newlines."""qa_prompt = ChatPromptTemplate.from_messages([("system", qa_system_prompt),("human", "{question}"),])rag_chain = (qa_prompt| llm| StrOutputParser())question_string = rag_chain.invoke({"question": query})lines_list = question_string.splitlines()queries = []queries = [query] + lines_listreturn queries#-------------------Retrieve Document and Cross Encoding--------------------from sentence_transformers import CrossEncoderfrom langchain_core.prompts import ChatPromptTemplatefrom langchain_core.runnables import RunnableLambda, RunnablePassthroughfrom langchain_core.output_parsers import StrOutputParserimport numpy as npcross_encoder = CrossEncoder('cross-encoder/ms-marco-MiniLM-L-6-v2')#Cross Encoding happens in heredef create_documents(queries):retrieved_documents = []for i in queries:results = vectordb.as_retriever().get_relevant_documents(i)docString = [doc.page_content for doc in results]retrieved_documents.extend(docString)unique_a = []#If there is duplication documents for each query, make it uniquefor item in retrieved_documents:if item not in unique_a:unique_a.append(item)unique_documents = list(unique_a)pairs = []for doc in unique_documents:pairs.append([queries[0], doc])#Cross Encoder Scoringscores = cross_encoder.predict(pairs)final_queries = []for x in range(len(scores)):final_queries.append({"score":scores[x],"document":unique_documents[x]})#Rerank the documents, return top 5sorted_list = sorted(final_queries, key=lambda x: x["score"], reverse=True)first_five_elements = sorted_list[:6]return first_five_elements#-----------------QnA Document-----------------------------------------------qa_system_prompt = """Assistant is a large language model trained by OpenAI. \Use the following pieces of retrieved context to answer the question. \If you don't know the answer, just say that you don't know. \{context}"""qa_prompt = ChatPromptTemplate.from_messages([("system", qa_system_prompt),("human", "{question}"),])def format(docs):doc_strings = [doc["document"] for doc in docs]return "\n\n".join(doc_strings)chain = (# Prepare the context using below pipeline# Generate Queries -> Cross Encoding -> Rerank ->return context{"context": RunnableLambda(create_original_query)| RunnableLambda(create_documents) | RunnableLambda(format), "question": RunnablePassthrough()}| qa_prompt| llm| StrOutputParser())result = chain.invoke({"question":"What Task Decomposition that work in 2022?"})
参考从上面的langchain脚本,创建2个自定义函数用于生成查询和交叉编码。
create_original_query是生成查询,基本上会返回5个生成的问题加上原始查询。
create_documents将用于检索基于6个问题的24个相关文档。这24份相关文件将被复制,因此我们需要保留唯一的文件并删除重复的文件。
scores = cross_encoder.predict(pairs)上述代码可以计算出文档和原始查询之间的交叉编码分数。最后,代码将尝试根据交叉编码得分对文档进行重新排序,并只保留前5个文档。
四、结论
这3种方法真的很有帮助,特别是如果你得到的反馈是RAG没有返回正确和详细的答案,你可以使用上面的查询扩展方法来解决这些问题。
参考文献:
[1] https://arxiv.org/pdf/2310.06117.pdf
[2] https://python.langchain.com/docs/modules/data_connection/retrievers/MultiQueryRetriever
这篇关于LLM之RAG实战(三十五)| 使用LangChain的3种query扩展来优化RAG的文章就介绍到这儿,希望我们推荐的文章对编程师们有所帮助!






