本文主要是介绍使用端到端深度学习模型完成PPI任务两篇论文笔记,希望对大家解决编程问题提供一定的参考价值,需要的开发者们随着小编来一起学习吧!
1.“Multifaceted protein–protein interaction prediction based on Siamese residual RCNN”
1.1PPI任务的难点:
(1)蛋白质的表征需要一个模型来有效地过滤和聚合它们的局部特征,同时保留重要的上下文和序列的氨基酸信息
(2)扩展深度神经结构经常导致低效的学习过程,并遭受臭名昭著的消失梯度问题
(iii)还需要一个有效的机制来理解蛋白质对在PPI预测中的相互影响。此外,框架必须具有大数据的可伸缩性(我们的任务要求用在多长的数据上?)可推广到不同的预测任务。
1.2 作者对于自己工作的概括
(1)训练端到端网络PIPR,从而减少了用户数据预处理的工作量。
PIPR requires only the primary protein sequences as the input, and is trained to automatically preserve the critical features from the sequences.
补充:

(2)强调了在PPI任务中考虑上下文化和顺序信息的需求。(也就是说序列信息和局部信息都很重要,可是现在我们思考的模型中还没有加入局部信息)
(3)Third, the architecture of PIPR can be flexibly used to address different PPI tasks
(4)这个工作中也预测了亲和度!且表现很良好,可以对细微变化做出反应。
1.3PPI任务相较于NLP任务的不同之处
(1)序列
In contrast to sentences, proteins are profiled in sequences with more intractable patterns, as well as in a drastically larger range of lengths.
(2)Precisely capturing the PPI requires much more comprehensive learning architectures to distill the latent information from the entire sequences, and to preserve the long-term ordering information.
1.4 处理PPI任务上,基于深度学习的方法的发展:
(1)第一项工作是基于深层CNN
One recent work (Hashemifar et al., 2018), DPPI, uses a deep CNN-based architecture which focuses on capturing local features from protein profiles. DPPI represents the first work to deploy deep learning to PPI prediction, and has achieved the state-of-the-art performance on the binary prediction task. However, it requires excessive efforts for data pre-processing such as constructing protein profiles by PSI-BLAST (Altschul et al., 1997), and does not incorp-
orate a neural learning architecture that captures the important contextualized and sequential features.
(2)DNN-PPI (Li et al., 2018) represents another relevant work of this line, which deploys a different learning structure with two separated CNN encoders. However, DNN-PPI does not incorporate physicochemical properties into amino acid representations, and does not employ a Siamese learning architecture to fully characterize pairwise relations of sequences.
1.5 方法介绍
(1)通过预训练氨基酸的嵌入表示
(这个是不是可以用在我们的任务中?)
我觉得是可以的,引入如果不用预训练的embedding ,需要使用PSI-BLAST构造protein profiles,非常麻烦和耗时。
而且

Each embedding vector is a concatenation of two sub-embeddings, i.e.
(1)The first part ac measures the co-occurrence similarity of the amino acids, which is obtained by pre-training the Skip-Gram model
(2)The second part aph represents the similarity of electrostaticity and hydrophobicity among amino acids. The 20 amino(哦一共有20种氨基酸!!) acids can be clustered into 7 classes based on their dipoles and volumes of the side chains to reflect this property. Thus, aphis a one-hot encoding based on the classification defined by Shen et al. (2007).
(2)RCNN

①CNN层:
最大池化discretize the convolution results, and preserve the most significant features within each n-stride. By definition, this mechanism divides the size of processed features by n. The outputs from the max-pooling are fed into the bidirectional gated recurrent units in our RCNN encoder.
②残差GRU层
一个疑问:残差机制是否也该应用在我们的工作中?
“In our development, we have found that the residual mechanism is able to drastically simplify the training process, and largely decreases the epochs of parameter updates for the model to converge.”
③
将上面的unit堆叠多次,将最后一层GRU的输出再经过一个CNN层和池化层得到最终的 high-level sequence embedding of the entire protein sequence
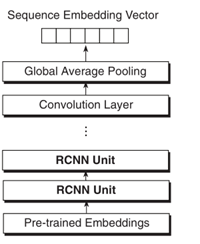
(3)孪生网络结构

(4)损失函数
①分类问题使用了Cross-entropy loss。
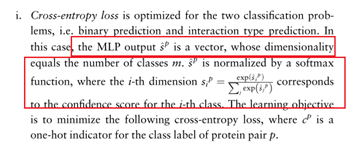
疑问:哪里用到了MLP??不是直接用的两个蛋白质序列的embedding做乘法吗?
②回归问题使用Mean squared loss

1.6 数据集
(1)
疑问:如果我们想与其他方法做比较是不是也需要用the Yeast dataset?
(2)

1.7 实验细节


疑问:它使用了交叉验证(而且以前很多工作也是这样做的),如果数据集不够大,我们是否也需要用?
补充交叉验证;

2.Sequence-based prediction of protein-protein interactions: a structure-aware interpretable deep learning mode
2.1与我们的任务比较相似的地方:
Our key conceptual advance is that a well-matched combination of input featurization and model architecture allow for the model to be trained solely from sequence data, supervised only with a binary interaction label, and yet produce an intermediate representation that substantially captures the structural mechanism of interaction between the protein pair.
Using Bepler and Berger’s [12] pre-trained language model, we construct informative protein embeddings(需要重点看) that are endowed with structural information about each of the proteins. The internal representation of our model uses these features to explicitly encode the intuition that a physical interaction between two proteins requires that a subset of the residues in each protein be in contact with the other protein
We note that the use of Bepler and Berger’s pre-trained model allows us to indirectly benefit from the rich data on 3-D structures of individual proteins. In contrast, a PPI prediction method that was directly supervised with 3-D structures of protein complexes, in order to
learn the physical mechanism of interaction, would need to contend with the relatively small size of that corpus [14–16].
疑问:我们能否使用说到的这个预训练模型?
D-SCRIPT, like other recent successful deep learning methods PIPR and DPPI [17, 20], belongs to the class of methods that perform PPI prediction from protein amino acid sequence alone, in contrast to a different class of highly successful PPI prediction methods based on network information
2.2 这个模型的效果:
(1)它的优势主要体现于跨物种,或者说训练集中比较少出现的PPI
We find, as expected, that state-of-the-art PIPR substantially outperforms D-SCRIPT
when predicting interactions between proteins that have many PPI examples in the training set, but the situation is reversed for proteins with a paucity of PPI interactions in the training set. A simple hybrid method that jointly incorporates the confidence of each method performs best of all.
Among sequence-based methods, D-SCRIPT’s strength is in its greater cross-species generalizability and more accurate predictions
in cases where the existing training data is sparse.
(2)On evaluating the physical plausibility of the intermediate contact map representation, we remarkably find that the map partially discovers the structural mechanism of an interaction despite the model having been trained only on sequence data.
2.3 任务定义(模型输入输出)
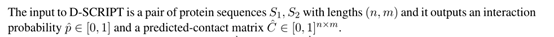
2.4 方法介绍

这篇文章的创新之处还在于 其得到第一阶段的embeddings后,在第二阶段首先预测两个蛋白质序列各氨基酸之间的交互情况

(1) 得到蛋白质的embeddings
使用了” Bepler, T. & Berger, B. Learning protein sequence embeddings using information from structure. In 7th International Conference on Learning Representations, ICLR 2019 (2019)”中的方法。这是一个基于Bi-LSTM的预训练模型。
作者把这种embeddings与PIPR中的embeddings进行了比较,而且还提供了两种其他embeddinging方法:

(2)将两个蛋白质序列转化为相同维度

(3)Residue Contact Module
假设蛋白质A的长度是m,蛋白质B的长度为n。那么这一部分最后得到的是一个m*n的矩阵,其中每一个值在0,1之间,代表两个蛋白质的每个氨基酸之间分别可能contact的概率。
(4)Interaction Prediction Module
从4.3中得到的contact矩阵中计算最后的两个蛋白质序列可能组成复合物的概率p
2.5 与PIPR的详细比较

这篇关于使用端到端深度学习模型完成PPI任务两篇论文笔记的文章就介绍到这儿,希望我们推荐的文章对编程师们有所帮助!




