本文主要是介绍第十二周项目5—— 迷宫问题之图深度优先遍历解法,希望对大家解决编程问题提供一定的参考价值,需要的开发者们随着小编来一起学习吧!
/*
*Copyright (c) 2015,烟台大学计算机学院
*All right reserved.
*文件名称:test.cpp
*作者:王雪洁
*完成日期:2015年11月30日
*版本号:v1.0
*问题描述:
设计一个程序,采用深度优先遍历算法的思路,解决迷宫问题。
(1)建立迷宫对应的图数据结构,并建立其邻接表表示。
(2)采用深度优先遍历的思路设计算法,输出从入口(1,1)点到出口(M,N)的所有迷宫路径。
*/
[模型建立]
将迷宫中的每一格作为一个顶点,相邻格子可以到达,则对应的顶点之间存在边相连。
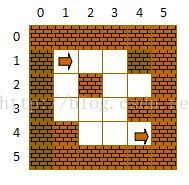
例如,下面的迷宫
在使用数组表示时,用0表示格子是空地,用1表示格子处是墙,对应的矩阵是:
<code class="hljs mathematica has-numbering"> int mg[M+<span class="hljs-number">2</span>][<span class="hljs-keyword">N</span>+<span class="hljs-number">2</span>]= //迷宫数组
<span class="hljs-list">{
{1,1,1,1,1,1}</span>,
<span class="hljs-list">{1,0,0,0,1,1}</span>,
<span class="hljs-list">{1,0,1,0,0,1}</span>,
<span class="hljs-list">{1,0,0,0,1,1}</span>,
<span class="hljs-list">{1,1,0,0,0,1}</span>,
<span class="hljs-list">{1,1,1,1,1,1}</span>
};</code>
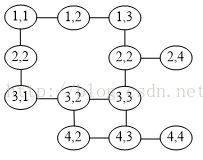
建立的图结构为:
于是,从(1,1)到(4,4)的迷宫问题,转化为寻找顶点(1,1)到顶点(4,4)的路径的问题。
代码:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <malloc.h>
#define MaxSize 100
#define M 4
#define N 4
//以下定义邻接表类型
typedef struct ANode //边的结点结构类型
{
int i,j; //该边的终点位置(i,j)
struct ANode *nextarc; //指向下一条边的指针
} ArcNode;
typedef struct Vnode //邻接表头结点的类型
{
ArcNode *firstarc; //指向第一条边
} VNode;
typedef struct
{
VNode adjlist[M+2][N+2]; //邻接表头节点数组
} ALGraph; //图的邻接表类型
typedef struct
{
int i; //当前方块的行号
int j; //当前方块的列号
} Box;
typedef struct
{
Box data[MaxSize];
int length; //路径长度
} PathType; //定义路径类型
int visited[M+2][N+2]= {0};
int count=0;
void CreateList(ALGraph *&G,int mg[][N+2])
//建立迷宫数组对应的邻接表G
{
int i,j,i1,j1,di;
ArcNode *p;
G=(ALGraph *)malloc(sizeof(ALGraph));
for (i=0; i<M+2; i++) //给邻接表中所有头节点的指针域置初值
for (j=0; j<N+2; j++)
G->adjlist[i][j].firstarc=NULL;
for (i=1; i<=M; i++) //检查mg中每个元素
for (j=1; j<=N; j++)
if (mg[i][j]==0)
{
di=0;
while (di<4)
{
switch(di)
{
case 0:
i1=i-1;
j1=j;
break;
case 1:
i1=i;
j1=j+1;
break;
case 2:
i1=i+1;
j1=j;
break;
case 3:
i1=i, j1=j-1;
break;
}
if (mg[i1][j1]==0) //(i1,j1)为可走方块
{
p=(ArcNode *)malloc(sizeof(ArcNode)); //创建一个节点*p
p->i=i1;
p->j=j1;
p->nextarc=G->adjlist[i][j].firstarc; //将*p节点链到链表后
G->adjlist[i][j].firstarc=p;
}
di++;
}
}
}
//输出邻接表G
void DispAdj(ALGraph *G)
{
int i,j;
ArcNode *p;
for (i=0; i<M+2; i++)
for (j=0; j<N+2; j++)
{
printf(" [%d,%d]: ",i,j);
p=G->adjlist[i][j].firstarc;
while (p!=NULL)
{
printf("(%d,%d) ",p->i,p->j);
p=p->nextarc;
}
printf("\n");
}
}
void FindPath(ALGraph *G,int xi,int yi,int xe,int ye,PathType path)
{
ArcNode *p;
visited[xi][yi]=1; //置已访问标记
path.data[path.length].i=xi;
path.data[path.length].j=yi;
path.length++;
if (xi==xe && yi==ye)
{
printf(" 迷宫路径%d: ",++count);
for (int k=0; k<path.length; k++)
printf("(%d,%d) ",path.data[k].i,path.data[k].j);
printf("\n");
}
p=G->adjlist[xi][yi].firstarc; //p指向顶点v的第一条边顶点
while (p!=NULL)
{
if (visited[p->i][p->j]==0) //若(p->i,p->j)方块未访问,递归访问它
FindPath(G,p->i,p->j,xe,ye,path);
p=p->nextarc; //p指向顶点v的下一条边顶点
}
visited[xi][yi]=0;
}
int main()
{
ALGraph *G;
int mg[M+2][N+2]= //迷宫数组
{
{1,1,1,1,1,1},
{1,0,0,0,1,1},
{1,0,1,0,0,1},
{1,0,0,0,1,1},
{1,1,0,0,0,1},
{1,1,1,1,1,1}
};
CreateList(G,mg);
printf("迷宫对应的邻接表:\n");
DispAdj(G); //输出邻接表
PathType path;
path.length=0;
printf("所有的迷宫路径:\n");
FindPath(G,1,1,M,N,path);
return 0;
}
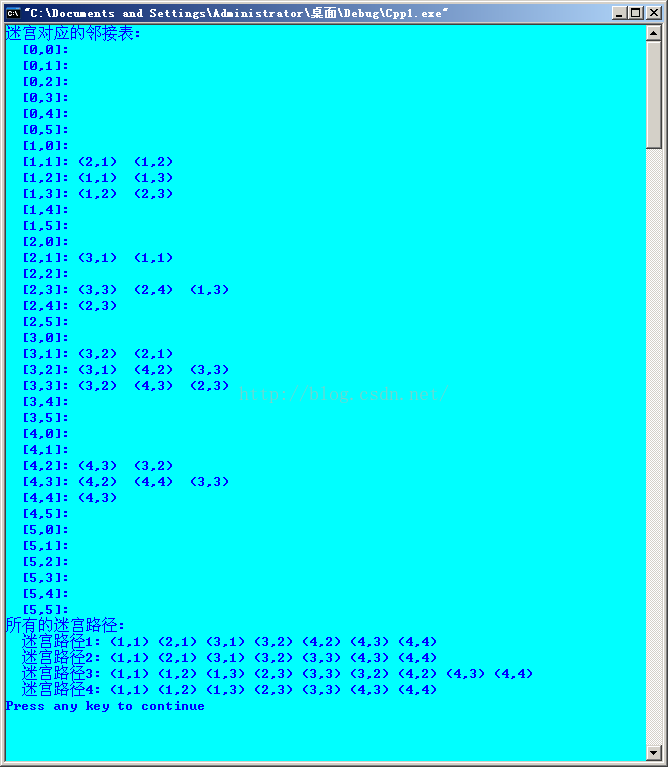
运行结果:
这篇关于第十二周项目5—— 迷宫问题之图深度优先遍历解法的文章就介绍到这儿,希望我们推荐的文章对编程师们有所帮助!