本文主要是介绍Sophus::SO3SE3_3dso36dse3_trajectoryErr,希望对大家解决编程问题提供一定的参考价值,需要的开发者们随着小编来一起学习吧!
Sophus::SO3SE3_3dso36dse3_trajectoryErr
- 引言
- 0.常用
- 1.Sophus库
- 2.Sophus安装方式:
- 3.Sophus的使用教程:
- 4.SO3,so3,SE3和se3初始化以及相互转换关系
- 5.求轨迹误差
引言
ch4.task3.
0.常用
- ref
李群:
- SO(3);R(3*3)
- SE(3);T(4*4)
李代数:
- so(3);(3*1)=>三个旋转
- se(3);(6*1)=>前三维平移,后三维旋转
定义:
- Sophus::SO3 SO3_R(R ); //旋转矩阵定义李群SO(3)
- Sophus::SO3 SO3_q(Q );//四元数定义李群SO(3)
- Sophus::SE3 SE3_Rt(R, t);//R,t构造SE(3)
- Sophus::SE3 SE3_qt(q,t); //q,t构造SE(3)
- Sophus::Vector3d so3 = SO3_R.log();//李代数so3为李群SO(3)的对数映射
- Sophus::Vector6d se3 = SE3_Rt.log();//李代数se(3) 是一个6维向量为李群SE3 的对数映射
- SE3_Rt = se3.exp();//李群SE3是李代数se3的指数映射
- SO3_R = so3.exp();//李群SO3是李代数so3的指数映射
注意:
- vector<Sophus::SE3, Eigen::aligned_allocator< Sophus::SE3>> poses;//这句实际上表达的是vector< Sophus::SE3> poses的意思。但是在Eigen管理内存和C++11中的方法是不一样的,所以需要单独强调元素的内存分配和管理。(特别注意Eigen库数据结构内存对齐问题)
1.Sophus库
Eigen库是一个开源的C++线性代数库,它提供了快速的有关矩阵的线性代数运算,还包括解方程等功能。但是Eigen库提供了集合模块,但没有提供李代数的支持。一个较好的李群和李代数的库是Sophus库,它很好的支持了SO(3),so(3),SE(3)和se(3)。Sophus库是基于Eigen基础上开发的,继承了Eigen库中的定义的各个类。因此在使用Eigen库中的类时,既可以使用Eigen命名空间,也可以使用Sophus命名空间。但最好使用Sophus命名空间,便于阅读。
Eigen::Matrix3d和Sophus::Matrix3d
Eigen::Vector3d和Sophus::Vector3d
此外,为了方便说明SE(4)和se(4),Sophus库还typedef了Vector4d、Matrix4d、Vector6d和Matrix6d等,即:
Sophus::Vector4d
Sophus::Matrix4d
Sophus::Vector6d
Sophus::Matrix6d
类型的转换:
Type conversion
// Eigen // Matlab
A.cast<double>(); // double(A)
A.cast<float>(); // single(A)
A.cast<int>(); // int32(A)
A.real(); // real(A)
A.imag(); // imag(A)
// if the original type equals destination type, no work is done
2.Sophus安装方式:
git clone https://github.com/strasdat/Sophus.gitcd Sophusgit checkout a621ffmkdir build cd buildcmake ..makesudo make install
3.Sophus的使用教程:
几个需要注意的地方:
-
Sophus库的各种形式的表示如下:
李代数so(3):Sophus::Vector3d //因为so(3)仅仅只是一个普通的3维向量
李代数se(3):Sophus::Vector6d //因为se(3)仅仅只是一个普通的6维向量 -
SO3的构造函数为:
SO3 ();
SO3 (const SO3 & other);
explicit SO3 (const Matrix3d & _R);
explicit SO3 (const Quaterniond & unit_quaternion);
SO3 (double rot_x, double rot_y, double rot_z); -
SE3的构造函数为:
SE3 ();
SE3 (const SO3 & so3,const Vector3d & translation);
SE3 (const Matrix3d & rotation_matrix,const Vector3d & translation);
SE3 (const Quaterniond & unit_quaternion,const Vector3d & translation_);
SE3 (const SE3 & other); -
SO3,SE3和se3的输出说明:
尽管SO3对应于矩阵群,但是SO3在使用cout时是以so3形式输出的,输出的是一个3维向量.SE3在使用cout输出时输出的是一个6维向量,其中前3维为对应的so3的值,后3维为实际的平移向量t.se3在使用cout输出时输出的也是一个6维向量,但是其前3维为平移值ρρ(注意此时的ρρ与SE3输出的t是不同的,t=Jρρ,其中J是雅克比矩阵),后3维为其对应的so3.
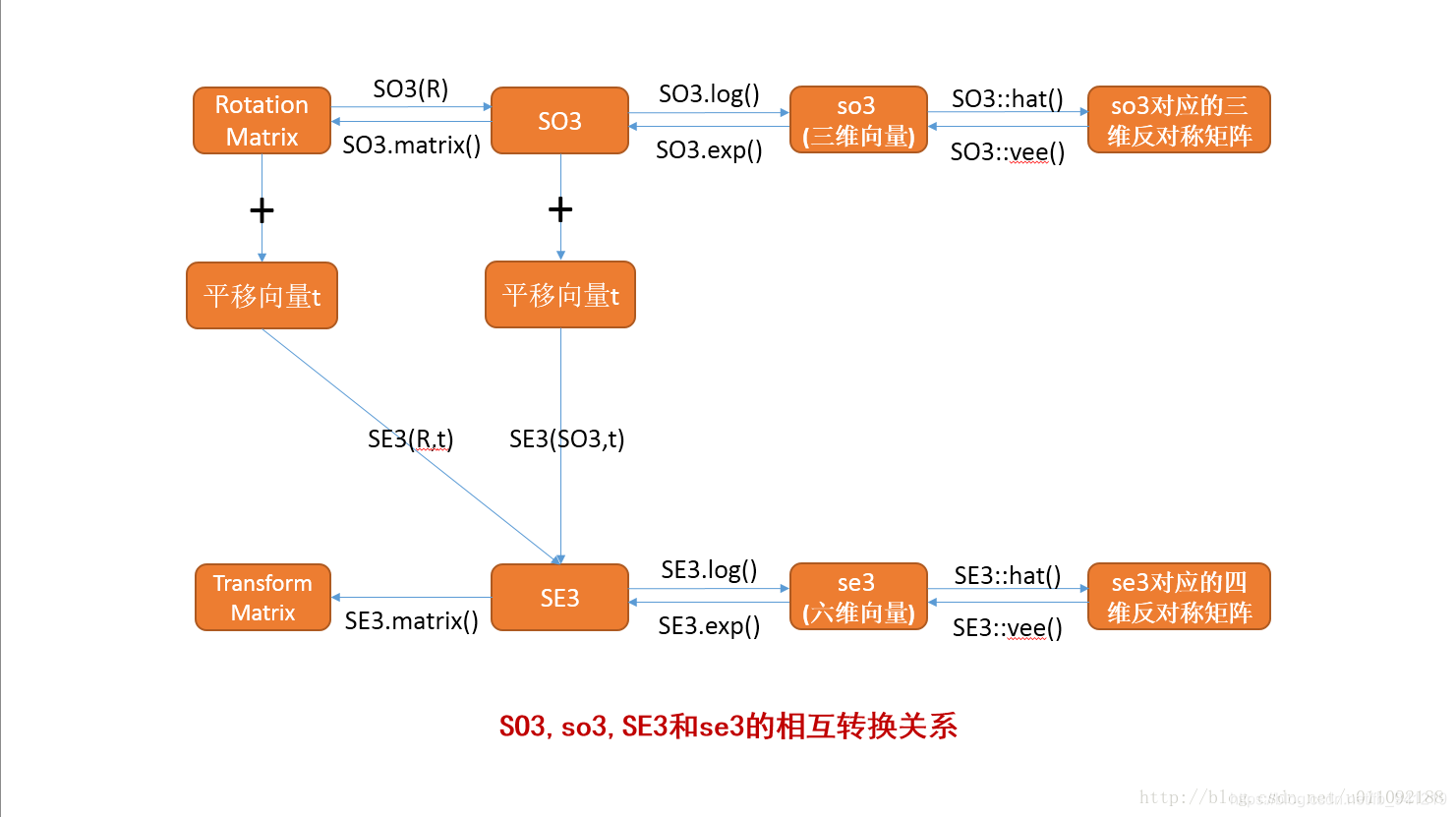
4.SO3,so3,SE3和se3初始化以及相互转换关系
1.转换关系图:

2.代码示意:
SO3,so3,SE3和se3初始化以及相互转换useSophusc:
#include <iostream>
#include <cmath>
using namespace std; #include <Eigen/Core>
#include <Eigen/Geometry>// 李群李代数 库
#include "sophus/so3.h"
#include "sophus/se3.h"
/********************************** sophus 库安装 * 本库为来版本 非模板的版本* git clone https://github.com//strasdat/Sophus.git* git checkout a621ff 版本* 在cmake编译* *欧拉角定义:旋转向量转旋转矩阵 Eigen::Matrix3d R = Eigen::AngleAxisd(M_PI/2, Eigen::Vector3d(0,0,1)).toRotationMatrix();旋转矩阵转四元数 Eigen::Quaterniond q(R); // 或者四元数(从旋转矩阵构造)平移Eigen::Vector3d t(1,0,0); // 沿X轴平移1SO(n) 特殊正交群 对应 n*n 的旋转矩阵 群(集合)SE(n+1) 特殊欧式群 对应 n*n 的旋转矩阵和 n*1的平移向量组合成的变换矩阵 群(集合)so(n) 对应的李代数为so(n) n×1 列向量,使得向量和代数一一对应可以使用代数的更新方法来更新矩阵SO(3) 表示三维空间的 旋转矩阵 集合 3×3SE(3) 表示三维空间的 变换矩阵 集合 4×4李代数 so3的本质就是个三维向量,直接Eigen::Vector3d定义.3个旋转李代数 se3的本质就是个六维向量,直接Eigen::Matrix<double,6,1>定义,3个旋转 + 3个平移旋转向量定义的李群SO(3) Sophus::SO3 SO3_v( 0, 0, M_PI/2 ); // 亦可从旋转向量构造 这里注意,不是旋转向量的三个坐标值,有点像欧拉角构造。旋转矩阵定义的李群SO(3) Sophus::SO3 SO3_R(R); // Sophus::SO(3)可以直接从旋转矩阵构造四元素定义的李群SO(3) Sophus::SO3 SO3_q(q);从旋转矩阵和平移t构造SE3 Sophus::SE3 SE3_Rt(R,t); // 从R,t构造SE(3)从四元素和平移t构造SE3 Sophus::SE3 SE3_qt(q,t); // 从q,t构造SE(3)李代数so3为李群SO(3)的对数映射 Eigen::Vector3d so3 = SO3_R.log();李代数se(3)是一个6维向量,为李群SE3 的对数映射typedef Eigen::Matrix<double,6,1> Vector6d;// Vector6d指代Eigen::Matrix<double,6,1>Vector6d se3 = SE3_Rt.log();李代数指数映射成旋转矩阵对应的李群Eigen::Vector3d so33 (1, 1, 1);Sophus::SO3 SO3 =Sophus::SO3::exp(so33);Sophus::SO3::hat(so3) //hat为向量到反对称矩阵,相当于^运算.Sophus::SO3::vee( Sophus::SO3::hat(so3) ).transpose() //vee为反对称矩阵到向量,相当于下尖尖运算 .**********************************/int main( int argc, char** argv )
{/*******************************************/// 旋转矩阵群/特殊正交群仅有旋转没有平移// 沿Z轴转90度的旋转矩阵// 旋转向量 角度 轴 罗德里格公式进行转换为旋转矩阵 Eigen::Matrix3d R = Eigen::AngleAxisd(M_PI/2, Eigen::Vector3d(0,0,1)).toRotationMatrix();cout<<"RotationMatrix R: \n"<<R<<endl;/***李群*****/Sophus::SO3 SO3_R(R); // Sophus::SO(3)可以直接从旋转矩阵构造Sophus::SO3 SO3_v( 0, 0, M_PI/2 ); // 亦可从旋转向量构造 这里注意,不是旋转向量的三个坐标值,有点像欧拉角构造。/*SO3 ::SO3(double rot_x, double rot_y, double rot_z) { unit_quaternion_ = (SO3::exp(Vector3d(rot_x, 0.f, 0.f)) *SO3::exp(Vector3d(0.f, rot_y, 0.f)) *SO3::exp(Vector3d(0.f, 0.f, rot_z))).unit_quaternion_; }显示的貌似是三个过程,先转X轴,再转Y轴,再转Z轴,完全跟旋转向量不搭边。瞅着过程有点像欧拉角的过程,三个轴分了三步。 我就有一个(1, 1, 1)旋转向量,如何构造成SO3呢?也就是让它输出(1, 1, 1)。Eigen::Vector3d so33 (1, 1, 1); Sophus::SO3 SO3 =Sophus::SO3::exp(so33); //李代数 指数映射成 旋转矩阵 对于的 李群cout<<"SO3=\n"<<SO3<<endl; */Eigen::Quaterniond q(R); // 或者四元数(从旋转矩阵构造)Sophus::SO3 SO3_q( q );// 上述表达方式都是等价的// 输出SO(3)时,以so(3)形式输出//从输出的形式可以看出,虽然SO3是李群,是旋转矩阵,但是输出形式还是向量(被转化成李代数输出)。// 重载了 << 运算符 out_str << so3.log().transpose() << std::endl; cout<<"SO(3) from matrix: "<<SO3_R<<endl; //SO(3) from matrix: 0 0 1.5708 cout<<"SO(3) from vector: "<<SO3_v<<endl;cout<<"SO(3) from quaternion :"<<SO3_q<<endl;/****李代数*****/// 使用对数映射获得它的李代数// 所以,李代数 so3的本质就是个三维向量,直接Eigen::Vector3d定义。Eigen::Vector3d so3 = SO3_R.log();cout<<"so3 = "<<so3.transpose()<<endl;// hat 为向量 到反对称矩阵 相当于 ^ 运算。cout<<"so3 hat=\n"<<Sophus::SO3::hat(so3)<<endl;// 相对的,vee为 反对称矩阵 到 向量 相当于下尖尖运算 cout<<"so3 hat vee= "<<Sophus::SO3::vee( Sophus::SO3::hat(so3) ).transpose()<<endl; // transpose纯粹是为了输出美观一些/****李代数求导 更新*****/// 增量扰动模型的更新Eigen::Vector3d update_so3(1e-4, 0, 0); //假设更新量为这么多Sophus::SO3 SO3_updated = Sophus::SO3::exp(update_so3)*SO3_R;// 在李群中连乘更新cout<<"SO3 updated = "<<SO3_updated<<endl;/********************萌萌的分割线*********************************//************特殊欧式群 变换矩阵群 有旋转有平移*********************/cout<<"************我是分割线*************"<<endl;// 李群 对SE(3)操作大同小异Eigen::Vector3d t(1,0,0); // 沿X轴平移1Sophus::SE3 SE3_Rt(R, t); // 从R,t构造SE(3)Sophus::SE3 SE3_qt(q,t); // 从q,t构造SE(3)cout<<"SE3 from R,t= "<<endl<<SE3_Rt<<endl;cout<<"SE3 from q,t= "<<endl<<SE3_qt<<endl;// 李代数se(3) 是一个六维向量,方便起见先typedef一下typedef Eigen::Matrix<double,6,1> Vector6d;// Vector6d指代 Eigen::Matrix<double,6,1>Vector6d se3 = SE3_Rt.log();cout<<"se3 = "<<se3.transpose()<<endl;// 观察输出,会发现在Sophus中,se(3)的平移在前,旋转在后.// 同样的,有hat和vee两个算符cout<<"se3 hat = "<<endl<<Sophus::SE3::hat(se3)<<endl;cout<<"se3 hat vee = "<<Sophus::SE3::vee( Sophus::SE3::hat(se3) ).transpose()<<endl;// 最后,演示一下更新Vector6d update_se3; //更新量update_se3.setZero();update_se3(0,0) = 1e-4d;Sophus::SE3 SE3_updated = Sophus::SE3::exp(update_se3)*SE3_Rt;cout<<"SE3 updated = "<<endl<<SE3_updated.matrix()<<endl;return 0;
}
5.求轨迹误差
#include <sophus/se3.h>
#include <string>
#include <iostream>
#include <fstream>//xiao的方法更直接易懂
// need pangolin for plotting trajectory
#include <pangolin/pangolin.h>using namespace std;// path to trajectory file
string trajectory_file = "./../trajectory.txt"; //"./trajectory.txt";
string groundtruth_file = "./../groundtruth.txt"; //"./groundtruth.txt";
string estimated_file = "./../estimated.txt"; //"./estimated.txt";// function for plotting trajectory, don't edit this code
// start point is red and end point is blue
void DrawTrajectory(vector<Sophus::SE3, Eigen::aligned_allocator<Sophus::SE3>>);
void Draw3Trajectory();
void computeErr();int main(int argc, char **argv) {//Draw3Trajectory();computeErr();return 0;
}void computeErr()
{ifstream g_file(groundtruth_file);ifstream e_file(estimated_file);if (!g_file||!e_file) {cout<<"unable to read file!"<<endl;exit(1);}int count = 0;double rmse_square = 0;double data1[8] = {0}; double data2[8] = {0};while(!g_file.eof() && !e_file.eof()) {for (auto &p:data1)g_file >> p;Eigen::Quaterniond q1(data1[7], data1[4], data1[5], data1[6]);Eigen::Vector3d t1(data1[1], data1[2], data1[3]);Sophus::SE3 SE3_g(q1,t1);for (auto &p:data2)e_file >> p;Eigen::Quaterniond q2(data2[7], data2[4], data2[5], data2[6]);Eigen::Vector3d t2(data2[1], data2[2], data2[3]);Sophus::SE3 SE3_e(q2,t2);Eigen::Matrix<double,4,4> m = (SE3_g.matrix().inverse())*SE3_e.matrix();//公式!Eigen::Matrix<double,3,3> R = m.topLeftCorner<3,3>();//函数名很直观Eigen::Matrix<double,3,1> t = m.topRightCorner<3,1>();Eigen::Quaterniond q(R);Eigen::Vector3d tt(t);Sophus::SE3 SE3_dot(q,tt); //q,t构建李群Sophus::Vector6d se3_dot = SE3_dot.log();//转为李代数double err = se3_dot.norm();//二范数rmse_square = (rmse_square + err*err); //公式count ++ ;}g_file.close();e_file.close();double rmse = sqrt(rmse_square/count);cout<< "the RMSE is:\n"<<rmse<<endl;}//画三段轨迹
void Draw3Trajectory()
{vector<Sophus::SE3, Eigen::aligned_allocator<Sophus::SE3>> poses;/// implement pose reading code// start your code here (5~10 lines)///**// Read1ifstream t_file(trajectory_file);ifstream g_file(groundtruth_file);ifstream e_file(estimated_file);if (!t_file) {cout<<"unable to read file!"<<endl;exit(1);}while(!t_file.eof()) {double data[8] = {0};for (auto &p:data)t_file >> p;Eigen::Quaterniond q(data[7], data[4], data[5], data[6]);Eigen::Vector3d t(data[1], data[2], data[3]);Sophus::SE3 pose(q,t);poses.push_back(pose);}t_file.close();// end your code hereif (!g_file) {cout<<"unable to read file!"<<endl;exit(1);}while(!g_file.eof()) {double data[8] = {0};for (auto &p:data)g_file >> p;Eigen::Quaterniond q(data[7], data[4], data[5], data[6]);Eigen::Vector3d t(data[1], data[2], data[3]);Sophus::SE3 pose(q,t);poses.push_back(pose);}g_file.close();if (!e_file) {cout<<"unable to read file!"<<endl;exit(1);}while(!e_file.eof()) {double data[8] = {0};for (auto &p:data)e_file >> p;Eigen::Quaterniond q(data[7], data[4], data[5], data[6]);Eigen::Vector3d t(data[1], data[2], data[3]);Sophus::SE3 pose(q,t);poses.push_back(pose);}e_file.close();//*///把三个轨迹都导入poses一起画出来就是,不用定义三个poses;//这种思路比另一个大神的要强一点!!// draw trajectory in pangolinDrawTrajectory(poses);
}/*******************************************************************************************/
void DrawTrajectory(vector<Sophus::SE3, Eigen::aligned_allocator<Sophus::SE3>> poses) {if (poses.empty()) {cerr << "Trajectory is empty!" << endl;return;}// create pangolin window and plot the trajectorypangolin::CreateWindowAndBind("Trajectory Viewer", 1024, 768);glEnable(GL_DEPTH_TEST);glEnable(GL_BLEND);glBlendFunc(GL_SRC_ALPHA, GL_ONE_MINUS_SRC_ALPHA);pangolin::OpenGlRenderState s_cam(pangolin::ProjectionMatrix(1024, 768, 500, 500, 512, 389, 0.1, 1000),pangolin::ModelViewLookAt(0, -0.1, -1.8, 0, 0, 0, 0.0, -1.0, 0.0));pangolin::View &d_cam = pangolin::CreateDisplay().SetBounds(0.0, 1.0, pangolin::Attach::Pix(175), 1.0, -1024.0f / 768.0f).SetHandler(new pangolin::Handler3D(s_cam));while (pangolin::ShouldQuit() == false) {glClear(GL_COLOR_BUFFER_BIT | GL_DEPTH_BUFFER_BIT);d_cam.Activate(s_cam);glClearColor(1.0f, 1.0f, 1.0f, 1.0f);glLineWidth(2);for (size_t i = 0; i < poses.size() - 1; i++) {glColor3f(1 - (float) i / poses.size(), 0.0f, (float) i / poses.size()); // start from red and end with blue color// start the drawingglBegin(GL_LINES);auto p1 = poses[i], p2 = poses[i + 1];// define two vertex, 1st is starting point, 2nd is ending point.glVertex3d(p1.translation()[0], p1.translation()[1], p1.translation()[2]);glVertex3d(p2.translation()[0], p2.translation()[1], p2.translation()[2]);glEnd();// finish the drawing}pangolin::FinishFrame();usleep(5000); // sleep 5 ms}}
这篇关于Sophus::SO3SE3_3dso36dse3_trajectoryErr的文章就介绍到这儿,希望我们推荐的文章对编程师们有所帮助!