本文主要是介绍(数据结构)如何手搓一棵伸展树(splay tree),希望对大家解决编程问题提供一定的参考价值,需要的开发者们随着小编来一起学习吧!
伸展树作为BST的又一个派生类
其主要特色是没每插入或查找一个节点,会把该节点通过一次次的旋转伸展至树根,并且减少树高
使得用户经过一段时间的使用后
高访问频率的数据集中在树根位置,查询深度浅,速度快
从而达到提高效率的目的
因此相较而言,AVL树更像是循规蹈矩,如履薄冰。而伸展树则更加潇洒,不羁小节。
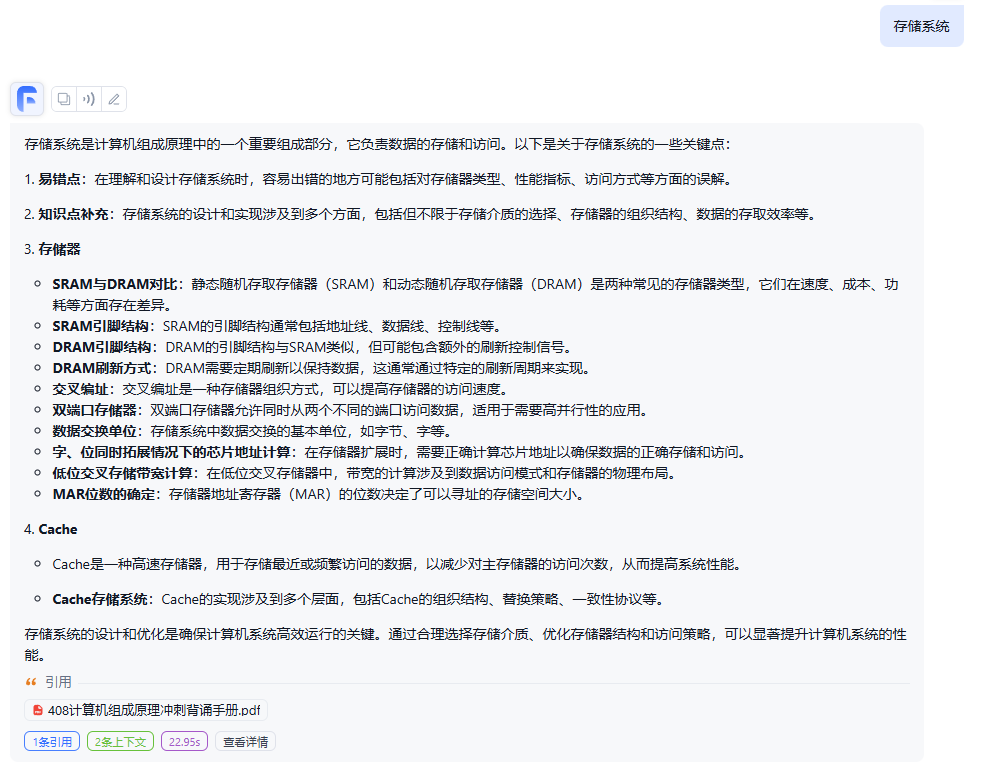
例如一颗这样的伸展树
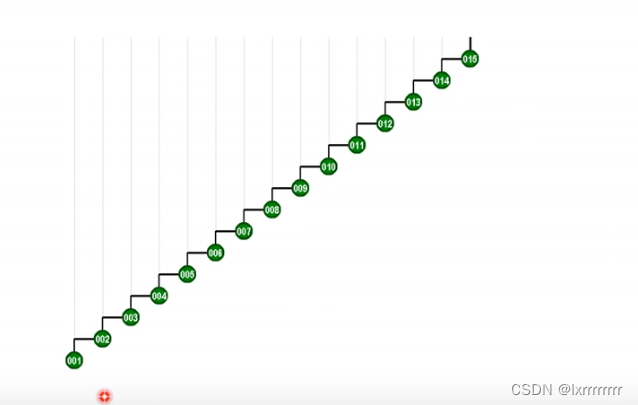
如果你访问001节点,即访问最底的节点
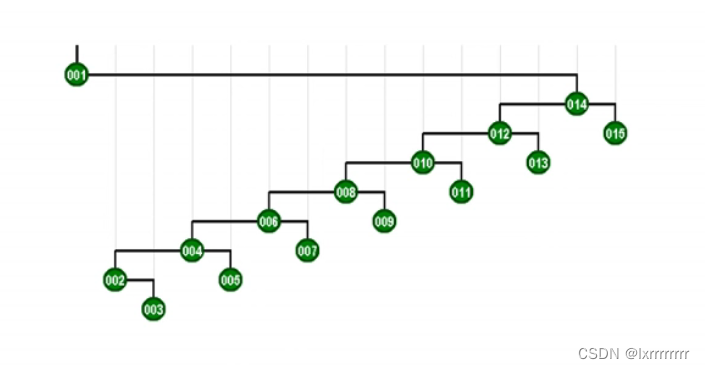
伸展树会把001伸展至根节点,同时缩短书高
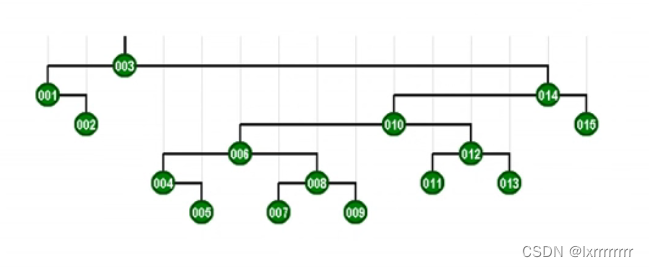
在访问一次003节点
树会伸展至如下图结构
为方便理解,首先介绍几个旋转方式:
zig为顺时针旋转,zag为逆时针旋转,可以看到,经过这种单层旋转
可以将V节点提升一层

而两个单层旋转互相组合,可以有四种双层旋转
分别为zag-zag,zig-zig zig-zag zag-zig四种
其中zig-zig旋转:

zag-zag旋转:

zag-zig旋转
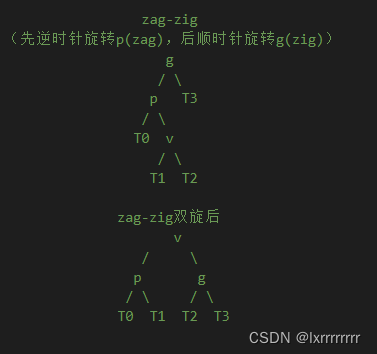
zig-zag旋转

可以看到以上节点都把V提升了两层
似曾相似对不对
zig-zag和zag-zig就是上篇中平衡AVL树的3+4重构的转法
一会代码也会有所体现
为什么要引入双层旋转:
因为如果全采用单层旋转,那么顺序访问节点后会发现树高没有变,复杂度会飙到n方
类似下图
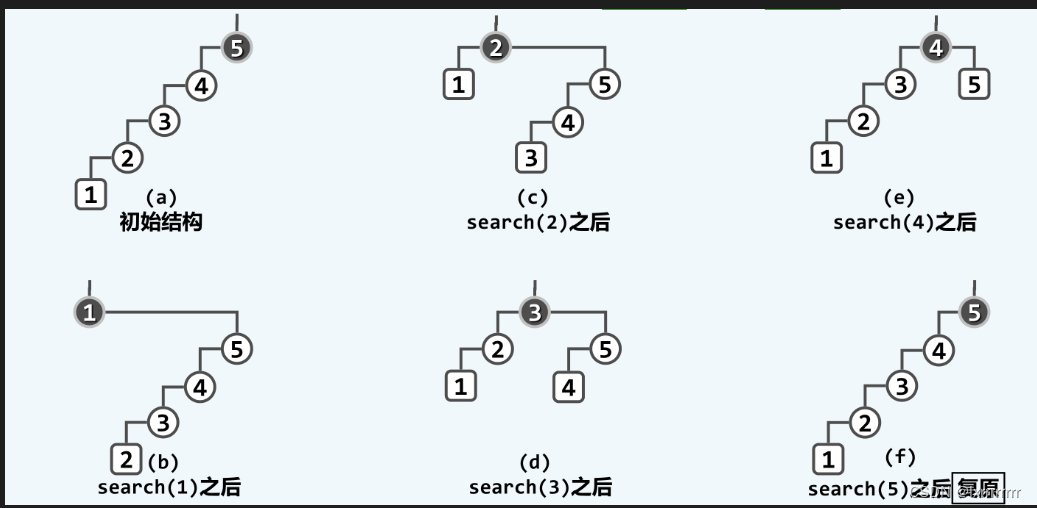
这里就不过多赘述推导过程了,可以去查下相关资料
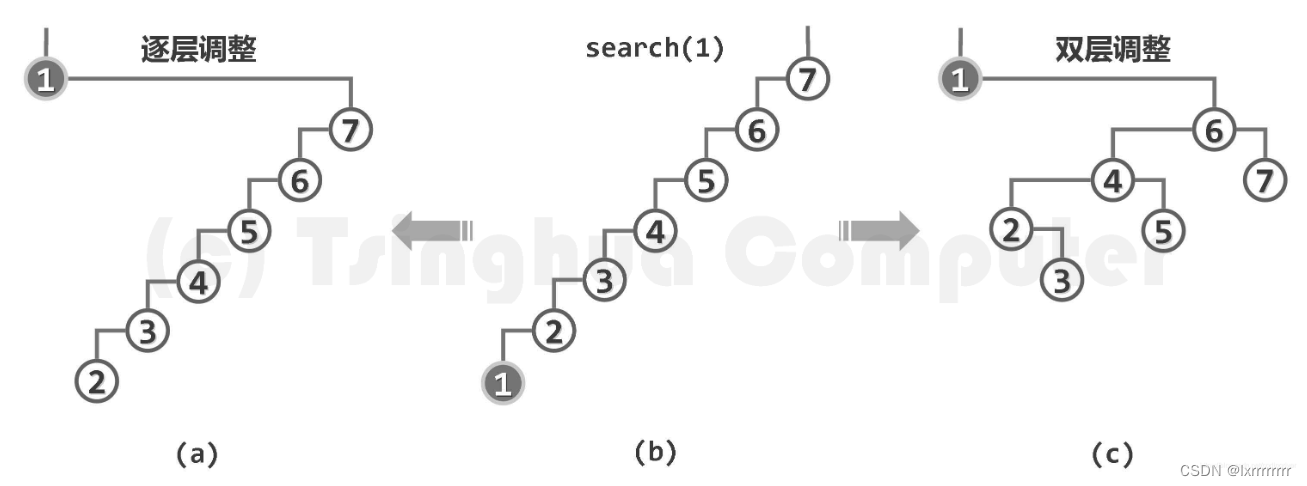
只有双层旋转才可以有效减少树高,提升效率
经过以上分析,我们先把前置的旋转函数写以下
毕竟我们以前的代码是处理不了单旋,zigzig,zagzag这四种情况的
相信对于聪明的你这并不难写
代码如下
旋转
template <typename K,typename V>
lxrbinnodeposi(T) lxrSplayTree<K,V>::zig(lxrbinnodeposi(T) p){lxrbinnodeposi(T) x=p->leftchild;p->leftchild=x->rightchild;if(x->rightchild) x->rightchild->parent=p;x->rightchild=p;p->parent=x;this->updateHeight(p);this->updateHeight(x);return x;
}template <typename K,typename V>
lxrbinnodeposi(T) lxrSplayTree<K,V>::zag(lxrbinnodeposi(T) p){lxrbinnodeposi(T) x=p->rightchild;p->rightchild=x->leftchild;if(x->leftchild) x->leftchild->parent=p;x->leftchild=p;p->parent=x;this->updateHeight(p);this->updateHeight(x);return x;
}template <typename K,typename V>
lxrbinnodeposi(T) lxrSplayTree<K,V>::zigzig(lxrbinnodeposi(T) g){lxrbinnodeposi(T) p=g->leftchild;lxrbinnodeposi(T) x=p->leftchild;p->leftchild=x->rightchild;if(x->rightchild) x->rightchild->parent=p;x->rightchild=p;p->parent=x;g->leftchild=p->rightchild;if(p->rightchild) p->rightchild->parent=g;p->rightchild=g;g->parent=p;this->updateHeight(g);this->updateHeight(p);this->updateHeight(x);return x;
}template <typename K,typename V>
lxrbinnodeposi(T) lxrSplayTree<K,V>::zagzag(lxrbinnodeposi(T) g){lxrbinnodeposi(T) p=g->rightchild;lxrbinnodeposi(T) x=p->rightchild;p->rightchild=x->leftchild;if(x->leftchild) x->leftchild->parent=p;x->leftchild=p;p->parent=x;g->rightchild=p->leftchild;if(p->leftchild) p->leftchild->parent=g;p->leftchild=g;g->parent=p;this->updateHeight(g);this->updateHeight(p);this->updateHeight(x);return x;
}有了以上基础我们就可以顺理成章写出伸展函数
Spaly
虽然代码看起来有些长,但大多数是分类讨论的内容
如果该节点只有父节点而没有祖父节点,那么只能进行单旋,如果他是左儿子就进行zig旋转
反之进行zag旋转
接下来如果x有祖父节点
那我们看他父节点和祖父节点的关系,他和他父节点的关系
按我们上面分析的关系分成四类
其中双左儿子/双右儿子需要进行我们的zigzig/zagzag旋转
余下两个进行3+4重构
按照此方法一直将x伸展至根节点
别忘了更新根节点和树高
代码如下
template <typename K,typename V>
lxrbinnodeposi(T) lxrSplayTree<K,V>::splay(lxrbinnodeposi(T) x){lxrbinnodeposi(T) p;lxrbinnodeposi(T) g;lxrbinnodeposi(T) hot;while(x!= this->__root){p=x->parent,g=p->parent;if(!g){hot=p->parent;x=(x==p->leftchild ? zig(p) : zag(p));x->parent=hot;if(hot) (p==hot->leftchild) ? hot->leftchild:hot->rightchild=x;}else{if(p==g->leftchild){if(x==p->leftchild){hot =g->parent;x =zigzig(g);x->parent=hot;if(hot) (g==hot->leftchild ? hot->leftchild : hot->rightchild)=x;}else{hot =g->parent;x =this->connect34(p,x,g,p->leftchild,x->leftchild,x->rightchild,g->rightchild);x->parent=hot;if(hot) g==hot->leftchild ? hot->leftchild : hot->rightchild=x;}}else{if(x==p->leftchild){hot =g->parent;x =this->connect34(g,x,p,g->leftchild,x->leftchild,x->rightchild,p->rightchild);x->parent=hot;if(hot) g==hot->leftchild ? hot->leftchild : hot->rightchild=x;}else{hot =g->parent;x =zagzag(g);x->parent=hot;if(hot) g==hot->leftchild ? hot->leftchild : hot->rightchild=x;}}}if(!x->parent) this->__root=x;}return x;
}写完了splay函数,伸展树就已经完成一大半了
剩下只要按照伸展树思想完成查找删除和插入函数即可
search
伸展树的search和BST差不多
只是再经过查找之后
我们要将返回的节点伸展至树根
如果返回的是空节点,那就将他的父节点伸展至树根,即__hot
代码如下
template <typename K,typename V>
lxrbinnodeposi(T)& lxrSplayTree<K,V>::search(K const &key){lxrbinnodeposi(T) x=this->searchIn(this->__root,key,(this->__hot)=nullptr);if(x) splay(x);else if(this->__hot) splay(this->__hot);return this->__root;
}insert
这里给出一种实现方式
直接调用上面伸展树的搜索算法,这样一次搜索必然会失败,但是此时`__hot`会被移动到根结点。我们可以直接比较待插入value与__hot的value的大小,从而直接将被插入结点插入到根结点。整个过程如下图所示:
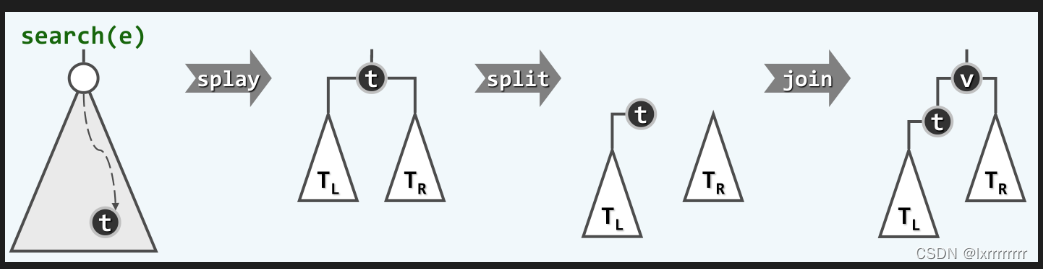
代码如下:
template <typename K,typename V>
lxrbinnodeposi(T) lxrSplayTree<K,V>::insert(K const &key,V const &value){lxrbinnodeposi(T) x=search(key);if(x&& x->data.key==key) return x;this->__root=new lxrbinnode<T>(entry<K,V>(key,value));++(this->__size);if(!x) return this->__root;if(key < x->data.key){this->__root->leftchild =x->leftchild;this->__root->rightchild=x;x->leftchild =nullptr;x->parent =this->__root;}else{this->__root->leftchild = x;this->__root->rightchild = x->rightchild;x->rightchild = nullptr;x->parent = this->__root;}this->updateHeight(x);this->updateHeight((this->__root));return this->__root;
}remove
删除函数会比较复杂,这里给出一种实现方式
首先调用伸展树的搜索算法,这样被删除结点就已经被移动到了根结点,因此可以直接将根结点删除。接下来的问题是,应该由哪个结点来作为新的根结点。
在根结点没有左子树或者没有右子树时,可以直接用那棵唯一的子树来替代根结点,从而完成了根结点的删除。但在根结点同时具有左右子树时,根据伸展树的局部性原理,仍可选取被删除结点的直接后继来作为新的根结点,这样数据的局部性仍然可以得到应用。
为了将根结点的直接后继提升为新的根结点,可以在TR中再次查找根结点的关键码,尽管这次查找必然失败,却可以将TR中的最小结点提升为根节点。并且由于它是最小结点,根据BST的局部有序性,新的根节点必然没有左子树,从而可以将TL作为左子树与新的根结点进行连接。这样,就得到了一棵完整的二叉搜索树。整个过程如下图所示:
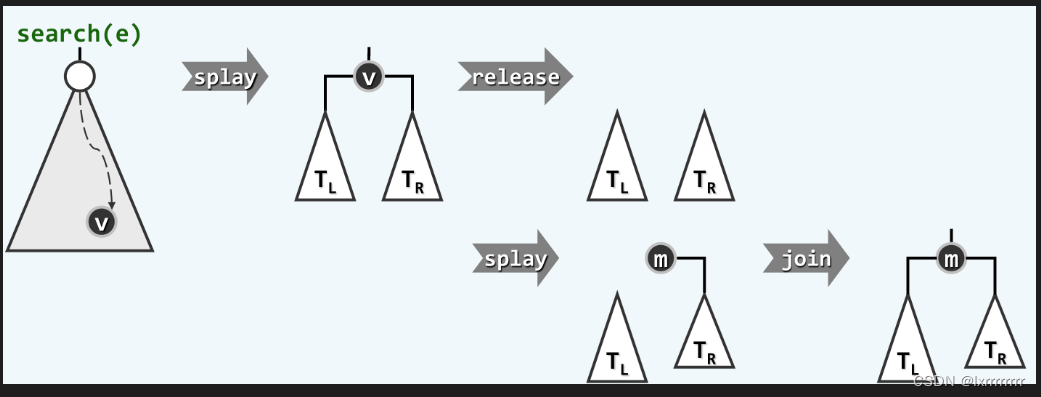
代码如下:
template <typename K,typename V>
bool lxrSplayTree<K,V>::remove(K const &key){lxrbinnodeposi(T) x=search(key);if(!x || x->data.key!=key) return false;if(!(this->__root)->leftchild){this->__root=this->__root->rightchild;if(this->__root) this->__root->parent=nullptr;search(key);}else if(!(this->__root)->rightchild){this->__root=this->__root->leftchild;this->__root->parent=nullptr;search(key);}else{this->__root=x->rightchild;this->__root->parent=nullptr;search(key); //move x's succ to root, this->__root->leftchild=x->leftchild; //and __root has no left child(for succ has the smallest keyx->leftchild->parent=this->__root;this->updateHeight(this->__root);}--(this->__size);delete x;return true;
}
完整代码
#ifndef LXRSPLAYTREE_H_
#define LXRSPLAYTREE_H_#include "../05 BST/lxrBST.h"#define T entry<K,V>
template <typename K,typename V>
class lxrSplayTree:public lxrBST<K,V>{
protected:lxrbinnodeposi(T) splay(lxrbinnodeposi(T) x);lxrbinnodeposi(T) zig(lxrbinnodeposi(T) p); //right rotationlxrbinnodeposi(T) zag(lxrbinnodeposi(T) p); //left rotationlxrbinnodeposi(T) zigzig(lxrbinnodeposi(T) g);lxrbinnodeposi(T) zagzag(lxrbinnodeposi(T) g);
public:lxrbinnodeposi(T)& search(K const &key);lxrbinnodeposi(T) insert(K const &key,V const &value);bool remove(K const &key);
};//protected methodstemplate <typename K,typename V>
lxrbinnodeposi(T) lxrSplayTree<K,V>::splay(lxrbinnodeposi(T) x){lxrbinnodeposi(T) p;lxrbinnodeposi(T) g;lxrbinnodeposi(T) hot;while(x!= this->__root){p=x->parent,g=p->parent;if(!g){hot=p->parent;x=(x==p->leftchild ? zig(p) : zag(p));x->parent=hot;if(hot) (p==hot->leftchild) ? hot->leftchild:hot->rightchild=x;}else{if(p==g->leftchild){if(x==p->leftchild){hot =g->parent;x =zigzig(g);x->parent=hot;if(hot) (g==hot->leftchild ? hot->leftchild : hot->rightchild)=x;}else{hot =g->parent;x =this->connect34(p,x,g,p->leftchild,x->leftchild,x->rightchild,g->rightchild);x->parent=hot;if(hot) g==hot->leftchild ? hot->leftchild : hot->rightchild=x;}}else{if(x==p->leftchild){hot =g->parent;x =this->connect34(g,x,p,g->leftchild,x->leftchild,x->rightchild,p->rightchild);x->parent=hot;if(hot) g==hot->leftchild ? hot->leftchild : hot->rightchild=x;}else{hot =g->parent;x =zagzag(g);x->parent=hot;if(hot) g==hot->leftchild ? hot->leftchild : hot->rightchild=x;}}}if(!x->parent) this->__root=x;}return x;
}template <typename K,typename V>
lxrbinnodeposi(T) lxrSplayTree<K,V>::zig(lxrbinnodeposi(T) p){lxrbinnodeposi(T) x=p->leftchild;p->leftchild=x->rightchild;if(x->rightchild) x->rightchild->parent=p;x->rightchild=p;p->parent=x;this->updateHeight(p);this->updateHeight(x);return x;
}template <typename K,typename V>
lxrbinnodeposi(T) lxrSplayTree<K,V>::zag(lxrbinnodeposi(T) p){lxrbinnodeposi(T) x=p->rightchild;p->rightchild=x->leftchild;if(x->leftchild) x->leftchild->parent=p;x->leftchild=p;p->parent=x;this->updateHeight(p);this->updateHeight(x);return x;
}template <typename K,typename V>
lxrbinnodeposi(T) lxrSplayTree<K,V>::zigzig(lxrbinnodeposi(T) g){lxrbinnodeposi(T) p=g->leftchild;lxrbinnodeposi(T) x=p->leftchild;p->leftchild=x->rightchild;if(x->rightchild) x->rightchild->parent=p;x->rightchild=p;p->parent=x;g->leftchild=p->rightchild;if(p->rightchild) p->rightchild->parent=g;p->rightchild=g;g->parent=p;this->updateHeight(g);this->updateHeight(p);this->updateHeight(x);return x;
}template <typename K,typename V>
lxrbinnodeposi(T) lxrSplayTree<K,V>::zagzag(lxrbinnodeposi(T) g){lxrbinnodeposi(T) p=g->rightchild;lxrbinnodeposi(T) x=p->rightchild;p->rightchild=x->leftchild;if(x->leftchild) x->leftchild->parent=p;x->leftchild=p;p->parent=x;g->rightchild=p->leftchild;if(p->leftchild) p->leftchild->parent=g;p->leftchild=g;g->parent=p;this->updateHeight(g);this->updateHeight(p);this->updateHeight(x);return x;
}//public interfavestemplate <typename K,typename V>
lxrbinnodeposi(T)& lxrSplayTree<K,V>::search(K const &key){lxrbinnodeposi(T) x=this->searchIn(this->__root,key,(this->__hot)=nullptr);if(x) splay(x);else if(this->__hot) splay(this->__hot);return this->__root;
}template <typename K,typename V>
lxrbinnodeposi(T) lxrSplayTree<K,V>::insert(K const &key,V const &value){lxrbinnodeposi(T) x=search(key);if(x&& x->data.key==key) return x;this->__root=new lxrbinnode<T>(entry<K,V>(key,value));++(this->__size);if(!x) return this->__root;if(key < x->data.key){this->__root->leftchild =x->leftchild;this->__root->rightchild=x;x->leftchild =nullptr;x->parent =this->__root;}else{this->__root->leftchild = x;this->__root->rightchild = x->rightchild;x->rightchild = nullptr;x->parent = this->__root;}this->updateHeight(x);this->updateHeight((this->__root));return this->__root;
}template <typename K,typename V>
bool lxrSplayTree<K,V>::remove(K const &key){lxrbinnodeposi(T) x=search(key);if(!x || x->data.key!=key) return false;if(!(this->__root)->leftchild){this->__root=this->__root->rightchild;if(this->__root) this->__root->parent=nullptr;search(key);}else if(!(this->__root)->rightchild){this->__root=this->__root->leftchild;this->__root->parent=nullptr;search(key);}else{this->__root=x->rightchild;this->__root->parent=nullptr;search(key); //move x's succ to root, this->__root->leftchild=x->leftchild; //and __root has no left child(for succ has the smallest keyx->leftchild->parent=this->__root;this->updateHeight(this->__root);}--(this->__size);delete x;return true;
}#undef T
#endif
但是伸展树并不能保证单次最坏情况的发生,所以不能适用于对效率非常敏感的场合,例如一些安全装置,应急装置,毕竟谁也不敢当赌怪
这篇关于(数据结构)如何手搓一棵伸展树(splay tree)的文章就介绍到这儿,希望我们推荐的文章对编程师们有所帮助!