本文主要是介绍前端vite+vue3——可视化页面性能耗时指标(fmp、fp),希望对大家解决编程问题提供一定的参考价值,需要的开发者们随着小编来一起学习吧!
文章目录
- ⭐前言
- 💖vue3系列文章
- ⭐可视化fmp、fp指标
- 💖 MutationObserver 计算 dom的变化
- 💖 使用条形图展示 fmp、fp时间
- ⭐项目代码
- ⭐结束

⭐前言
大家好,我是yma16,本文分享关于 前端vite+vue3——可视化页面性能耗时(fmp、fp)。
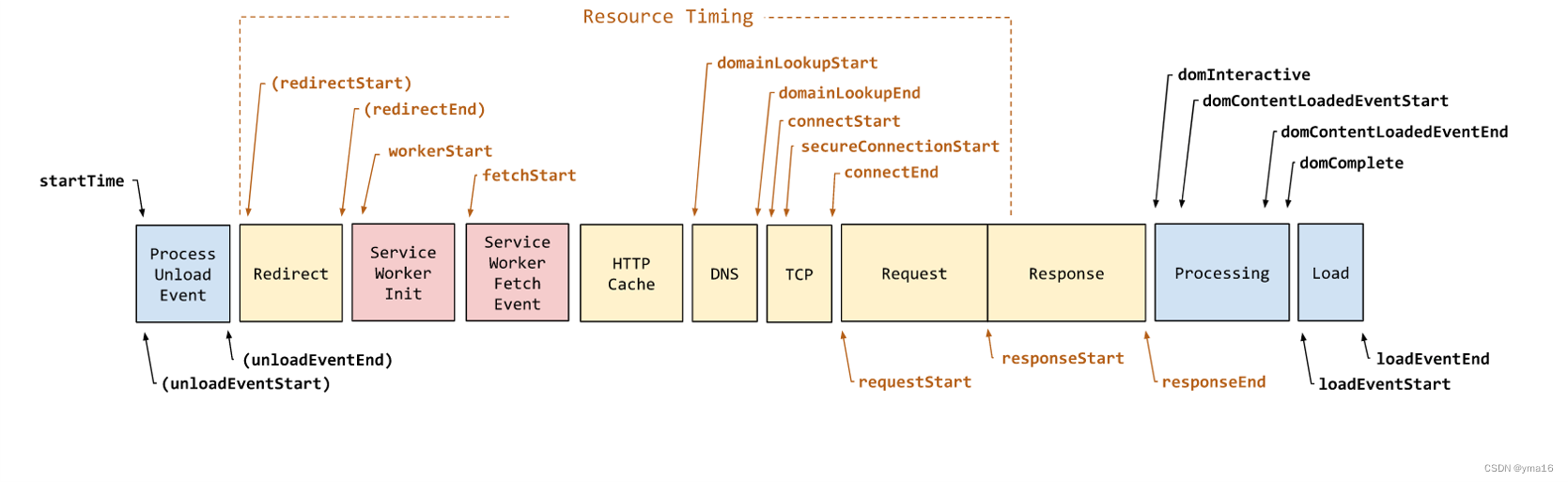
fmp的定义
FMP(First Meaningful Paint)是一种衡量网页加载性能的指标。它表示在加载过程中,浏览器首次渲染出有意义的内容所花费的时间。有意义的内容指的是用户可以看到和交互的元素,如文本、图片、按钮等。
首次渲染的定义可以根据具体的要求和场景而有所不同。通常情况下,首次渲染是指在页面加载过程中,浏览器首次绘制出用户能够理解和识别的内容,而不是空白页面或加载指示符。
FMP的计算方法可以根据不同的标准和工具而有所差异,但通常会考虑页面上可见的内容和用户可交互的元素。在计算FMP时,一般会排除一些延迟加载的元素,如懒加载的图片或动态加载的内容,以确保测量的是真正有意义的渲染时间。
fp的定义
FP(First Paint)是指浏览器首次将像素渲染到屏幕上的时间点

💖vue3系列文章
vue3 + fastapi 实现选择目录所有文件自定义上传到服务器
前端vue2、vue3去掉url路由“ # ”号——nginx配置
csdn新星计划vue3+ts+antd赛道——利用inscode搭建vue3(ts)+antd前端模板
认识vite_vue3 初始化项目到打包
python_selenuim获取csdn新星赛道选手所在城市用echarts地图显示
让大模型分析csdn文章质量 —— 提取csdn博客评论在文心一言分析评论区内容
前端vue3——html2canvas给网站截图生成宣传海报
vue3+echarts可视化——记录我的2023编程之旅
前端vite+vue3——自动化配置路由布局
⭐可视化fmp、fp指标
由于vue是SPA(single-page application)单页面项目,会导致首次加载时间长:SPA需要加载整个应用的代码和资源,首次加载时间可能会比传统的多页面应用长。
以下是我个人计算fmp的逻辑
- fmp:监听 vue挂载的节点(dom的id为root)首次变化时间
- fp: 监听 beforeMounted的时间为白屏结束时间
计算的单位使用performance.now
performance.now()是一个JavaScript方法,用于获取当前时间戳,精确到毫秒级。它返回一个DOMHighResTimeStamp对象,表示从性能测量器启动到调用performance.now()的时间间隔。这个方法通常用于性能测量和性能优化,可以用于计算代码执行时间、动画帧率、网络请求延迟等。
💖 MutationObserver 计算 dom的变化
MutationObserver 接口提供了监视对 DOM 树所做更改的能力
使用示例:
// 选择需要观察变动的节点
const targetNode = document.getElementById("some-id");// 观察器的配置(需要观察什么变动)
const config = { attributes: true, childList: true, subtree: true };// 当观察到变动时执行的回调函数
const callback = function (mutationsList, observer) {// Use traditional 'for loops' for IE 11for (let mutation of mutationsList) {if (mutation.type === "childList") {console.log("A child node has been added or removed.");} else if (mutation.type === "attributes") {console.log("The " + mutation.attributeName + " attribute was modified.");}}
};// 创建一个观察器实例并传入回调函数
const observer = new MutationObserver(callback);// 以上述配置开始观察目标节点
observer.observe(targetNode, config);// 之后,可停止观察
observer.disconnect();
在vue的入口页面app.vue编写监听rootDom变化的逻辑
mutationAction 函数如下(将节点的高度大于0作为结束监听的条件即fmp的结束时间)
// 监听 dom变化
mutationAction(listenDom, callbackAction) {// 观察器的配置(需要观察什么变动)const config = { attributes: true, childList: true, subtree: true };// 当观察到变动时执行的回调函数const callback = function (mutationsList, observer) {// 渲染高度const renderHeight = listenDom.offsetHeightif (parseInt(renderHeight)) {// 第一次监听dom 存在高度则判定已经渲染完root节点callbackAction()// 停止观察observer.disconnect();}};// 创建一个观察器实例并传入回调函数const observer = new MutationObserver(callback);// 以上述配置开始观察目标节点observer.observe(listenDom, config);
}
在App.vue的声明周期onBerforeMount运行
<script setup>
import { ref, onBeforeMount } from "vue";
// 查找次数,用于统计最大查找次数避免奔溃
const findAppCount = ref(0)// 监听 dom变化
mutationAction(listenDom, callbackAction) {// 观察器的配置(需要观察什么变动)const config = { attributes: true, childList: true, subtree: true };// 当观察到变动时执行的回调函数const callback = function (mutationsList, observer) {// 渲染高度const renderHeight = listenDom.offsetHeightif (parseInt(renderHeight)) {// 第一次监听dom 存在高度则判定已经渲染完root节点callbackAction()// 停止观察observer.disconnect();}};// 创建一个观察器实例并传入回调函数const observer = new MutationObserver(callback);// 以上述配置开始观察目标节点observer.observe(listenDom, config);
}const findAppDom = () => {const appDom = document.getElementById('app')findAppCount.value += 1if (appDom) {mutationAction(appDom, () => {const fmp=performance.now()})}else if (findAppCount <= 1000) {findAppDom()}
}
onBeforeMount(() => {// 白屏时间const fp = performance.now()findAppDom();
})
</script>
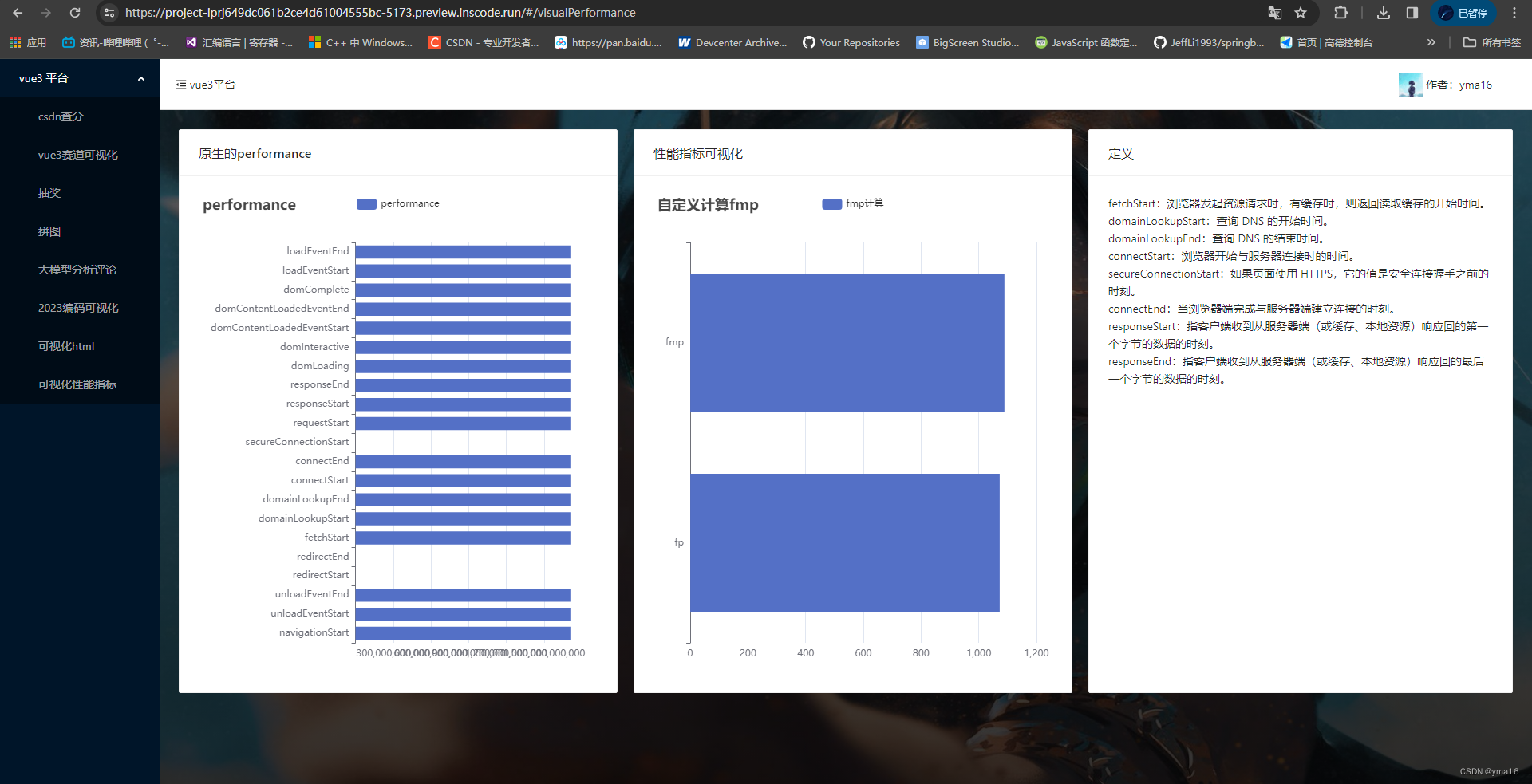
💖 使用条形图展示 fmp、fp时间
使用条形图对性能指标耗时进行可视化
条形图展示数据的vue界面编写
<script lang="js" setup>
import { reactive, onMounted } from 'vue';
import * as echarts from 'echarts';import { useStore } from "vuex";const store = useStore();
const state = reactive({leftTitle: '原生的performance',leftDomId: 'visual-performance-id',rightTitle: '性能指标可视化',rightDomId: 'visual-performance-id-right',chartTitle: '性能指标',echartInstance: null,})const initLeftChart = () => {// 基于准备好的dom,初始化echarts实例const domInstance = document.getElementById(state.leftDomId)if (domInstance) {domInstance.removeAttribute('_echarts_instance_')}else {return}console.log(performance)console.log(Object.keys(performance.timing))const label = []const data = []for (let key in performance.timing) {if (key != 'toJSON') {label.push(key)data.push(performance.timing[key])}}const myChart = echarts.init(domInstance);const option = {title: {text: 'performance'},tooltip: {trigger: 'axis',axisPointer: {type: 'shadow'}},legend: {},grid: {left: '3%',right: '4%',bottom: '3%',containLabel: true},xAxis: {type: 'value',boundaryGap: [0, 0.01]},yAxis: {type: 'category',data: label},series: [{name: 'performance',type: 'bar',data: data}]};console.log('option', option)// 使用刚指定的配置项和数据显示图表。myChart.setOption(option, true);// 监听state.echartInstance = myChart;myChart.on('click', function (params) {console.log('params', params)});window.onresize = myChart.resize;
}const initRightChart = () => {// 基于准备好的dom,初始化echarts实例const domInstance = document.getElementById(state.rightDomId)if (domInstance) {domInstance.removeAttribute('_echarts_instance_')}else {return}const performanceConfig = store.getters["common/performanceConfig"]console.log('performanceConfig________________', performanceConfig)const label = []const data = []Object.keys(performanceConfig).forEach(key => {data.push(performanceConfig[key])label.push(key)})const myChart = echarts.init(domInstance);const option = {title: {text: '自定义计算fmp'},tooltip: {trigger: 'axis',axisPointer: {type: 'shadow'}},legend: {},grid: {left: '3%',right: '4%',bottom: '3%',containLabel: true},xAxis: {type: 'value',boundaryGap: [0, 0.01]},yAxis: {type: 'category',data: label},series: [{name: 'fmp计算',type: 'bar',data: data}]};console.log('option', option)// 使用刚指定的配置项和数据显示图表。myChart.setOption(option, true);// 监听state.echartInstance = myChart;myChart.on('click', function (params) {console.log('params', params)});window.onresize = myChart.resize;
}onMounted(() => {initLeftChart()initRightChart()
})
</script>
<template><div><div style="display:flex;"><a-card :title="state.leftTitle" style="width: 600px"><div :id="state.leftDomId" style="width: 500px;height:600px;"></div></a-card><a-card :title="state.rightTitle" style="width: 600px;margin-left:20px"><div :id="state.rightDomId" style="width: 500px;height:600px;"></div><div></div></a-card><a-card style="margin-left:20px" title="定义"><div><div>fetchStart:浏览器发起资源请求时,有缓存时,则返回读取缓存的开始时间。<br>domainLookupStart:查询 DNS 的开始时间。<br>domainLookupEnd:查询 DNS 的结束时间。<br>connectStart:浏览器开始与服务器连接时的时间。<br>secureConnectionStart:如果页面使用 HTTPS,它的值是安全连接握手之前的时刻。<br>connectEnd:当浏览器端完成与服务器端建立连接的时刻。<br>responseStart:指客户端收到从服务器端(或缓存、本地资源)响应回的第一个字节的数据的时刻。<br>responseEnd:指客户端收到从服务器端(或缓存、本地资源)响应回的最后一个字节的数据的时刻。<br></div></div></a-card></div></div>
</template>
效果:
⭐项目代码
前端项目inscode如下:
⭐结束
本文分享到这结束,如有错误或者不足之处欢迎指出!

👍 点赞,是我创作的动力!
⭐️ 收藏,是我努力的方向!
✏️ 评论,是我进步的财富!
💖 最后,感谢你的阅读!
这篇关于前端vite+vue3——可视化页面性能耗时指标(fmp、fp)的文章就介绍到这儿,希望我们推荐的文章对编程师们有所帮助!






