本文主要是介绍数据结构之霍夫曼树,希望对大家解决编程问题提供一定的参考价值,需要的开发者们随着小编来一起学习吧!
计算机里每个字符在没有压缩的文本文件中都由一个字节(如ASCII码)或两个字节(如Unicode码)表示。这些方案中,每个字符需要相同的位数
下表列出了字母对应的ASCII码
字母 十进制 二进制
A 65 01000001
B 66 01000010
C 67 01000011
……
X 88 01011000
Y 89 01011001
Z 90 01011010
在英文中,字母E的使用频率最高,而字母Z的使用频率最低,但是,无论使用频率高低,我们一律使用相同位数的编码来存储,是不是有些浪费空间呢?试想,如果我们对使用频率高的字母用较少的位数来存储,而对使用频率低的字母用较多的位数来存储,会大大提升存储效率
霍夫曼编码就是根据以上的设想来处理数据压缩的
例如,我们要发送一句消息:
SUSIE SAYS IT IS EASY
统计所有符号出现的频率:
换行符 1次
T 1次
U 1次
A 2次
E 2次
Y 2次
I 3次
空格 4次
S 6次
S出现的频率最多,我们可以将它的编码设为10,其次是空格,我们将它设置为00,接下来的编码必须增加位数了。三位码我们有八种选择:000,001,010,011,100,101,110,111。但是,以10或00开头的是不能使用的,只能从010,011,110,111中选择。因为如果我们用101表示I,用010表示Y,101010既可以分解为101,010两个有意义的编码,也能分解为10,10,10三个有意义的编码,这显然是不允许的。我们必须保证,任何信息编码之后,解码时都不会出现歧义。借助霍夫曼树就能便捷的实现编码
霍夫曼树是最优二叉树。树的带权路径长度规定为所有叶子结点的带权路径长度之和,带权路径长度最短的树,即为最优二叉树。在最优二叉树中,权值较大的结点离根较近。
首先就需要构建一个霍夫曼树,一般利用优先级队列来构建霍夫曼树
以上面的消息为例,我们先来分析一下构建霍夫曼树的过程,下图中,if代表换行符,sp代表空格
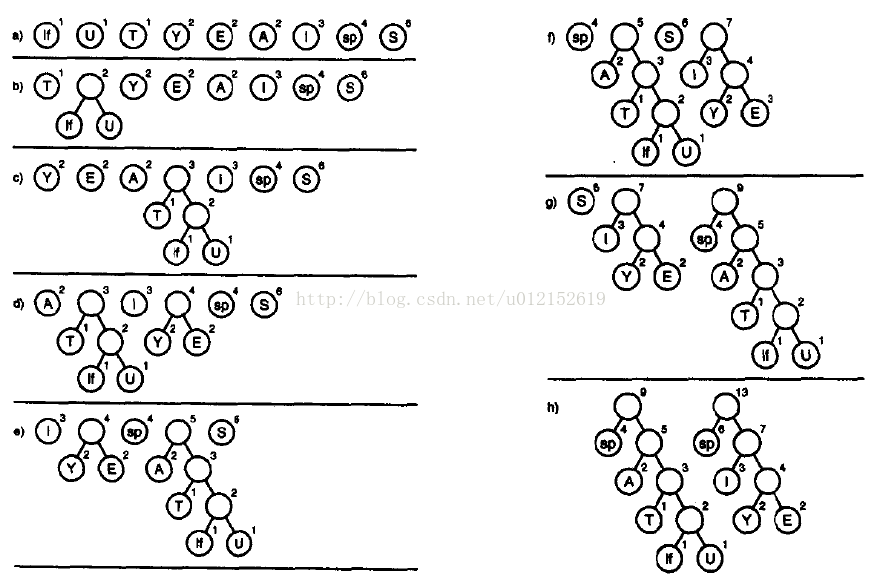
首先,将字符按照频率插入一个优先级队列,频率越低越靠近队头,然后循环执行下面的操作:
1、取出队头的两个树
2、以它们为左右子节点构建一棵新树,新树的权值是两者之和
3、将这棵新树插入队列
直到队列中只有一棵树时,这棵树就是我们需要的霍夫曼树
接下来我们用Java来实现上面的过程,代码如下:
-
- public class Node{
- private String key;
- private int frequency;
- private Node left;
- private Node right;
- private Node next;
-
- public Node(int fre,String str){
- frequency = fre;
- key = str;
- }
- public Node(int fre){
- frequency = fre;
- }
-
- public String getKey() {
- return key;
- }
- public void setKey(String key) {
- this.key = key;
- }
- public Node getLeft() {
- return left;
- }
- public void setLeft(Node left) {
- this.left = left;
- }
- public Node getRight() {
- return right;
- }
- public void setRight(Node right) {
- this.right = right;
- }
- public Node getNext() {
- return next;
- }
- public void setNext(Node next) {
- this.next = next;
- }
- public int getFrequency() {
- return frequency;
- }
- public void setFrequency(int frequency) {
- this.frequency = frequency;
- }
- }
-
- public class PriorityQueue{
- private Node first;
- private int length;
-
- public PriorityQueue(){
- length = 0;
- first = null;
- }
-
-
- public void insert(Node node){
- if(first == null){
- first = node;
- }else{
- Node cur = first;
- Node previous = null;
- while(cur.getFrequency()< node.getFrequency()){
- previous = cur;
- if(cur.getNext() ==null){
- cur = null;
- break;
- }else{
- cur =cur.getNext();
- }
-
- }
- if(previous == null){
- node.setNext(first);
- first = node;
- }else if(cur == null){
- previous.setNext(node);
- }else{
- previous.setNext(node);
- node.setNext(cur);
- }
- }
- length++;
- }
-
-
- public Node delete(){
- Node temp = first;
- first = first.getNext();
- length--;
- return temp;
- }
-
-
- public int getLength(){
- return length;
- }
-
-
- public void display(){
- Node cur = first;
- System.out.print("优先级队列:\t");
- while(cur != null){
- System.out.print(cur.getKey()+":"+cur.getFrequency()+"\t");
- cur = cur.getNext();
- }
- System.out.println();
- }
-
-
- public HuffmanTree buildHuffmanTree(){
- while(length > 1){
- Node hLeft = delete();
- Node hRight = delete();
-
- Node hRoot = new Node(hLeft.getFrequency()+hRight.getFrequency());
- hRoot.setLeft(hLeft);
- hRoot.setRight(hRight);
- insert(hRoot);
- }
-
- return new HuffmanTree(first);
- }
-
- }
- import java.util.HashMap;
- import java.util.Map;
-
- public class HuffmanTree {
- private Node root;
- private Map codeSet = new HashMap();
-
- public HuffmanTree(Node root){
- this.root = root;
- buildCodeSet(root,"");
- }
-
-
-
- private void buildCodeSet(NodecurrentNode,String currentCode){
- if(currentNode.getKey() != null){
-
- codeSet.put(currentNode.getKey(),currentCode);
- }else{
-
- buildCodeSet(currentNode.getLeft(),currentCode+"0");
-
- buildCodeSet(currentNode.getRight(),currentCode+"1");
- }
- }
-
-
- public Map getCodeSet(){
- return codeSet;
- }
-
- }
-
- public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{
- PriorityQueue queue = new PriorityQueue();
- Node n1 = new Node(1,"if");
- Node n2 = new Node(1,"U");
- Node n3 = new Node(1,"T");
- Node n4 = new Node(2,"Y");
- Node n5 = new Node(2,"E");
- Node n6 = new Node(2,"A");
- Node n7 = new Node(3,"I");
- Node n8 = new Node(4,"sp");
- Node n9 = new Node(5,"S");
- queue.insert(n3);
- queue.insert(n2);
- queue.insert(n1);
- queue.insert(n6);
- queue.insert(n5);
- queue.insert(n4);
- queue.insert(n7);
- queue.insert(n8);
- queue.insert(n9);
- queue.display();
-
- HuffmanTree tree =queue.buildHuffmanTree();
- Map map = tree.getCodeSet();
- Iterator it =map.entrySet().iterator();
- System.out.println("霍夫曼编码结果:");
- while(it.hasNext()){
- Entry<String,String>entry = (Entry)it.next();
- System.out.println(entry.getKey()+"——>"+entry.getValue());
- }
- }
控制台打印结果如下图所示:

可见,达到了预期的效果
秉承没有最好,只有更好的精神,我们不应该就此止步。现在我们做到的只是得到某个字符对应的霍夫曼编码,但是这个字符的词频仍然需要我们手工去统计、输入,更深入的思考一下,能不能更智能化一点,只要我们输入完整的一段消息,就能给出对应的霍夫曼编码,而且能对编码进行解码呢?
显然是可以的,先面就让我们用神奇的java语言来对上面的底层操作进行更高级的封装,来达到预期的功能
就是说,我们要利用上面已经写出的代码来封装一个编码类,这个类的一个方法接受一个字符串消息,返回霍夫曼编码,此外,还有一个解码类,接受一段完整的霍夫曼编码,返回解码后的消息内容。这实际上就是压缩与解压的模拟过程
- import java.util.HashMap;
- import java.util.Iterator;
- import java.util.Map;
- import java.util.Map.Entry;
-
-
- public class HuffmanEncoder {
- private PriorityQueue queue;
- private HuffmanTree tree;
- private String [] message;
- private Map keyMap;
- private Map codeSet;
-
- public HuffmanEncoder(){
- queue = new PriorityQueue();
- keyMap = new HashMap<String,Integer>();
- }
-
-
- public String encode(String msg){
- resolveMassage(msg);
- buildCodeSet();
- String code = "";
- for(inti=0;i<message.length;i++){
- code =code+codeSet.get(message[i]);
- }
- return code;
- }
-
-
- private void resolveMassage(String msg){
-
- char [] chars =msg.toCharArray();
- message = new String[chars.length];
- for(int i =0;i<chars.length;i++){
- String key = "";
- key =chars[i]+"";
-
- message [i] = key;
- if(keyMap.containsKey(key)){
- keyMap.put(key,(Integer)keyMap.get(key)+1);
- }else{
- keyMap.put(key,1);
- }
- }
- }
-
-
- private void buildCodeSet(){
- Iterator it =keyMap.entrySet().iterator();
- while(it.hasNext()){
- Entry entry =(Entry)it.next();
-
- queue.insert(new Node((Integer)entry.getValue(),(String)entry.getKey()));
- }
- queue.display();
- tree =queue.buildHuffmanTree();
- codeSet = tree.getCodeSet();
- }
-
-
- public void printCodeSet(){
- Iterator it =codeSet.entrySet().iterator();
- System.out.println("代码集:");
- while(it.hasNext()){
- Entry entry =(Entry)it.next();
- System.out.println(entry.getKey()+"——>"+entry.getValue());
- }
- System.out.println();
- }
-
-
- public Map getCodeSet(){
- return codeSet;
- }
- }
- import java.util.Iterator;
- import java.util.Map;
- import java.util.Map.Entry;
-
-
- public class HuffmanDecoder {
- private Map codeSet;
-
- public HuffmanDecoder(Map map){
- codeSet = map;
- }
-
-
- public String decode(String code){
- String message = "";
- String key = "";
- char [] chars = code.toCharArray();
- for(int i=0;i<chars.length;i++){
- key += chars[i];
- if(codeSet.containsValue(key)){
- Iterator it =codeSet.entrySet().iterator();
- while(it.hasNext()){
- Entry entry = (Entry)it.next();
- if(entry.getValue().equals(key)){
- message+= entry.getKey();
- }
- }
- key ="";
- }else{
- continue;
- }
- }
- return message;
- }
- }
-
- public static void main(String[] args){
-
- String message = "chen long fei is hero !";
- HuffmanEncoder encoder = new HuffmanEncoder();
- String code =encoder.encode(message);
-
- encoder.printCodeSet();
- System.out.print("编码结果:");
- System.out.println(code);
-
- HuffmanDecoder decoder = new HuffmanDecoder(encoder.getCodeSet());
- String message2 =decoder.decode(code);
- System.out.print("解码结果:");
- System.out.println(message);
- }
运行结果如下图所示:

这篇关于数据结构之霍夫曼树的文章就介绍到这儿,希望我们推荐的文章对编程师们有所帮助!