本文主要是介绍数据结构与算法大作业——四叉树自适应模糊,希望对大家解决编程问题提供一定的参考价值,需要的开发者们随着小编来一起学习吧!
四叉树自适应模糊
- 一.实验要求
- 二.背景知识
- PPM文件格式理解
- 四叉树
- 高斯模糊
- 三.思路总结:
- 四.代码实现(由于未到作业截止时间,只给出代码框架,后续更新)
- Quadtree.h
- Quadtree.cpp
- main.cpp
- 五. 效果展示
- 六.总结反思
一.实验要求
能够正确的对图像建立四叉树;
对于输入的图像,四叉树能够输出模糊的结果
对颜色相近的区域进行模糊
二.背景知识
PPM文件格式理解
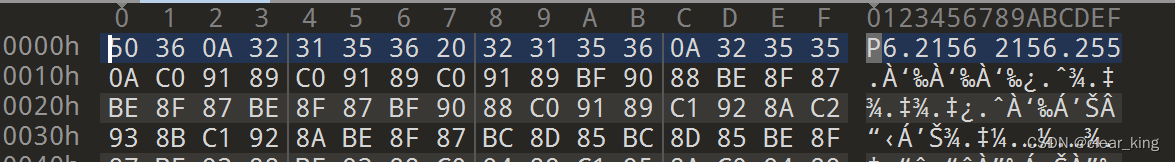
可通过十六进制编辑器 010editor 打开查看二进制信息
官网获取 010editor
| 信息 | 含义 |
|---|---|
| P6 | 指明PPM的编码格式 |
| 2156 2156 | 图像大小为2156*2156 |
| 255 | RGB的每个色彩值范围为0~255 |
| C0 91 89(16进制第二行) | 表示一个像素的RGB颜色(后面类推) |
用 Photoshop 打开ppm文件查看图片
四叉树
四叉树,又称四元树,是一种树状数据结构。四元树常应用于二维空间数据的分析与分类
四叉树(Q-Tree)是一种树形数据结构。四叉树的定义是:它的每个节点下至多可以有四个子节点,通常把一部分二维空间细分为四个象限或区域并把该区域里的相关信息存入到四叉树节点中 。这个区域可以是正方形、矩形或是任意形状。以下为四叉树的二维空间结构(左)和存储结构(右)示意图(注意节点颜色与网格边框颜色):
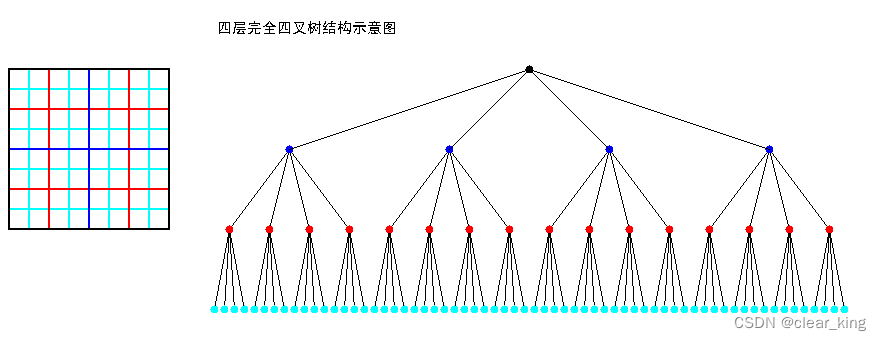
四叉树的每一个节点代表一个矩形区域(如上图黑色的根节点代表最外围黑色边框的矩形区域),每一个矩形区域又可划分为四个小矩形区域,这四个小矩形区域作为四个子节点所代表的矩形区域。(递归)
四叉树把2D空间进行了分组
类似的,较之四叉树,八叉树将场景从二维空间延伸到了三维空间。
更多关于四叉树的抽象的描述
高斯模糊
它将正态分布(又名"高斯分布")用于图像处理。本质上,它是一种数据平滑技术(data smoothing)
原理大概就是,每一个像素都取周边像素的平均值,“中间点"取"周围点"的平均值,实现数值上的一种"平滑化”,图形上的模糊效果
这里用结论就好, 具体数学处理 我们不用太过关心
用到一个做高斯模糊用的权重矩阵:
{{0.0453542, 0.0566406, 0.0453542}, {0.0566406, 0.0707355, 0.0566406}, {0.0453542, 0.0566406, 0.0453542}}对于RGB三个数值分别经过多轮高斯模糊处理详见后面
三.思路总结:
- 先将图片整个像素信息存储进一个数据类型(后面用color构成的二维数组来存)
- 抽象四叉树结点,每一个结点包含一部分二维图像的信息
- 根据对应二维图像像建立四叉树(图像的模糊、压缩)——若其图像的R或G或B值任意一个大于标准设定方差,则该子叶继续往下划分; 若小于等于,则不再划分,并将该子叶的矩形区域内的所有RGB值赋予其为平均值
- 再通过高斯模糊处理数据(图像的平滑处理)
- 再将此数据输出到结果ppm文件
四.代码实现(由于未到作业截止时间,只给出代码框架,后续更新)
Quadtree.h
struct color{unsigned char r;unsigned char g;unsigned char b;
} ;int operator== (color c1, color c2);
//color operator==(const color other);
void Guass(color **colors, int width);
//对处理过的图像(细分矩阵的程度不同)进行高斯模糊,半径为1class Node {
private:int width; //当前像素区块的宽度int height; //当前像素区块的高度int x; //当前像素区块左上角顶点像素的横坐标int y; //当前像素区块左上角顶点像素的纵坐标int mean_r; //Rmeanint mean_g; //Gmeanint mean_b; //BmeanNode *children1; //pointer to four other nodeNode *children2; //pointer to four other nodeNode *children3; //pointer to four other nodeNode *children4; //pointer to four other nodepublic:Node();~Node();Node(int input_width, int input_height, int x, int y);void QuadCreateBranch(color **colors, int fangcha);void QuadPrint(color **colors);
};
Quadtree.cpp
#include "Quadtree.h"
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;Node::Node() {//TODOmean_r = 0;mean_g = 0;mean_b = 0;
// p = nullptr;width = 0;height = 0;x = 0;y = 0;children1 =children2 =children3= children4= nullptr;
}Node::Node(int input_width, int input_height, int x, int y) {children1 = nullptr;children2 = nullptr;children3 = nullptr;children4 = nullptr;mean_r = 0;mean_g = 0;mean_b = 0;width = input_width;height = input_height;this->x = x;this->y = y;
}void Node::QuadCreateBranch(color **colors, int fangcha) {求该节点对应二维图像的RGB均值int ave_r = 0;int ave_g = 0;int ave_b = 0;for (int i=x;i<x+width;i++){for (int j=y;j<y+height;j++){ave_r += colors[i][j].r;ave_g += colors[i][j].g;ave_b += colors[i][j].b;}}ave_r /= width*height;ave_g /= width*height;ave_b /= width*height;mean_r = ave_r;mean_g = ave_g;mean_b = ave_b;求该节点的RGB方差long long fangcha_r = 0;long long fangcha_g = 0;long long fangcha_b = 0;for (int i=x;i<x+width;i++){for (int j=y;j<y+height;j++){fangcha_r += (colors[i][j].r - ave_r)*(colors[i][j].r - ave_r);fangcha_g += (colors[i][j].g - ave_g)*(colors[i][j].g - ave_g);fangcha_b += (colors[i][j].b - ave_b)*(colors[i][j].b - ave_b);}}fangcha_r /= width*height;fangcha_g /= width*height;fangcha_b /= width*height;方差满足一定条件就递归建立儿子if (fangcha <= 1000){if ( (fangcha_r > fangcha || fangcha_g > fangcha || fangcha_b > fangcha) ){
/*创建各孩子分支*/
// int input_width, int input_height, int x, int y// |// children2 | children1// ______________// |// children3 | children4children1 = new Node(width/2,height/2, x+width/2, y);children1->QuadCreateBranch(colors, fangcha);children2 = new Node(width/2,height/2,x, y);children2->QuadCreateBranch(colors,fangcha);children3= new Node(width/2,height/2,x, y+height/2);children3->QuadCreateBranch(colors,fangcha);children4 = new Node(width/2,height/2,x+width/2,y+height/2);children4->QuadCreateBranch(colors,fangcha);}}else {if ( (fangcha_r > fangcha || fangcha_g > fangcha || fangcha_b > fangcha)&& width > 100){children1 = new Node(width/2,height/2, x+width/2, y);children1->QuadCreateBranch(colors, fangcha);children2 = new Node(width/2,height/2,x, y);children2->QuadCreateBranch(colors,fangcha);children3= new Node(width/2,height/2,x, y+height/2);children3->QuadCreateBranch(colors,fangcha);children4 = new Node(width/2,height/2,x+width/2,y+height/2);children4->QuadCreateBranch(colors,fangcha);}}}void Node::QuadPrint(color **colors) {for (int i=x;i<x+width;i++){for (int j=y;j<y+height;j++){colors[i][j].r = mean_r;colors[i][j].g = mean_g;colors[i][j].b = mean_b;}}if (children1 != nullptr) children1->QuadPrint(colors);if (children2 != nullptr) children2->QuadPrint(colors);if (children3 != nullptr) children3->QuadPrint(colors);if (children4 != nullptr) children4->QuadPrint(colors);
}int operator==(color c1, color c2){if (c1.b == c2.b && c1.r == c2.r && c1.g == c2.g) return true;return false;
}/*第二部分:高斯模糊*/
void Guass(color **colors, int width)//对处理过的图像(细分矩阵的程度不同)进行高斯模糊,半径为1
{double quanzhong[3][3] = {{0.0453542, 0.0566406, 0.0453542},{0.0566406, 0.0707355, 0.0566406},{0.0453542, 0.0566406, 0.0453542}};for(int i=1; i<width-1; i++)for(int j=1; j<width-1; j++){double gave = 0, rave = 0, bave = 0;for(int k=-1; k<=1; k++)//对于每一个点都进行高斯模糊,之前每一个点都处理过了,相当于压缩后(抛去细节)再模糊?for(int l=-1; l<=1; l++){rave += (double)(colors[j+k][i+l].r) * quanzhong[k+1][l+1] / 0.4787147;gave += (double)(colors[j+k][i+l].g) * quanzhong[k+1][l+1] / 0.4787147;bave += (double)(colors[j+k][i+l].b) * quanzhong[k+1][l+1] / 0.4787147;}colors[j][i].r = rave;colors[j][i].g = gave;colors[j][i].b = bave;}
}
main.cpp
#include "Quadtree.h"
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;int main(){char *inFile="/Project/C/Quadtree Adaptive Blurring/yue.ppm";FILE *f = fopen(inFile, "rb");char u[3]; // placehoderint width, height, max_value;fscanf(f, "%s%d%d%d%c", u, &width, &height, &max_value, &u[0]);将图片整个像素信息存储进colorsint i;color **colors;//[height][width]colors = (color **)malloc(width*sizeof(color*));for (i = 0; i < height; i++)colors[i] = (color *)malloc(width*sizeof(color));for (i = 0; i < height; i++)fread(colors[i], sizeof(color), width, f);fclose(f);给定模糊程度int FangCha,tolerance;int FangCha_L[6]={100,300,500,900, 1400,2200};cout << "input tolerance(1~5):";cin >> tolerance;FangCha = FangCha_L[tolerance];递归建立四叉树Node *root = new Node(width, height, 0, 0);root->QuadCreateBranch(colors, FangCha);树写到colors里root->QuadPrint(colors);多次高斯模糊for (int i = 1;i<=20;i++)//这里为20次Guass(colors,width);将此数据输出到结果ppm文件char *outfile = "/Project/C/Quadtree Adaptive Blurring/result.ppm";FILE *rf = fopen(outfile, "wb");fprintf(rf, "P6\n");fprintf(rf, "%d %d\n", width, width);fprintf(rf, "255\n");for (int i = 0; i < width; i++)fwrite(colors[i], sizeof(color), width, f);fclose(f);cout << "Blurring finished, please preview result.ppm with ps" << endl;
}
五. 效果展示
本实现可输入模糊程度1~5(凭视觉效果让模糊程度对应方差)
当然也可以自己给定任意非负整数为方差。
分别对应以下图片:
程度1(对应方差300)

程度2(对应方差500)

程度3(对应方差900)

程度4(对应方差1400);(一些比价精细的地方如螃蟹腿,尽管方差很大,但是不希望再继续建立子节点,所以添加条件:图片大小<100,不再递归建立四叉树)

程度5(对应方差2200) 惊现?!!!(咱可不是黑子)

用写好的程序模糊处理 自家piu亮的瓜蛋儿~嘿嘿嘿
六.总结反思
本次作业个人感觉难在将图像信息和四叉树结构对应的抽象上,各个模块功能的实现还是比较简单。
代码个人感觉写得还是很漂亮,当然做这么一个视觉反馈很直观的东西还是比较有趣的,出于时间精力有限,后续同学们有精力还可以尝试添加可视化可交互的图像处理小程序,向P图软件那样快捷调节模糊程度,或者在选定区域内模糊
当然不足很明显,本作业虽然实现了图片模糊,“屏蔽”掉了图片的一部分信息,但是借助ppm文件储存模糊图片信息,其大小并无显著改变

参考文章
- https://blog.csdn.net/zhanxinhang/article/details/6706217
- https://blog.csdn.net/kinghzkingkkk/article/details/70226214
- https://blog.csdn.net/m0_68136379/article/details/129100656
- https://blog.csdn.net/Quincuntial/article/details/50625389
这篇关于数据结构与算法大作业——四叉树自适应模糊的文章就介绍到这儿,希望我们推荐的文章对编程师们有所帮助!






