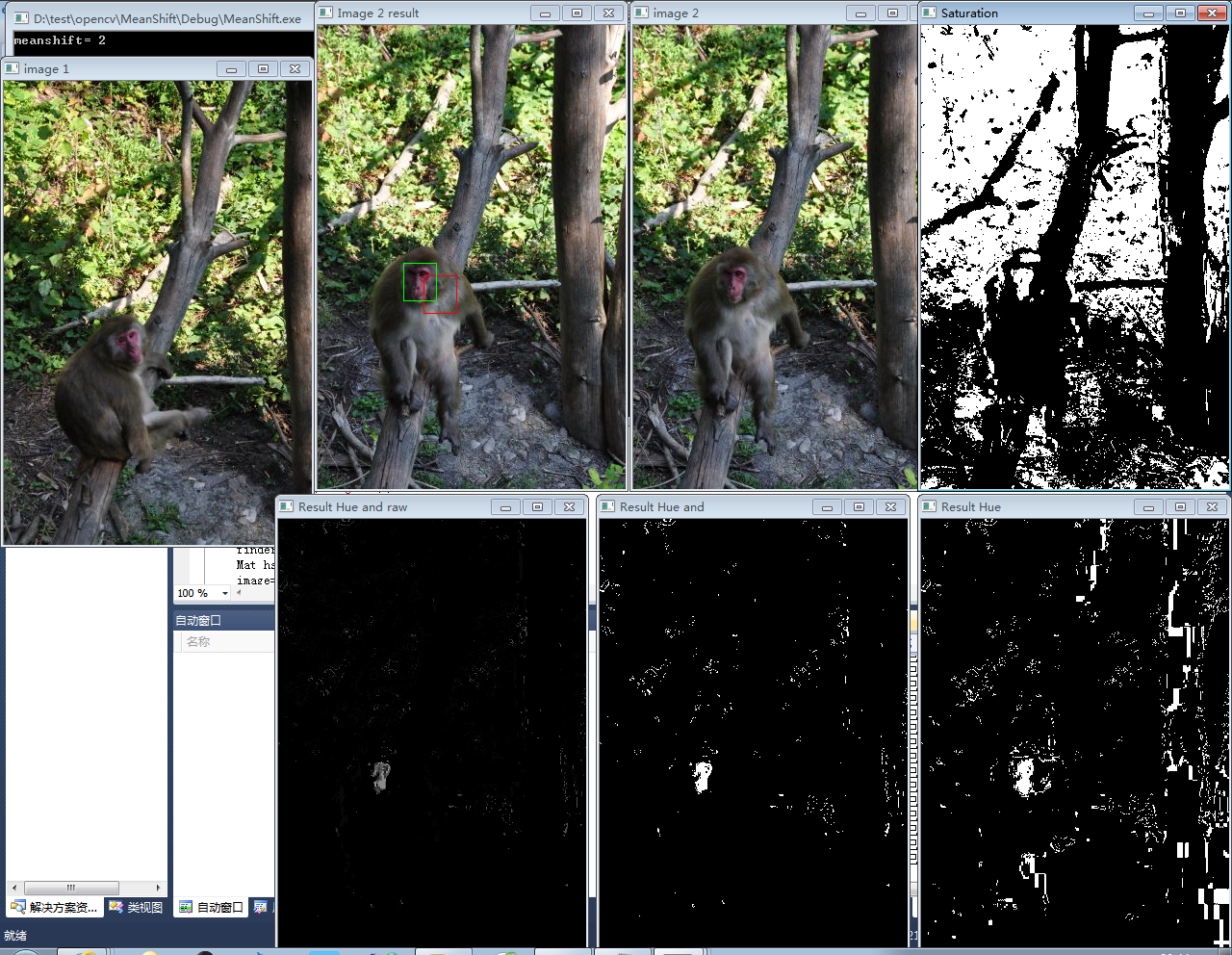
本文主要是介绍使用均值漂移算法查找物体,源代码,希望对大家解决编程问题提供一定的参考价值,需要的开发者们随着小编来一起学习吧!
- #if !defined OFINDER
- #define OFINDER
- #include <opencv2\core\core.hpp>
- #include <opencv2\imgproc\imgproc.hpp>
- class ContentFinder {
- private:
- float hranges[2];
- const float* ranges[3];
- int channels[3];
- float threshold;
- cv::MatND histogram;
- cv::SparseMat shistogram;
- bool isSparse;
- public:
- ContentFinder() : threshold(0.1f), isSparse(false) {
- ranges[0]= hranges; // all channels have the same range
- ranges[1]= hranges;
- ranges[2]= hranges;
- }
- // Sets the threshold on histogram values [0,1]
- void setThreshold(float t) {
- threshold= t;
- }
- // Gets the threshold
- float getThreshold() {
- return threshold;
- }
- // Sets the reference histogram
- void setHistogram(const cv::MatND& h) {
- isSparse= false;
- histogram= h;
- cv::normalize(histogram,histogram,1.0);
- }
- // Sets the reference histogram
- void setHistogram(const cv::SparseMat& h) {
- isSparse= true;
- shistogram= h;
- cv::normalize(shistogram,shistogram,1.0,cv::NORM_L2);
- }
- cv::Mat find(const cv::Mat& image) {
- cv::Mat result;
- hranges[0]= 0.0; // range [0,255]
- hranges[1]= 255.0;
- channels[0]= 0; // the three channels
- channels[1]= 1;
- channels[2]= 2;
- if (isSparse) { // call the right function based on histogram type
- cv::calcBackProject(&image,
- 1, // one image
- channels, // vector specifying what histogram dimensions belong to what image channels
- shistogram, // the histogram we are using
- result, // the resulting back projection image
- ranges, // the range of values, for each dimension
- 255.0 // the scaling factor is chosen such that a histogram value of 1 maps to 255
- );
- } else {
- cv::calcBackProject(&image,
- 1, // one image
- channels, // vector specifying what histogram dimensions belong to what image channels
- histogram, // the histogram we are using
- result, // the resulting back projection image
- ranges, // the range of values, for each dimension
- 255.0 // the scaling factor is chosen such that a histogram value of 1 maps to 255
- );
- }
- // Threshold back projection to obtain a binary image
- if (threshold>0.0)
- cv::threshold(result, result, 255*threshold, 255, cv::THRESH_BINARY);
- return result;
- }
- cv::Mat find(const cv::Mat& image, float minValue, float maxValue, int *channels, int dim) {
- cv::Mat result;
- hranges[0]= minValue;
- hranges[1]= maxValue;
- for (int i=0; i<dim; i++)
- this->channels[i]= channels[i];
- if (isSparse) { // call the right function based on histogram type
- cv::calcBackProject(&image,
- 1, // we only use one image at a time
- channels, // vector specifying what histogram dimensions belong to what image channels
- shistogram, // the histogram we are using
- result, // the resulting back projection image
- ranges, // the range of values, for each dimension
- 255.0 // the scaling factor is chosen such that a histogram value of 1 maps to 255
- );
- } else {
- cv::calcBackProject(&image,
- 1, // we only use one image at a time
- channels, // vector specifying what histogram dimensions belong to what image channels
- histogram, // the histogram we are using
- result, // the resulting back projection image
- ranges, // the range of values, for each dimension
- 255.0 // the scaling factor is chosen such that a histogram value of 1 maps to 255
- );
- }
- // Threshold back projection to obtain a binary image
- if (threshold>0.0)
- cv::threshold(result, result, 255*threshold, 255, cv::THRESH_BINARY);
- return result;
- }
- };
- #endif
- #if !defined COLHISTOGRAM
- #define COLHISTOGRAM
- #include <opencv2\core\core.hpp>
- #include <opencv2\imgproc\imgproc.hpp>
- #include<opencv2/highgui/highgui.hpp>
- class ColorHistogram {
- private:
- int histSize[3];
- float hranges[2];
- const float* ranges[3];
- int channels[3];
- public:
- ColorHistogram() {
- // Prepare arguments for a color histogram
- histSize[0]= histSize[1]= histSize[2]= 256;
- hranges[0]= 0.0; // BRG range
- hranges[1]= 255.0;
- ranges[0]= hranges; // all channels have the same range
- ranges[1]= hranges;
- ranges[2]= hranges;
- channels[0]= 0; // the three channels
- channels[1]= 1;
- channels[2]= 2;
- }
- // Computes the histogram.
- cv::MatND getHistogram(const cv::Mat &image) {
- cv::MatND hist;
- // BGR color histogram
- hranges[0]= 0.0; // BRG range
- hranges[1]= 255.0;
- channels[0]= 0; // the three channels
- channels[1]= 1;
- channels[2]= 2;
- // Compute histogram
- cv::calcHist(&image,
- 1, // histogram of 1 image only
- channels, // the channel used
- cv::Mat(), // no mask is used
- hist, // the resulting histogram
- 3, // it is a 3D histogram
- histSize, // number of bins
- ranges // pixel value range
- );
- return hist;
- }
- // Computes the 1D Hue histogram with a mask.
- // BGR source image is converted to HSV
- cv::MatND getHueHistogram(const cv::Mat &image) {
- cv::MatND hist;
- // Convert to Lab color space
- cv::Mat hue;
- cv::cvtColor(image, hue, CV_BGR2HSV);
- // Prepare arguments for a 1D hue histogram
- hranges[0]= 0.0;
- hranges[1]= 180.0;
- channels[0]= 0; // the hue channel
- // Compute histogram
- cv::calcHist(&hue,
- 1, // histogram of 1 image only
- channels, // the channel used
- cv::Mat(), // no mask is used
- hist, // the resulting histogram
- 1, // it is a 1D histogram
- histSize, // number of bins
- ranges // pixel value range
- );
- return hist;
- }
- cv::MatND getHueHistogram(const cv::Mat &image,int minSaturation)
- {
- cv::MatND hist;
- cv::Mat hsv;
- cv::cvtColor(image,hsv,CV_BGR2HSV);
- cv::Mat mask;
- if(minSaturation>0)
- {
- std::vector<cv::Mat>v;
- cv::split(hsv,v);
- cv::threshold(v[1],mask,minSaturation,255,cv::THRESH_BINARY);
- }
- hranges[0]=0.0;
- hranges[1]=180.0;
- channels[0]=0;
- calcHist(&hsv,1,channels,mask,hist,1,histSize,ranges);
- return hist;
- }
- };
- #endif
- #include<opencv2/core/core.hpp>
- #include<opencv2/highgui/highgui.hpp>
- #include<opencv2/imgproc/imgproc.hpp>
- #include<opencv2/video/video.hpp>
- #include<iostream>
- #include"colorhistogram.h"
- #include"ContentFinder.h"
- using namespace std;
- using namespace cv;
- int main()
- {
- Mat image=imread("d:/test/opencv/baboon1.jpg");
- Mat imageROI=image(Rect(110,260,35,40));
- int minSat=65;
- ColorHistogram hc;
- MatND colorhist=hc.getHueHistogram(imageROI,minSat);
- namedWindow("image 1");
- imshow("image 1",image);
- ContentFinder finder;
- finder.setHistogram(colorhist);
- Mat hsv;
- image=imread("d:/test/opencv/baboon3.jpg");
- namedWindow("image 2");
- imshow("image 2",image);
- cvtColor(image,hsv,CV_BGR2HSV);
- vector<Mat>v;
- split(hsv,v);
- threshold(v[1],v[1],minSat,255,THRESH_BINARY);
- cv::namedWindow("Saturation");
- cv::imshow("Saturation",v[1]);
- int channel[1]={0};
- Mat result=finder.find(hsv,0.0f,180.0f,channel,1);
- cv::namedWindow("Result Hue");
- cv::imshow("Result Hue",result);
- cv::bitwise_and(result,v[1],result);
- cv::namedWindow("Result Hue and");
- cv::imshow("Result Hue and",result);
- finder.setThreshold(-1.0f);//
- result= finder.find(hsv,0.0f,180.0f,channel,1);
- cv::bitwise_and(result,v[1],result);
- cv::namedWindow("Result Hue and raw");
- cv::imshow("Result Hue and raw",result);
- cv::Rect rect(110,260,35,40);
- cv::rectangle(image, rect, cv::Scalar(0,0,255));
- cv::TermCriteria criteria(cv::TermCriteria::MAX_ITER,10,0.01);
- cout << "meanshift= " << cv::meanShift(result,rect,criteria) << endl;//
- cv::rectangle(image, rect, cv::Scalar(0,255,0));//
- // Display image
- cv::namedWindow("Image 2 result");
- cv::imshow("Image 2 result",image);
- cv::waitKey();
- return 0;
- }
#if !defined OFINDER
#define OFINDER#include <opencv2\core\core.hpp>
#include <opencv2\imgproc\imgproc.hpp>class ContentFinder {private:float hranges[2];const float* ranges[3];int channels[3];float threshold;cv::MatND histogram;cv::SparseMat shistogram;bool isSparse;public:ContentFinder() : threshold(0.1f), isSparse(false) {ranges[0]= hranges; // all channels have the same range ranges[1]= hranges; ranges[2]= hranges; }// Sets the threshold on histogram values [0,1]void setThreshold(float t) {threshold= t;}// Gets the thresholdfloat getThreshold() {return threshold;}// Sets the reference histogramvoid setHistogram(const cv::MatND& h) {isSparse= false;histogram= h;cv::normalize(histogram,histogram,1.0);}// Sets the reference histogramvoid setHistogram(const cv::SparseMat& h) {isSparse= true;shistogram= h;cv::normalize(shistogram,shistogram,1.0,cv::NORM_L2);}cv::Mat find(const cv::Mat& image) {cv::Mat result;hranges[0]= 0.0; // range [0,255]hranges[1]= 255.0;channels[0]= 0; // the three channels channels[1]= 1; channels[2]= 2; if (isSparse) { // call the right function based on histogram typecv::calcBackProject(&image,1, // one imagechannels, // vector specifying what histogram dimensions belong to what image channelsshistogram, // the histogram we are usingresult, // the resulting back projection imageranges, // the range of values, for each dimension255.0 // the scaling factor is chosen such that a histogram value of 1 maps to 255);} else {cv::calcBackProject(&image,1, // one imagechannels, // vector specifying what histogram dimensions belong to what image channelshistogram, // the histogram we are usingresult, // the resulting back projection imageranges, // the range of values, for each dimension255.0 // the scaling factor is chosen such that a histogram value of 1 maps to 255);}// Threshold back projection to obtain a binary imageif (threshold>0.0)cv::threshold(result, result, 255*threshold, 255, cv::THRESH_BINARY);return result;}cv::Mat find(const cv::Mat& image, float minValue, float maxValue, int *channels, int dim) {cv::Mat result;hranges[0]= minValue;hranges[1]= maxValue;for (int i=0; i<dim; i++)this->channels[i]= channels[i];if (isSparse) { // call the right function based on histogram typecv::calcBackProject(&image,1, // we only use one image at a timechannels, // vector specifying what histogram dimensions belong to what image channelsshistogram, // the histogram we are usingresult, // the resulting back projection imageranges, // the range of values, for each dimension255.0 // the scaling factor is chosen such that a histogram value of 1 maps to 255);} else {cv::calcBackProject(&image,1, // we only use one image at a timechannels, // vector specifying what histogram dimensions belong to what image channelshistogram, // the histogram we are usingresult, // the resulting back projection imageranges, // the range of values, for each dimension255.0 // the scaling factor is chosen such that a histogram value of 1 maps to 255);}// Threshold back projection to obtain a binary imageif (threshold>0.0)cv::threshold(result, result, 255*threshold, 255, cv::THRESH_BINARY);return result;}};#endif#if !defined COLHISTOGRAM
#define COLHISTOGRAM#include <opencv2\core\core.hpp>
#include <opencv2\imgproc\imgproc.hpp>
#include<opencv2/highgui/highgui.hpp>
class ColorHistogram {private:int histSize[3];float hranges[2];const float* ranges[3];int channels[3];public:ColorHistogram() {// Prepare arguments for a color histogramhistSize[0]= histSize[1]= histSize[2]= 256;hranges[0]= 0.0; // BRG rangehranges[1]= 255.0;ranges[0]= hranges; // all channels have the same range ranges[1]= hranges; ranges[2]= hranges; channels[0]= 0; // the three channels channels[1]= 1; channels[2]= 2; }// Computes the histogram.cv::MatND getHistogram(const cv::Mat &image) {cv::MatND hist;// BGR color histogramhranges[0]= 0.0; // BRG rangehranges[1]= 255.0;channels[0]= 0; // the three channels channels[1]= 1; channels[2]= 2; // Compute histogramcv::calcHist(&image, 1, // histogram of 1 image onlychannels, // the channel usedcv::Mat(), // no mask is usedhist, // the resulting histogram3, // it is a 3D histogramhistSize, // number of binsranges // pixel value range);return hist;}// Computes the 1D Hue histogram with a mask.// BGR source image is converted to HSVcv::MatND getHueHistogram(const cv::Mat &image) {cv::MatND hist;// Convert to Lab color spacecv::Mat hue;cv::cvtColor(image, hue, CV_BGR2HSV);// Prepare arguments for a 1D hue histogramhranges[0]= 0.0;hranges[1]= 180.0;channels[0]= 0; // the hue channel // Compute histogramcv::calcHist(&hue, 1, // histogram of 1 image onlychannels, // the channel usedcv::Mat(), // no mask is usedhist, // the resulting histogram1, // it is a 1D histogramhistSize, // number of binsranges // pixel value range);return hist;}cv::MatND getHueHistogram(const cv::Mat &image,int minSaturation){cv::MatND hist;cv::Mat hsv;cv::cvtColor(image,hsv,CV_BGR2HSV);cv::Mat mask;if(minSaturation>0){std::vector<cv::Mat>v;cv::split(hsv,v);cv::threshold(v[1],mask,minSaturation,255,cv::THRESH_BINARY);}hranges[0]=0.0;hranges[1]=180.0;channels[0]=0;calcHist(&hsv,1,channels,mask,hist,1,histSize,ranges);return hist;}};#endif#include<opencv2/core/core.hpp>
#include<opencv2/highgui/highgui.hpp>
#include<opencv2/imgproc/imgproc.hpp>
#include<opencv2/video/video.hpp>
#include<iostream>
#include"colorhistogram.h"
#include"ContentFinder.h"using namespace std;
using namespace cv;int main()
{Mat image=imread("d:/test/opencv/baboon1.jpg");Mat imageROI=image(Rect(110,260,35,40));int minSat=65;ColorHistogram hc;MatND colorhist=hc.getHueHistogram(imageROI,minSat);namedWindow("image 1");imshow("image 1",image);ContentFinder finder;finder.setHistogram(colorhist);Mat hsv;image=imread("d:/test/opencv/baboon3.jpg");namedWindow("image 2");imshow("image 2",image);cvtColor(image,hsv,CV_BGR2HSV);vector<Mat>v;split(hsv,v);threshold(v[1],v[1],minSat,255,THRESH_BINARY);cv::namedWindow("Saturation");cv::imshow("Saturation",v[1]);int channel[1]={0};Mat result=finder.find(hsv,0.0f,180.0f,channel,1);cv::namedWindow("Result Hue");cv::imshow("Result Hue",result);cv::bitwise_and(result,v[1],result);cv::namedWindow("Result Hue and");cv::imshow("Result Hue and",result);finder.setThreshold(-1.0f);//result= finder.find(hsv,0.0f,180.0f,channel,1);cv::bitwise_and(result,v[1],result);cv::namedWindow("Result Hue and raw");cv::imshow("Result Hue and raw",result);cv::Rect rect(110,260,35,40);cv::rectangle(image, rect, cv::Scalar(0,0,255));cv::TermCriteria criteria(cv::TermCriteria::MAX_ITER,10,0.01);cout << "meanshift= " << cv::meanShift(result,rect,criteria) << endl;//cv::rectangle(image, rect, cv::Scalar(0,255,0));//// Display imagecv::namedWindow("Image 2 result");cv::imshow("Image 2 result",image);cv::waitKey();return 0;}
这篇关于使用均值漂移算法查找物体,源代码的文章就介绍到这儿,希望我们推荐的文章对编程师们有所帮助!