本文主要是介绍合工大 程序设计艺术 实验二 骑士游历问题(马踏棋盘),希望对大家解决编程问题提供一定的参考价值,需要的开发者们随着小编来一起学习吧!
题目
在国际棋盘上使一个骑士遍历所有的格子一遍且仅一遍,对于任意给定的顶点, 输出一条符合上述要求的路径。
题意
让骑士在国际棋盘上一个格子开始走,保证每个格子都会走一遍,也只能走一遍,不可以重复走。
说明
国际象棋的棋盘大小为8*8;
国际象棋中的骑士就类似于中国象棋中的马,因此骑士每一步怎么走我们是可以知道的(马走日)。
解题思路
这题主要就是用DFS+回溯算法。
让骑士从棋盘上的一点开始DFS,未走之前该格子对应的二维数组为0,走过之后将其赋值为当前走的步数,代表这个格子已经被走过,用步数代表方便最后输出矩阵观察骑士走的路径。如果走到一点发现走不下去了就回溯。结束条件为走了64步,也就是棋盘已经走完了。
用两个方向数组,方便代表骑士向八个方向移动。
static const int dx[] = { -1,-2,-2,-1,1,2,2,1 };
static const int dy[] = { 2,1,-1,-2,2,1,-1,-2 };
运行结果
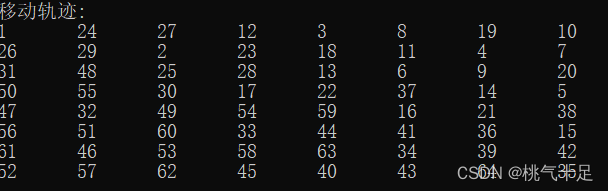
源代码
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
#define MAXSIZE 8//国际象棋 棋盘大小为8*8
int count1 = 0;//记录遍历次数
vector<vector<int>>vis;
//表示点
struct P {int x;int y;
};
vector<P>Point;//存储走过的点
bool KnightTravel(P& point) {Point.push_back(point);//放入容器中count1++;//遍历次数+1if (count1 == MAXSIZE*MAXSIZE) {return true;//棋盘上所有点都已经走过}//方向数组,方便之后对8个方向进行标记static const int dx[] = { -1,-2,-2,-1,1,2,2,1 };static const int dy[] = { 2,1,-1,-2,2,1,-1,-2 };//循环找位置for (int i = 0; i < MAXSIZE; i++) {P next = point;next.x = next.x + dx[i];next.y = next.y + dy[i];//没越界也没走过if (next.x >= 0 && next.x < MAXSIZE && next.y >= 0 && next.y < MAXSIZE && vis[next.x][next.y] == 0) {vis[next.x][next.y] = count1 + 1;//标记已经走过if (KnightTravel(next)) {//搜索下一个点return true;}vis[next.x][next.y] = 0;//回溯}}Point.pop_back();//取出容器中的点count1--;return false;
}
int main()
{int x, y;cout << "请输入起始坐标:";cin >> x >> y;P point;point.x = x;point.y = y;//初始化vis数组for (int i = 0; i < MAXSIZE; i++) {vis.push_back((std::vector<int>()));for (int j = 0; j < MAXSIZE; j++) {vis[i].push_back(0);}}vis[x][y] = 1;//标记起点//开始游历KnightTravel(point);int i = 0;for (vector<P>::iterator it = Point.begin(); it != Point.end(); it++) {i++;cout << "第" << i << "步 : ";cout << "(" << it->x << "," << it->y << ")" << endl;}cout << "移动轨迹:" << endl;for (int i = 0; i < MAXSIZE; i++) {for (int j = 0; j < MAXSIZE; j++) {cout << vis[i][j] << '\t';}cout << endl;}return 0;
}这篇关于合工大 程序设计艺术 实验二 骑士游历问题(马踏棋盘)的文章就介绍到这儿,希望我们推荐的文章对编程师们有所帮助!









