本文主要是介绍MIT | 数据分析、信号处理和机器学习中的矩阵方法 笔记系列 Lecture 5 Positive Definite and Semidefinite Matrices,希望对大家解决编程问题提供一定的参考价值,需要的开发者们随着小编来一起学习吧!
本系列为MIT Gilbert Strang教授的"数据分析、信号处理和机器学习中的矩阵方法"的学习笔记。
- Gilbert Strang & Sarah Hansen | Sprint 2018
- 18.065: Matrix Methods in Data Analysis, Signal Processing, and Machine Learning
- 视频网址: https://ocw.mit.edu/courses/18-065-matrix-methods-in-data-analysis-signal-processing-and-machine-learning-spring-2018/
- 关注下面的公众号,回复“ 矩阵方法 ”,即可获取 本系列完整的pdf笔记文件~
内容在CSDN、知乎和微信公众号同步更新
- CSDN博客
- 知乎
- 微信公众号

- Markdown源文件暂未开源,如有需要可联系邮箱
- 笔记难免存在问题,欢迎联系邮箱指正
Lecture 0: Course Introduction
Lecture 1 The Column Space of A A A Contains All Vectors A x Ax Ax
Lecture 2 Multiplying and Factoring Matrices
Lecture 3 Orthonormal Columns in Q Q Q Give Q ′ Q = I Q'Q=I Q′Q=I
Lecture 4 Eigenvalues and Eigenvectors
Lecture 5 Positive Definite and Semidefinite Matrices
Lecture 6 Singular Value Decomposition (SVD)
Lecture 7 Eckart-Young: The Closest Rank k k k Matrix to A A A
Lecture 8 Norms of Vectors and Matrices
Lecture 9 Four Ways to Solve Least Squares Problems
Lecture 10 Survey of Difficulties with A x = b Ax=b Ax=b
Lecture 11 Minimizing ||x|| Subject to A x = b Ax=b Ax=b
Lecture 12 Computing Eigenvalues and Singular Values
Lecture 13 Randomized Matrix Multiplication
Lecture 14 Low Rank Changes in A A A and Its Inverse
Lecture 15 Matrices A ( t ) A(t) A(t) Depending on t t t, Derivative = d A / d t dA/dt dA/dt
Lecture 16 Derivatives of Inverse and Singular Values
Lecture 17 Rapidly Decreasing Singular Values
Lecture 18 Counting Parameters in SVD, LU, QR, Saddle Points
Lecture 19 Saddle Points Continued, Maxmin Principle
Lecture 20 Definitions and Inequalities
Lecture 21 Minimizing a Function Step by Step
Lecture 22 Gradient Descent: Downhill to a Minimum
Lecture 23 Accelerating Gradient Descent (Use Momentum)
Lecture 24 Linear Programming and Two-Person Games
Lecture 25 Stochastic Gradient Descent
Lecture 26 Structure of Neural Nets for Deep Learning
Lecture 27 Backpropagation: Find Partial Derivatives
Lecture 28 Computing in Class [No video available]
Lecture 29 Computing in Class (cont.) [No video available]
Lecture 30 Completing a Rank-One Matrix, Circulants!
Lecture 31 Eigenvectors of Circulant Matrices: Fourier Matrix
Lecture 32 ImageNet is a Convolutional Neural Network (CNN), The Convolution Rule
Lecture 33 Neural Nets and the Learning Function
Lecture 34 Distance Matrices, Procrustes Problem
Lecture 35 Finding Clusters in Graphs
Lecture 36 Alan Edelman and Julia Language
文章目录
- Lecture 5 Positive Definite and Semidefinite Matrices
- 5.1 Positive Definite Matrix
- 正定矩阵的性质
- 正定矩阵的energy function及其在优化理论中的应用
- 正定矩阵的判定
- 5.2 Positive Semi-Definite (PSD) Matrix
- 半正定矩阵的性质
- 半正定矩阵举例
Lecture 5 Positive Definite and Semidefinite Matrices
5.1 Positive Definite Matrix
正定矩阵的性质
Topics in this lecture:
-
For Symmetric Positive Definite Matrix S S S (实矩阵: 正定矩阵 (一定是对称阵) ⇒ \Rightarrow ⇒ 且特征值>0)
- All λ i \lambda_i λi > 0
- Energy x T S x > 0 x^T S x > 0 xTSx>0 (all x ≠ 0 x\not ={0} x=0)
- S = A T A S = A^T A S=ATA (independent cols in A)
- All leading determinants > 0 > 0 >0
- All points in elimination > 0 > 0 >0
-
An Example:
-
S = [ 3 4 4 5 ] S = \begin{bmatrix} 3 & 4\\ 4 & 5 \end{bmatrix} S=[3445]
▪ S S S is symmetric
-
-
Is S S S Positive Definite?
-
D e t ( S ) = 15 − 16 = − 1 Det(S) = 15 -16 = -1 Det(S)=15−16=−1
-
意味着 λ 1 λ 2 = − 1 \lambda_1 \lambda_2 = -1 λ1λ2=−1, 特征值不可能都是正的
-
-
如何make S be positive?
▪ add stuff to the main diagonal ⇒ \Rightarrow ⇒ make S S S more positive
▪ 将S的右下角替换为6
▪ S = [ 3 4 4 6 ] S = \begin{bmatrix} 3 & 4\\ 4 & 6 \end{bmatrix} S=[3446]
-
需要 All leading determinants > 0 > 0 >0 pivot
- S = [ − 3 4 4 − 6 ] S = \begin{bmatrix} -3 & 4\\ 4 & -6 \end{bmatrix} S=[−344−6] 非正定
-
再看 All points in elimination > 0 > 0 >0
▪ 1st pivot = 3;
▪ S S S → \rightarrow → [ 3 4 0 2 / 3 ] \begin{bmatrix} 3 & 4\\ 0 & 2/3 \end{bmatrix} [3042/3] ⇒ \Rightarrow ⇒ 2nd pivot = 2 / 3 > 0 2/3 > 0 2/3>0
正定矩阵的energy function及其在优化理论中的应用
- 关于 Energy x T S x > 0 x^T S x > 0 xTSx>0 (all x ≠ 0 x\not ={0} x=0)
-
记 f ( x ) = x T S x = [ x 1 x 2 ] [ 3 4 4 6 ] [ x 1 x 2 ] = [ x 1 x 2 ] [ 3 x 1 + 4 x 2 4 x 1 + 6 x 2 ] f(x) = x^T S x = \begin{bmatrix} x_1 & x_2 \end{bmatrix} \begin{bmatrix} 3 & 4\\ 4 & 6 \end{bmatrix} \begin{bmatrix} x_1 \\ x_2 \end{bmatrix} = \begin{bmatrix} x_1 & x_2 \end{bmatrix} \begin{bmatrix} 3x_1 + 4x_2 \\ 4x_1 + 6x_2 \end{bmatrix} f(x)=xTSx=[x1x2][3446][x1x2]=[x1x2][3x1+4x24x1+6x2] = 3 x 1 2 + 6 x 2 2 + 8 x 1 x 2 3x_{1}^2 + 6 x_{2}^2 + 8x_1 x_2 3x12+6x22+8x1x2
-
f ( x ) f(x) f(x) = 3 x 1 2 + 6 x 2 2 + 8 x 1 x 2 3x_{1}^2 + 6 x_{2}^2 + 8x_1 x_2 3x12+6x22+8x1x2
▪ f(x) 关于 x 1 x_1 x1和 x 2 x_2 x2的函数如下图所示 (图中使用(x,y)表示 x x x的坐标)
▪ 此即 f ( x ) f(x) f(x)能量函数 (Energy function), and a convex function
▪ 该能量函数始终大于0 (all x ≠ 0 x\not ={0} x=0) --> 正定矩阵
▪ deep learning 中的 loss function 也是此类 energy function ⇒ \Rightarrow ⇒ minimize the function
-
Therefore, f ( x ) > 0 f(x) > 0 f(x)>0 (for all x ≠ 0 x\not ={0} x=0)
🚩 对于 quadratic , convex means positive definite / positive semidefinite
🚩 使用gradient descent 进行求解, the big algorithm of deep learning、 neural nets and machine learning
🚩 特征值决定了the energy function的形状: If you have a very small eigenvalue and a very large eigenvalue, the shape of the “bowl” will be thin and deep ⇒ \Rightarrow ⇒ difficult for the gradient descent algorithms !!
🚩 这也是正定矩阵非常重要的一个原因:能够确定根据损失函数解优化问题的性质,并根据特征值估计难度
-
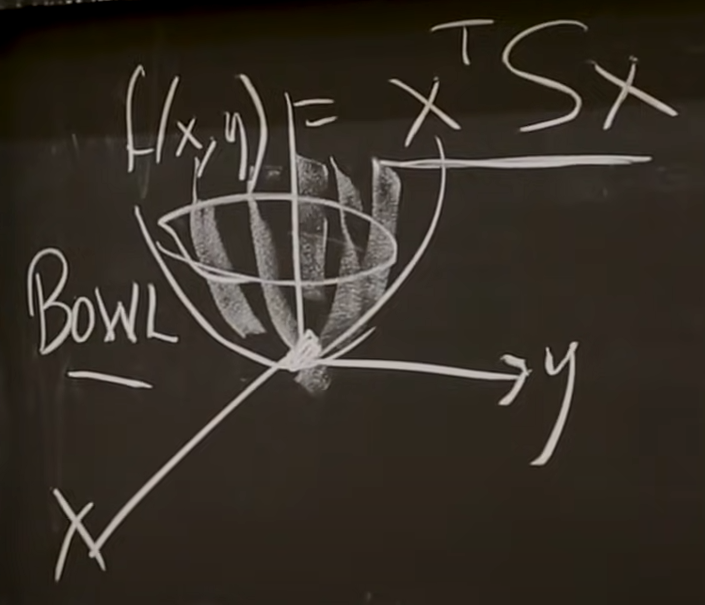
正定矩阵的判定
-
Question 1: If S S S and T T T are positive definite matrices, Is S = S 1 + S 2 S = S_1 + S_2 S=S1+S2 a positive definite matrix?
-
S,T are pos. def.
-
What about S+T?
-
思路:使用最开始的5个test:
▪ 1 All λ i \lambda_i λi > 0
▪ 2 Energy x T S x > 0 x^T S x > 0 xTSx>0 (all x ≠ 0 x\not ={0} x=0)
▪ 3 S = A T A S = A^T A S=ATA (independent cols in A)
▪ 4 All leading determinants > 0 > 0 >0
▪ 5 All points in elimination > 0 > 0 >0
-
Test 1: Eigenvalues – Eigenvalue of (S+T) is not clear from S and T
-
Test 2: Energy x T ( S + T ) x > 0 ? x^T (S+T) x > 0 ? xT(S+T)x>0? for all x ≠ 0 \not ={0} =0
✅ Yes! x T ( S + T ) x = x T S x + x T T x > 0 x^T (S+T) x = x^T S x + x^T T x > 0 xT(S+T)x=xTSx+xTTx>0
✅ So the answer is yes: (S+T) is pos. def.
-
-
Question 2: If S S S is a positive definite matrix, Is S − 1 S^{-1} S−1 a positive definite matrix?
- Test 1: Good!
- S − 1 S^-1 S−1 has eigenvalues 1 / λ 1/\lambda 1/λ
- So, Yes – S − 1 S^{-1} S−1 is a positive definite matrix
-
Question 3: If S S S is a positive definite matrix, Is S M SM SM a positive definite matrix? (M is another matrix)
-
ans: the question was not any good
-
S M SM SM is probably not symmetric 只有对称矩阵,才能确保特征值都是实数,才有之前的5个test
-
How about Q T S Q Q^T S Q QTSQ (Q is a orthogonal matrix)
▪ Q T S Q Q^T S Q QTSQ is a symmetric matrix
▪ Yes!
▪ Test 1: Q T S Q Q^T S Q QTSQ = Q − 1 S Q Q^{-1} S Q Q−1SQ 与 matrix S S S similar ⇒ \Rightarrow ⇒ the consequence of being similar: same eigenvalues Pos. def.
▪ Test 2: x T Q T S Q x = ( Q x ) T S ( Q x ) > 0 x^T Q^T S Q x = (Qx)^T S (Qx) > 0 xTQTSQx=(Qx)TS(Qx)>0 ⇒ \Rightarrow ⇒ Pos. def.
-
5.2 Positive Semi-Definite (PSD) Matrix
半正定矩阵的性质
-
For Semi-Positive Definite Matrix S S S (实矩阵: 正定矩阵 (一定是对称阵) ⇒ \Rightarrow ⇒ 且特征值>0)
- All λ i \lambda_i λi ≥ \geq ≥ 0
- Energy x T S x ≥ 0 x^T S x \geq 0 xTSx≥0 (all x ≠ 0 x\not ={0} x=0)
- S = A T A S = A^T A S=ATA (dependent columns allowed)
- All leading determinants ≥ 0 \geq 0 ≥0
- All points in elimination ≥ 0 \geq 0 ≥0
-
Semi-Positive Definite is the borderline
-
Example: S = [ 3 4 4 16 / 3 ] S = \begin{bmatrix} 3 & 4 \\ 4 & 16/3 \end{bmatrix} S=[34416/3]
-
(Test 1)关于eigenvalues:
▪ 根据 determinant ⇒ \Rightarrow ⇒ λ 2 = 0 \lambda_2 = 0 λ2=0
▪ 根据 trace ⇒ \Rightarrow ⇒ λ 1 = 3 + 16 / 3 \lambda_1 = 3 + 16/3 λ1=3+16/3
-
半正定矩阵举例
- An example: S = [ 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 ] S = \begin{bmatrix} 1 & 1 & 1 \\ 1 & 1 & 1 \\ 1 & 1 & 1 \end{bmatrix} S=⎣⎡111111111⎦⎤
-
Semidef
-
Test 1: Its eigenvalues: {3,0,0}
-
如何看出来它的特征值? ↓ \downarrow ↓
🚩 Because the rank is 1 ⇒ \Rightarrow ⇒ only one non-zero eigenvalues;
🚩 and the trace is 3 3 3 ⇒ \Rightarrow ⇒ the eigenvalues are {3,0,0}
-
Test 3: write it as S = A T A S = A^T A S=ATA
🚩 becaues it is symmetric, it can be write as:
🚩 S = Q Λ Q T S = Q \Lambda Q^T S=QΛQT = λ 1 q 1 q 1 T + λ 2 q 2 q 2 T + λ 3 q 3 q 3 T \lambda_{1} q_1 q_1^T + \lambda_2 q_2 q_2^T + \lambda_3 q_3 q_3^T λ1q1q1T+λ2q2q2T+λ3q3q3T, 其中 λ 2 \lambda_2 λ2 and λ 3 \lambda_3 λ3 = 0 ⇒ \Rightarrow ⇒ S = λ 1 q 1 q 1 T = 3 ( [ 1 , 1 , 1 ] T / ( 3 ) ) × [ 1 , 1 , 1 ] / ( 3 ) = q 1 T q 1 S = \lambda_1 q_1 q_1^T = 3 ([1,1,1]^T / (\sqrt{3})) \times [1,1,1] / (\sqrt{3}) = q_1^T q_1 S=λ1q1q1T=3([1,1,1]T/(3))×[1,1,1]/(3)=q1Tq1
-
Next week:
- singular value decomposition
这篇关于MIT | 数据分析、信号处理和机器学习中的矩阵方法 笔记系列 Lecture 5 Positive Definite and Semidefinite Matrices的文章就介绍到这儿,希望我们推荐的文章对编程师们有所帮助!





