本文主要是介绍【计算几何4】正交区域查询和KD-Tree概念,希望对大家解决编程问题提供一定的参考价值,需要的开发者们随着小编来一起学习吧!

目录
一、说明
二、正交区域查找
2.1 定义
2.2 引进KD树
2.3 构造Kd树
2.4 二维的例子说明原理
三、三维度示例研究
3.1 假如下面例子
3.2 构建示例代码(python)
一、说明
kd 树是一种二叉树数据结构,可以用来进行高效的 kNN 计算。kd 树算法偏于复杂,本篇将先介绍以二叉树的形式来记录和索引空间的思路,以便读者更轻松地理解 kd 树。
二、正交区域查找
2.1 定义
对于k维空间的张量数据表格,如果需要找出超立方体的区域内部数据的查找方法。之所以称之为正交区域查找,是因为在k维张量中,属性维度的空间相互无关。
而许多信息的查询是可以转化为正交区域查找的,例如问一堆员工中,年龄在[a,b],工资在[l,r]中的有几个,家庭人数为【n,m】。这个有很多做法,什么树套树之类的。而一种思路是,把员工的年龄x、工资y、家庭成员z,映射到三维平面上的点(x,y,z)上,这样就可以进行正交区域查找了,即查找一个矩形中点的个数。

对于更高维查询,我们需要一个数据结构,该结构可以在任何维数下使用 。* 注意:如果用树嵌套查询不足以构成各维度对等模型,因此,二叉树的迭代查询是不可取的。
2.2 引进KD树
先解释一下名字,K是维数,D是Dimension,即维。“树”表明他是树的结构。基本地,KD树中一个节点储存了:
- K维空间域,(例如三维中的一个长方体),
- 一个K维点的坐标
- 两个儿子下标
在平衡树中,我们知道:可以维护以每个节点为根的子树权值的min和max。
如法泡制,K维空间域与此很类似,维护的是子树点的坐标范围。
const int K=3;
struct KD_Tree
{int d[K],son[2];int x[2],y[2],z[2] ;//Range[K][2];
} tr[N];如上代码,P为节点储存的原图的点坐标,son为儿子,第二行储存了K维空间域。
2.3 构造Kd树
基本思想:
- KD树是一颗平衡二叉树,其中每个非叶节点,可以想象一个超平面,用来分割其储存的空间域,其中超平面垂直于坐标轴。
- 树尽量平衡,超平面划分的两个空间内的点尽量一样多。
- 为了有扩展性,树的每一层的超平面垂直的坐标轴,要轮流来取。即第一层垂直x轴,第二层垂直y轴,第三层垂直z轴····
垂直某个轴,意味着以这个轴的坐标为关键字来操作。
例如这次要垂直x轴,我们取当前点集的x坐标的中位数,然后把它作为切分点,切分点作为父节点,即KD树中新节点储存的点;切开的两边的点分别属于左右子树的点集。
2.4 二维的例子说明原理
1)有二维点如下图:

2)建立2d的平衡树x轴节点
在x轴上找二分线l1

3)建立2d的平衡树y轴节点
深度优先算法:
- 在x的l1线的左侧找到y轴上的二分线l2

- 在l1和l2包含区域找x的二分线l4




完成图:

三、三维度示例研究
3.1 假如下面例子
这是一个例子:血型、血小板数、血压三个指标。就按照x,y,z交替选中进行二叉树构建。
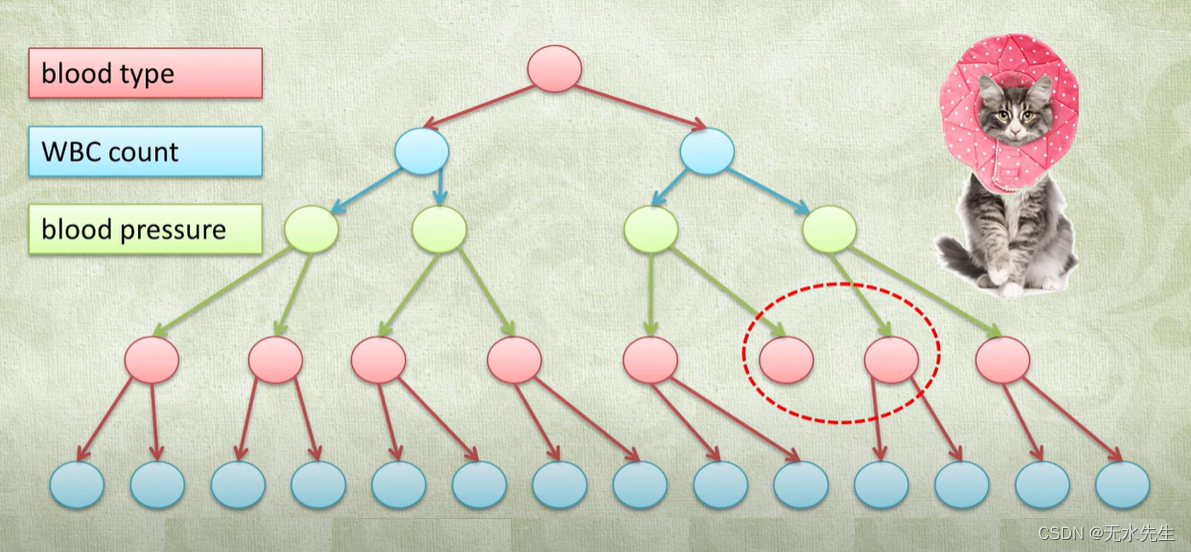
3.2 构建示例代码(python)
下面给出构造代码
class KDTree(object):"""A super short KD-Tree for points...so concise that you can copypasta into your homework without arousing suspicion.This implementation only supports Euclidean distance. The points can be any array-like type, e.g: lists, tuples, numpy arrays.Usage:1. Make the KD-Tree:`kd_tree = KDTree(points, dim)`2. You can then use `get_knn` for k nearest neighbors or `get_nearest` for the nearest neighborpoints are be a list of points: [[0, 1, 2], [12.3, 4.5, 2.3], ...]"""def __init__(self, points, dim, dist_sq_func=None):"""Makes the KD-Tree for fast lookup.Parameters----------points : list<point>A list of points.dim : int The dimension of the points. dist_sq_func : function(point, point), optionalA function that returns the squared Euclidean distancebetween the two points. If omitted, it uses the default implementation."""if dist_sq_func is None:dist_sq_func = lambda a, b: sum((x - b[i]) ** 2 for i, x in enumerate(a))def make(points, i=0):if len(points) > 1:points.sort(key=lambda x: x[i])i = (i + 1) % dimm = len(points) >> 1return [make(points[:m], i), make(points[m + 1:], i), points[m]]if len(points) == 1:return [None, None, points[0]]def add_point(node, point, i=0):if node is not None:dx = node[2][i] - point[i]for j, c in ((0, dx >= 0), (1, dx < 0)):if c and node[j] is None:node[j] = [None, None, point]elif c:add_point(node[j], point, (i + 1) % dim)import heapqdef get_knn(node, point, k, return_dist_sq, heap, i=0, tiebreaker=1):if node is not None:dist_sq = dist_sq_func(point, node[2])dx = node[2][i] - point[i]if len(heap) < k:heapq.heappush(heap, (-dist_sq, tiebreaker, node[2]))elif dist_sq < -heap[0][0]:heapq.heappushpop(heap, (-dist_sq, tiebreaker, node[2]))i = (i + 1) % dim# Goes into the left branch, then the right branch if neededfor b in (dx < 0, dx >= 0)[:1 + (dx * dx < -heap[0][0])]:get_knn(node[b], point, k, return_dist_sq, heap, i, (tiebreaker << 1) | b)if tiebreaker == 1:return [(-h[0], h[2]) if return_dist_sq else h[2] for h in sorted(heap)][::-1]def walk(node):if node is not None:for j in 0, 1:for x in walk(node[j]):yield xyield node[2]self._add_point = add_pointself._get_knn = get_knn self._root = make(points)self._walk = walkdef __iter__(self):return self._walk(self._root)def add_point(self, point):"""Adds a point to the kd-tree.Parameters----------point : array-likeThe point."""if self._root is None:self._root = [None, None, point]else:self._add_point(self._root, point)def get_knn(self, point, k, return_dist_sq=True):"""Returns k nearest neighbors.Parameters----------point : array-likeThe point.k: int The number of nearest neighbors.return_dist_sq : booleanWhether to return the squared Euclidean distances.Returns-------list<array-like>The nearest neighbors. If `return_dist_sq` is true, the return will be:[(dist_sq, point), ...]else:[point, ...]"""return self._get_knn(self._root, point, k, return_dist_sq, [])def get_nearest(self, point, return_dist_sq=True):"""Returns the nearest neighbor.Parameters----------point : array-likeThe point.return_dist_sq : booleanWhether to return the squared Euclidean distance.Returns-------array-likeThe nearest neighbor. If the tree is empty, returns `None`.If `return_dist_sq` is true, the return will be:(dist_sq, point)else:point"""l = self._get_knn(self._root, point, 1, return_dist_sq, [])return l[0] if len(l) else None下面给出测试代码
import unittest
import random
import cProfile
from kd_tree import *class KDTreeUnitTest(unittest.TestCase):def test_all(self):dim = 3def dist_sq_func(a, b):return sum((x - b[i]) ** 2 for i, x in enumerate(a))def get_knn_naive(points, point, k, return_dist_sq=True):neighbors = []for i, pp in enumerate(points):dist_sq = dist_sq_func(point, pp)neighbors.append((dist_sq, pp))neighbors = sorted(neighbors)[:k]return neighbors if return_dist_sq else [n[1] for n in neighbors]def get_nearest_naive(points, point, return_dist_sq=True):nearest = min(points, key=lambda p:dist_sq_func(p, point))if return_dist_sq:return (dist_sq_func(nearest, point), nearest) return nearestdef rand_point(dim):return [random.uniform(-1, 1) for d in range(dim)]points = [rand_point(dim) for x in range(10000)]additional_points = [rand_point(dim) for x in range(100)]query_points = [rand_point(dim) for x in range(100)]kd_tree_results = []naive_results = []global test_and_bench_kd_treeglobal test_and_bench_naivedef test_and_bench_kd_tree():global kd_treekd_tree = KDTree(points, dim)for point in additional_points:kd_tree.add_point(point)kd_tree_results.append(tuple(kd_tree.get_knn([0] * dim, 8)))for t in query_points:kd_tree_results.append(tuple(kd_tree.get_knn(t, 8)))for t in query_points:kd_tree_results.append(tuple(kd_tree.get_nearest(t)))def test_and_bench_naive():all_points = points + additional_pointsnaive_results.append(tuple(get_knn_naive(all_points, [0] * dim, 8)))for t in query_points:naive_results.append(tuple(get_knn_naive(all_points, t, 8)))for t in query_points:naive_results.append(tuple(get_nearest_naive(all_points, t)))print("Running KDTree...")cProfile.run("test_and_bench_kd_tree()")print("Running naive version...")cProfile.run("test_and_bench_naive()")print("Query results same as naive version?: {}".format(kd_tree_results == naive_results))self.assertEqual(kd_tree_results, naive_results, "Query results mismatch")self.assertEqual(len(list(kd_tree)), len(points) + len(additional_points), "Number of points from iterator mismatch")if __name__ == '__main__':unittest.main()参考文章:
GitHub - Vectorized/Python-KD-Tree: A simple and fast KD-tree for points in Python for kNN or nearest points. (damm short at just ~60 lines) No libraries needed.
这篇关于【计算几何4】正交区域查询和KD-Tree概念的文章就介绍到这儿,希望我们推荐的文章对编程师们有所帮助!






