本文主要是介绍牛客周赛 Round 20 解题报告 | 珂学家 | 状压DP/矩阵幂优化 + 前缀和的前缀和,希望对大家解决编程问题提供一定的参考价值,需要的开发者们随着小编来一起学习吧!
前言

整体评价
这场比赛很特别,是牛客周赛的第20场,后两题难度直线飙升了。
前四题相对简单,E题是道状压题,历来状压题都难,F题压轴难题了,感觉学到了不少。
A. 赝品
先求的最大值
然后统计非最大值的个数,即可。
import java.io.*;
import java.util.*;public class Main {public static void main(String[] args) {Scanner sc = new Scanner(new BufferedInputStream(System.in));int n = sc.nextInt();int[] arr = new int[n];for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {arr[i] = sc.nextInt();}// 获取数组的最大值int maxValue = Arrays.stream(arr).max().getAsInt();// 过滤最大值,并计数System.out.println(Arrays.stream(arr).filter(x -> x != maxValue).count());}}
B. 小红的01连续段
状态机DP
令opt[n][2], 0表示第n字母以0结尾,往前扩展的最长连续0子串的数量,1状态亦是如此定义。
则遇到‘0’, ‘1’, ‘?’, 会有不同的转移
最后的结果为
m a x i = 0 i = n − 1 ( o p t [ i ] [ s ] ) , s ∈ ( 0 , 1 ) max_{i=0}^{i=n-1}(opt[i][s]), s\in(0,1) maxi=0i=n−1(opt[i][s]),s∈(0,1)
这边可以滚动优化,使得时间复杂度降为2个变量
import java.io.*;
import java.util.*;public class Main {public static void main(String[] args) {Scanner sc = new Scanner(new BufferedInputStream(System.in));String s = sc.next();int res = 0;int s0 = 0, s1 = 0;for (char c: s.toCharArray()) {if (c == '0') {s0++;s1 = 0;} else if (c == '1') {s1++;s0 = 0;} else {// 遇到?号s0++;s1++;}res = Math.max(res, Math.max(s0, s1));}System.out.println(res);}}
C. 小红的01串构造
这题挺有趣的
其实你只要观察到
111000100
110001100
这两个是等价的
即聚合的1从一个组,转移另一个组,不改变相邻的总对数
因此可以构造一个,所有相邻对数t都在第一个组中,然后多余的1,独立为一组
这样保证 t+1<=k && t+1 + (k - (t+1)) * 2 <= n, 必然有解
import java.io.*;
import java.util.*;public class Main {public static void main(String[] args) {Scanner sc = new Scanner(new BufferedInputStream(System.in));int n = sc.nextInt(), k = sc.nextInt(), t = sc.nextInt();if (k > n || k - 1 < t) {System.out.println(-1);} else {int k1 = t + 1;int k2 = k - t - 1;if (k1 + k2 * 2 <= n) {StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();for (int i = 0; i < k1; i++) sb.append("1");for (int i = 0; i < k2; i++) sb.append("01");for (int i = k1 + k2 * 2; i < n; i++) sb.append("0");System.out.println(sb);} else {System.out.println(-1);}}}}
D. 小红的数位删除
这题,其实题目少了一个重要的条件
最后a,b不能为0
1. 二进制枚举
因为只有9位数,所以可以使用二进制枚举
这样时间复杂度为 O ( 2 9 ∗ 2 9 ∗ 9 ∗ 9 ) = 2 ∗ 1 0 8 O(2^9 * 2^9 * 9 * 9)=2*10^8 O(29∗29∗9∗9)=2∗108, 枚举常数小,在合理的范围内
- 从大到小枚举
- 引入剪枝
import java.io.*;
import java.util.*;
import java.util.function.BiFunction;public class Main {public static void main(String[] args) {Scanner sc = new Scanner(new BufferedInputStream(System.in));char[] astr = sc.next().toCharArray();char[] bstr = sc.next().toCharArray();int inf = Integer.MAX_VALUE;int n1 = astr.length, n2 = bstr.length;int ans = inf;BiFunction<Integer, char[], Integer> calculate = (s, str) -> {int val = 0;for (int t = 0; t < str.length; t++) {if ((s & (1 << t)) != 0) {val = val * 10 + (str[t] - '0');}}return val;};for (int i = (1 << n1) - 1; i > 0; i--) {int r1 = n1 - Integer.bitCount(i);if (r1 >= ans) continue;int a = calculate.apply(i, astr);if (a == 0) continue;for (int j = (1 << n2) - 1; j > 0; j--) {int r2 = n2 - Integer.bitCount(j);if (r1 + r2 >= ans) continue;int b = calculate.apply(j, bstr);if (b == 0) continue;if (a % b == 0 || b % a == 0) {ans = Math.min(ans, r1 + r2);}}}System.out.println(ans == inf ? -1 : ans);}}2. BFS解
这题的话,感觉还可以BFS,这样的话,找到解后可以立马退出。
E. 小红的漂亮串
思路: 状压DP
这题有’red’, 'der’限制,所以直接想O(1)求容斥解,行不通.
1. 正向状压解
回到状压的思路
引入5种状态
- 0, any是1,2,3,4以外的所有状态
- 1, 以r字母结尾
- 2,以d字母结尾
- 3,以re字母结尾
- 4,以de字母结尾
先聊下如何解决
Q: 子串不包含‘der’
只要在递推过程中, 对der的状态构造忽略即可
Q: 需要包含至少一个‘red’
额外引入一维的状态0/1, 表示当前字符串以包含red, 和暂时不包含red
设计好了状态, 以及解决思路
来看一下如何设计状态转移
令 dp[2][5], 前一维表示是否包含’red’, 后一维表示以什么结尾的状态
DP递推的话,以下两种都可以
- 填表法
- 刷表法
为啥要两者都介绍下呢?
主要是如果某一种实现,遇到了wa,这个时候可以用另一种思路去check/verify, 看看哪里的转移有遗漏。
状态迁移还是太多,这边选用一个 (0, 3)来分析,它涉及一个阶级跃迁
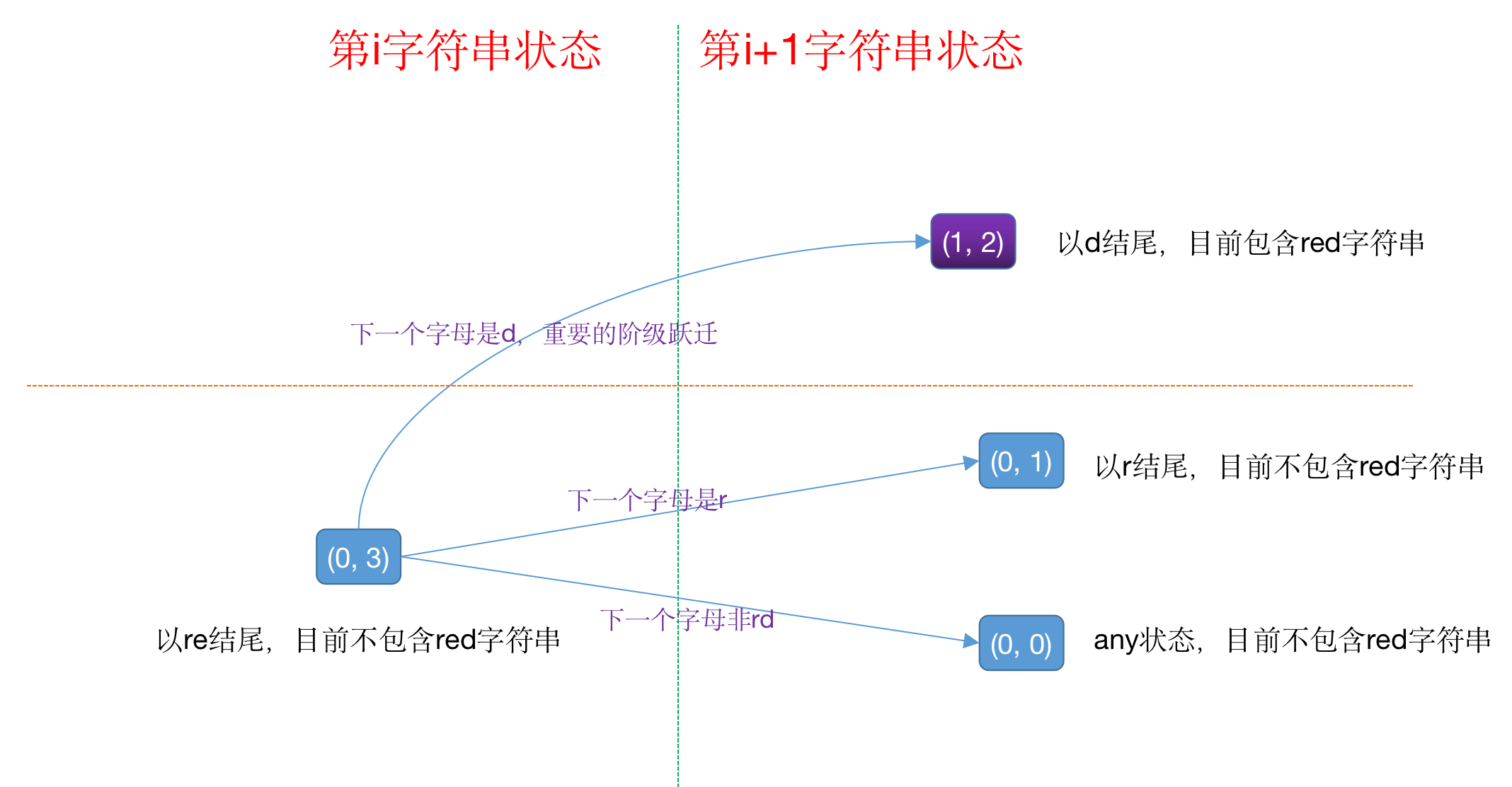
import java.io.BufferedInputStream;
import java.util.Scanner;public class Main {public static void main(String[] args) {Scanner sc = new Scanner(new BufferedInputStream(System.in));int n = sc.nextInt();// any// r, d// re, de,long mod = 10_0000_0007l;// red, derlong[][] dp = new long[2][5];dp[0][0] = 24;dp[0][1] = dp[0][2] = 1;for (int i = 1; i < n; i++) {long[][] dp2 = new long[2][5];// 不包含red字符串(在本身的圈子内转移)dp2[0][0] = (dp[0][0] * 24 % mod + dp[0][1] * 23 % mod + dp[0][2] * 23 % mod + dp[0][3] * 24 % mod + dp[0][4] * 24 % mod) % mod;dp2[0][1] = (dp[0][0] + dp[0][1] + dp[0][2] + dp[0][3]) % mod;dp2[0][2] = (dp[0][0] + dp[0][1] + dp[0][2] + dp[0][4]) % mod;dp2[0][3] = dp[0][1];dp2[0][4] = dp[0][2];// 包含red字符串(在本身的圈子内转移)dp2[1][0] = (dp[1][0] * 24 % mod + dp[1][1] * 23 % mod + dp[1][2] * 23 % mod + dp[1][3] * 24 % mod + dp[1][4] * 24 % mod) % mod;dp2[1][1] = (dp[1][0] + dp[1][1] + dp[1][2] + dp[1][3]) % mod;dp2[1][2] = (dp[1][0] + dp[1][1] + dp[1][2] + dp[1][3] + dp[1][4]) % mod;dp2[1][3] = dp[1][1];dp2[1][4] = dp[1][2];// 非常俏皮的阶级跃迁(最特别),单独拎出来dp2[1][2] = (dp2[1][2] + dp[0][3]) % mod;dp = dp2;}// 只累加包含red字符串的状态long res = 0;for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {res += dp[1][i];res %= mod;}System.out.println(res);}}
2. 容斥状压解
这题还可以容斥解,不过这个容斥解也是基于状压的
大致的思路
- 求解不存在der的字符串总个数S1
- 求解同时不存在der,red的字符串总个数S2
- S1 - S2, 即为不存在der,但是存在red的字符串总方案数
3. 矩阵幂优化
如果n在大点,n只要大于10^9,那矩阵幂才是唯一解
矩阵的构造,源于方法一,把2*5摊平成为1维
然后构建一个状态转移矩阵即可。
import java.io.BufferedInputStream;
import java.util.Scanner;public class Main {public static void main(String[] args) {Scanner sc = new Scanner(new BufferedInputStream(System.in));int n = sc.nextInt();long mod = 10_0000_0007l;long[][] translate = new long[][] {{24, 23, 23, 24, 24, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0},{1, 1, 1, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0},{1, 1, 1, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0},{0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0},{0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0},{0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 24, 23, 23, 24, 24},{0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 1, 1, 1, 0},{0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1},{0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0},{0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0},};Matrix matrix = new Matrix(translate);Matrix matrix2 = Matrix.quickPow(matrix, n, mod);Matrix vec = new Matrix(new long[][] {{1}, {0}, {0}, {0}, {0}, {0}, {0}, {0}, {0}, {0}});Matrix res = matrix2.mul(vec, mod);long ans = 0;for (int i = 5; i < 10; i++) {ans += res.arr[i][0];ans %= mod;}System.out.println(ans);}static class Matrix {long[][] arr;int r, c;Matrix(long[][] arr) {this.arr = arr;this.r = arr.length;this.c = arr[0].length;}Matrix mul(Matrix other, long mod) {int nr = this.r, nc = other.c;long[][] res = new long[nr][nc];for (int i = 0; i < nr; i++) {for (int j = 0; j < nc; j++) {long temp = 0;for (int k = 0; k < c; k++) {temp = (temp + arr[i][k] * other.arr[k][j] % mod) % mod;}res[i][j] = temp;}}return new Matrix(res);}static Matrix E(int n) {long[][] arr = new long[n][n];for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {arr[i][i] = 1;}return new Matrix(arr);}static Matrix quickPow(Matrix base, long k, long mod) {Matrix r = Matrix.E(base.r);while (k > 0) {if (k % 2 == 1) {r = r.mul(base, mod);}k /= 2;base = base.mul(base, mod);}return r;}}}
F. 小红的零
整数末尾0的个数,取决于2和5的因子个数的最小值.
难点就在于:最小值
先来看2道基础题
对于一个数组arr, 给予一个x, 求 ∑ i = 0 i = n − 1 ∣ a r r [ i ] − x ∣ \sum_{i=0}^{i=n-1}|arr[i] - x| ∑i=0i=n−1∣arr[i]−x∣
这题的思路,就是对arr进行排序,然后绝对值去掉,这样就划分为2个部分,一部分小于x,另一部分大于等于x
利用前缀和预处理,可以二分到分界点, O ( l o g ( n ) ) O(log(n)) O(log(n))解决问题
求一个数组的所有子区间(2的因子个数)累加和
这是弱化版本,那其思路遍历右端点,然后累计
设S(i)为第i元素为右端点的所有区间的累加和
S(i) = S(i-1) + (i+1)*f(i)
最终S(i)的累加和 \sum S(i)
而这题的核心思路,其实上延续了类似思想
令f(x)为前x项的2因子的前缀和,
g(x)为前x项的5因子的前缀和
对于某个区间[l, r]
贡献 = m i n ( f ( r ) − f ( l − 1 ) , g ( r ) − g ( l − 1 ) ) 贡献 = min(f(r) - f(l - 1), g(r) - g(l - 1)) 贡献=min(f(r)−f(l−1),g(r)−g(l−1))
令 z ( x ) = f ( x ) − g ( x ) z(x) = f(x) - g(x) z(x)=f(x)−g(x)
则区间[l, r] 其贡献为
-
z ( r ) − z ( l − 1 ) ≥ 0 z(r) - z(l - 1) \ge 0 z(r)−z(l−1)≥0
- 贡献为 g® - g(l - 1)
-
z ( r ) − z ( l − 1 ) < 0 z(r) - z(l - 1) \lt 0 z(r)−z(l−1)<0
- 贡献为f® - f(l - 1)
本质上这题的巧妙之处在于
- 维护2因子多的区间(累加和,个数)
- 维护5因子多的区间 (累加和,个数)
而这个因子多少,是一个变动的过程,根据右端点来决定范围
-
大于z(x),为2因子多的区间
n x ∗ f ( x ) − ∑ y ∈ ( z ( y ) > z ( x ) ) f ( y ) n_x * f(x) - \sum_{y\in({z(y)>z(x)})} f(y) nx∗f(x)−y∈(z(y)>z(x))∑f(y)
-
小于等于z(x), 则为5因子多的区间
n y ∗ g ( x ) − ∑ y ∈ ( z ( y ) < = z ( x ) ) g ( y ) n_y * g(x) - \sum_{y\in({z(y)<=z(x))}} g(y) ny∗g(x)−y∈(z(y)<=z(x))∑g(y)
所以这边采用4个树状数组
fw2, fwc2代表2因子的前缀和f(x),对应2因子的区间个数,
fw5, fwc5代表5因子的前缀和g(x),对应5因子的区间个数
而把 z(x) 作为 树状数组的 index-key
因为2因子和5因子个数,最多30n,考虑到负值,最多60n
引入offset作为偏移,不需要离散化
感觉这题思路还是挺绕的,可能直接看代码,更容易理解
感觉这题掺杂了 前缀和的前缀和
import java.io.*;
import java.util.*;public class Main {static class BIT {int n;long[] arr;public BIT(int n) {this.n = n;this.arr = new long[n + 1];}void update(int p, long v) {while (p <= n) {this.arr[p] += v;p += p&-p;}}long query(int p) {long res = 0;while (p > 0) {res += this.arr[p];p -= p&-p;}return res;}}static int split(int v, int b) {int cnt = 0;while (v % b == 0) {v /= b;cnt++;}return cnt;}public static void main(String[] args) {Scanner sc = new Scanner(new BufferedInputStream(System.in));int n = sc.nextInt();int mx = 60 * n; // 2^30 > 1e9, 因为绝对值的问题,所以30*2*nint offset = 30 * n; // 引入offset,是因为这边没有离散化,而是做了一个偏移,平衡负值BIT fw2 = new BIT(mx); // 2的因子累加和BIT fwc2 = new BIT(mx); // 2的因子计数BIT fw5 = new BIT(mx); // 5的因子累加和BIT fwc5 = new BIT(mx); // 5的因子计数long res = 0;int acc2 = 0, acc5 = 0;int diff = 0;for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {// 前缀和为keyfw2.update(diff + offset, acc2);fwc2.update(diff + offset, 1);fw5.update(diff + offset, acc5);fwc5.update(diff + offset, 1);int v = sc.nextInt();int n2 = split(v, 2);int n5 = split(v, 5);diff += (n2 - n5);acc2 += n2;acc5 += n5;// 进行统计计算long sum2 = fw2.query(mx) - fw2.query(diff + offset);long cnt2 = fwc2.query(mx) - fwc2.query(diff + offset);long sum5 = fw5.query(diff + offset);long cnt5 = fwc5.query(diff + offset);res += (acc2 * cnt2 - sum2) + (acc5 * cnt5 - sum5);}System.out.println(res);}}
写在最后

这篇关于牛客周赛 Round 20 解题报告 | 珂学家 | 状压DP/矩阵幂优化 + 前缀和的前缀和的文章就介绍到这儿,希望我们推荐的文章对编程师们有所帮助!


