本文主要是介绍【Codeforces Round 333 (Div 2)E】【期望DP概率做法 树状数组转前缀和】Kleofáš and the n-thlon n场比赛m个人获得总名次的期望,希望对大家解决编程问题提供一定的参考价值,需要的开发者们随着小编来一起学习吧!
【Codeforces Round 333 (Div 2)E】【期望DP概率做法 树状数组转前缀和】Kleofáš and the n-thlon n场比赛m个人获得总名次的期望 250ms
#include<stdio.h>
#include<string.h>
#include<ctype.h>
#include<math.h>
#include<iostream>
#include<string>
#include<set>
#include<map>
#include<vector>
#include<queue>
#include<bitset>
#include<algorithm>
#include<time.h>
using namespace std;
void fre(){freopen("c://test//input.in","r",stdin);freopen("c://test//output.out","w",stdout);}
#define MS(x,y) memset(x,y,sizeof(x))
#define MC(x,y) memcpy(x,y,sizeof(x))
#define MP(x,y) make_pair(x,y)
#define ls o<<1
#define rs o<<1|1
typedef long long LL;
typedef unsigned long long UL;
typedef unsigned int UI;
template <class T> inline void gmax(T &a,T b){if(b>a)a=b;}
template <class T> inline void gmin(T &a,T b){if(b<a)a=b;}
const int N=100+5,M=1000+5,S=1e5+5,Z=1e9+7,ms63=1061109567;
int n,m,k;
int TOP;
struct BIT
{double f[S];double query(int x){if(++x<=0)return 0;double tmp=0;for(;x;x-=x&-x)tmp+=f[x];return tmp;}void modify(int x,double v){if(++x<=0)return;for(;x<=TOP+1;x+=x&-x)f[x]+=v;}
}bit[2];
int main()
{while(~scanf("%d%d",&n,&m)){if(m==1){puts("1");return 0;}TOP=n*m;double mu=1.0/(m-1);MS(bit,0);bit[0].modify(0,1);int mysco=0;int pre=0,now=1;for(int i=1;i<=n;++i){scanf("%d",&k);mysco+=k;MS(bit[now].f,0);int top=i*m;for(int j=i;j<=top;++j){double rate=(bit[pre].query(j-1)-bit[pre].query(j-m-1))-(bit[pre].query(j-k)-bit[pre].query(j-k-1));bit[now].modify(j,rate*mu);}pre^=1;now^=1;}double ans=bit[pre].query(mysco-1);ans=ans*(m-1)+1;printf("%.12f\n",ans);}return 0;
}
/*
【trick&&吐槽】
1,这道题看似很难,然而只要沉下心来思考,发现问题细细化简后,还是完全可思考的。
2,复杂度看似很高,然而就是可以这样暴力过掉,真是暴力出奇迹的有效印证啊!
3,所以说敢想敢试是ACMer的基本素养>_<~~4,CF多组数据一定要确保完全读入才能用continue。否则是坑自己多次输出,还不如用return 0 TwT
5,树状数组的下标要从1开始不要忘记了。
6,DP的边界处理,再树状数组内部特判一下,写起来就很方便啦。【题意】
这题比较奇怪。题意是说——
有m(1000)个人,他们一同参加了n(100)场比赛。
对于每场比赛,m个人的排名都构成[1,m]的全排列。排名第i的人会得到分数i。
我们知道自己在每场比赛中的名次(设第i场的名次为a[i]),自然,也就知道了自己在每场比赛中的得分。
现在我们想要求,我们最终的比赛名次的期望。最终的比赛名次是指,如果最终时刻有k个人的分数严格比我们小,那么我们的名次便是k+1。现在求得就是这个值的期望。【类型】
期望DP【分析】
设计到期望的题目,并不一定就难得不可做。
我们发现,一共有m个人。除了我们自己之外,还有m-1个人。这m-1个人,每个人的期望得分的状况其实都是相同的。
更加具体而言,我们还有——每个人的可能得分都必然是整数。整数的范围是[n*1,n*m].
如果我们暴力一点,求得每个人对于每个得分x的概率p[x],我们自己的得分是u的话,那答案就是p[1,u)*(m-1)+1
这个显然成立,因为:一个人比我们分数低的概率*人数=比我们分数低的人数的期望,+1后就是我们名次的期望。于是问题就只剩下——p[x]怎么求?
n和m并不大,甚至说,我们感觉到人数n * 分数的上限n*m 也不过1e7。
于是,我们DP一个人的得分状况——
定义f[i][j]表示"经过了前i次考试,这个人得分为j的概率"。那么有——
f[i][j]=(f[i-1][j-1]+f[i-1][j-2]+...+f[i-1][m]-f[i-1][j-a[i]])/(m-1)这个DP的意义很简单,就是说,我们枚举这个状态,然后看看有哪些状态可以到达它。
而之前的每个可以转移状态,转移到当前状态的当步转移概率都是均等的,都是1/(m-1)。
于是,只要这一个简单的DP,就能实现题目的要求。
然而这个DP的时间复杂度却是O(n * n*m * m) 要爆炸!这里涉及到区间和,于是我们想到用树状数组优化——
把DP的时间复杂度可达O(n*n*m log(m)),然而却依然可以无压力在250ms内AC啦,啦啦啦啦!然而,树状数组还是傻叉做法。
因为这里又不涉及到动态修改,我为什么用树状数组?!
直接搞一个前缀和就好啦!【时间复杂度&&优化】
O(n*n*m log(m)) -> O(n*n*m)*/
【Codeforces Round 333 (Div 2)E】【期望DP概率做法 前缀和】Kleofáš and the n-thlon n场比赛m个人获得总名次的期望 46ms
#include<stdio.h>
#include<string.h>
#include<ctype.h>
#include<math.h>
#include<iostream>
#include<string>
#include<set>
#include<map>
#include<vector>
#include<queue>
#include<bitset>
#include<algorithm>
#include<time.h>
using namespace std;
void fre(){freopen("c://test//input.in","r",stdin);freopen("c://test//output.out","w",stdout);}
#define MS(x,y) memset(x,y,sizeof(x))
#define MC(x,y) memcpy(x,y,sizeof(x))
#define MP(x,y) make_pair(x,y)
#define ls o<<1
#define rs o<<1|1
typedef long long LL;
typedef unsigned long long UL;
typedef unsigned int UI;
template <class T> inline void gmax(T &a,T b){if(b>a)a=b;}
template <class T> inline void gmin(T &a,T b){if(b<a)a=b;}
const int N=100+5,M=1000+5,S=1e5+5,Z=1e9+7,ms63=1061109567;
int n,m,k,pre,now;
double s[2][S+M];
inline double query(int x)
{return x<0?0:s[pre][x];
}
int main()
{while(~scanf("%d%d",&n,&m)){if(m==1){puts("1");return 0;}int top=n*m;double mu=1.0/(m-1);for(int i=0;i<=top;++i)s[0][i]=1;int mysco=0;pre=0;now=1;for(int i=1;i<=n;++i){scanf("%d",&k);mysco+=k;for(int j=0;j<i;++j)s[now][j]=0;for(int j=i;j<=top;++j){double rate=(query(j-1)-query(j-m-1))-(query(j-k)-query(j-k-1));s[now][j]=s[now][j-1]+rate*mu;}pre^=1;now^=1;}double ans=s[pre][mysco-1];ans=ans*(m-1)+1;printf("%.12f\n",ans);}return 0;
}
/*
【trick&&吐槽】
1,这道题看似很难,然而只要沉下心来思考,发现问题细细化简后,还是完全可思考的。
2,复杂度看似很高,然而就是可以这样暴力过掉,真是暴力出奇迹的有效印证啊!
3,所以说敢想敢试是ACMer的基本素养>_<~~4,CF多组数据一定要确保完全读入才能用continue。否则是坑自己多次输出,还不如用return 0 TwT
5,树状数组的下标要从1开始不要忘记了。
6,DP的边界处理,再树状数组内部特判一下,写起来就很方便啦。【题意】
这题比较奇怪。题意是说——
有m(1000)个人,他们一同参加了n(100)场比赛。
对于每场比赛,m个人的排名都构成[1,m]的全排列。排名第i的人会得到分数i。
我们知道自己在每场比赛中的名次(设第i场的名次为a[i]),自然,也就知道了自己在每场比赛中的得分。
现在我们想要求,我们最终的比赛名次的期望。最终的比赛名次是指,如果最终时刻有k个人的分数严格比我们小,那么我们的名次便是k+1。现在求得就是这个值的期望。【类型】
期望DP【分析】
设计到期望的题目,并不一定就难得不可做。
我们发现,一共有m个人。除了我们自己之外,还有m-1个人。这m-1个人,每个人的期望得分的状况其实都是相同的。
更加具体而言,我们还有——每个人的可能得分都必然是整数。整数的范围是[n*1,n*m].
如果我们暴力一点,求得每个人对于每个得分x的概率p[x],我们自己的得分是u的话,那答案就是p[1,u)*(m-1)+1
这个显然成立,因为:一个人比我们分数低的概率*人数=比我们分数低的人数的期望,+1后就是我们名次的期望。于是问题就只剩下——p[x]怎么求?
n和m并不大,甚至说,我们感觉到人数n * 分数的上限n*m 也不过1e7。
于是,我们DP一个人的得分状况——
定义f[i][j]表示"经过了前i次考试,这个人得分为j的概率"。那么有——
f[i][j]=(f[i-1][j-1]+f[i-1][j-2]+...+f[i-1][m]-f[i-1][j-a[i]])/(m-1)这个DP的意义很简单,就是说,我们枚举这个状态,然后看看有哪些状态可以到达它。
而之前的每个可以转移状态,转移到当前状态的当步转移概率都是均等的,都是1/(m-1)。
于是,只要这一个简单的DP,就能实现题目的要求。
然而这个DP的时间复杂度却是O(n * n*m * m) 要爆炸!这里涉及到区间和,于是我们想到用树状数组优化——
把DP的时间复杂度可达O(n*n*m log(m)),然而却依然可以无压力在250ms内AC啦,啦啦啦啦!然而,树状数组还是傻叉做法。
因为这里又不涉及到动态修改,我为什么用树状数组?!
直接搞一个前缀和s[2][S]就好啦!【时间复杂度&&优化】
O(n*n*m log(m)) -> O(n*n*m)*/这篇关于【Codeforces Round 333 (Div 2)E】【期望DP概率做法 树状数组转前缀和】Kleofáš and the n-thlon n场比赛m个人获得总名次的期望的文章就介绍到这儿,希望我们推荐的文章对编程师们有所帮助!
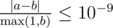 .
.




