本文主要是介绍CLIP算法的Loss详解 和 交叉熵CrossEntropy实现,希望对大家解决编程问题提供一定的参考价值,需要的开发者们随着小编来一起学习吧!
CLIP:Contrastive Language–Image Pre-training(可对比语言-图像预训练算法)是OpenAI提出的多模态预训练的算法,在各种各样的**样本对(图像、文本)**上训练的神经网络。
具体参考:CLIP、OpenCLIP
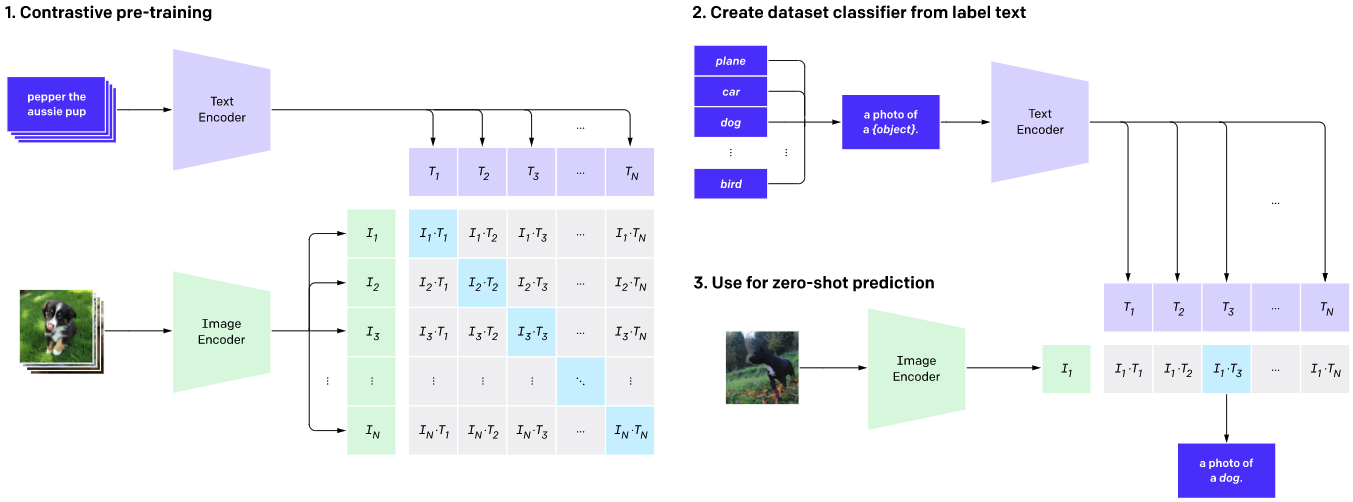
其中,流程:
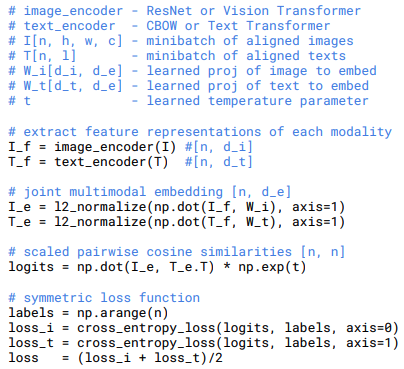
loss_i和loss_t的具体源码如下,参考 model.py:
def forward(self, image, text):image_features = self.encode_image(image)text_features = self.encode_text(text)# normalized featuresimage_features = image_features / image_features.norm(dim=1, keepdim=True)text_features = text_features / text_features.norm(dim=1, keepdim=True)# cosine similarity as logitslogit_scale = self.logit_scale.exp()logits_per_image = logit_scale * image_features @ text_features.t()logits_per_text = logits_per_image.t()# shape = [global_batch_size, global_batch_size]return logits_per_image, logits_per_text
其中,labels是torch.arange(batch_size, device=device).long(),参考train.py,具体如下
with torch.no_grad():for i, batch in enumerate(dataloader):images, texts = batchimages = images.to(device=device, non_blocking=True)texts = texts.to(device=device, non_blocking=True)with autocast():image_features, text_features, logit_scale = model(images, texts)# features are accumulated in CPU tensors, otherwise GPU memory exhausted quickly# however, system RAM is easily exceeded and compute time becomes problematicall_image_features.append(image_features.cpu())all_text_features.append(text_features.cpu())logit_scale = logit_scale.mean()logits_per_image = logit_scale * image_features @ text_features.t()logits_per_text = logits_per_image.t()batch_size = images.shape[0]labels = torch.arange(batch_size, device=device).long()total_loss = (F.cross_entropy(logits_per_image, labels) +F.cross_entropy(logits_per_text, labels)) / 2
交叉熵函数:y就是label,x_softmax[i][y[i]],表示在x_softmax中筛选第i个sample的第y[i]个值,作为log的输入,全部log负向求和,再求均值。
- y所对应的就是CLIP的np.arange(n),也就是依次是第0个位置~第n-1个位置,计算log。
# 定义softmax函数
def softmax(x):return np.exp(x) / np.sum(np.exp(x))# 利用numpy计算
def cross_entropy_np(x, y):x_softmax = [softmax(x[i]) for i in range(len(x))]x_log = [np.log(x_softmax[i][y[i]]) for i in range(len(y))]loss = - np.sum(x_log) / len(y)return loss# 测试逻辑
x = [[1.9269, 1.4873, 0.9007, -2.1055]]
y = [[2]]
v1 = cross_entropy_np(x, y)
print(f"v1: {v1}")x = torch.unsqueeze(torch.Tensor(x), dim=0)
x = x.transpose(1, 2) # CrossEntropy输入期望: Class放在第2维,Batch放在第1维y = torch.Tensor(y)
y = y.to(torch.long) # label的类型为longv2 = F.cross_entropy(x, y, reduction="none")
print(f"v2: {v2}")
输出:
v1: 1.729491540989093
v2: tensor([[1.7295]])
参考:
- arxiv文章下载很慢怎么办?
- CLIP-对比图文多模态预训练的读后感
- CrossEntropy的numpy实现和Pytorch调用
这篇关于CLIP算法的Loss详解 和 交叉熵CrossEntropy实现的文章就介绍到这儿,希望我们推荐的文章对编程师们有所帮助!






